Bones Quiz
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
185 Terms
How many bones in the body?
206
What are the parts of the skeletal system?
bones, joints, cartilages, ligaments
What are the two divisions of the skeletal system?
axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton
What are the functions of bones?
Support, Protection, Allows Movement, Stores Minerals and Fats, and Blood Cell Formation
What are the two types of bone tissue?
compact and spongy
what are long bones?
longer than they are wide
what are examples of long bones?
femur, humerus
What are short bones?
cube shaped bones
Examples of short bones?
carpals and tarsals
What are flat bones?
thin, flat, slightly curved
Examples of flat bones
skull, ribs, sternum
What are irregular bones?
bones that do not fit one of the preceding categories
An example of irregular bones
vertebrae
gross anatomy of a long bone
diaphysis and epiphysis
diaphysis
shaft composed of compact bone
epiphysis
end of bone composed of spongy bone
changes in human skeleton
- In embryos, the skeleton is primarily hyaline cartilage
- During development, much of this cartilage is
replaced by bone
- Cartilage remains in isolated areas: Bridge of the nose, Parts of ribs, Joints
the fetal skull
-A large compared to the infant's total body length
-Fontanels
*Allow the brain to grow
*Convert bone within 24 months after birth
fontanels
fibrous membranes connecting the cranial bones
bone growth
Epiphyseal plates allow for growth of long bone during childhood
New cartilage is continuously formed
Older cartilage becomes ossified
Cartilage is broken down
Bone replaces cartilage
ossified
tending to become more rigid, conventional, sterile, and reactionary with age; literally, turned into bone
types of bone cells
osteocytes, osteoblasts, osteoclasts
osteocytes
mature bone cells
osteoblasts
bone forming cells
osteoclasts
Bone-destroying cells
bone remodeling
a process by both osteoblasts and osteoclasts
bone fractions
a break in the bone
types of bone fractures
-closed (simple) fracture
-open (compound) fracture
closed fracture (simple)
break that does not penetrate the skin
open fracture (compound)
broken bone penetrates through the skin
how are bone fractures treated
reduction and immobilization (realignment of the bone)
stages in the healing of a bone fracture
hematoma forms,
fibrocartilaginous callus forms,
bony callus forms,
bone remodeling occurs.
Axial skeleton
forms the longitudinal axis of the body
what are the 3 parts of the axial skeleton
skull, vertebral column, bony thorax
appendicular skeleton
limbs, pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle
what two bones composes the appendicular skeleton
clavicle and scapula
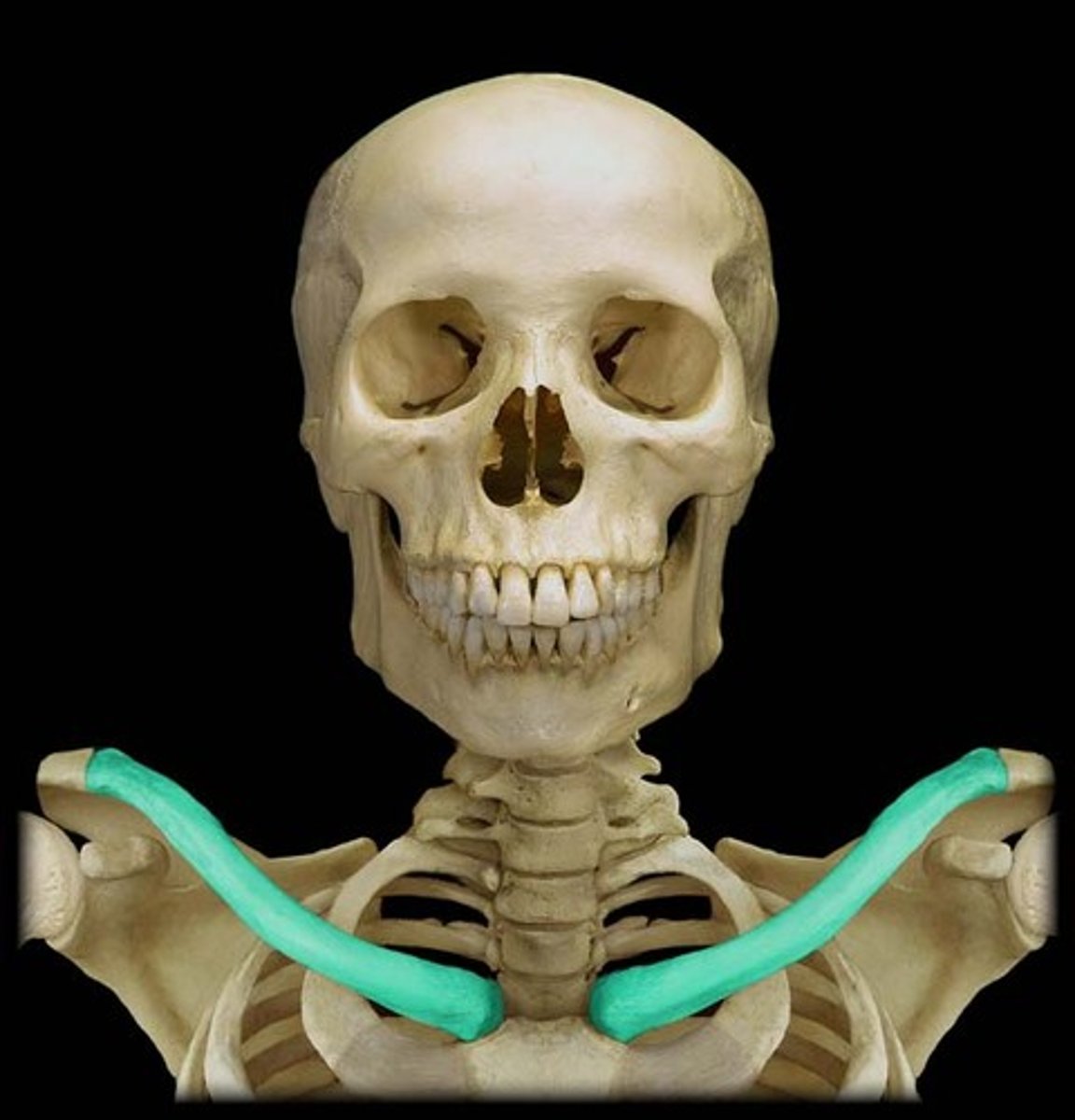
clavicle
collar bone
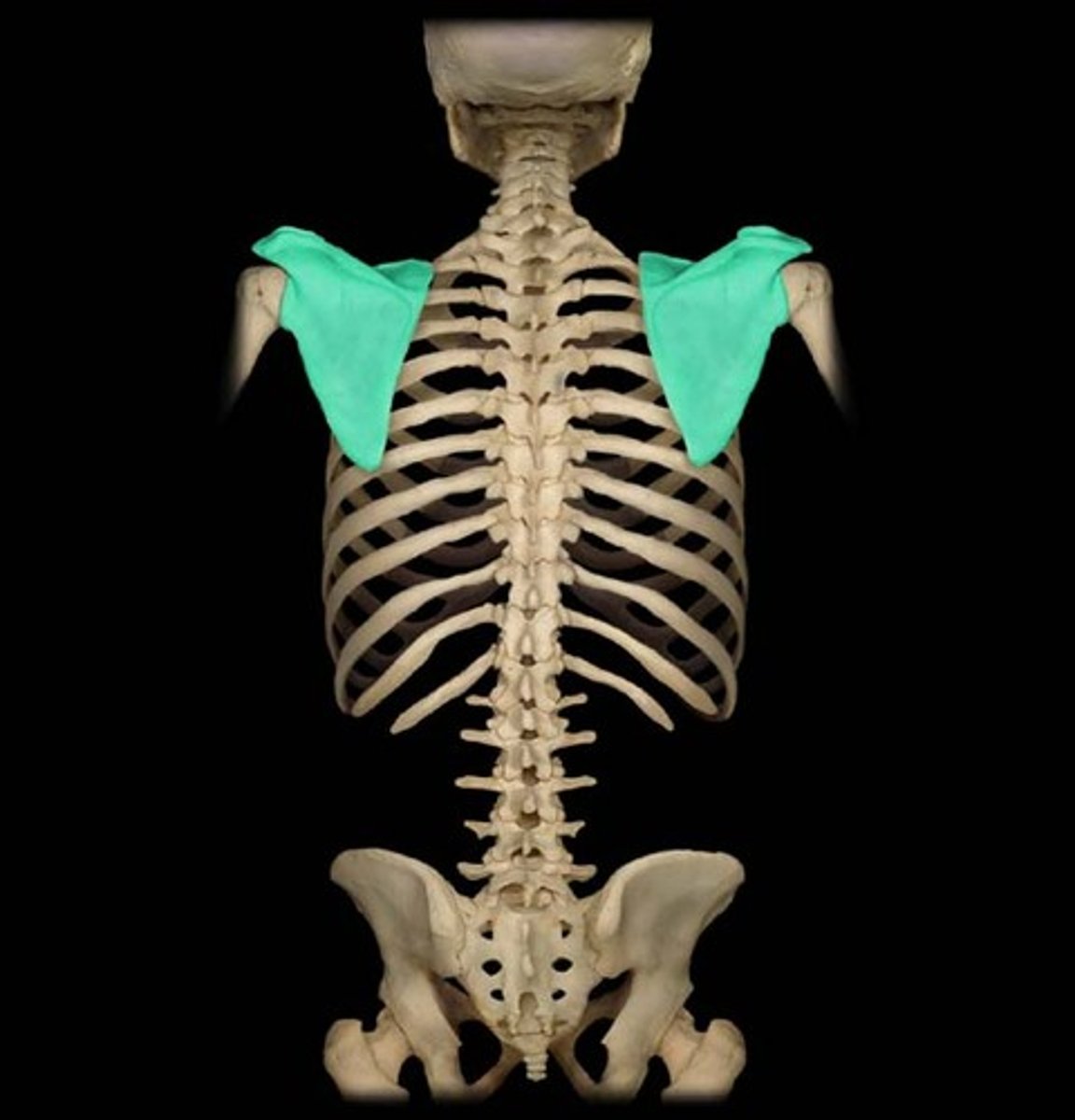
scapula
shoulder blade
what does the clavicle and scapula allow the body to do
have exceptionally free movement
bones of the upper limb
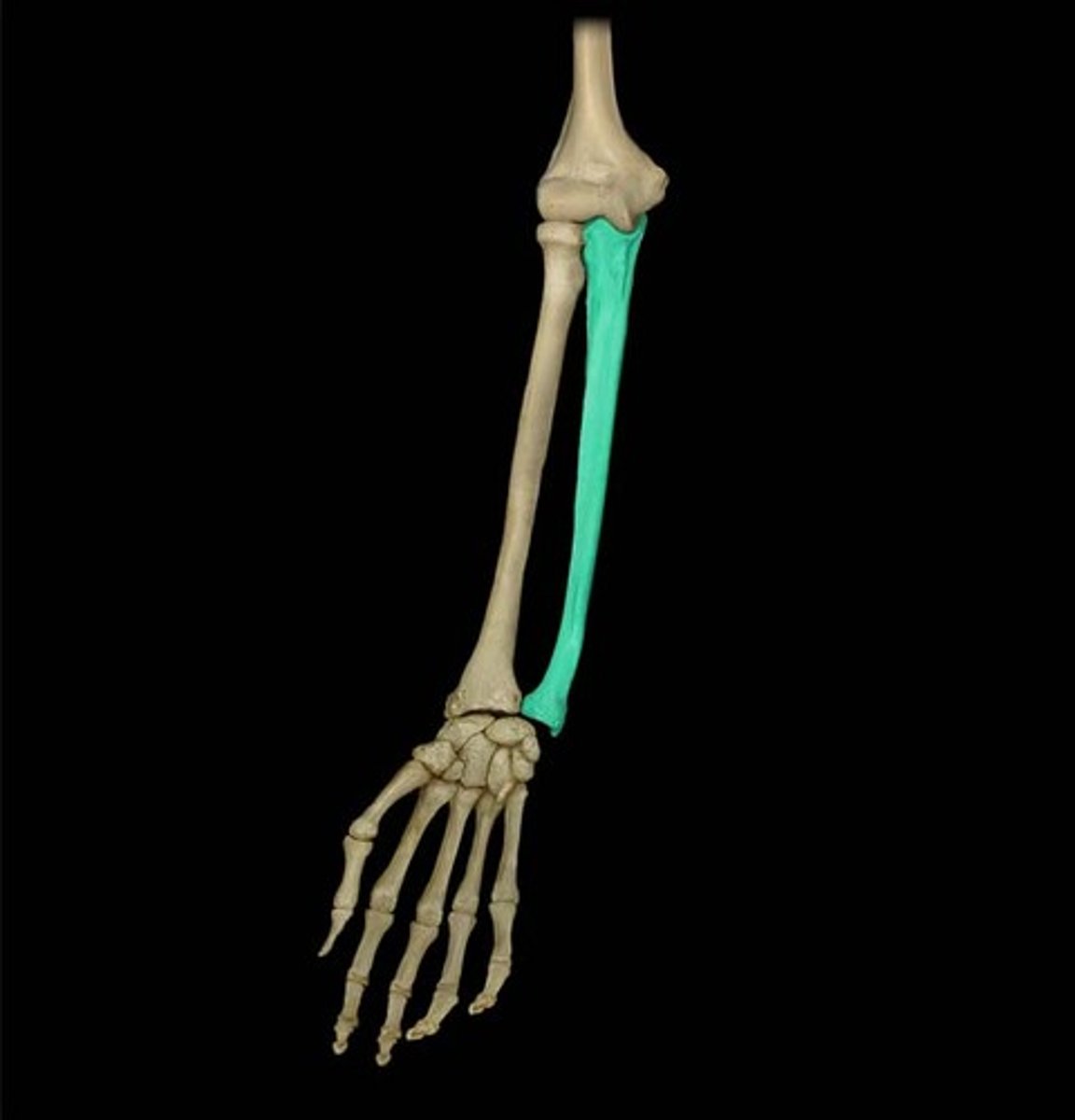
foramen, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges
Foramen
for a vein or artery to go through the bone
Radius and ulna cross over each other
True
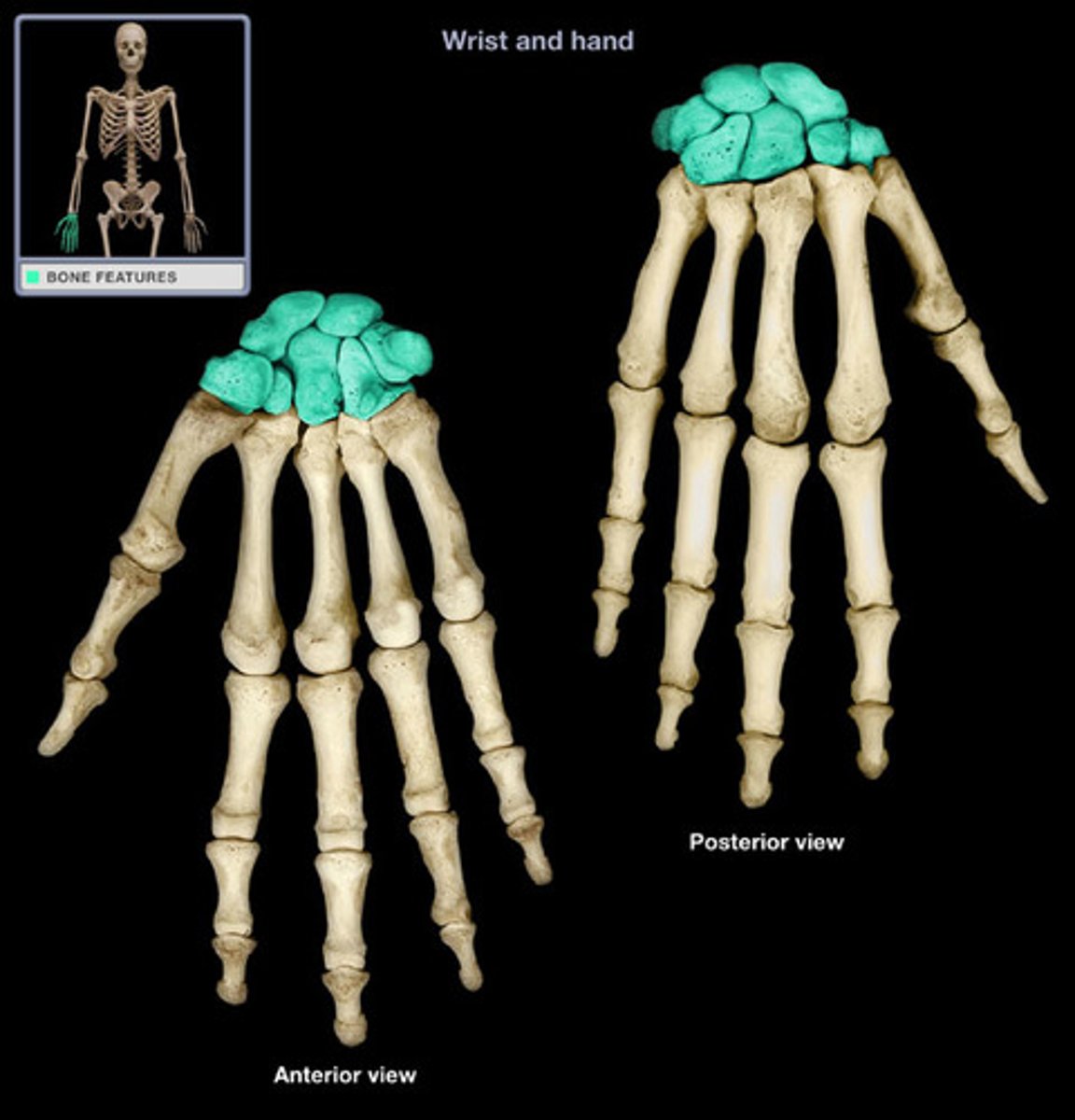
Carpals
wrist bones
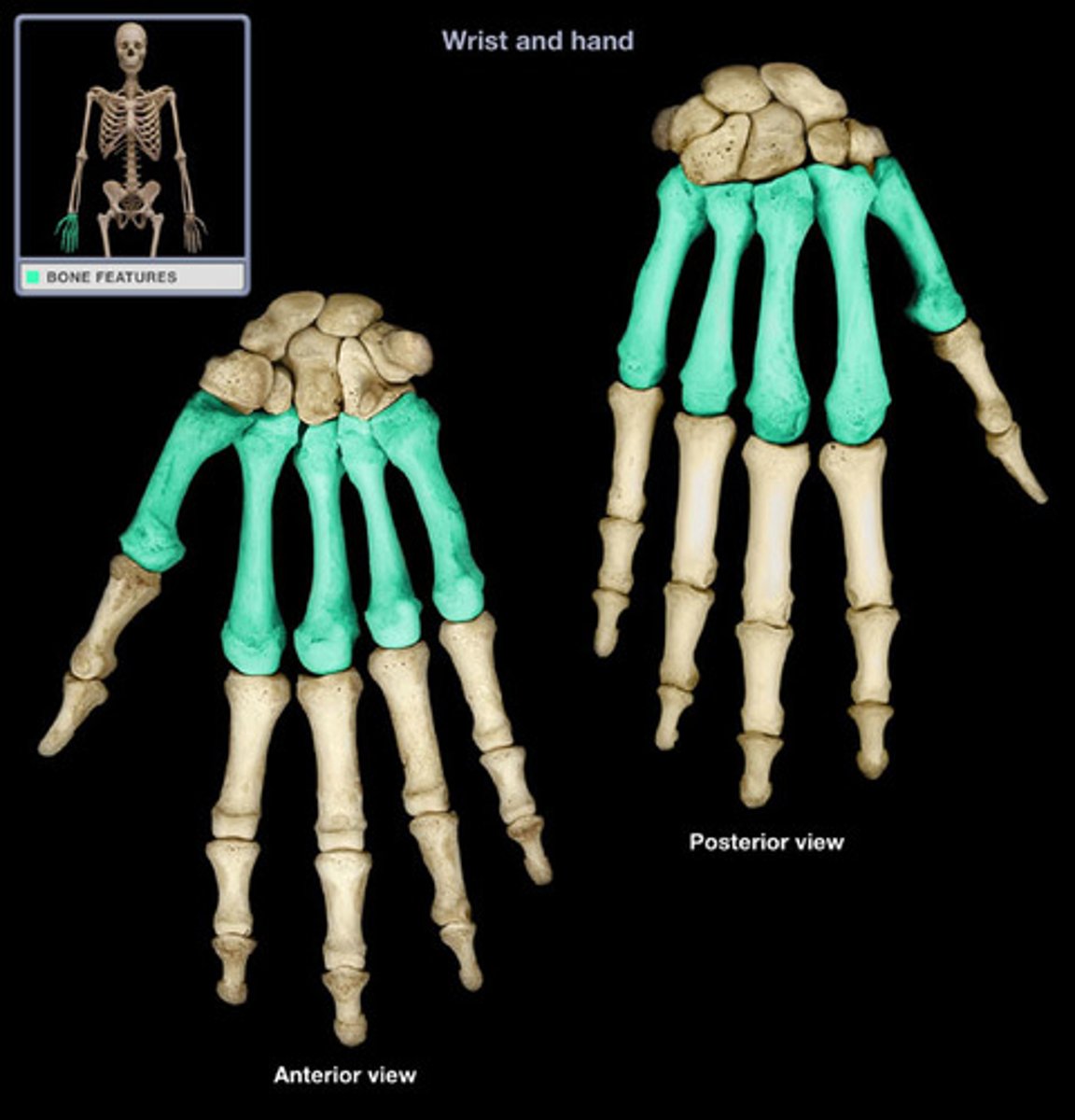
metacarpals
the five bones that form the palms of the hand
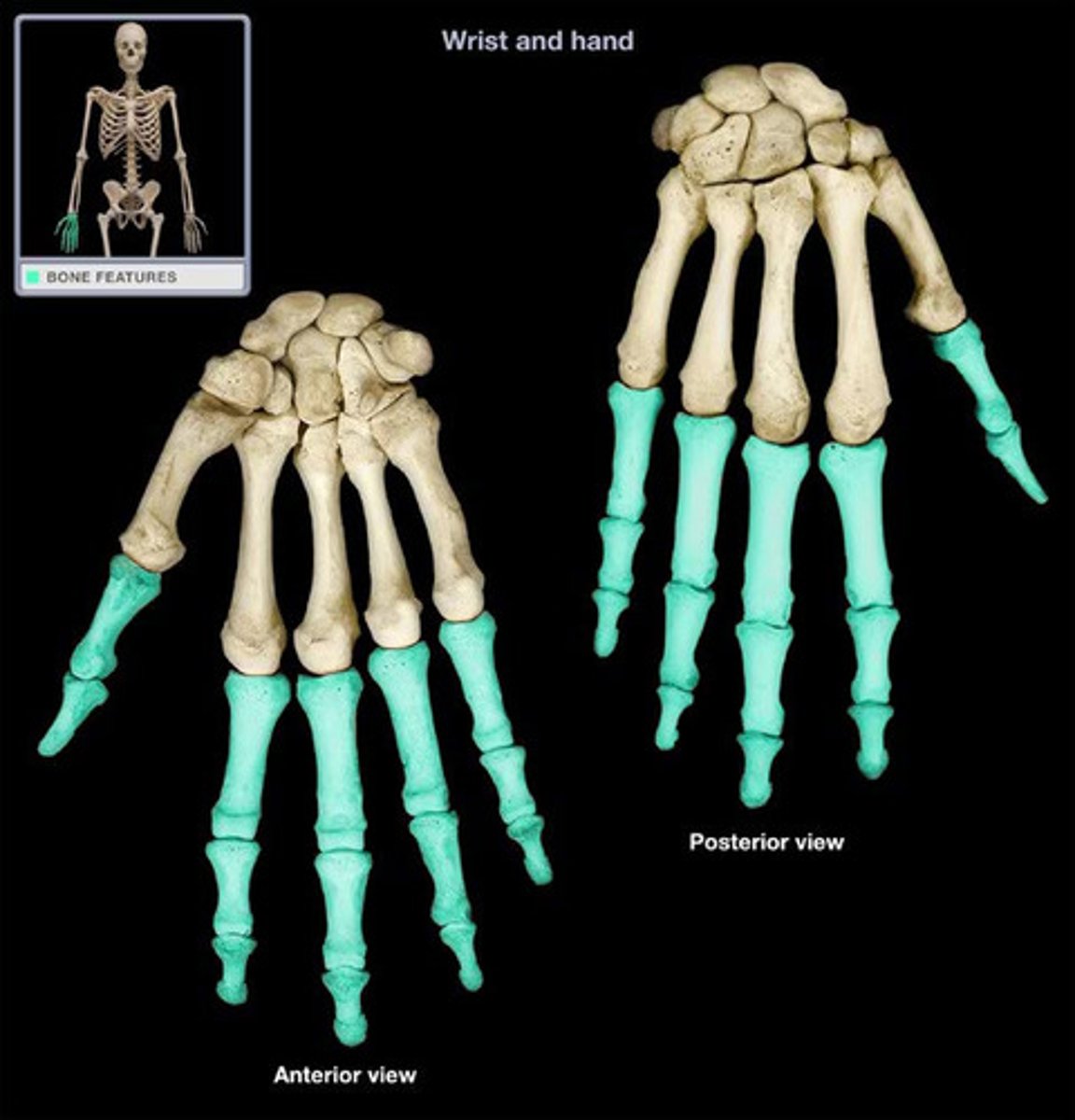
phalanges
fingers, toes
bones of the pelvic girdle
coxal bones
Coxal bones
ilium, ischium, pubis
Which organs does the pelvic girdle protect?
Reproductive organs, urinary bladder, and part of the large intestine
Total weight of the upper body rests on what?
the pelvis
Gender differences of the pelvis
Females have a wider pelvis and wider pubic arch. A wider pelvis opens the pelvis outlet across the bottom. Allows for the passage of a baby.
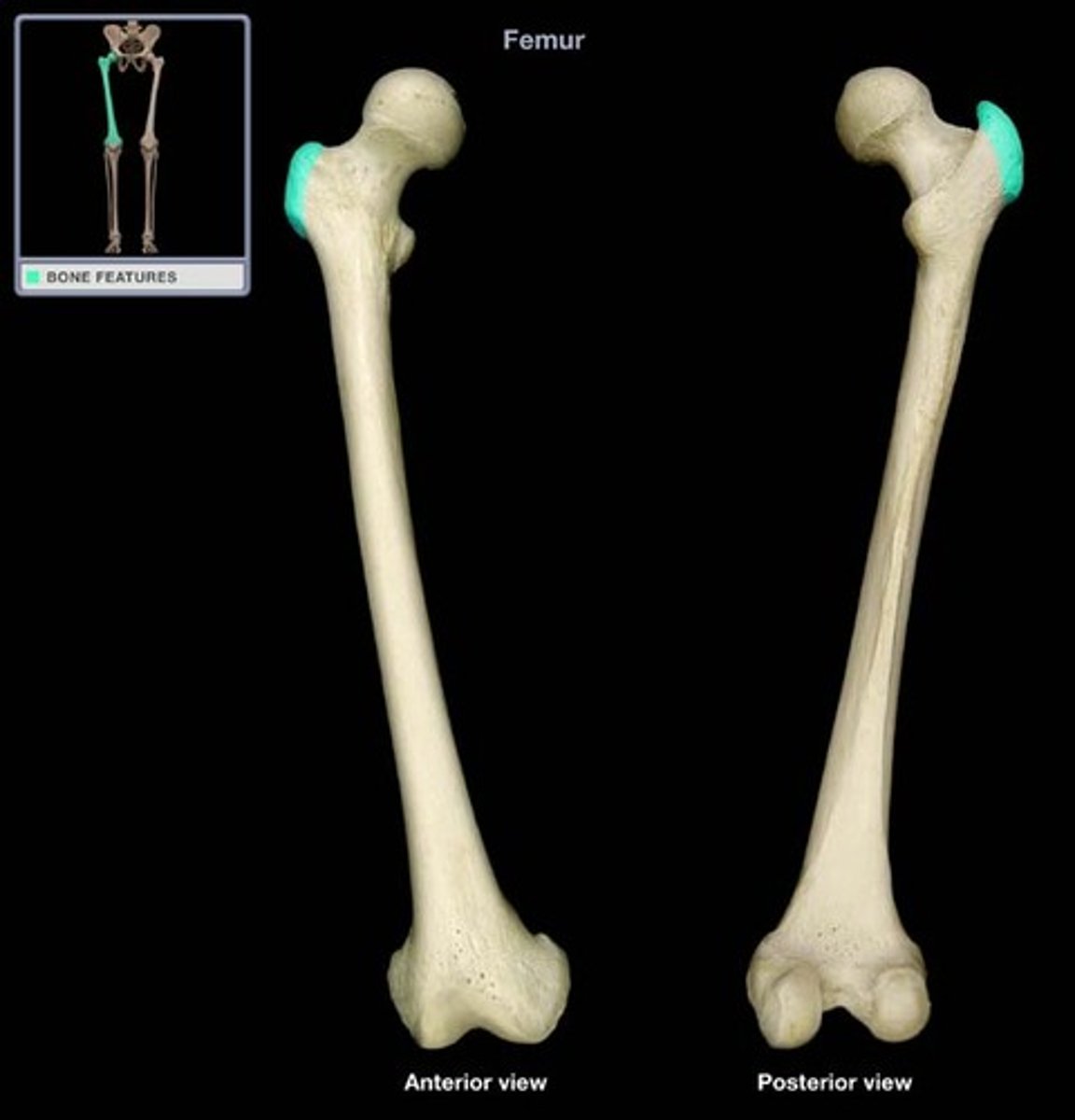
Femur
longest and hardest bone in the whole body
What two parts connect to the femur?
Tibia and Fibula
tibia
shin bone
Fibula
calf bone
Bones of the foot
tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges
tarsals
ankle bones
metatarsals
bones of the foot between ankle and toes
inflammatory conditions associated with joints
bursitis, tendonitis, arthritis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gouty arthritis, osteoporosis
Bursitis
inflammation of a bursa usually caused by a blow or friction
Tendonitis
inflammation of tendon sheaths
Arthritis
inflammatory or degenerative diseases of joints, over 100 types
most widespread crippling disease in the U.S?
arthritis
Osteoarthritis
most common form of arthritis
rheumatoid arthritis
An autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the joints. Symptoms begin with bilateral inflammation of certain joints. Often leads to deformities.
gouty arthritis
A deposition causes inflammation of joints of urate crystals from the blood, can usually be controlled with a diet
Osteoporosis
Bone resorption greater than bone deposit
What causes osteoporosis?
Age, decline in sex hormones, immobility =, poor protein/calcium, corticosteroids
Dens
allows movement of head
What does the atlas sit on?
axis
Where is the trochanter?
femur
What is not a function of the bone?
Blood cell formation
What is the baby skeleton made up of?
Hyaline Cartlidge
fontinalis
soft spot on baby's head
Which type of vertebra connects to the ribs?
thoracic
How many thoracic vertebrae are there?
12
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
7
How many lumbar vertebrae are there?
5
How many vertebrae are there?
24
What are the bones in the wrist?
scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
Way to remember wrist bones
some lovers try position that they can't handle
Which arthritis is an autoimmune disease?
rheumatoid arthritis
how many bones in the wrist?
8
Clavicle
Scapula
sternum
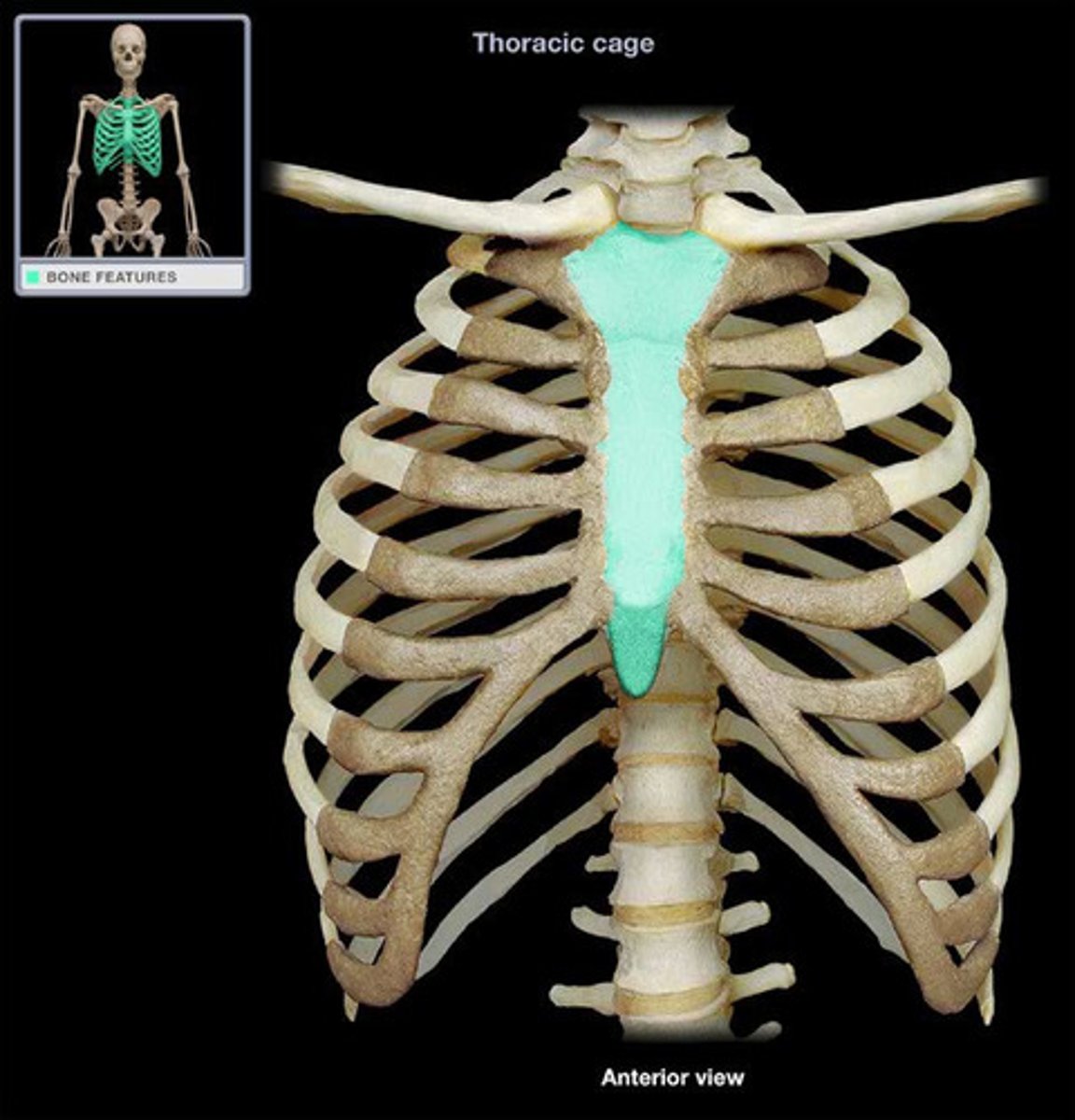
vertebrosternal ribs
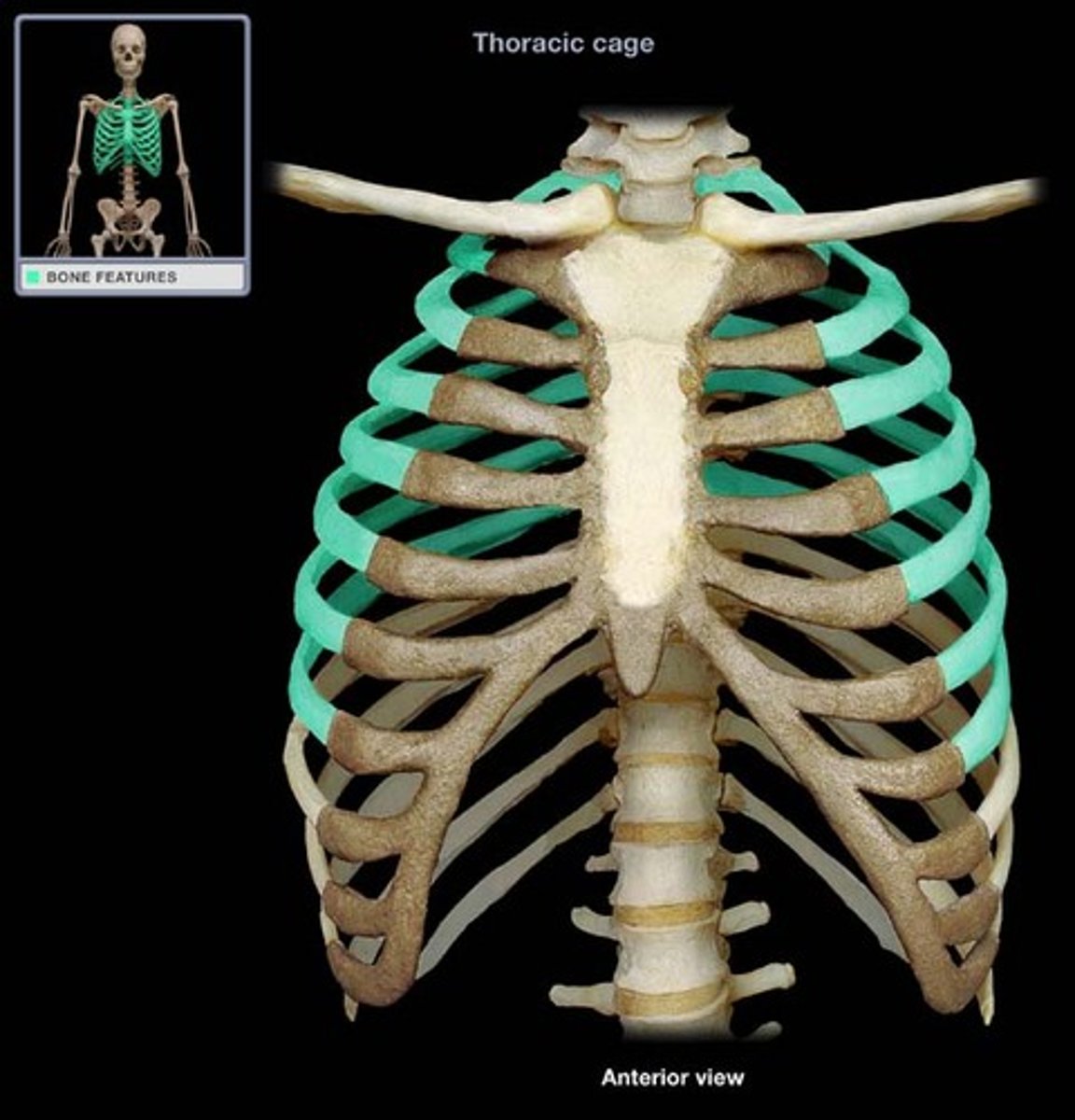
vertebrochondral ribs
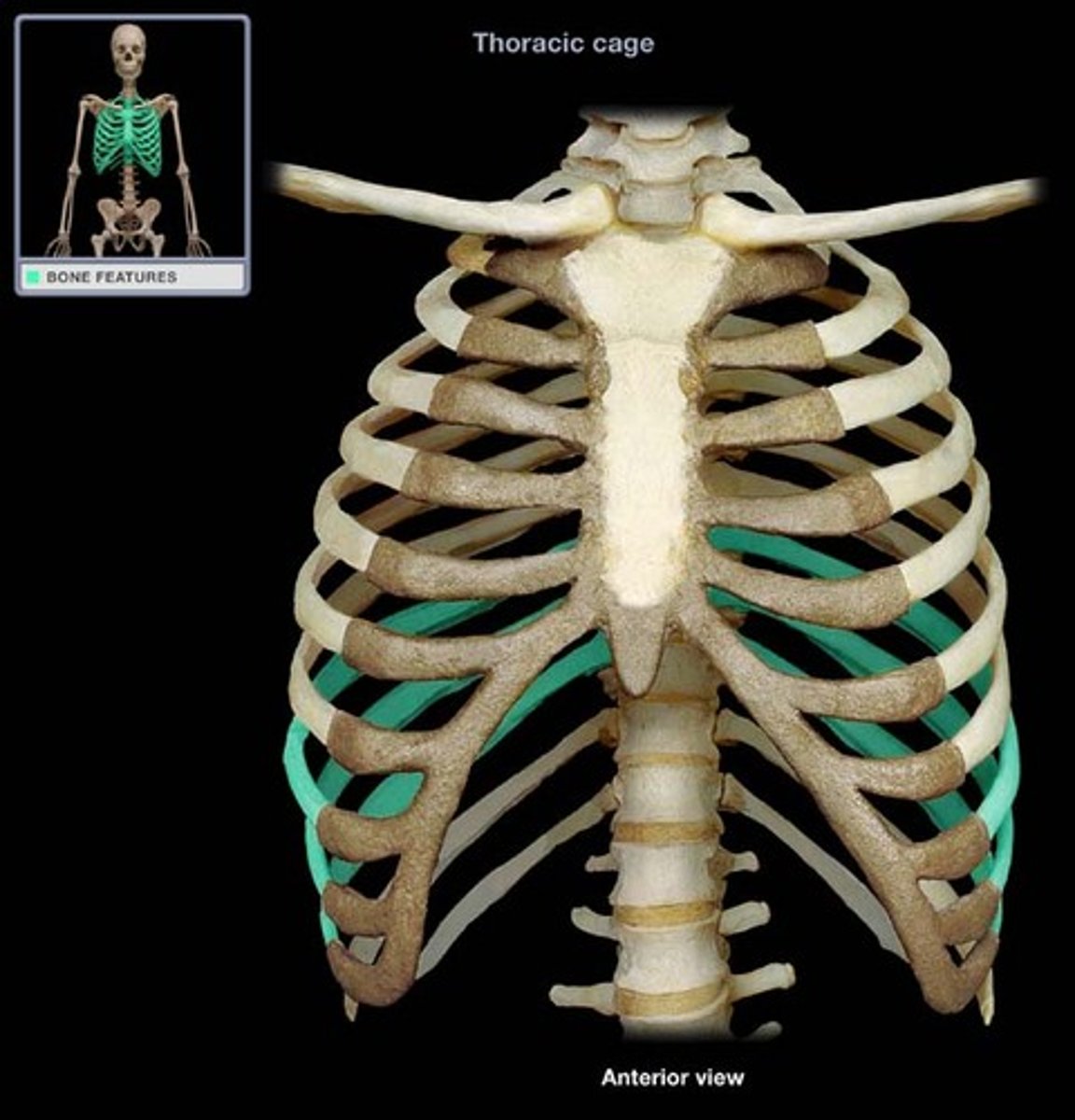
Vertebral ribs
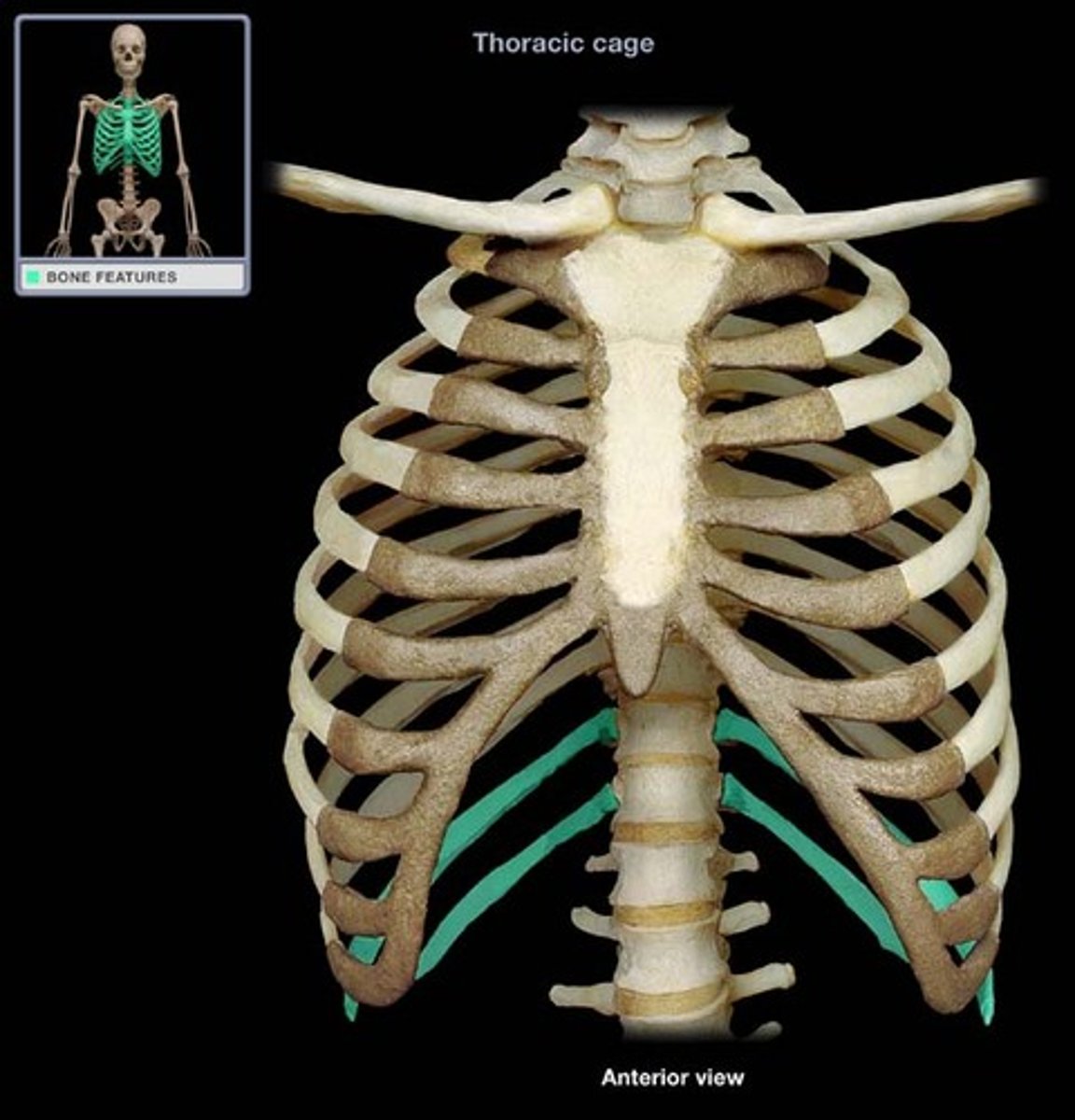
humerus
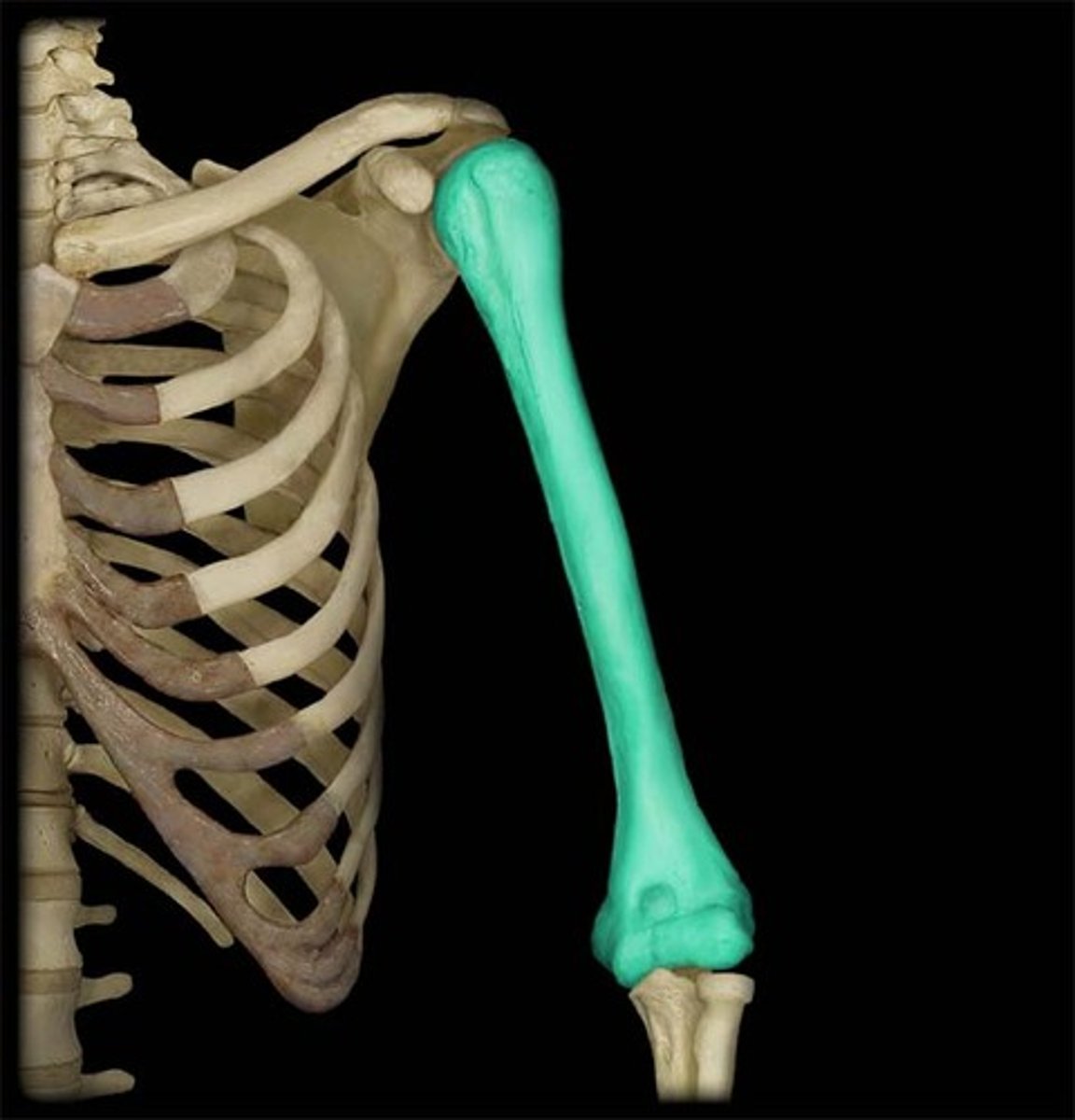
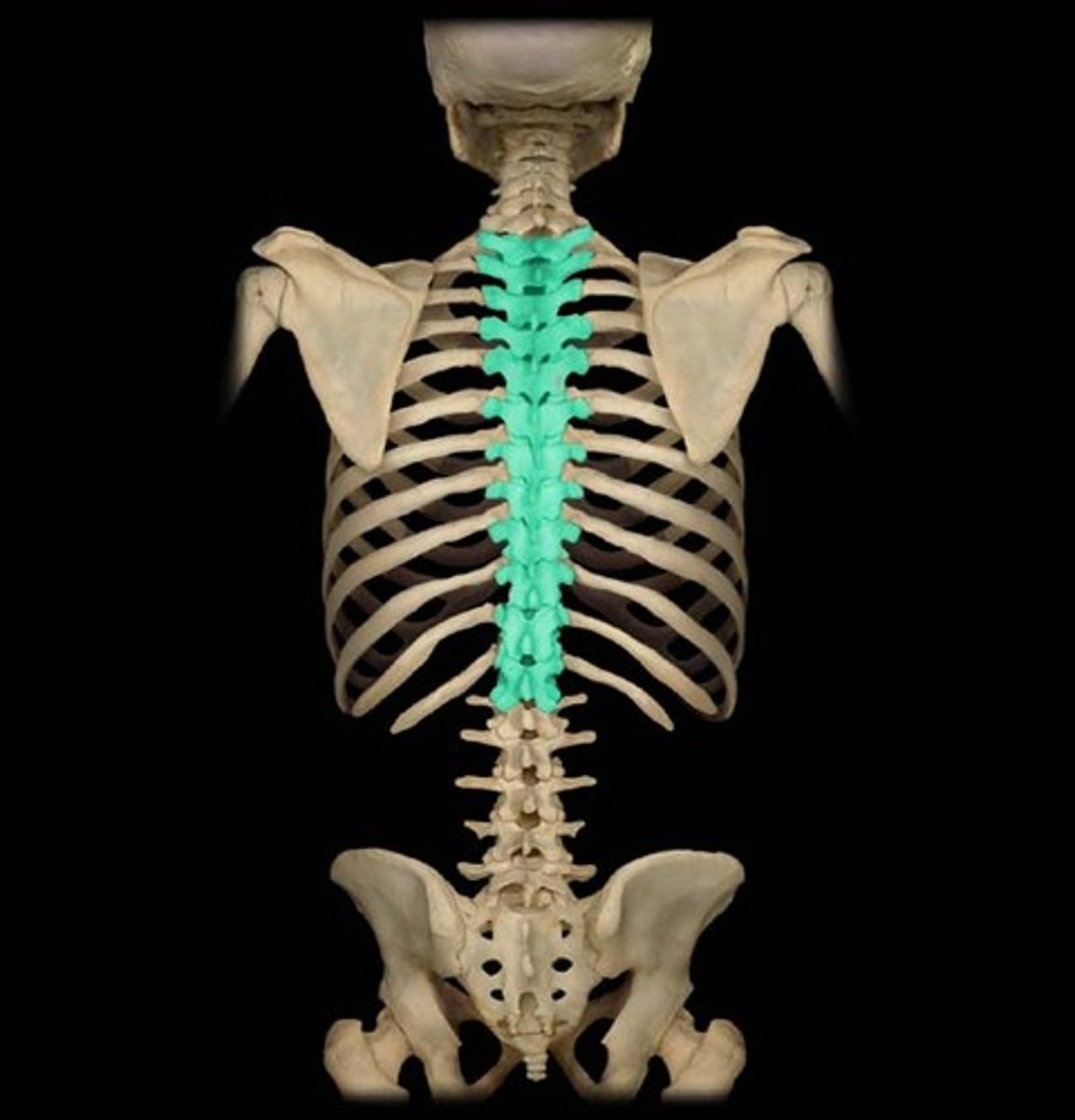
thoracic vertebrae
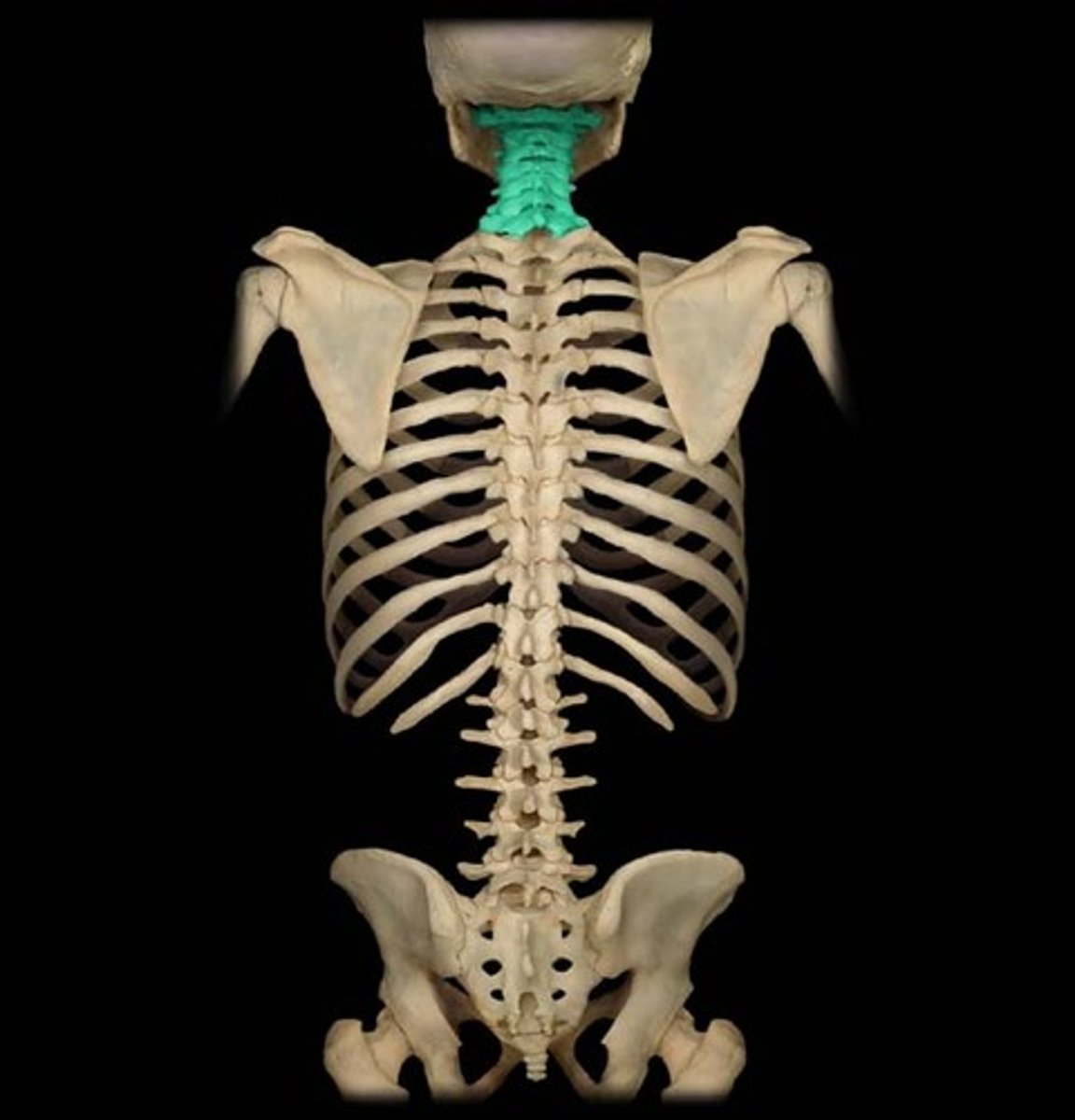
cervical vertebrae
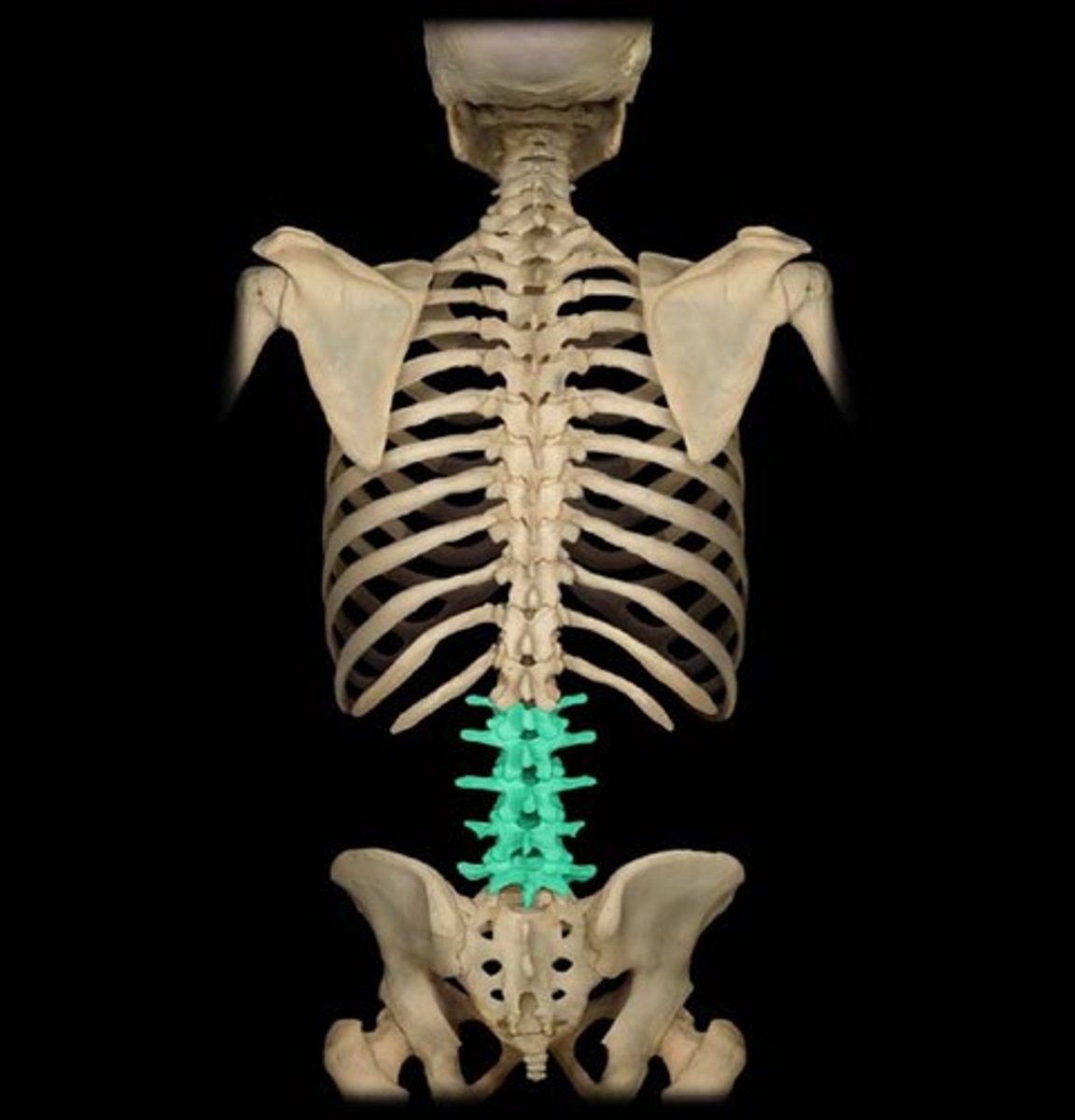
lumbar vertebrae
radius
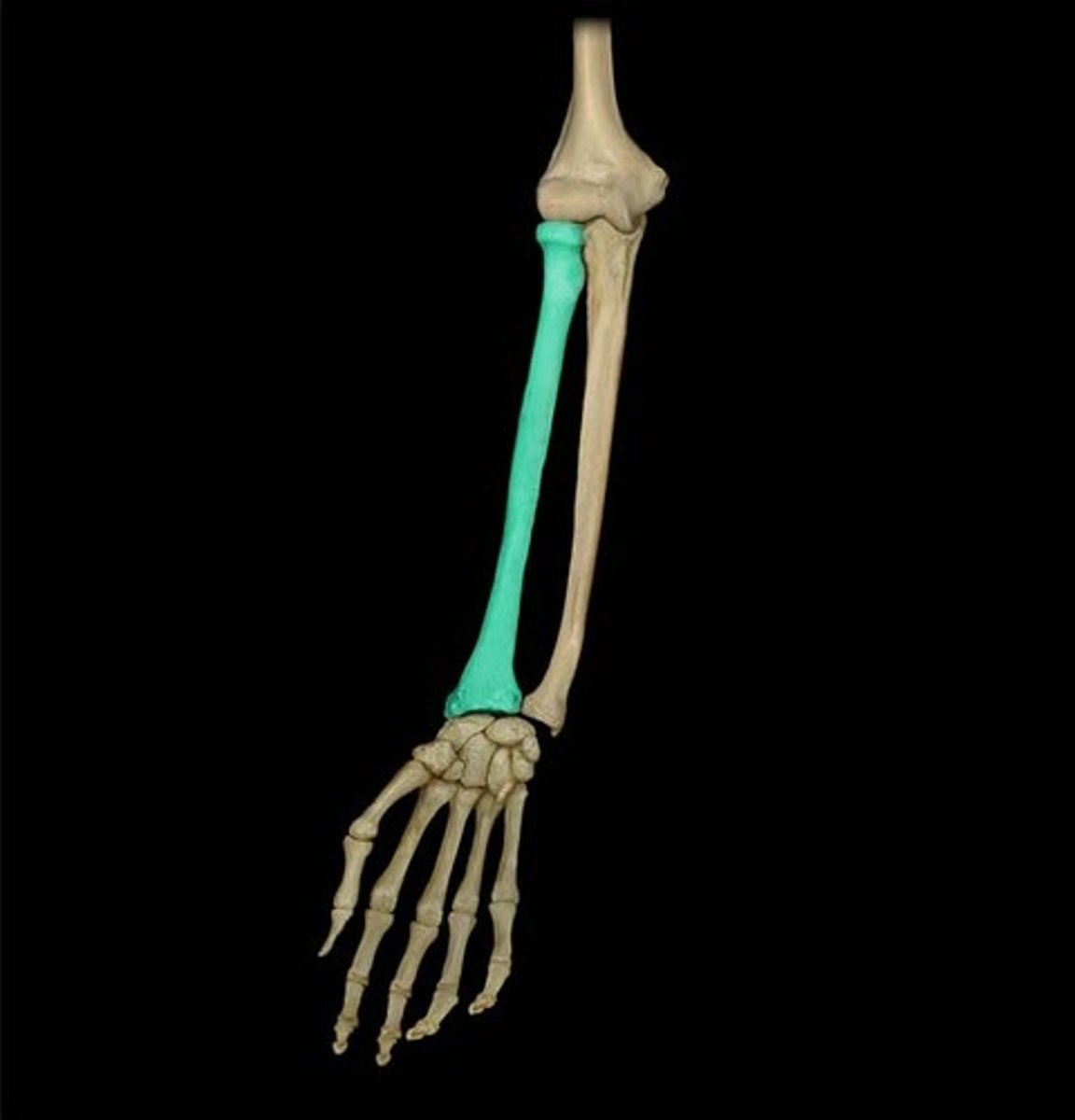
ulna
carpals
metacarpals (picture)
Phalanges (hand)
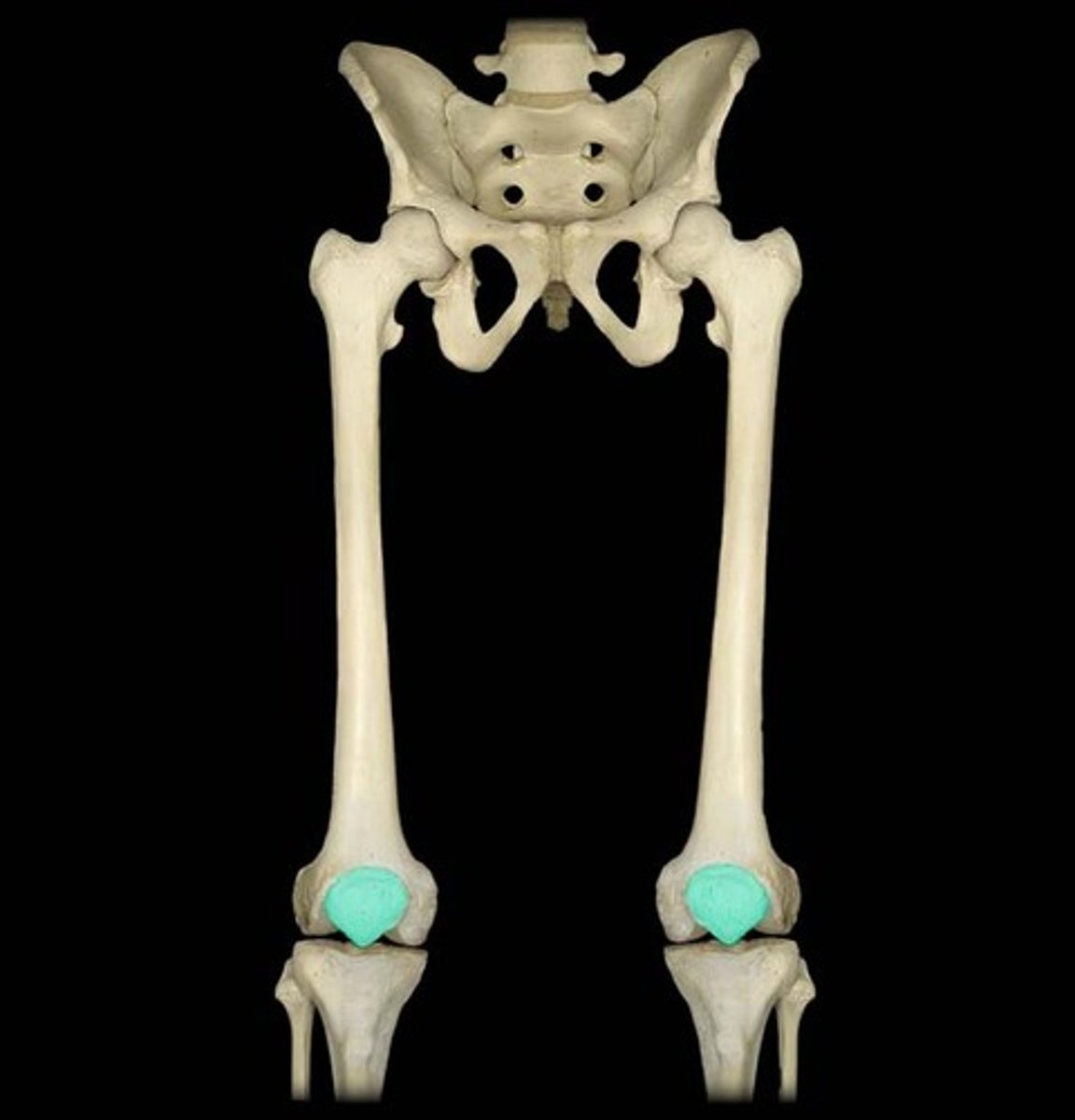
femur (picture)
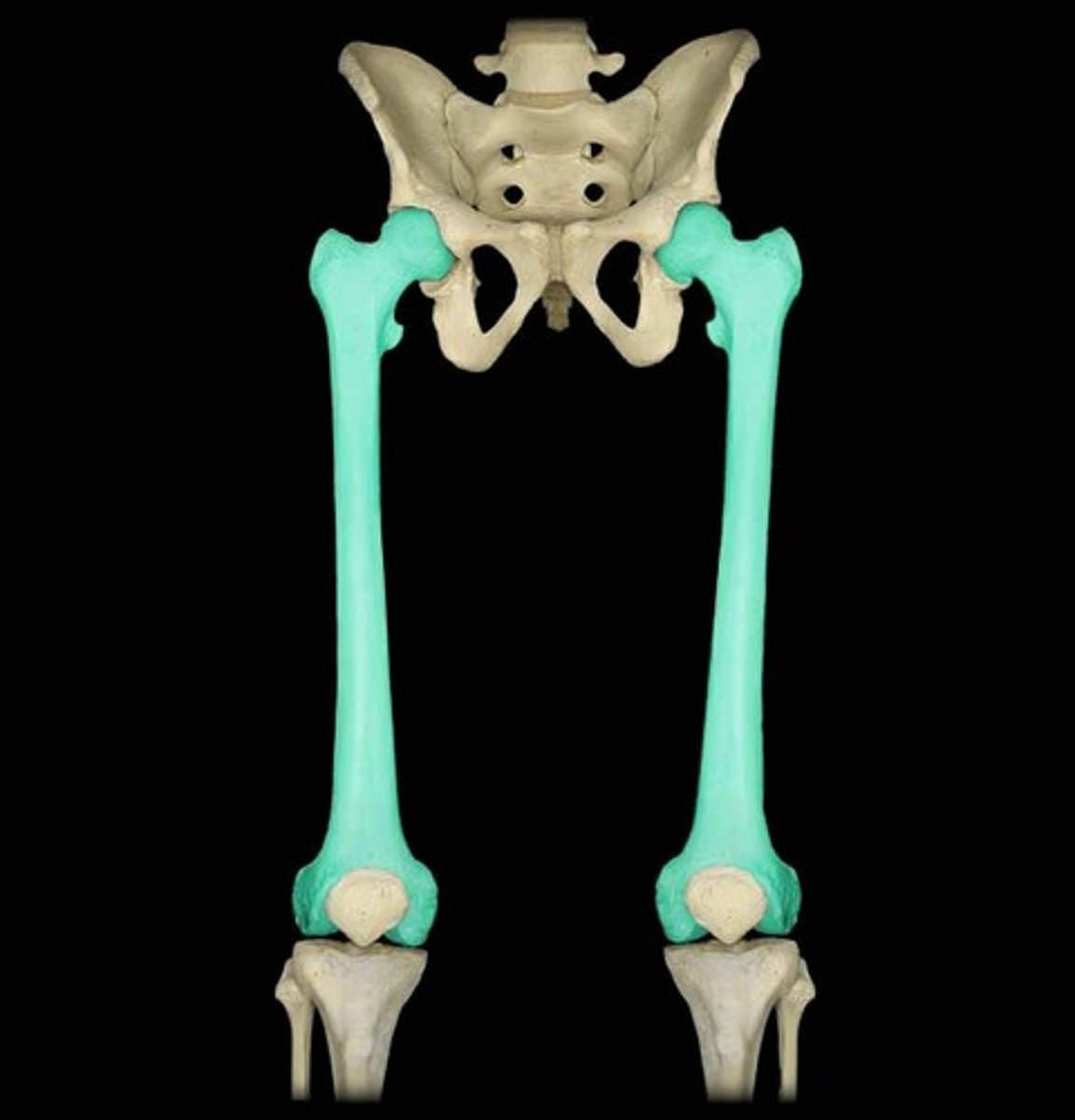
trochanter
patella