bone composition
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
function of the skeleton
support
protection
movement
mineral homeostasis
haematopoiesis
energy storage
what is mineral homeostasis?
calcium and phosphate storage
99% of body’s calcium is contained within bones
haematopoiesis
red bone marrow
medulla ossium rubra
energy storage
yellow bone marrow
medulla ossium flava
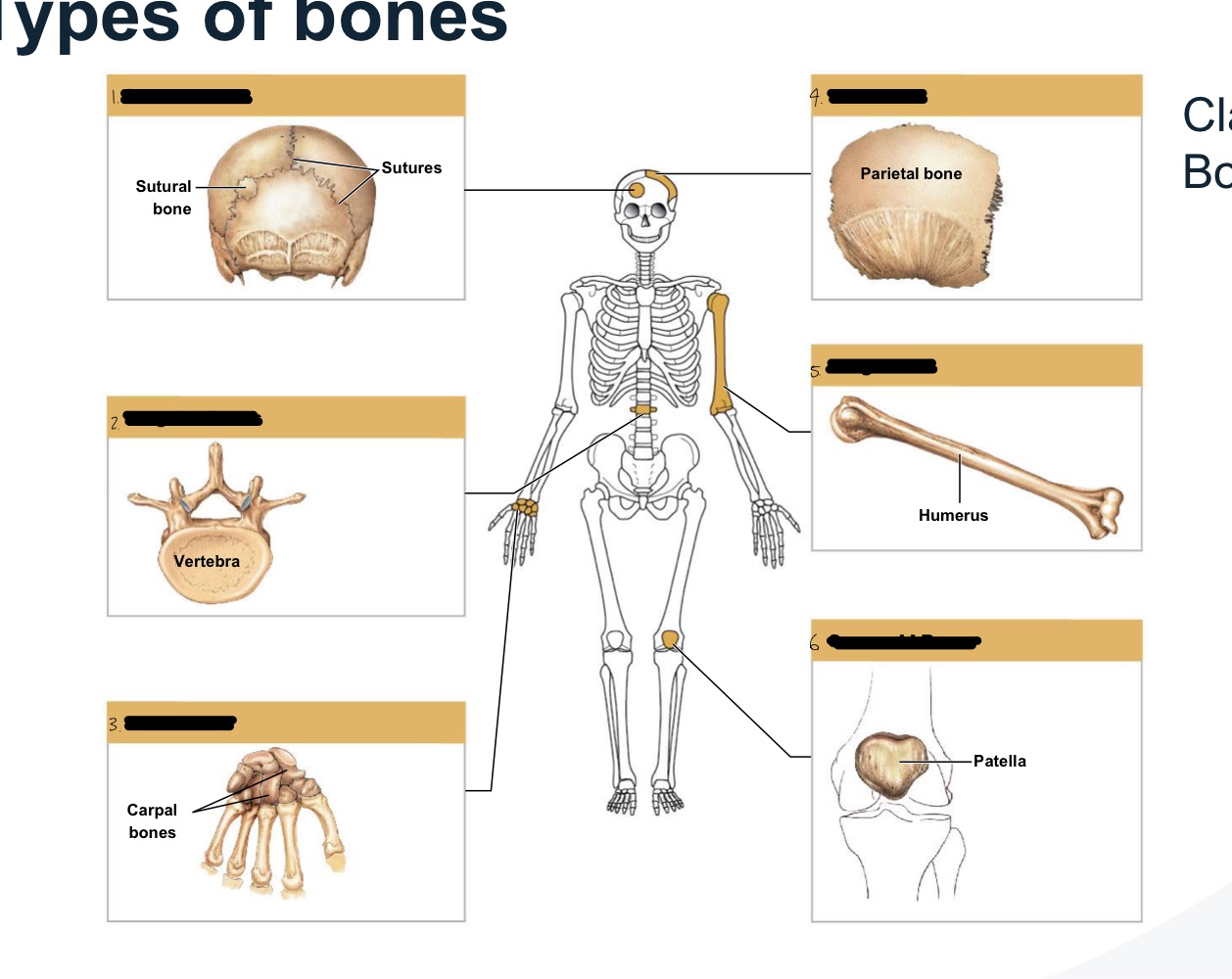
types of bones
bones are classified based on shape
what is the composition of bone?
inorganic components - stiffness
mineral hydroxyapatite crystals
calcium, carbonate, phosphate
organic component - flexibility and strength
organic matrix
collagen type 1
cells
promote and help maintain mineral density and content
other components
water
lipids
characteristics of trabecular/spongy bone
makes 20 percent of long bone
located inner side of bone
spongy
high surface area to mass ratio
softer, weaker, more flexible
composition of trabecular/spongy bone
highly vascular
space is filled by red bone marrow
lamellae are arranged in irregular latticework → trabeculae
characteristics of compact/cortical bone
makes 80 percent long bone
outer side of bone
compact and strong
does not have spaces or hollows visible to the eye
composition of compact/cortical bone
has unique concentric arrangement of haversian system → osteon
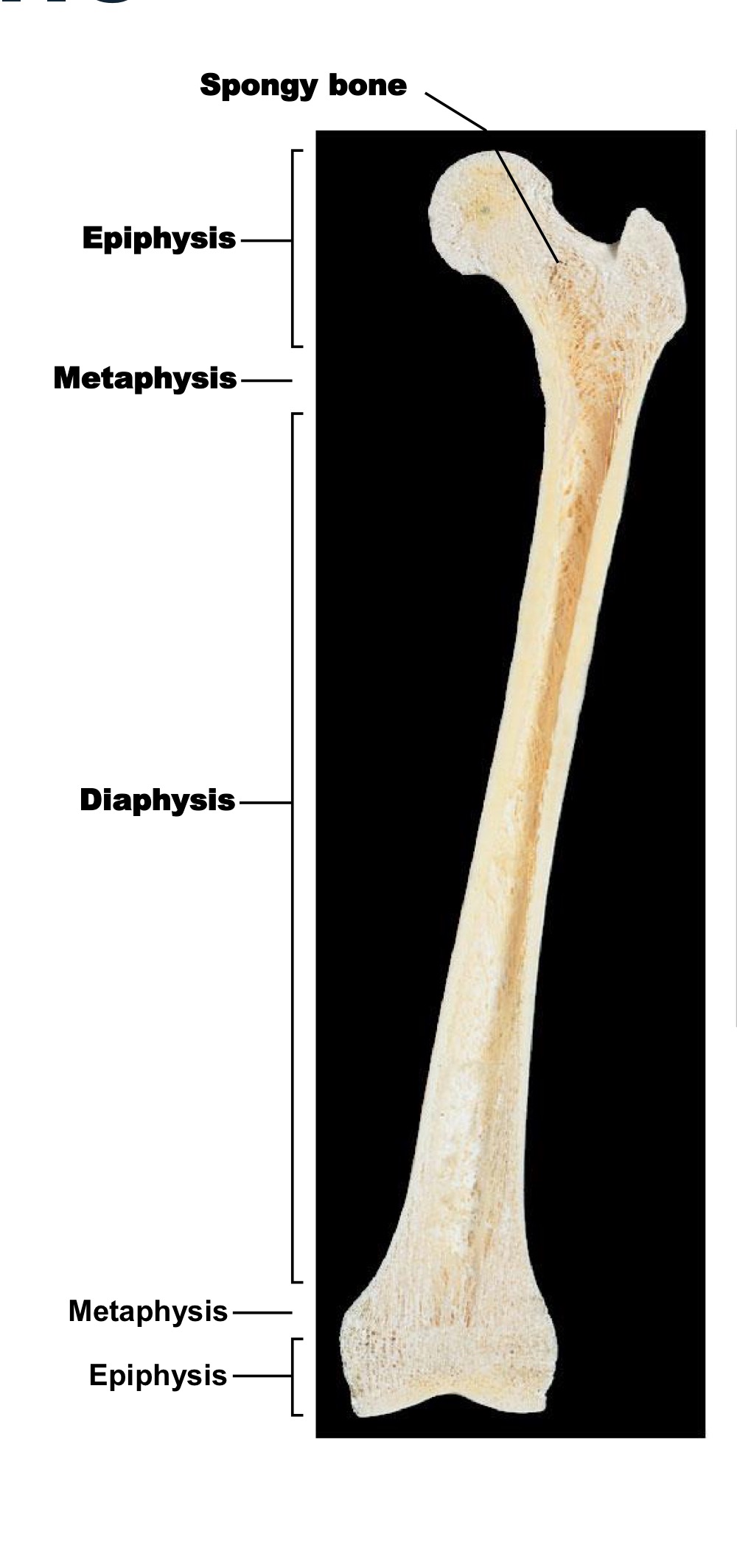
label long bone
components of osteon
haversian canal (HC)
contains blood vessels and nerves
concentric lamellae
concentric arrangement of collagen fibres
surrounds the haversian canal
osteocytes send out protrusions through canaliculi to communicate through blood vessels