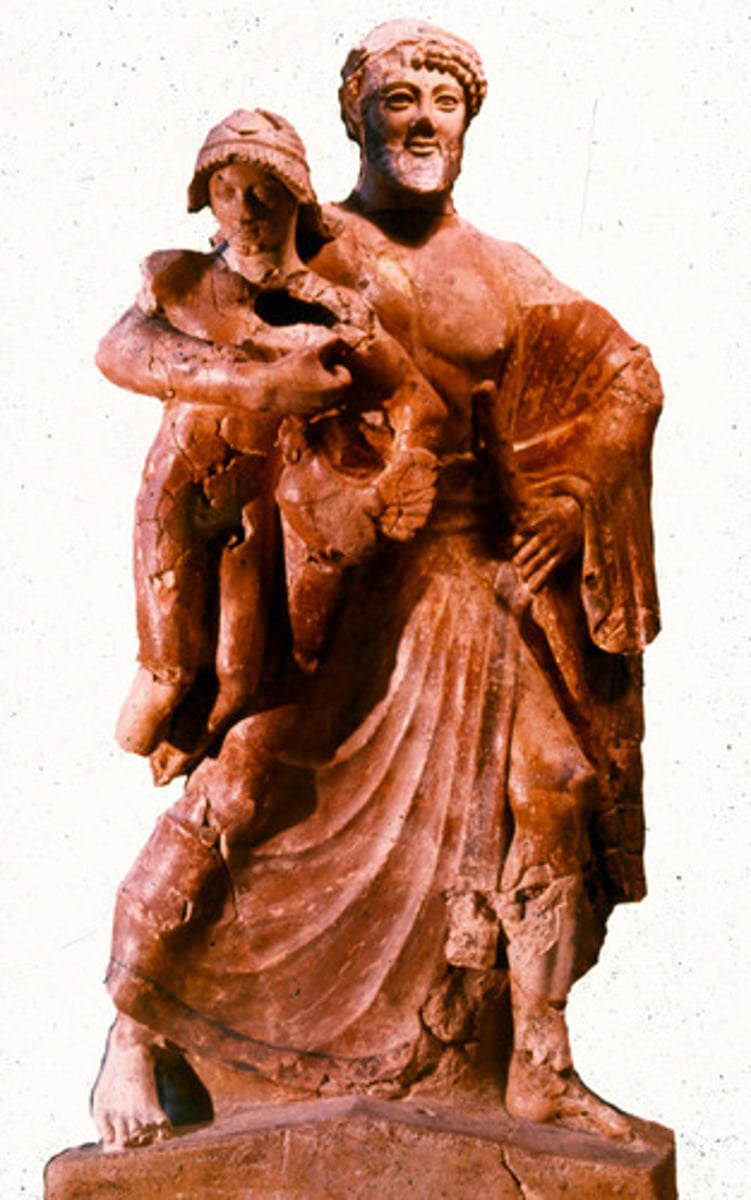
CLAS 2010: Greek Civilization - Final
1/215
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
216 Terms
Peisistratus
Born an aristocrat; was a war leader (polemarch) against Megara; a demagogue; seized office by armed coup. Solons protests to no avail, right back at the beginning
Cleisthenes
"father of democracy" provided fundamental frame for democracy; increased power of Ekklesia (Assembly) and reduced power of nobility
Phidias
Greek sculptor, painter, and architect; designed the statue of the goddess Athena on the Athenian Acropolis, namely the Athena Parthenos inside the Parthenon
Harmodius
tyrant killer; kills Hipparchus in 514 BC; portrayed as not killing out of vengeance, but out of love for the city (intentional history).
Aristogeiton
tyrant killer; kills Hipparchus in 514 BC; portrayed as not killing out of vengeance, but out of love for the city (intentional history).
acropolis
"hilltop city"; place of the most important buildings and places of worship in all of Athens i.e. the Parthenon, Erechtheum
agora
central square in Athens
Athena Parthenos
statue of Athena the "virgin" made by Phidias and in the Parthenon; most renowned cult image of Athens
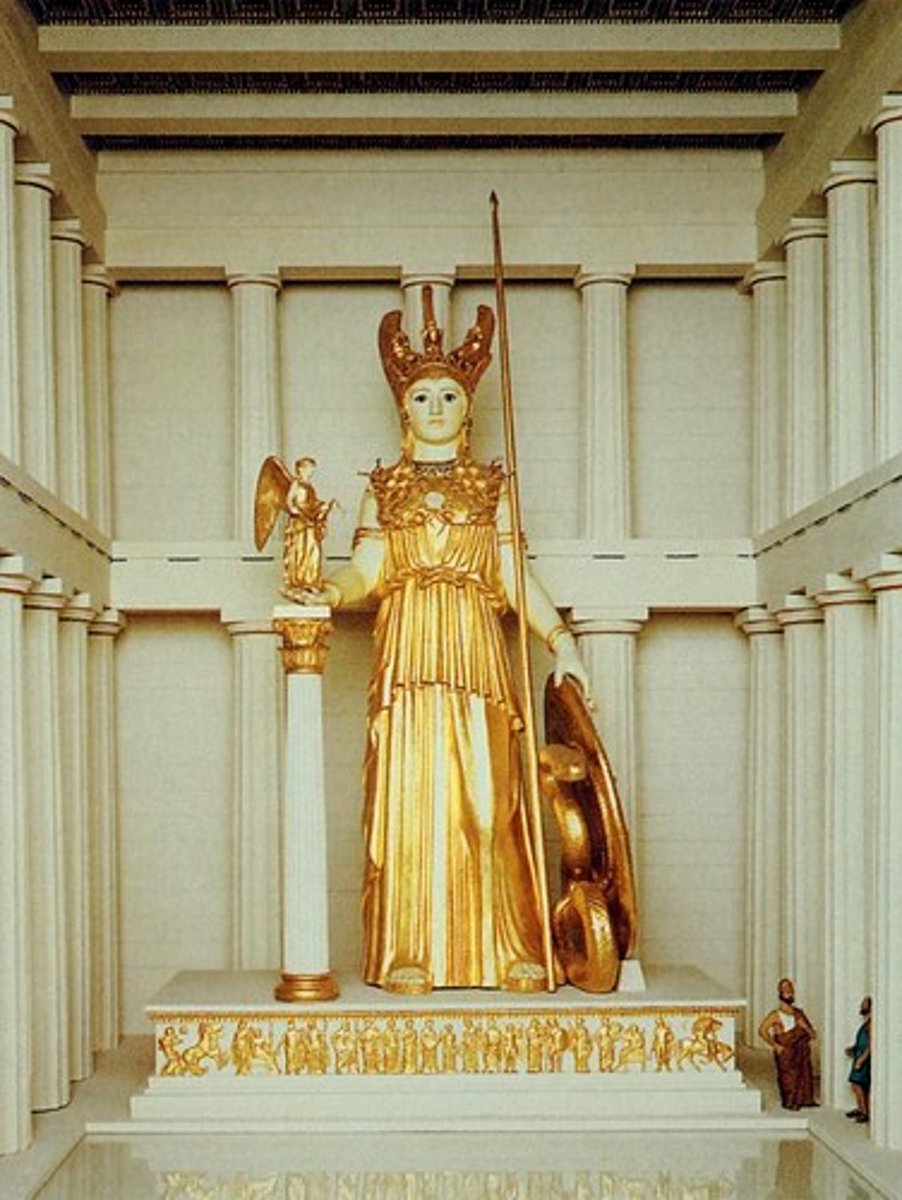

Athena Promachos
Holding god Nike, holding spear; embodied political and military power of Athens; on top of acropolis, seen from afar

deme
"neighborhood"; local districts of a polis; establishment of demes as the fundamental units of the state weakened the aristocratic family groups
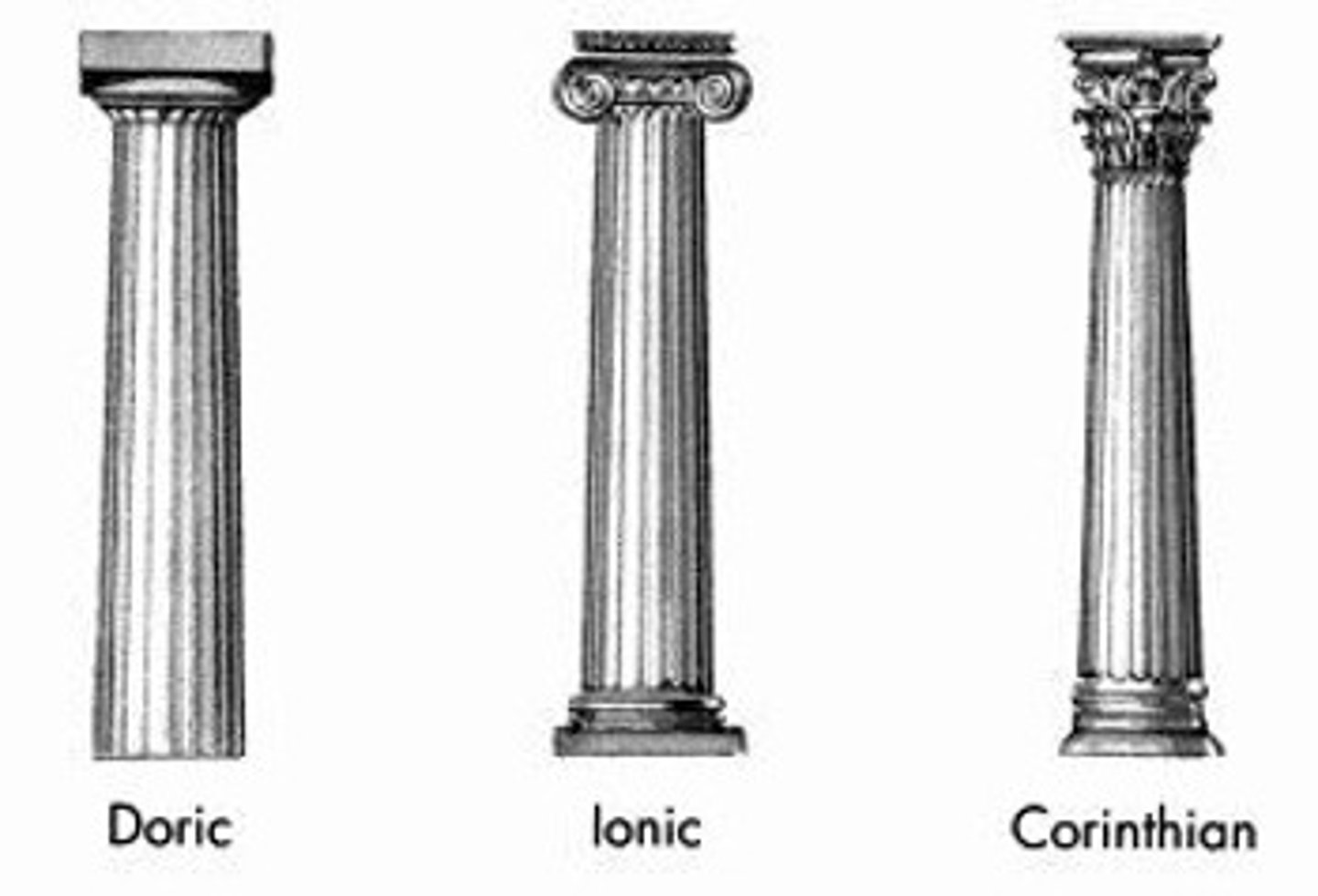
Doric/Ionic/Corinthian Order
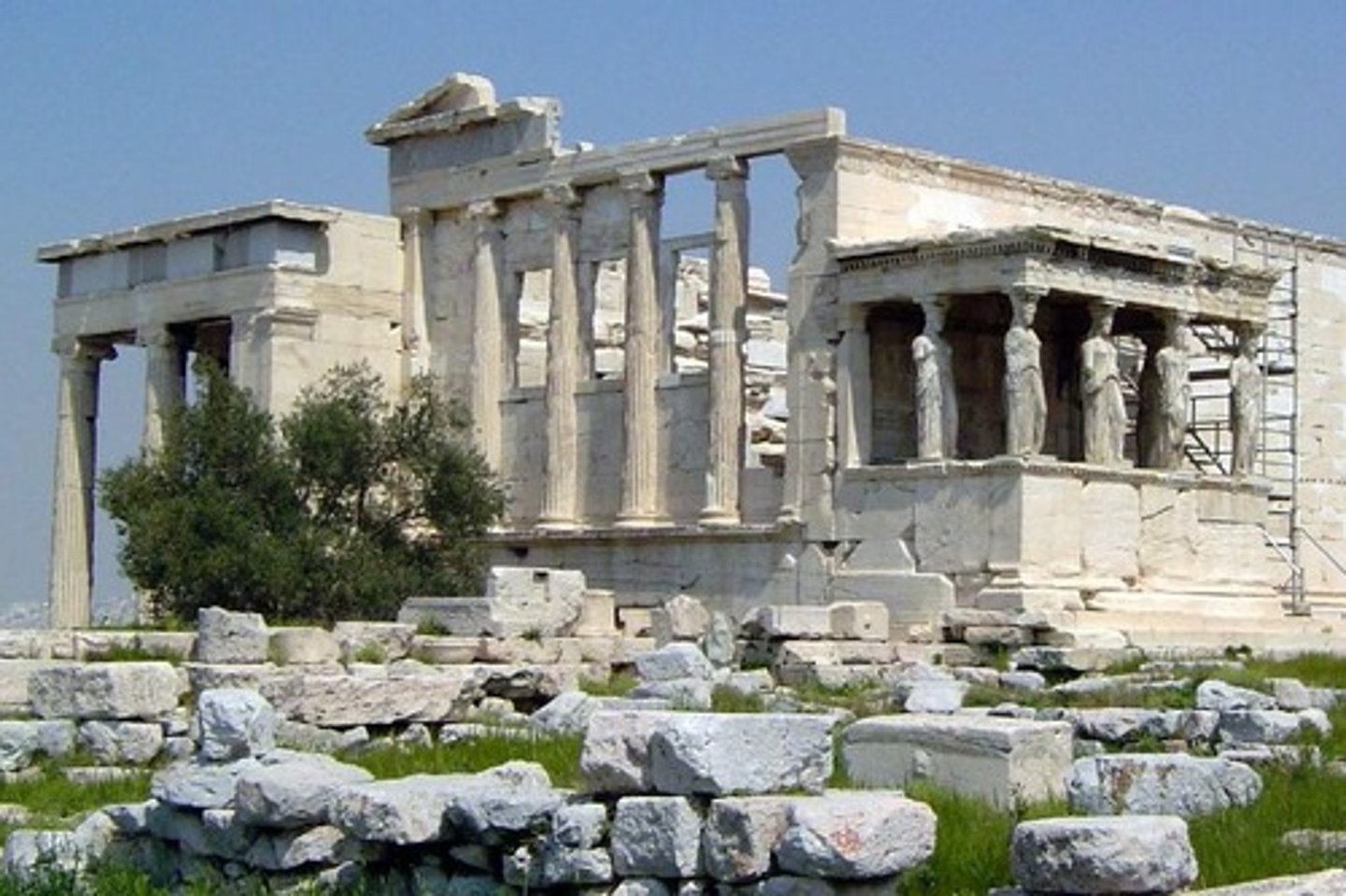
Erechtheum
temple on the acropolis dedicated to Athena and Poseidon; important in the Panathenaea for clothing Athena Polias with a new peplos

isegoria
"equality of speech"; one of the foundations of Cleisthenes' reforms
isokratia
"equality of power"; one of the foundations of Cleisthenes' reforms
isonomia
"equality under law"; one of the foundations of Cleisthenes' reforms
Peloponnesian War
431-404 BC; war fought between Athens in Sparta in which Sparta emerged victorious; marked the fall of democracy, and end of Greek hegemony in the Mediterranean
Persian Wars
wars between Greece and Perisa from 490-479 BC; as a result, Athens becomes imperial force in Mediterranean, which led to heavy taxes on other Greek city-states
polemarch
war leader
telesterion
Devoted to Demeter and Persephone, these initiation ceremonies were the most sacred and ancient of all the religious rites celebrated in Greece

Tyrant-slayers
see Harmodius and Aristogeiton
Aeschylus
"The Father of Tragedy"; oldest plays surviving; first to add a second actor to allow for dialogue in the play; winner of festival of Dionysus 14 times; wrote Persians
Sophocles
considered "best of the three"; writer of Antigone and Oedipus the King; addition of third actor
Euripides
most unique of the three tragedians; first to combine tragedy and comedy elements; wrote Bacchae
Aristophanes
"The Father of Comedy"; comic playwright; wrote Lysistrata and Thesmophoriazusae; focuses on the role of women in society, often depicting them as sex-crazed individuals
Aristotle
greatest thinker in ancient Greece; wrote Poetics and importantly defined the elements of tragedy such as anagnorisis and peripeteia
Dionysus
God of wine, madness and ecstasy; "the god that comes"; important because he is the most prominent of the gods among mortals:

Pentheus
a character in Euripides' Bacchae who does not acknowledge Dionysus as a God; as a consequence, he is driven to death and represented as a theomachos ('god fighter') by Dionysus

'original sin'
the sin committed in the name of humanity; the idea that out of the ashes of the Titans who were destroyed by Zeus come humans, meaning we are both flawed and divine
anagnorisis
"knowing again"; recognition; a change from ignorance to awareness of a bond of love or hate
(Greater) Dionysia
most important theatrical event, festival celebrated in honor of Dionysus; featured yearly competition among playwrights and a chance to see the latest plays by Aeschylus, Sophocles, Euripides, Aristophanes
Dionysus thrice-born
(1) Semele, II) Zeus' thigh, III) sparagmos by the Titans and reassembling by Rhea
dithyrambos
It was an ancient Greek hymn sung and danced in honour of Dionysus, the god of wine and fertility; the term was also used as an epithet of the god: Plato, in The Laws, while discussing various kinds of music mentions "the birth of Dionysos, called, I think, the dithyramb."
epiphany
Demonstration of gods' power among mortals; seen in most prominently in Dionysian festivals and plays
heorte
"holiday"
Maenads
female followers of Dionysus and the most significant members of the Thiasus, the god's retinue. Their name literally translates as "raving ones"

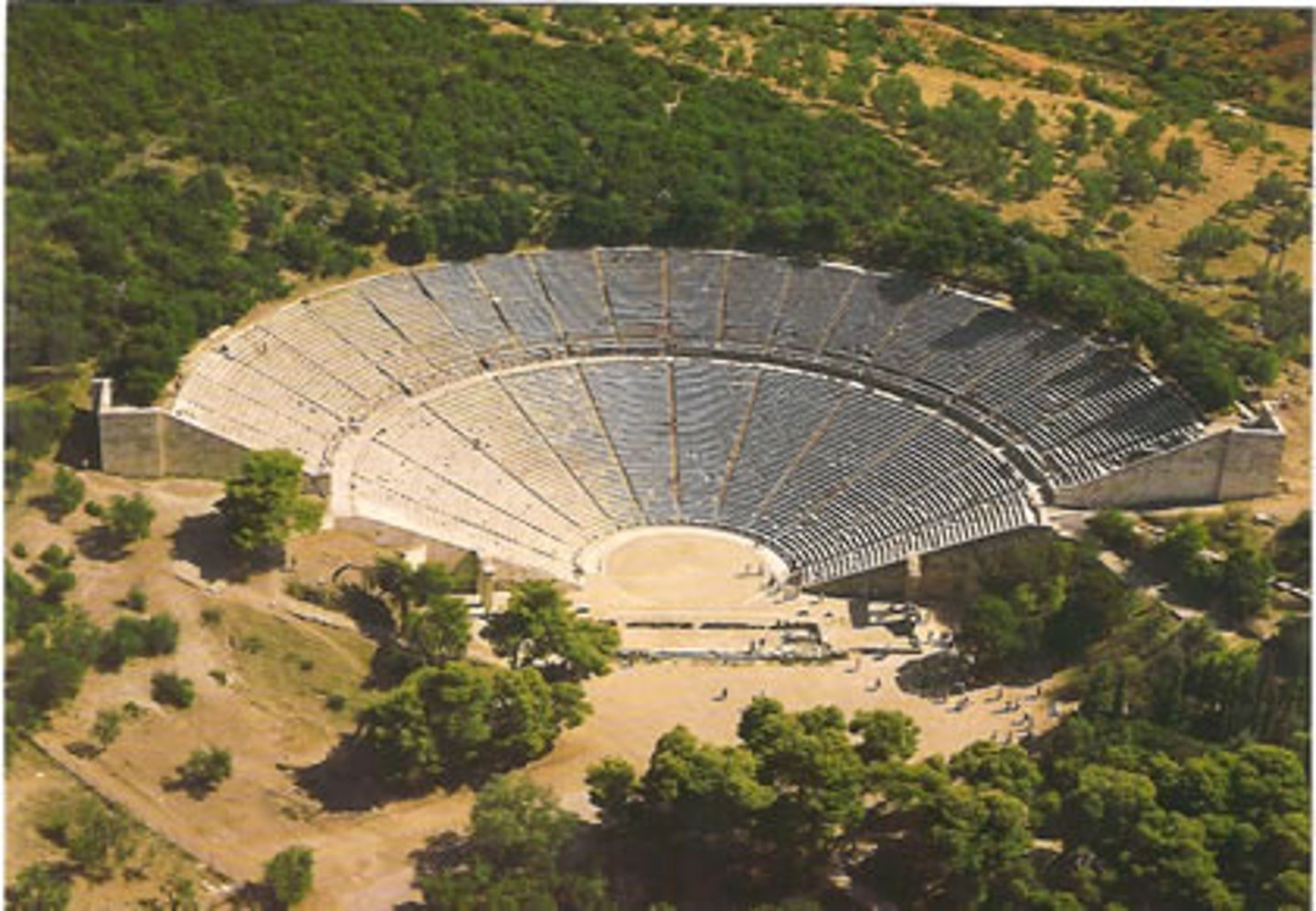
orchestra
large area in front of the stage where the chorus sang and danced
Panathenaea
most important Athenian festival; Celebrates unification of Athens. City used to be individual places all worshipping Athena. During this time they consider what it means to be Athenian
peplos
dress made for the statue of Athena in the Panathenaea

peripeteia
"reversal"; occurs when a situation seems to be developing in one direction, then suddenly "reverses" to another; example: Creon in Antigone
pompe
public procession; there would be one of these during the Greater Dionysia from outside the city to the theater
skene
building that contained the actors' dressing rooms
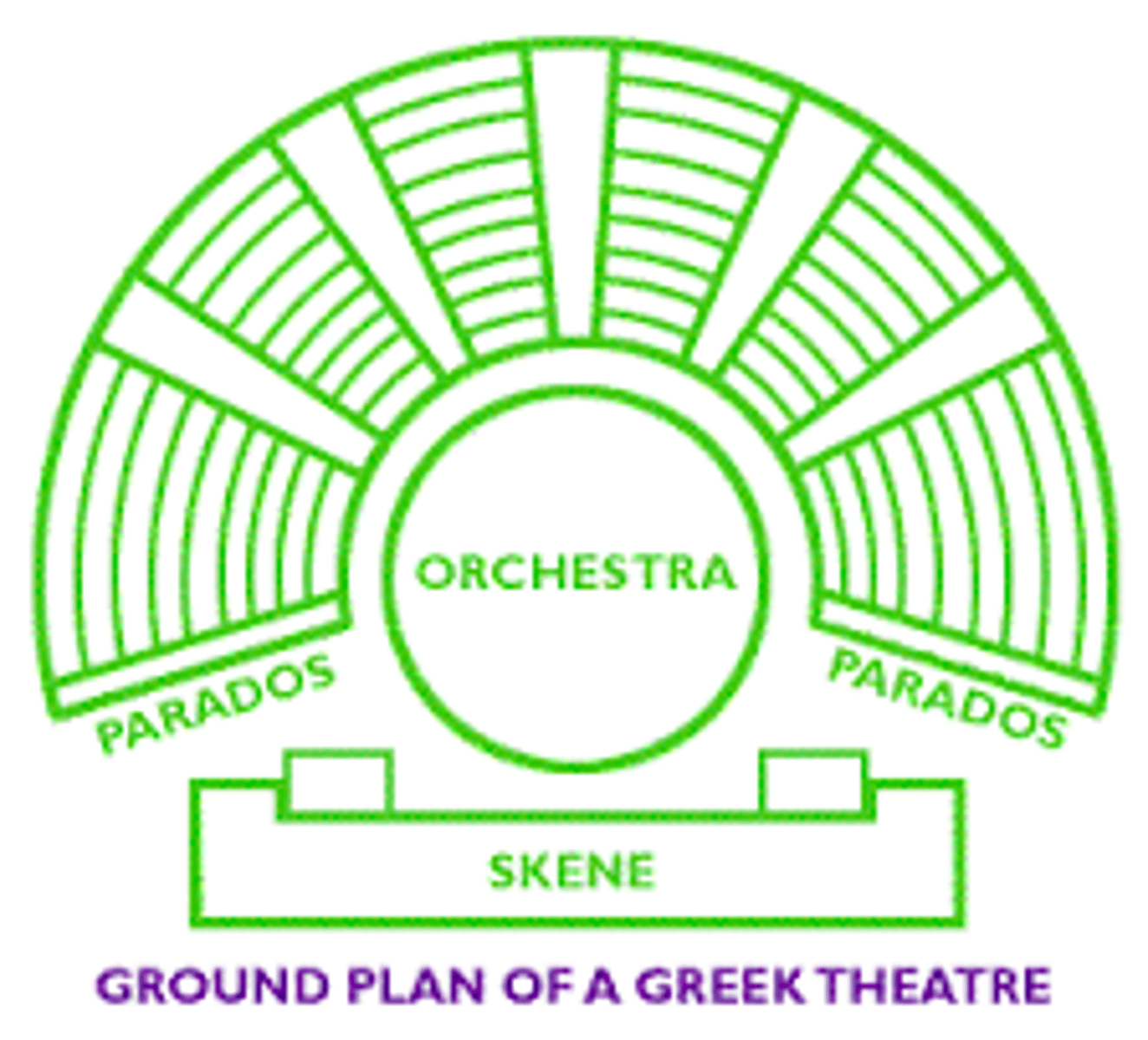
theatron
area of seats for the audience hollowed out from the hillside

theomachos
god-fighter; someone who opposes/fails to recognize the Gods; most important example is Pentheus in the Bacchae
thyrsos
a tall staff which has ribbons. Dionysus is often depicted riding a panther holding this

Hecateus
early Greek historian and logographer; writer of periegetic literature
Hellanicus
ancient Greek logographer; influence on the historiography of Athens was considerable
Herodotus
"Father of History" first of the historians to come up with the historiographical methodology, causation; lays down aims and objectives of his work in the proem (first to do this); also called 'father of lies' because he comes up with crazy stories to explain things in history (i.e. flying snakes in Arabia); first surviving large-scale work in prose; 'Well-travelled Herodotus'
Panyassis
Herodotus' uncle, a famous local epic poet; "the glorious lord of verse"; mentioned as contributing to the "Pride of Halicarnassus"
akoe
'hear-say'; oral sources; things he learned from others, about an area, battle, etc.; one of Herodotus' categories of sources
autopsia
personal witness; what you have seen yourself; categorized by Herodotus
causation
figuring out the cause of an event; first used as a method by Herodotus, who attributes cause to both divine and human agents in his works
cyclicity
certain historical patterns are repeated in identical or very similar fashions; one of the methods of enquiry ('historie') that Herodotus first used
historie
enquiry
logographer
writers of periegetic literature (= descriptions of geographical regions)
periegesis, periegetic literature
descriptions of geographical regions
poikilia
'variety' | Herodotus writes in highly literary Ionic
programmatic proem
opening to an enquiry; most famous is Herodotus's: "This is the display of the inquiry of Herodotus of Halicarnassus, so that things done by man not be forgotten in time, and that great and marvelous deeds, some displayed by the Hellenes, some by the barbarians, not lose their glory, including among others what was the cause of their waging war on each other."
sophist
A specific kind of teacher in ancient Greece, in the fifth and fourth centuries BCE. Many of these specialized in using the tools of philosophy and rhetoric, though others taught subjects such as music, athletics, and mathematics.
Thucydides
Ancient historian 5th c BC - chronicled the events of the Peloponessian War; significant because he introduced the scientific method into his writing; he has taken out a lot about the Gods; first ancient historian who writes on contemporary events, unlike Herodotus.
Pericles
Greek statesman, orator and general; creator of the Athenian Empire; builds a naval empire, and extends her power to man Greek cities whose freedom becomes conditional
Xenophon
contemporary with Thucydides; significant because he writes on the Peloponnesian War in Hellenica which continues Thucydides' History of it which had no logical ending
Diodorus of Sicily
ancient Greek historian; important because he is our most significant source on the the events after the Megarian decree
'Thucydides trap'
the idea that fear motivates people into action, and that the conviction that the hegemonic force must stop the emerging power to fulfill its own potential; seem most strongly through Athens' aggression but also works well throughout history.
Archidamian war
war between Athens and Sparta; showed that while Sparta had the superior military, Athens dominated the seas with their navy; first part won by Athenians, second part truce
demagogue (δημαγωγός)
'leader of the people' | practically minded people who don't think about the health of the city-state but only about their power. Primary aim is to convince the masses that the way that they operate is the only just way to operate. Use convincing words to justify actions
helot
people who contributed resources to the Spartans, in Messinia, slaves
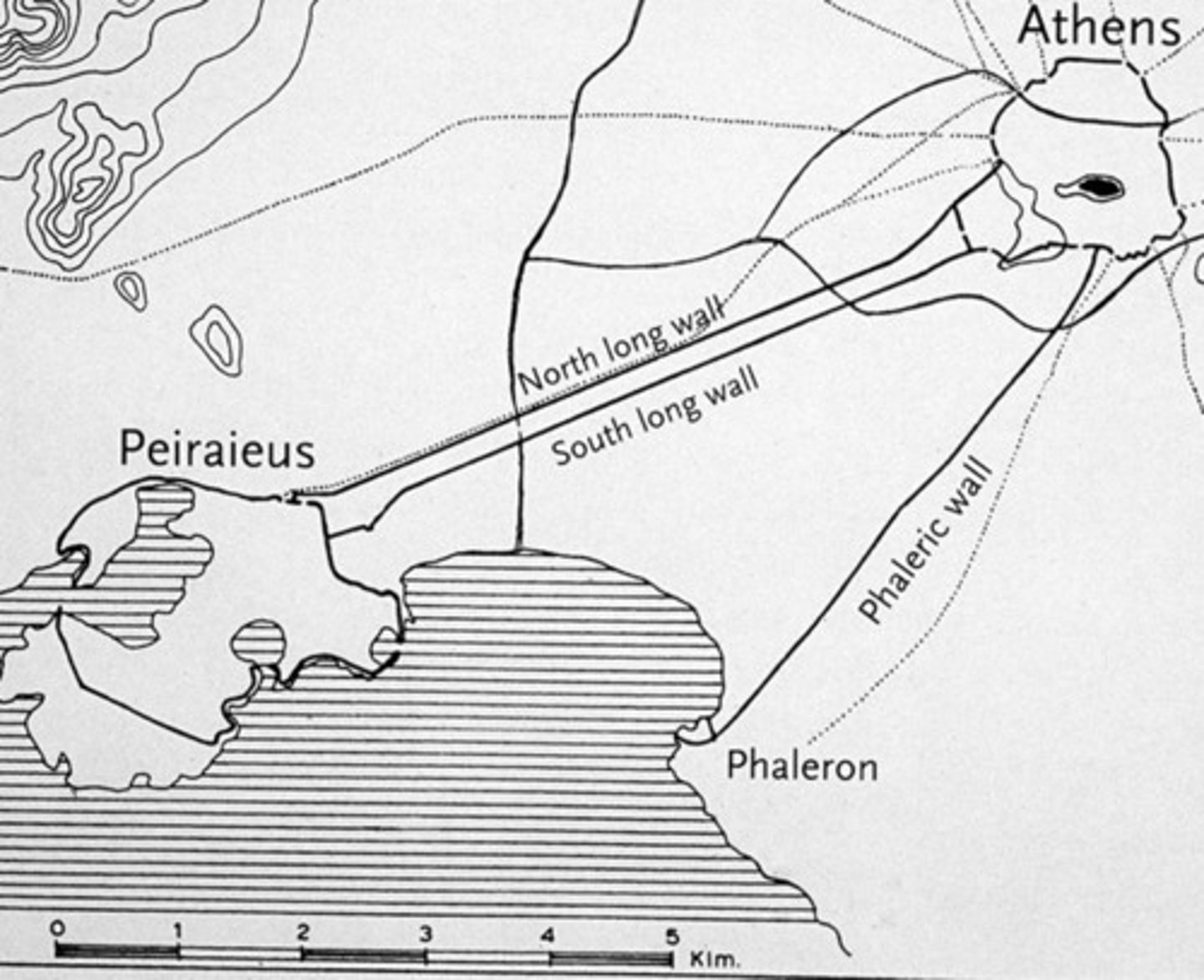
Long walls
expensive project by Athens to connect the harbor of Piraeus to the city. Allies at this point have no idea that the money is theirs being used for this; important because Sparta starts wondering why Athenians are putting up walls and leads to increase in tensions/opposition to Athens
Megarian decree
Economic sanctions on Corinth by Athens; important because economic sanctions as an element of political pressure; Hostile Bipolarisation ['we will protect our welfare with any means necessary!']
Peace of Nicias
also known as the Fifty-Year Peace; a peace treaty signed between the Greek city-states of Athens and Sparta in 421 BC, ending the first half of the Peloponnesian War.
Peloponnesian league
all the Peloponnese cities; formed in order to be aware of the threat of Delian League; had issues with helots and natural disasters
Pentekontaetia
50 year period | period of the rise of Athens as a hegemonic power in the Mediterranean
Plague of Athens
Athens overcrowded which leads to plague outbreak; 1/3rd of people and army lost; Pericles, the great general died, decline in morale
Political realism
the view that Athens was displaying in the Megarian decree, that "we have the army"
strategos
military general
Athena (= Pallas)
meaning "youth, young woman"; term used to denote that Athena is the main goddess of girls/youth.
Artemis
goddess of the hunt and protector of young girls; Greek girls would celebrate her in the Brauronia
Aphrodite
goddess of grown Greek women;
Iphigenia
priestess of Artemis in Brauron; Girl comes to Artemis' temple, brother kills her favorite bear, so now all the girls have to play the part of a she-bear before they get married
aiora
"swing" | ritual for virgins to stabilize them; she is betwixt and between; empty pot metaphorically denotes the womb. The pot needs to be 'filled'
aletrides
the ones who pound the barley for Archegetis [the ritual of oxen, pigs]; age 10
arkteia
an initiation period for young girls to become women, where they would remain at the sanctuary for a period of time and participate in the various rites and rituals; girls that participated in Brauronia

arrephoria
carrying the sacred basket for Artemis/Athena; age 7 phase
Brauronia
festival dedicated to Artemis. They would celebrate Artemis. They had to basically become wild creatures; rite of passage for sexual maturation

cursus honorum
progression through the ranks (of Athenian woman)
kanephoros
basket carrier for the most important Athenian festivals; age 12; Typically placed @ front of every procession in the city. So that men can look at you and assess you.

miasma
('stain') term that denotes the human pollution at large
parthenos
virgin
Ephorus
ancient Greek historian who wrote about institutionalized homosexuality in Cretan rituals
Strabo
Main source on Cretan education; wrote on the three stages of the Athenian rite of passage (separation, liminality, reintegration)
Plutarch
main source on Spartan agoge; biographer of Lycurgus
Lycurgus
established the military-oriented reformation of Spartan society; father of Spartan constitution and way of life
"black hunter"
Person who is mostly active by night, hunts by night; a) dressed in black, b) living outside, c) hunting for food, d) active at night, sleeping during the day; one of the ways a Spartan a boy is transformed into a man
secret band of Thebes
Most efficient military unit in the world. 150 homosexual couples; justification from Plato: "who would desert his beloved or fail him in the hour of danger?"
"sacred prostitution"
A woman has to have sex with the first stranger who enters a temple once in her life.
Ritual abduction
regulated by the state; the act of taking a boy away for a couple months to the chora and then brought back and monitored; Ganymedes = origin
agela
'a herd of animals'
agoge
"the leading", Rite of passage; Come back with your shield or on your shield (corpse); Victory or death
andreia
'manliness' | public mess halls; and they sit together on the ground as they eat their food, clad in shabby garments
Erastes and eromenos
older man, 'lover' | child, 'beloved'
Ganymedes
Trojan Ganymedes is in exile. Like many other heroes in their youth. Zeus sees him and falls in love with him, has him abducted. He becomes Zeus's lover and cup-bearer.
