Physiology of Arteries and Veins
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
What is the formula for vascular compliance (C)?
C = ΔV / ΔP (Change in volume over change in pressure)
What does vascular compliance represent?
The total quantity of blood that can be stored in a portion of the circulation for each mmHg of pressure.
What does high vascular compliance mean?
More volume can be stored at a given pressure.
What does vascular compliance indicate about a vessel?
How easily the vessel can be stretched.
What is the relationship between elasticity and compliance?
Elasticity is the inverse of compliance.
Are arteries more or less compliant than veins?
Less compliant
How much volume do arteries contain, and under what pressure?
Low volume under high pressure
How does the compliance of veins compare to arteries?
Veins are about 24 times more compliant than arteries.
What kind of volume and pressure do veins typically hold?
Large volume under low pressure
How much more distensible are veins compared to arteries?
About 8 times more distensible
How does vein volume compare to artery volume?
Veins hold about 3 times greater volume than arteries
What effect does vasoconstriction have on vascular tone?
It increase vascular tone.
What effect does vasodilation have on vascular tone?
It decrease vascular tone.
What happens in a compliant artery during ventricular systole?
A substantial fraction of stroke volume is stored in the artery as the arterial wall stretches.
What happens in a compliant artery during diastole?
The stretched arteries recoil and blood continues to flow into the capillaries.
What happens in a rigid artery during systole?
The stroke volume cannot be stored in the arteries.
What happens in a rigid artery during diastole?
The arteries cannot recoil and flow through the capillaries stops.
What generates blood pressure in the circulatory system?
Contraction of the ventricles
What is systolic blood pressure?
The highest pressure attained in the arteries during systole
What is diastolic blood pressure?
The lowest arterial pressure during diastole
How does blood pressure change as blood moves away from the heart?
Pressure falls progressively with distance from the left ventricle
What factor, besides ventricular contraction, also influences blood pressure?
Total volume of blood
What is the formula for Pulse Pressure (PP)?
PP = Ps - Pd (systolic pressure minus diastolic pressure)
What does PP (pulse pressure) represent?
The difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
What does MAP stand for in cardiovascular physiology?
Mean Arterial Pressure
What does the upper limit of systolic oscillations represent?
Systolic pressure
What does the pressure at the end of diastole represent?
Diastolic pressure
What is Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)?
The average pressure in a complete cardiac cycle.
What is the most common clinical formula for calculating MAP?
MAP = 1/3 SBP + 2/3 DBP
What is an alternative formula for MAP when cardiac output (CO) and total peripheral resistance (TPR) are known?
MAP = CO × TPR
A patient has a blood pressure of 150/90 mmHg. What is their pulse pressure (PP)?
PP = 150 – 90 = 60 mmHg
Using the clinical formula, what is the MAP for a patient with BP 150/90 mmHg?
MAP = 1/3 × 60 + 90 = 20 + 90 = 110 mmHg
What is the formula for calculating MAP using cardiac output and total peripheral resistance?
MAP = CO × TPR
How is cardiac output (CO) calculated?
CO = Heart Rate (HR) × Stroke Volume (SV)
give the equation for stroke volume
SV = (EDV - ESV) / EDV
A patient has a HR of 85 bpm and SV of 60 mL/beat. What is their cardiac output (CO)?
If the TPR is 20 mmHg/L/min and CO is 5.1 L/min, what is the MAP?
CO = 85 × 60 = 5100 mL/min = 5.1 L/min
MAP = 5.1 × 20 = 102 mmHg
What is the clinical formula for calculating Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)?
MAP = 1/3 SBP + 2/3 DBP
A patient has a blood pressure of 135/85 mmHg. What is the MAP using the clinical formula?
MAP = 1/3(135) + 2/3(85) = 45 + 56.66 = 101.66 mmHg ≈ 102 mmHg
What do SBP and DBP stand for?
SBP = Systolic Blood Pressure, DBP = Diastolic Blood Pressure
Why is the clinical MAP formula weighted more toward DBP?
Because the heart spends more time in diastole than systole during the cardiac cycle.
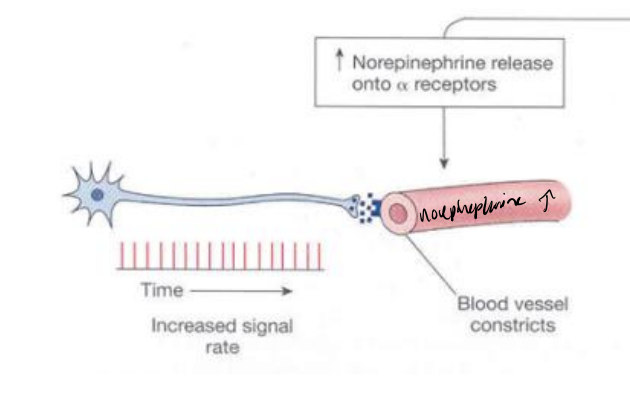
What effect does increased norepinephrine release have on blood vessels?
It activates α-receptors, causing vasoconstriction, which increases vascular tone and raises blood pressure.
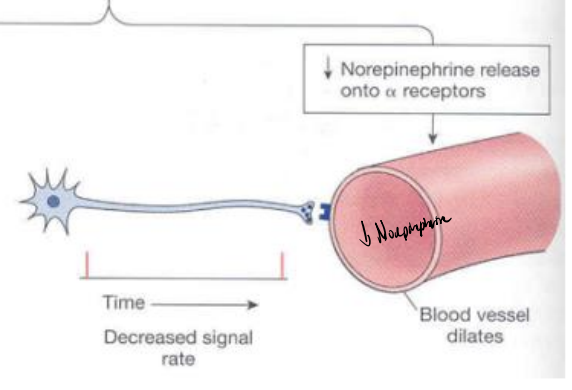
What happens when norepinephrine release decreases from sympathetic neurons?
There is less α-receptor activation, leading to vasodilation, which reduces vascular tone and lowers blood pressure.
What is vascular tone and how is it controlled?
Vascular tone refers to the baseline level of contraction in blood vessel walls, primarily controlled by sympathetic nerve activity via norepinephrine.
What does increased signal rate from a sympathetic neuron do to the vessel?
Increases norepinephrine → activates α-receptors → vasoconstriction.
What does decreased signal rate from a sympathetic neuron lead to?
Decreases norepinephrine → reduced α-receptor activation → vasodilation.
What is the primary physiological determinant of pulse pressure (PP)?
Stroke Volume (SV)
What are the physical determinants of pulse pressure?
Arterial compliance and change in arterial volume
What are the physiological determinants of mean arterial pressure (MAP)?
Cardiac Output (CO) and Total Peripheral Resistance (TPR)
How is cardiac output (CO) calculated?
CO = Stroke Volume (SV) × Heart Rate (HR)
How does arterial compliance affect pulse pressure?
Decreased compliance (stiffer arteries) leads to increased pulse pressure
What is the relationship between mean arterial pressure (MAP), cardiac output (CO), and resistance (TPR)?
MAP ∝ CO × TPR
What are the four key determinants of mean arterial pressure (MAP)?
Cardiac Output (CO = SV × HR)
Peripheral Resistance (TPR)
Blood Volume
Arterial Compliance
How does decreased compliance affect mean arterial pressure?
Decreased compliance increases MAP, especially systolic pressure, due to reduced arterial expansion
What effect does increased blood volume have on MAP?
It increases MAP by raising preload and cardiac output.
What is the primary site of variable resistance affecting MAP?
The arterioles.
What is the formula for cardiac output (CO)?
CO = Stroke Volume (SV) × Heart Rate (HR)
Which factor is the most important in determining systolic blood pressure on a beat-to-beat basis?
Stroke Volume (SV)
What does cardiac output represent?
The amount of blood ejected by the left ventricle per minute.
What is another formula for cardiac output that includes pressures and resistance?
CO = (MAP – RAP) / TPR
(Mean Arterial Pressure minus Right Atrial Pressure, divided by Total Peripheral Resistance)
What happens to MAP if cardiac output (CO) increases and TPR remains constant?
MAP increases.
What happens to MAP if cardiac output (CO) decreases and TPR remains constant?
MAP decreases.
What is the equation that shows the relationship between MAP, CO, and TPR?
MAP = CO × TPR
How can changes in SV or HR affect MAP?
Changes in SV or HR → change CO → change MAP.
What is the expanded version of the MAP formula including SV and HR?
MAP = SV × HR × TPR
What happens to CO if stroke volume (SV) increases while heart rate (HR) stays the same?
CO increases.
What happens if SV increases and HR decreases proportionally, while TPR remains constant?
CO and MAP remain constant.
What happens to systolic pressure (Ps) when SV increases?
Ps increases due to more volume being ejected.
What happens to diastolic pressure (Pd) when HR decreases?
Pd decreases because diastolic time is longer.
In the context of the equation MAP = SV × HR × TPR, what effect does an increase in SV have if HR and TPR stay the same?
MAP increases.
What is the main factor determining diastolic blood pressure?
Arteriole (TPR) resistance.
What happens to MAP and arterial volume if TPR increases while HR and SV remain constant?
MAP and arterial volume increase.
What happens to MAP and arterial volume if TPR decreases while CO remains constant?
MAP and arterial volume decrease.
What cardiovascular effect is most likely expected in atherosclerosis?
Increased TPR due to rigid arteries, leading to increased arterial pressure (AP).
How does increased TPR affect MAP based on the formula MAP = CO × TPR?
MAP increases.
What is the effect of arteriolar dilation on diastolic blood pressure (DBP)? TPR : total peripheral resistances
It reduces diastolic blood pressure.
What is the effect of arteriolar constriction on diastolic blood pressure (DBP)? TPR: total peripheral resistance
It increases diastolic blood pressure.
What happens to circulating blood volume and cardiac output during hemorrhage?
Both decrease.
How does the body compensate for hemorrhage via the carotid reflex?
Increases TPR and venoconstriction.
What is the result of the body's compensation during hemorrhage on MAP?
It reduces the drastic drop in MAP.
What happens to TPR during exercise?
It decreases due to arteriolar dilation.
What happens to cardiac output during exercise?
It increases.
What is the net effect on MAP during exercise?
Only a small increase in MAP.
How is arterial compliance defined?
Compliance = ΔV / ΔP (change in volume over change in pressure).
What is the relationship between compliance and elastic recoil in arteries?
Compliance is inversely related to elastic recoil.
What happens to pulse pressure when arterial compliance decreases?
Pulse pressure increases.
What is the formula for pulse pressure (PP)?
PP = Ps - Pd (Systolic pressure minus diastolic pressure).
What happens to pulse pressure if arterial volume increases and compliance decreases?
Pulse pressure increases.
What two factors primarily determine pulse pressure (PP)?
Stroke volume (arterial volume change) and arterial compliance.
What is the relationship between pulse pressure and arterial compliance?
Pulse pressure increases as compliance decreases.
What determines mean arterial pressure (Pa)?
Cardiac output (CO) and total peripheral resistance (TPR).
How does the equation MAP = CO × TPR relate to Pa?
Mean arterial pressure (Pa) is calculated as CO × TPR.
If cardiac output increases but TPR stays the same, what happens to Pa?
Pa (mean arterial pressure) increases.
What happens to systolic and diastolic pressure when arterial compliance decreases?
Ps increases and Pd decreases.
What is the effect on pulse pressure (PP) when arterial compliance decreases?
Pulse pressure increases.
What happens to systolic and diastolic pressure when arterial compliance increases?
Ps decreases and Pd increases.
What is the effect on pulse pressure (PP) when arterial compliance increases?
Pulse pressure decreases.
What is the relationship between compliance and pulse pressure transmission?
Pulse pressure transmission is inversely proportional to compliance.
What happens to the velocity of pulse pressure transmission when vessel compliance is high?
The velocity of transmission is slower.
How does compliance affect pressure pulsations as blood moves through the arterial system?
Higher compliance reduces pressure pulsations by the time blood reaches the capillaries.
What is the typical pulse pressure transmission velocity in the aorta?
3–5 m/sec