Chapter 19: Allosteric Regulation (Exam 2)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
does allosteric regulation increase or decrease protein function?
it can do either
what is coopertivity?
when the binding of a regulator to one subunit of a multimeric protein affects the binding of other substrates to other subunits of the protein
what is orthosteric regulation?
when the regulator binds to the active site; ex: competitive inhibition
describe the concerted model of allosteric regulation
when all subunits of the protein experience the conformation change at the same time
describe the sequential model of allosteric regulation
when the binding of the ligand changes conformation of the subunit it's bound to; not all subunits change at the same time
what equation do we use to find theta?
theta = [L]^n / Kd + [L]^n
what happens when n is >/</= 1?
> 1: positive coopertivity (increases binding affinity of other subunits); < 1: negative coopertivity; = 1: no effect
what is n?
the slope of the tangent line of the rate graph
how do you find Ka?
[ES] / [E]*[S]
how do you find Kd?
[E]*[S] / [ES]
what's the difference between Ka and Kd?
Ka is rate of ES complex formation; Kd is rate of ES complex breakdown
lower Kd values indicate...
better binding
what is hemoglobin?
a tetrameric protein containing 2 alpha subunits, 2 beta subunits, and a heme
describe the binding system of the heme in hemoglobin
the one Fe2+ ion can form 6 coordinate covalent bonds: 4 bonds to N, 1 bond to proximal histidine, and 1 bond to O2
how many molecules of O2 can bind to one hemoglobin?
4 molecules
describe the coopertivity effects of oxygen binding to hemoglobin?
1. oxygen binds 2. conformational change that causes subsequent subunits to have increased affinity for oxygen; positive coopertivity
at high O2 concentrations hemoglobin ___ to oxygen. at low?
high: holds on; low: lets go
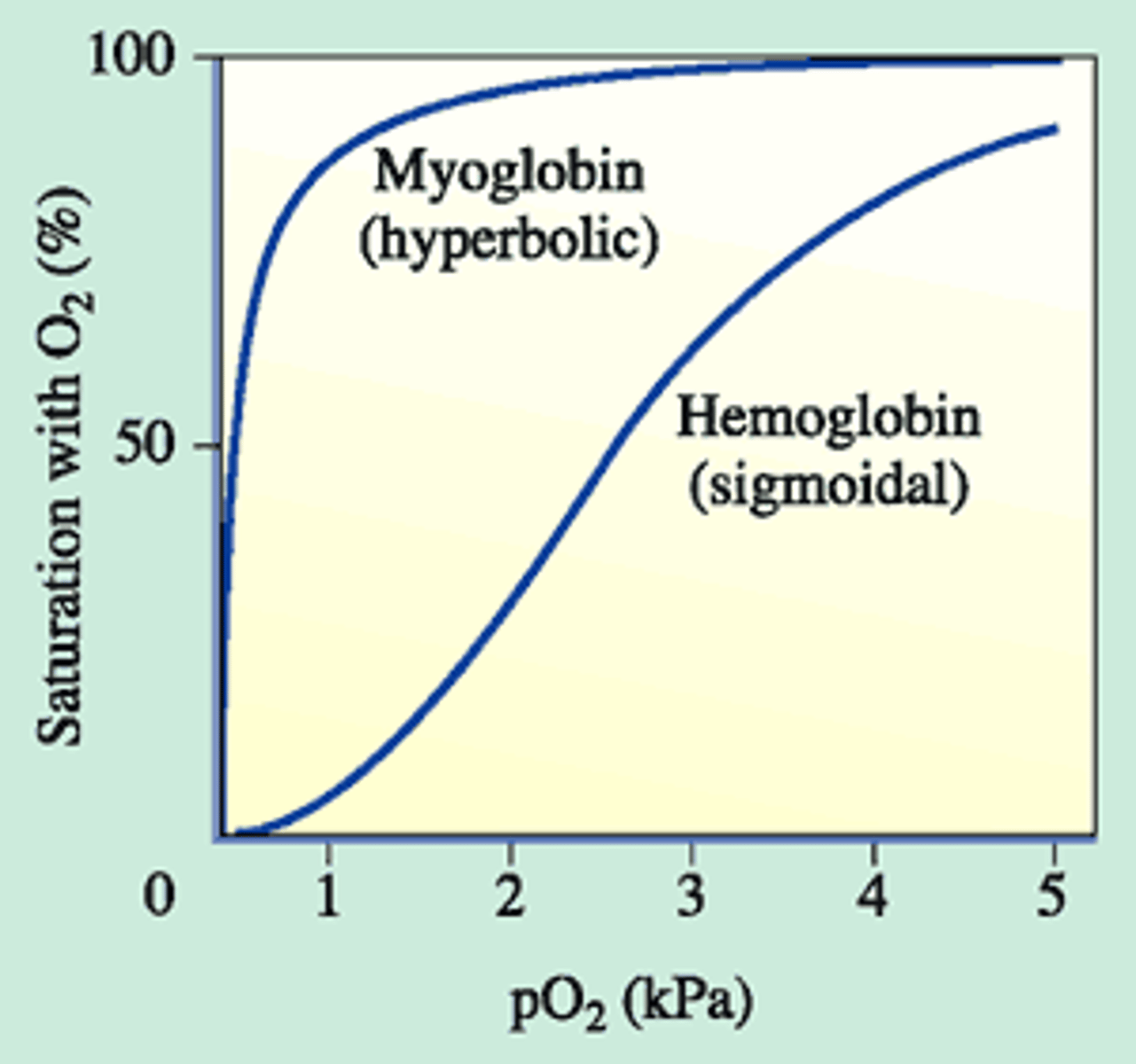
what is myoglobin
monomeric protein that has a heme with Fe2+ that can bind O2; found in muscle tissue; graph has hyperbolic shape
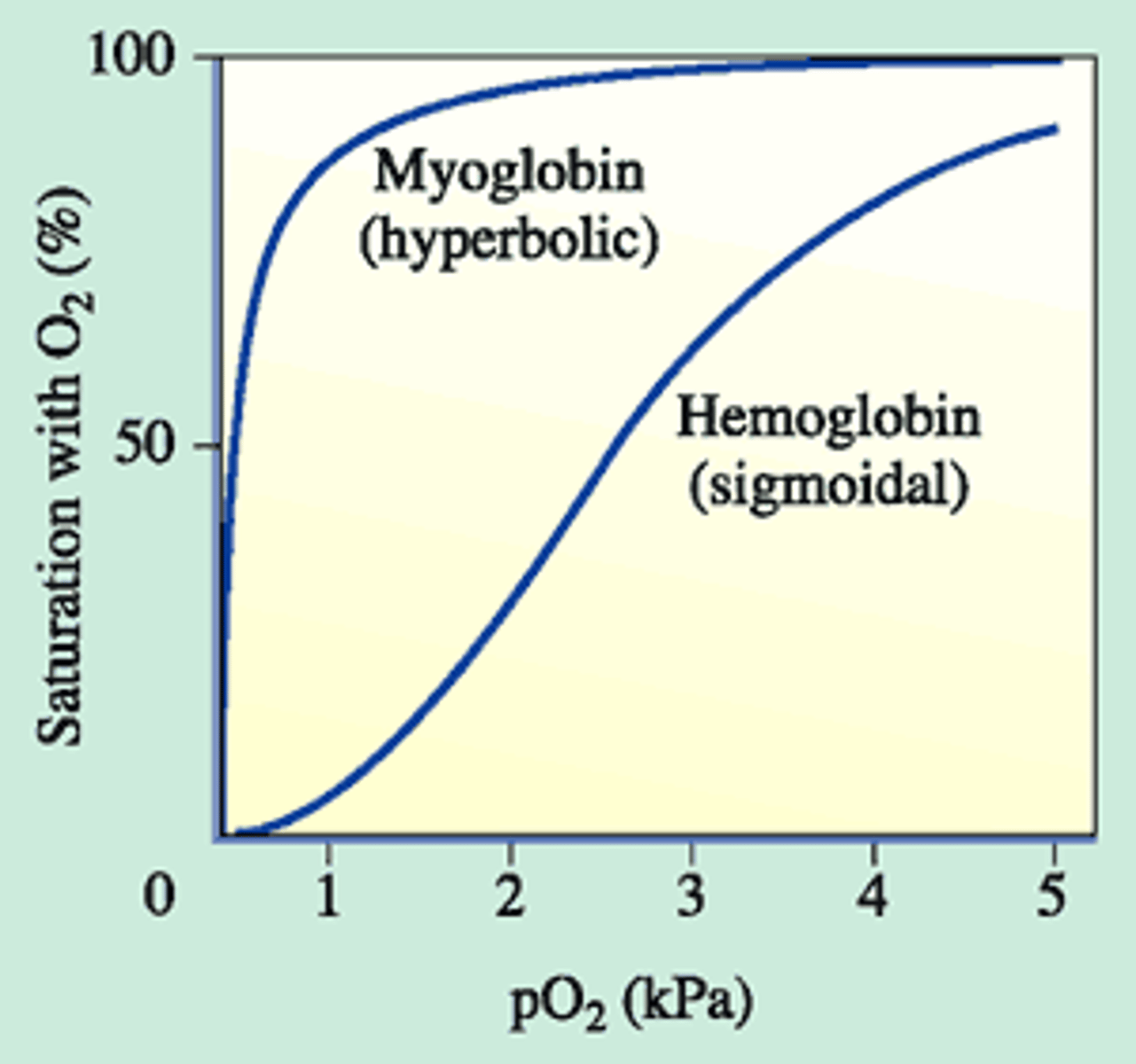
is O2 binding to hemo/myoglobin reversible?
yes
what happens when CO binds to hemoglobin?
it binds better than O2, but doesn't release as readily which can lead to CO poisoning
what is 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate?
a negative allosteric regulator; two phosphate groups and an hydroxyl
at high altitudes where there is less O2 available, why would our bodies produce more 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate?
to help hemoglobin release oxygen more easily to oxygenate our tissues
does hemoglobin release all of the O2 that it carries?
no; usually only about 80%
what is the difference between adult hemoglobin (HbA) and fetal hemoglobin (HbF)?
HbA has 2 alpha and 2 beta subunits; HbF has 2 alpha and 2 gamma subunits; HbF has Ser instead of His residues which can't bind 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate as good as HbA so it binds O2 better
what does HbF have to bind O2 stronger?
because the fetus gets its O2 from across the placental barrier
what is a homotropic effector for oxygen binding to hemoglobin? heterotrophic?
homo: oxygen; hetero: 2.3-bisphosphoglycerate
how does H+/an acidic environment affect Hb binding to O2?
negative allosteric effector; decrease binding, increase release
under acidic conditions or when bound to CO2, how does the graph of hemoglobin binding change? with no 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate?
acidic: right shift, increase release; no 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate: left shift into a myoglobin like curve
what is a coordinate covalent bond?
both shared electrons in the bond come from the same atom
how many 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate molecules can bind to one hemoglobin?
1
describe the conformational change that O2 causes when it binds to Fe2+ at the heme
the Fe2+ ion will get smaller (loosing electrons to coordinate covalent bond) so that it moves better into the heme plane with histidine
why is the distal histidine in hemoglobin important?
it prevents perpendicular binding of O2 which weakens the O2 bond and allows it to be release more readily; 90 degree bonds are stronger than bent bonds
briefly describe what causes sickle cell anemia
a beta-globin mutation; a Val instead of Glu which causes some beta subunits to stick together/polymerize
how can hydroxyurea be used to help treat sickle cell anemia
increases production of the gamma subunit, so the beta subunits are less likely to polymerize
briefly describe beta-thalassemia
the subunits do not bind to each other completely, so there is no coopertivity between them; decreased affinity for oxygen binding than normal
what interesting benefit to hemoglobin mutations have?
immunity to malaria; due to the misshapen blood cells they can't carry the infection