4ABCD
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:08 AM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
1
New cards
**Autocrine Signalling**
signals that act on the cell that secreted them
2
New cards
**Paracrine Signalling**
signalling molecules that act on cells that are close by
3
New cards
**Endocrine Signalling**
signalling molecules that act on cells that are far from the gland/organ
4
New cards
Types of Hormones
Peptides (proteins), Steroids (lipids)
5
New cards
Ways cells communicate w/ each other
Hormones, Neurotransmitters, Cytokines, Pheromones
6
New cards
Cytokines
•Involved in communication between immune cells
•Regulating inflammation
•Response to cell damage or pathogens (autocrine or paracrine)
•Fighting infection
•Regulating inflammation
•Response to cell damage or pathogens (autocrine or paracrine)
•Fighting infection
7
New cards
Pheromones
Signalling that is excreted into the external environment
Influence behaviour or physiology of another organism (unconscious communications)
E.g. triggering aggressive behaviour, attracting a mate, food trails
Influence behaviour or physiology of another organism (unconscious communications)
E.g. triggering aggressive behaviour, attracting a mate, food trails
8
New cards
Stimulus Response Model (Cells)
Signalling molecule → reception → Transduction → Cellular response
9
New cards
Transduction
Converting the signal in a form that can be relayed to its final destination (can be one step or many)
10
New cards
Compare and contrast hormones and neurotransmitters
Hormones: Hormones are produced in endocrine glands and are secreted into the blood stream. Neurotransmitters: Neurotransmitters are released by presynaptic nerve terminal into the synapse.
Hormones: have stronger effects but are slower, Neurotransmitters: have weaker effects but are faster
Hormones: act on distant target cells (endocrine signalling)
Neurotransmitters: act on cells close by (paracrine signalling)
Hormones: have stronger effects but are slower, Neurotransmitters: have weaker effects but are faster
Hormones: act on distant target cells (endocrine signalling)
Neurotransmitters: act on cells close by (paracrine signalling)
11
New cards
Why would multi cellular organisms have different types of cell signalling?
multicellular organisms, cell signaling allows for specialization of groups of cells.
12
New cards
compartmentalisation
By concentrating the necessary components inside a small region within the cell, cell compartmentalization improves the efficiency of several subcellular activities. Intracellular membrane systems create enclosed compartments separated from the cytoplasm of the cell.
13
New cards
Cells replicate exponentially
after each round of replication the number of cells present doubles
14
New cards
Purposes of cell division
**Growth and Development**
As we grow larger, our cells don’t actually become larger. Instead, we are simply made of more cells. Therefore, for a multicellular organism to grow and develop, it is important that cells replicate.
**Maintenance and Repair**
Cells are constantly dying as they age or become damaged. Cell replication allows these cells to be replaced
**Reproduction**
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells replicate to reproduce. When they replicate, they are enlarging their population.
As we grow larger, our cells don’t actually become larger. Instead, we are simply made of more cells. Therefore, for a multicellular organism to grow and develop, it is important that cells replicate.
**Maintenance and Repair**
Cells are constantly dying as they age or become damaged. Cell replication allows these cells to be replaced
**Reproduction**
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells replicate to reproduce. When they replicate, they are enlarging their population.
15
New cards
Binary Fission Step 1
A prokaryotic cell before binary fission
16
New cards
Binary Fission Step 2
The circular chromosome is uncoiled and is replicated. Plasmids are replicated too
17
New cards
Binary Fission Step 3
The cell elongates to prepare for cell division
18
New cards
Binary Fission Step 4
Cell undergoes cytokinesis in which the cell pinches inwards creating a septum
19
New cards
Binary Fission Step 5
A new cell wall and cell membrane is formed
20
New cards
Binary Fission Step 6
Two genetically identical daughter cells are created
21
New cards
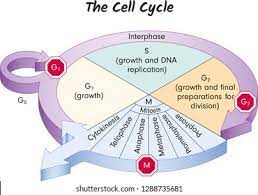
Cell Cycle Stages
**Gap 1 G1**:
The new cell starts growing and replicating its organelles
**Synthesis (S):**
DNA replication occurs
**Gap 2 (G2):**
The cell continues to grow in preparation for division
**Mitosis (M) and cytokinesis:**
The single parent cell gives rise to two identical daughter cells.
The new cell starts growing and replicating its organelles
**Synthesis (S):**
DNA replication occurs
**Gap 2 (G2):**
The cell continues to grow in preparation for division
**Mitosis (M) and cytokinesis:**
The single parent cell gives rise to two identical daughter cells.
22
New cards
Gap 0 G0
Performing all cell function but not preparing for cell division
23
New cards
difference of mitosis and cytokinesis
Mitosis is a type of cell division in which a whole cell divides
Cytokinesis is one of the steps of mitosis in which the cytoplasm of the cell divides.
Cytokinesis is one of the steps of mitosis in which the cytoplasm of the cell divides.
24
New cards
Interphase
•Occurs between divisions
•Longest part of cycle
•‘Normal life’ of cell
•DNA replication happens here
•Longest part of cycle
•‘Normal life’ of cell
•DNA replication happens here
25
New cards
1\. Prophase
Chromosomes appear, nuclear membrane disappears and centrioles form as well as spindles made up from microtubules
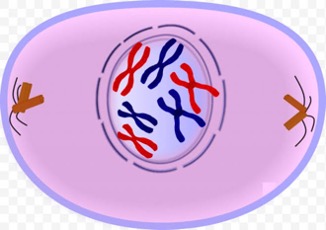
26
New cards
2\. Metaphase
Chromosomes line up across the center of the cell and attach to a spindle fiber
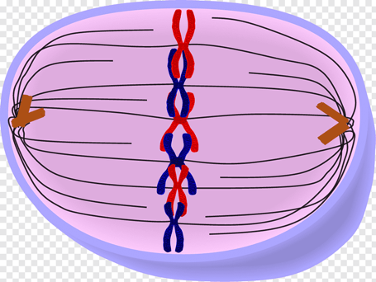
27
New cards
3\. Anaphase
•Each pair of chromatids are separated at the centromere and moves to the opposite pole
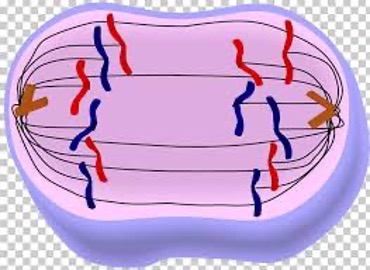
28
New cards
4\. Telophase
•Nucleus membrane forms
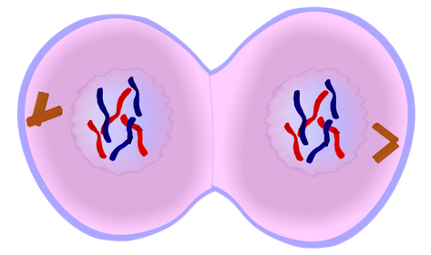
29
New cards
5\. Cytokinesis
•Cytoplasm divides into two
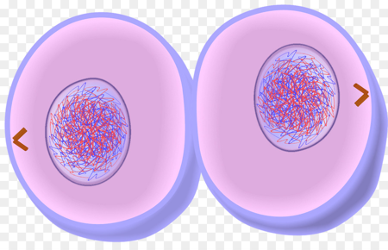
30
New cards
Why is it important for DNA to replicate before cell division?
DNA needs to replicate before cell division in order for new body cells to maintain the same number of chromosomes as their parent cell.
31
New cards
Checkpoints
**End of G1**,
grow or divide? Delay
•Checking DNA for any damage
•Got enough nutrients
•Cell size and growth is normal -> G0
**End of G2**,
* has an error occurred during DNA replication? If yes, then the cell must undergo apoptosis (programmed cell death).
* Check size is normal
**During Mitosis (end of metaphase)**,
are the chromosomes aligned ok? Are the spindle fibres attached correctly? If not, apoptosis will occur.
grow or divide? Delay
•Checking DNA for any damage
•Got enough nutrients
•Cell size and growth is normal -> G0
**End of G2**,
* has an error occurred during DNA replication? If yes, then the cell must undergo apoptosis (programmed cell death).
* Check size is normal
**During Mitosis (end of metaphase)**,
are the chromosomes aligned ok? Are the spindle fibres attached correctly? If not, apoptosis will occur.
32
New cards
What happens if the checkpoints don’t work?
uncontrolled and unmonitored cell division, this is commonly known as cancer.
33
New cards
**Apoptosis**
the controlled death of cells in the body also called programmed cell death.
34
New cards
Cell death is required for a number of reasons
•Eg Tadpoles losing its tail and becomes a frog, or a human embryo losing the webbing between fingers and toes.
•Or when cells have reached the end of their life span, ware and tare or infection
•Controlling the number of cells in the body
•Damaged DNA
•Infection
•Or when cells have reached the end of their life span, ware and tare or infection
•Controlling the number of cells in the body
•Damaged DNA
•Infection
35
New cards
How apoptosis occurs
**•Caspase enzyme is responsible for apoptosis**
•Signalling molecule produced
•Signal transduction occurs
•Stimulates enzymes
•It occurs in a number of steps
•Signalling molecule produced
•Signal transduction occurs
•Stimulates enzymes
•It occurs in a number of steps
36
New cards
Pathways that initiate apoptosis
1\.Mitochondrial Pathway (or intrinsic pathway)
\
2\.Death Receptor Pathway (extrinsic pathway)
\
\
2\.Death Receptor Pathway (extrinsic pathway)
\
37
New cards
1\.Mitochondrial Pathway (or intrinsic pathway)
•Detect damage and release **cytochrome c** into the cytosol which activate caspase enzymes
38
New cards
1\.Death Receptor Pathway (extrinsic pathway)
•Immune cells release death signalling molecules that bind to the receptor proteins on the cell membrane, this initiates the caspase enzymes
39
New cards
Steps of apoptosis
1\.Activation of caspase enzyme
2\.Separation of adjacent cells
3\.Collapse of the cells cytoskeleton
4\.Cell shrinkage
5\.Breakdown of organelles and nucleus
6\.Blebbing of plasma membrane
7\.Membrane breaks apart into vesical that secrete toxins
8\.Phagocytosis of the apoptotic bodies by specialised cells (without spilling cells condense)
2\.Separation of adjacent cells
3\.Collapse of the cells cytoskeleton
4\.Cell shrinkage
5\.Breakdown of organelles and nucleus
6\.Blebbing of plasma membrane
7\.Membrane breaks apart into vesical that secrete toxins
8\.Phagocytosis of the apoptotic bodies by specialised cells (without spilling cells condense)
40
New cards
***Phagocytosis***
the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (form of endocytosis)
**Vacuole v.s. Vesical**
•Both are membrane bound organelles
•Vacuole is larger / Vesical is smaller
•Vacuole cannot fuse with the plasma membrane / vesical can
**Vacuole v.s. Vesical**
•Both are membrane bound organelles
•Vacuole is larger / Vesical is smaller
•Vacuole cannot fuse with the plasma membrane / vesical can
41
New cards
Cell Cell Diagram
42
New cards
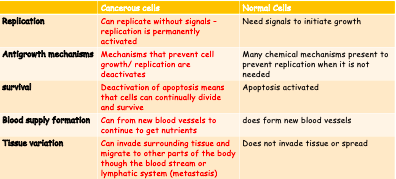
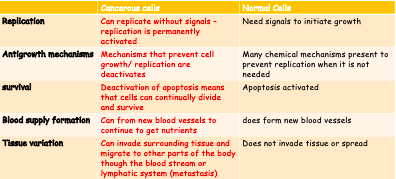
Compare and contrast cancer cells with normal cells
\
\
\
\
\
43
New cards
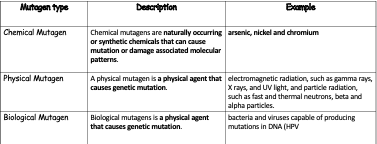
Mutagens
44
New cards
Stem cells
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells which can differentiate into specialised cells
45
New cards
Differentiation
development of a stem cell into a specialized cell with a particular function
46
New cards
Specialised cells
cells which serve a unique particular function (and have a particular structure)
47
New cards
Properties of Stem Cells
**Self-renewal**
Can replicate without disrupting their ability to differentiate (by producing both a differentiated cell and a new stem cell when they replicate)
\
**Potency**
Has the capacity to differentiate into different cell types (the higher the potency of a stem cell, the greater the number of cell types it can differentiate into)
Can replicate without disrupting their ability to differentiate (by producing both a differentiated cell and a new stem cell when they replicate)
\
**Potency**
Has the capacity to differentiate into different cell types (the higher the potency of a stem cell, the greater the number of cell types it can differentiate into)
48
New cards
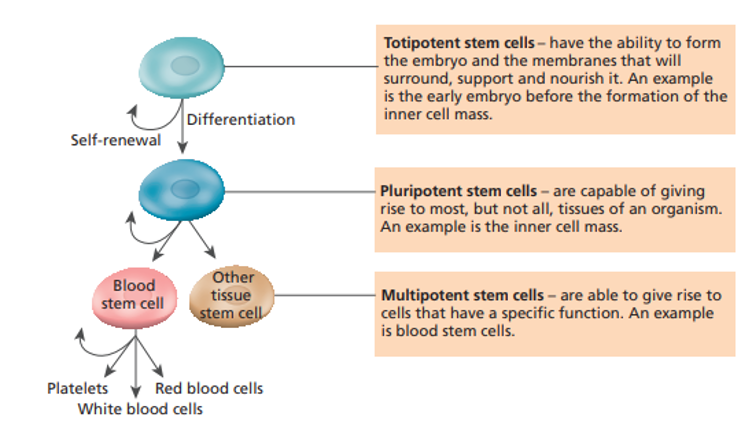
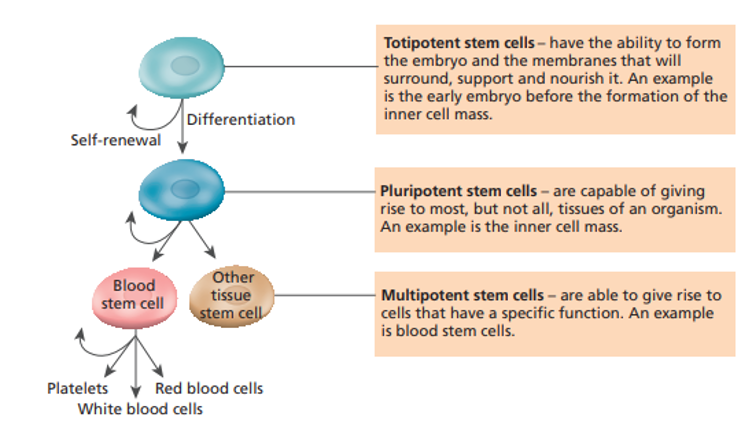
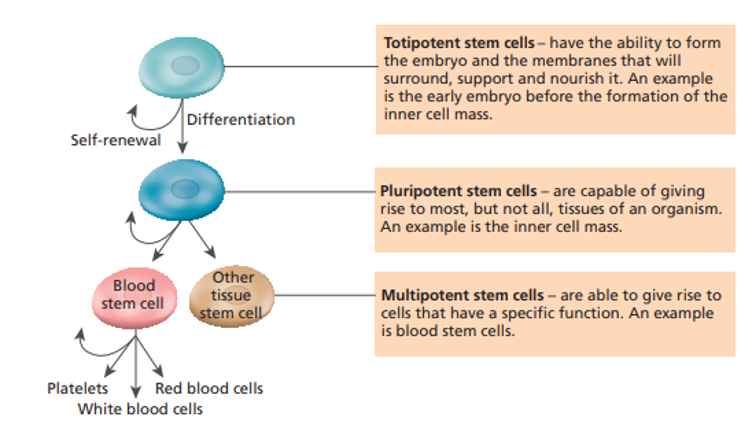
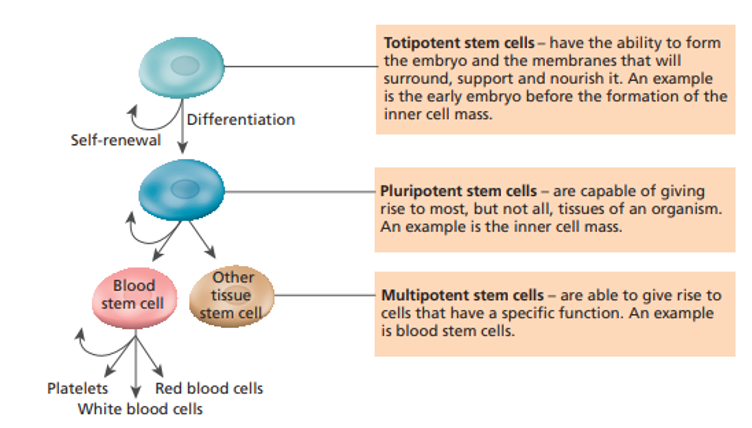
Types of stem cells
1\.**Totipotent stem cells**
1\.**Pluripotent stem cells**
1\.**Multipotent stem cells**
1\.**Pluripotent stem cells**
1\.**Multipotent stem cells**
49
New cards
1\.**Totipotent stem cells**
•Have the potential to become any cells/a complete new organism
•Occur in embryos (first month of development before the baby becomes a fetus)
•Then change into **blastocyst** which is a ball of cells with hollow outer layer (becomes placenta) with an inner mass (becomes fetus)
•Occur in embryos (first month of development before the baby becomes a fetus)
•Then change into **blastocyst** which is a ball of cells with hollow outer layer (becomes placenta) with an inner mass (becomes fetus)
50
New cards
2\.**Pluripotent stem cells**
•Can give rise to all types of cells in a fetus (not placenta)
•These are the cells we are investigating for medical use
•These are the cells we are investigating for medical use
51
New cards
3\.**Multipotent stem cells**
Give rise to cells that have a particular function \n (e.g. multipotent blood stem cells make white/ red blood cells and platelets)
52
New cards
Compare and Contrast Embryonic vs Adult Stem Cell
53
New cards
Example of differentiated cells
blood cells, skin cells, muscle cells, nerves
54
New cards
induced pluripotent stem cells (IPSCs)
are a type of pluripotent stem cell derived from adult somatic cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to an embryonic stem
(differentiation reversed)
(differentiation reversed)
55
New cards
Ethical Concepts
•**Beneficence**
•Is there a benefit to this initiative?
•**Non-maleficence**
•Does it cause harm?
•**Justice**
•Is it fair to everyone? Does it benefit everyone equally?
•**Respect**
•Does it show respect/provide dignity to all affected?
•**Integrity**
•Is research doing what it's saying it is going to do?
•Is there a benefit to this initiative?
•**Non-maleficence**
•Does it cause harm?
•**Justice**
•Is it fair to everyone? Does it benefit everyone equally?
•**Respect**
•Does it show respect/provide dignity to all affected?
•**Integrity**
•Is research doing what it's saying it is going to do?
56
New cards
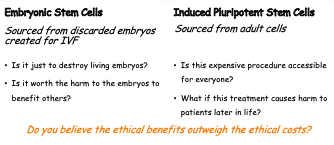
Ethics of Stem Cells for Medical Use
57
New cards
Media Response to Article
1\.**Beneficence** Is there a benefit to this initiative?
2\.**Non-maleficence** Does it cause harm?
3\.**Justice** Is it fair to everyone? Does it benefit everyone equally?
4\.**Respect** Does it show respect/provide dignity to all affected?
5\.**Integrity** Is research doing what it's saying it is going to do?
2\.**Non-maleficence** Does it cause harm?
3\.**Justice** Is it fair to everyone? Does it benefit everyone equally?
4\.**Respect** Does it show respect/provide dignity to all affected?
5\.**Integrity** Is research doing what it's saying it is going to do?