Blood Bank - Clinical Rotation Study Guide
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Component Preparation - Whole Blood
CPD, C2PD - 21 days
CDPA - 35 days
AS - 42 days
Storage temp - 1-6 C
Volume - 450-500 mL
Dosage - H&H increase by 1 g/dL + 3%
Component Preparation - Irradiated Whole Blood
Original expiration or 28 days after IRR
Storage temp - 1-6 C
QC - IRR label color change
Volume - 450-500 mL
Dosage - H&H increase by 1 g/dL + 3%
Component Preparation - pRBCs
CPD, C2PD - 21 days
CDPA - 35 days
AS - 42 days
Storage temp - 1-6 C
Volume - 450-500 mL
Dosage - H&H increase by 1 g/dL + 3%
Component Preparation - RBC aliquots
Closed - no change to exp
Open - 24 hour exp
Storage temp - 1-6 C
Volume - varies based on weight of Pt
Dosage - per 10 mL/kg increase HGB 2 g/dL
Component Preparation - RBC IRR
Original expiration or 28 days after IRR
Storage temp - 1-6 C
QC - IRR label must change color
Volume - 300-500 mL
Dosage - H&H increase by 1 g/dL + 3%
Component Preparation - RBC LR
Closed = no change to exp
Open = 24 hour exp
Storage temp - 1-6 C
QC - >85% RBC mass, <5×10^6 WBCs
Volume - 300-500 mL
Dosage - H&H increase by 1 g/dL + 3%
Component Preparation - Washed RBC
24 hour expiration
Storage temp - 1-6 C
QC - HCT 70-80%
Volume - 200 mL
Dosage - H&H increase by 1 g/dL + 3%
Component Preparation - Frozen RBC
10 year exp
Storage temp - < -65 C
Component Preparation - Deglycerolized RBC
24 hour exp
Storage temp - 1-6 C
QC - 80% RBC recovery + <1% detectable glycerol
Volume - 200 mL
Dosage - H&H increase by 1 g/dL + 3%
Component Preparation - Random Donor PLT
5-7 day exp
Storage temp - 20-24 C
QC - >5.5×10^10 PLTs, pH >6.2
Volume - 50-100 mL
Dosage - PLT count 5-10,000
Component Preparation - Single Donor PLT
5-7 day exp
Storage temp - 20-24 C
QC - >3×10^11 PLTs, pH >6.2
Volume - 200-400 mL
Dosage - PLT count 30-60,000
Component Preparation - PLTs IRR
5 day exp
Storage temp - 20-24 C
QC - IRR label color change
Volume - varies by RDP vs SDP
Dosage - varies by RDP vs SDP
Component Preparation - PLTs Pooled
4 hour exp
Storage temp - 20-24 C
QC - pH >6.2
Volume - varies
Dosage - varies
Component Preparation - FFP - Frozen, 1 year, 7 years
1 year exp, 7 year exp
Storage temp - < -18 C, < -65 C
Volume - 200-400 mL, 200-1,000 mL
Dosage - Coag factors by 20-30% per 10-20 mL
Component Preparation - FFP - Thawed
24 hour exp
Storage temp - 1-6 C
Volume - 200-400 mL
Dosage - Coag factors by 20-30% per 10-20 mL
Component Preparation - PF24 - Frozen, 1 year, 7 years
1 year exp, 7 year exp
Storage temp - < -18 C, < -65 C
Volume - 200-400 mL
Dosage - Coag factors by 20-30% per 10-20 mL
Component Preparation - PF24 - Thawed
5 day exp
Storage temp - 1-6 C
Volume - 200-400 mL
Dosage - Coag factors by 20-30% per 10-20 mL
Component Preparation - Cryoprecipitate
Frozen - 1 year exp
Thawed - 6 hour exp
Pooled / Open - 4 hours exp
Storage temp - frozen @ < -18 C, thawed @ 20-24 C
Volume - 10-25 mL
Dosage - FBG + coag factors per 5-10 mL
Component Preparation - Granulocytes + IRR Granulocytes
24 hour exp
Storage temp - 20-24 C
QC - > 1×10^10 IRR
Volume - 200-600 mL
Antibody Identification - Impacts of Dosage
Different strength reactions
If panel cells are homozygous, a strong reaction may be seen
If panel cells are heterozygous, reaction may be weak or even non-reactive
Duffy, Rh, Kidd, MNSs all exhibit dosage
Antibody Identification - Impacts of Multiple Antibodies
Different strength reactions
Matching pattern is difficult
Number of selected cells needed depends on how many antibodies are identified
Emergency Issue of Blood Products - General Policy
Emergencies or life-threatening situations (no time for T/S results)
Emergency issue blood products require physician signature to accept risks associated w/ uncrossmatched blood
Emergency issue blood may be sent through the tube system or in a cooler, but must be specially labeled from regular blood products
BB must obtain: ordering provider, patient’s name, patient’s MRN, patient’s approximate age, patient’s sex, + location of patient
WellSky: from patient dropdown menu, use Patient Registry tab to search for patient’s MRN
If purple click on Registry button + save; if not purple continue on to Emergency Issue
Proceed to Product Selection + Emergency Issue
Emergency Issue:
Select appropriate number of requested products
If RBC/WB requested: label tube w/ unit number + remove a segment from each unit for compatibility testing, apply bright orange “Uncrossmatched Blood” label front of RBC unit or on transfusion tag, apply a Hemo Temp II temperature indicator on the back of the unit
Click on “Emergency Issue” tab
Enter patient’s MRN into the field + tab. Information will populate or register the patient if not
Enter pickup information: ID, location, inspection, physician. Select Products button will become active
Click on Select Products button
The Product Code Selection form appears. The product group, number of units, + attending physician all must be entered in order to select units. Click OK when fields are complete
The Product Selection window appears. Scan the unit number + product code of each unit. Once all units are entered, click OK
Verify all information on screen. Click Save
Select Emergency Issue + then say yes
Print Emergency Release tag. Confirm information on tag. Write time + date of issue. Attach tag to unit
What pRBC products are issued
O pos → men + women >50 years old
O neg → women <50 years old
What plasma products are issued
A FFP
Fisher Race + Weiner Conversions
dce → r
dCe → r’
dcE → r”
dCE → ry
Dce → R0
DCe → R1
DcE → R2
DCE → Rz
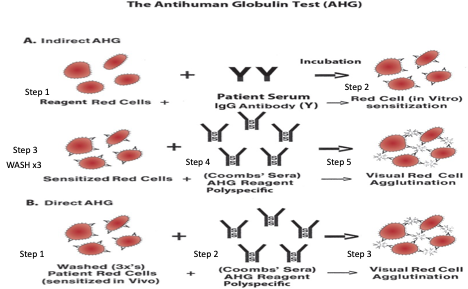
DAT
Detects in vivo sensitization of RBCs w/ IgG or complement that is associated w/ the following conditions: Transfusion reactions - alloantibodies coating donor cells; HDFN - maternal antibodies coating fetal cells; Autoimmune disorders hemolytic anemia - autoantibodies coating self cells; Drug-induced hemolytic anemia - drug reactions in plasma destroy RBCs
DAT is not required in pre transfusion testing for blood products
DAT is positive - something (IgG or C3b) is coating the surface of the patient’s RBCs in-vivo; IgG AHG+ implies antibody is coating RBC cell surface → investigate; C3b AHG+ implies complement is coating RBC cells surface → no further workup
DAT Procedure - Tube Method
Blood collection in EDTA tube
Blood made into 3-5% cell suspension + 2 drops are added to a new tube
New tube’s blood is washed x3 w/ saline
Reagent AHG is added →
If no agglutination occurs → indicator cells are added; new reaction should be positive = negative interpretation
If agglutination occurs → follow up w/ an eluate if patient has been transfused in last 2-3 weeks = positive interpretation
IAT
In-vitro test to evaluate the presence of allo or auto antibodies in patient plasma via 3 commonly performed tests: Antibody screening/Antibody ID (panels)/Antibody titers, Antigen typing, Crossmatching
A positive IAT test typically means that in-vitro sensitization of RBCs w/ IgG or complement has occurred due to: Alloimmunization from previous transfusions; Alloimmunization from previous or current pregnancy; Autoimmune disorders; Drugs or medications that may cause hemolysis
IAT Procedure - Tube Method
Blood collected in EDTA tube + centrifuged
Patient plasma added to tube w/ reagent cells
Centrifuged + read at immediate spin
Add enhancement media (LISS, PEG, 22% Albumin)
Incubate at 37 C for 15 min
Centrifuge + read at 37 C (LISS + Albumin)
Wash x3 w/ saline
Add AHG →
If negative → indicator cells added to validate reaction; should be positive = negative interpretation
If positive → follow up w/ appropriate reflex test = positive interpretation
DAT vs IAT
Cord Blood Testing On
Infants born to Rh negative mothers
Infants born from Group O mothers
Infants in the NICU
Infants born from mothers w/ clinically significant antibodies
Infants born from mothers w/ no prenatal history
Candidates for RhIG
Rh negative women
Weak D negative women
Non-immunized Rh-negative women
Rh negative mothers w/ Rh positive infants
After invasive procedures (miscarriages, abortions, ectopic, + amniocentesis)
Process for Receiving Units from Licensed Blood Supplies
Unpack carefully + inspect products for proper storage temp + condition
Mark on supplier’s packing list in appropriate area whether or not the units were received in good condition + the temp was satisfactory
Use the Inventory Module, Receive Blood Products pane: Enter batch details at top of the window: for receipt number enter your initials, enter supplier, enter received date/time, enter temp/inspection/quantity of products to receive
Tab to Unit Number field + scan the product’s unit number → tab to ABO/Rh field + scan the product’s ABO/Rh barcode → tab to Product code field + scan the product code → tab to Exp D/T field + scan product’s expiration date barcode → tab to volume field, if necessary, enter the volume of unit (Ex: FFP + Plateletpheresis) → if unit is Autologous/Directed/Reserved, enter the corresponding letter into A/D/R field → if unit has any special attributes, such as CMV negative, HGB S negative, or antigen typings, enter “Y” in AAA field (to select attributes) or scan corresponding barcode → tab through remaining fields, pane will expand to next line for any additional units to be received → after all units have been entered, click the Save button → file all checked forms in the file “Miller Shipping Forms” + return originals to supplier
Process for Confirming Units from Licensed Blood Suppliers
WB/RBC/AGRs (storage = refrigeration 1-6 C): detach 3 segments from unit → attach unit number to each segment + place 2 labeled segments into biohazard bag labeled w/ date received. Place bar-coded unit number on test tube for UNIT ABORH confirmation testing + place a segment in this test tube → place bag of segments into current week’s storage box → segments are retained for minimum of 7 weeks → using remaining segment, confirm ABO/Rh typing by performing unit ABO/Rh confirmation testing (only need forward type)
Results reporting: results of unit confirmation entered in LIS Testing Module using Active Tests pane: highlight all units to be tested, right click Enter Test Results → batch worksheet without Observations for Ortho Vision results, batch worksheet w/ Observations for manual tube/gel results; for Batch worksheets without Observations (Ortho Vision results) → reactions from Ortho Vision will appear in corresponding fields, click Verify + Save; for Batch worksheet w/ Observations (manual results) → enter reagent rack, enter reactions + interpretations for each unit to be tested, click Verify + Save
ABO Antigen Frequencies
O = 45%
A = 35%
B = 15%
AB - 5%
Rh Antigen Frequencies
D = 85%
C = 70%
E = 30%
c = 80%
e = 98%
K Antigen Frequencies
K = 9%
k = 98%
Kpa = 2%
Kpb = 99%
Jsa = <1%
Jsb = 99%
Duffy Antigen Frequencies
Fya = 65%
Fyb = 83%
Kidd Antigen Frequencies
Jka = 77%
Jkb = 73%
Lewis Antigen Frequencies
Lea = 22%
Leb = 72%
P Antigen Frequencies
P = 100%
P1 = 79%
MNSs (U) Antigen Frequencies
M = 78%
N = 72%
S = 55%
s = 89%
U = 99%
Lutheran Antigen Frequencies
Lua = 8%
Lub = 99%
Probability of Finding Compatible Donor Units
# of units needed / antigen frequency (decimal)
If more than one antigen frequencies multiply them together (decimal)
ABID Panels
All panel cells are Group O
Cells have been fully phenotyped: + refers to presence of antigen in reagent cell, 0 refers to absence of antigen in reagent cell
Autocontrol run to determine if antibody is an allo or auto-antibody
1 drop of panel cell + 2 drops of patient’s serum
Add 2 drops of AHG
Centrifuge + examine for agglutination
Add 1 drop of Coombs control cells (should agglutinate)
“Ruling out” means crossing out antigens that did not react w/ the patient’s plasma (which contains antibody): antibody will only react w/ cells that have the corresponding antigen
Consider antibody’s usual phase of reactivity - IgM like it cold (RT) while IgG like it hot (37 C)
Look for matching pattern
Electronic Crossmatch
Detect ABO incompatibilities between donor red cells + recipient serum using computer LIS system
Requires:
Patient has 2 separate ABO/Rh typings on record
Patient has no clinically significant antibodies or history of a clinically significant antibodies
Patient has a current specimen
Immediate Spin Crossmatch
Detect ABO incompatibilities between donor red cells + recipient serum
Requires:
Patient has no present or previous clinically significant antibodies
In-date T&S
Extended Crossmatch
Recipient plasma + donor red blood cells are mixed, incubated, + taken through to Coombs
Prevents transfusion of incompatible red cells + to select blood products that when transfused to the recipient will have acceptable survival
Requires:
Patient has positive antibody screen
History of an antibody (including non-specific, non-clinically significant antibody, WAA, + cold reacting antibodies
Selection of Appropriate Blood Products Based on Patient + Donor Blood Types
A - WB = A, RBC = A or O, Plasma = A or AB, PLTs = A or O
B - WB = B, RBC = B or O, Plasma = B or AB, PLTs = B or O
AB - WB = AB, RBC = AB or A or B or O, Plasma = AB, PLTs = AB or A or B or O
O - WB = O, RBC = O, Plasma = O or A or B or AB, PLTs = O
Acute Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction
Chills accompanied by 1 or more of the following signs or symptoms:
Shock, hypotension, back pain, dyspnea, chest pain, nausea, hemoglobinuria, oliguria or anuria, generalized bleeding, flushing
Febrile Non-Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction
Temperature rise of 1 C or more occurring in association w/ transfusion + without any other explanation
Temp rise may occur early in the transfusion or may not occur until an hour or 2 after the transfusion has finished
Anaphylactic Transfusion Reaction
Occur after an infusion of only a few mLs of blood or plasma
No fever or temp rise
Following symptoms may occur: coughing, bronchospasm, respiratory distress, vascular instability, nausea, abdominal cramps, vomiting, diarrhea, shock, or loss of conscientiousness
Urticaria/Allergic Transfusion Reactions
Characterized by local erythema, hives, + itching usually without fever or other adverse effects
Hypotensive Transfusion Reaction
Characterized by hypotension occurring during or within 1 hour after cessation of transfusion (all other adverse reactions presenting w/ hypotension are excluded)
Adults experience a drop in systolic BP of >30 mmHg + systolic BP <80 mmHg
Infants, children, adolescents experience >25% drop in systolic BP from baseline
TACO
Characterized by hypervolemia due to excess volume or speed of infusion
Symptoms may include: congestive heart failure, dyspnea, severe headache, peripheral edema during or soon after transfusion
TRALI
Characterized by acute respiratory distress, bilateral pulmonary edema, + hypoxemia in setting of transfusion of plasma-containing blood components
Hypotension + fever are frequent symptoms
Onset of symptoms is 1-2 hours following beginning of transfusion (can be up to 6 hours after transfusion)
TAD
Characterized by acute respiratory distress occurring within 24 hours of cessation of transfusion + without any other explanation
Delayed Serological Transfusion Reaction - Primary Immunization
Mild, occurs several weeks after transfusion + result of patient’s initial development of antibody
Antibodies are detectable no earlier than 7-10 days after transfusion + usually several weeks or months later
Unexplained fall in HGB concentration, positive DAT, detection of new red cell alloantibody
Delayed Serological Transfusion Reaction - Anamnestic Responses
Secondary response to transfused red cell antigens in a previously immunized recipient
Some alloantibodies formed after primary immunization may diminish to levels undetectable in serum
Pre-transfusion testing reveals no unexpected antibody + no serologic incompatibility, but within 3-7 days after transfusion, an anamnestic response leads to high levels of IgG antibodies that react w/ the transfused cells
Fever, unexplained fall in patient’s HGB, mild jaundice, hemoglobinuria may occur; acute renal failure is uncommon
Use of Ficin / Enzyme Treated Panels + How That Impacts ABID Workup
Can be used to modify the RBC surface of reagent cells of an ABID panel to increase or decrease expression of non-ABO blood group antigen systems
Used when there is reason to suspect underlying alloantibodies in the presence of an antibody to a high prevalence antigen on the reagent cell panel
Cannot rule out antigens that are destroyed by enzymes even if the reagent cell is unreactive
Enhanced activity - Rh, Kidd, Lewis, I / i, ABO
Decreased / No activity - Duffy, MNSs, Xga
Unaffected - Kell
Weak D Testing for Rh-negative Babies
Prepare a 3-5% solution of patient’s cord red cells in isotonic saline - add 2 drops cord RBCs, add 2 mL saline + mix well
Add 1 drop of D antisera + 1 drop of 3-5% cord red cell suspension + mix well in new test tube
To another test tube add 1 drop of D control + 1 drop of 3-5% red cell suspension
Incubate at 37 C for 15-60 min
Wash cells (4x) w/ isotonic saline
Add 2 drops of IgG AHG
Mix well + centrifuge for 15 secs at 3400 rpm
Resuspend cells by gentle agitation + examine macroscopically for agglutination
Add Ortho Coombs Control to negative tests
Weak D - Explanations
Position effect - due to location of D + C genes, RhD is on the opposite chromosome (in trans) w/ the RhCE gene, DO NOT make an anti-D
Quantitative changes - D antigen is completely formed but not fully expressed, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) that subtly change the D antigen structure, very very rarely make an anti-D
Del - extremely low number of D antigens
Partial D or D Mosaic - incomplete epitopes within the entire D protein, may make an anti-D antibody against the epitope(s) that they lack
PEG Adsorption Technique
PEG - enhances antibody uptake by removing water
Used to confirm the presence of the warm-reactive autoantibody + detect or identify any additional alloantibody(ies) that may be present
PEG treatment removes autoantibody → reducing the strength of the positive DAT + free antigen sites for adsorption
Used for patients that have not been transfused in the past 3 months
PEG Adsorption Procedure
Make 1:1 ratio of patient’s pRBCs, plasma + PEG
Mix well + incubate at 37 C for 15 min
Centrifuge at 3500 rpm for 5-10 min
Harvest the adsorbed plasma using a transfer pipette
Test absorbed plasma w/ non-treated screening cells I + II + the patient’s own cells (auto control) by the antiglobulin technique by: add 4 drops of adsorbed plasma + 1 drop of respective screening cells I + II + auto suspension, incubate screening cells + autocontrol at 37 C for 30 min, wash the contents of the tubes (4x), add 2 drops of Anti-IgG, mix well, + spin (centrifuge)
If 2 cell screen + autocontrol are negative - adorption is complete → crossmatch w/ adsorbed plasma, using the same procedure as for screening cells
If only one of the cells or both of the screening cells in the 2 cell screen are positive, the auto is negative, then a panel must be performed using the one-time adsorbed plasma to identify any underlying allo-antibody
If the 2 cell screen + autocontrol are positive - repeat adsorption using the 1x adsorbed plasma + new aliquot of patient’s untreated red cells (DO NOT add more PEG)
LISS (OAES) Enhancement Media + Why we Use it
Enhances antibody uptake + decreases incubation to 15 mins by reducing zeta potential (increases serum:cell ratio so increases ionic strength of Ab/Ag complexes)
FMH Testing
Massive Fetomaternal Hemorrhage (FMH) → 30 mL of whole blood, specimen must be post-delivery/trauma
Diagnostic test: Fetal Screen or rosette test:
Qualitative test
Purpose: detects Rh positive cells
Procedure: maternal red cells incubated w/ Anti-D serum → test washed to remove any unbound antibody → D positive indicator cells are then added → test is spun + read MICROSCOPICALLY
Interpretation: Positive = rosette formations, Negative = only loose red cells
Kleihauer-Betke Test
Quantitative test
Principle: Fetal HGB is resistant to acid elution, therefore fetal cells retain HGB + stain bright pink; Adult cells are not resistant, so they lose HGB + are only left w/ stroma (appear as ghost cells); Enables the calculation of additional doses of RhIG
Procedure: prepare slide + stain, count 2000 adult cells + note the number of fetal cells within that 2000 count, perform RhIG calculations
Negative FMS or KB testing of an Rh neg woman that gave birth to an Rh pos baby results in 1 vial of RhIg given
RhIG Calculations
% fetal cells = # of fetal cells / total cells counted
Volume of FMH (mL) = % fetal cells x 5000 (estimated total fetal blood in maternal circulation / volume of fetal blood)
Doses of RhIG = volume of FMH / 30 (1 vial of RhIG neutralizes 30 mL of whole blood)
>.5 = round up
<.5 = round down
Add safety vial