Electronics Fundamentals: Atomic Structure, Circuit Components, and Electrical Units
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
173 Terms
The Bohr atom
The Bohr atom is useful for visualizing atomic structure.
Nucleus
The nucleus is positively charged and has the protons and neutrons.
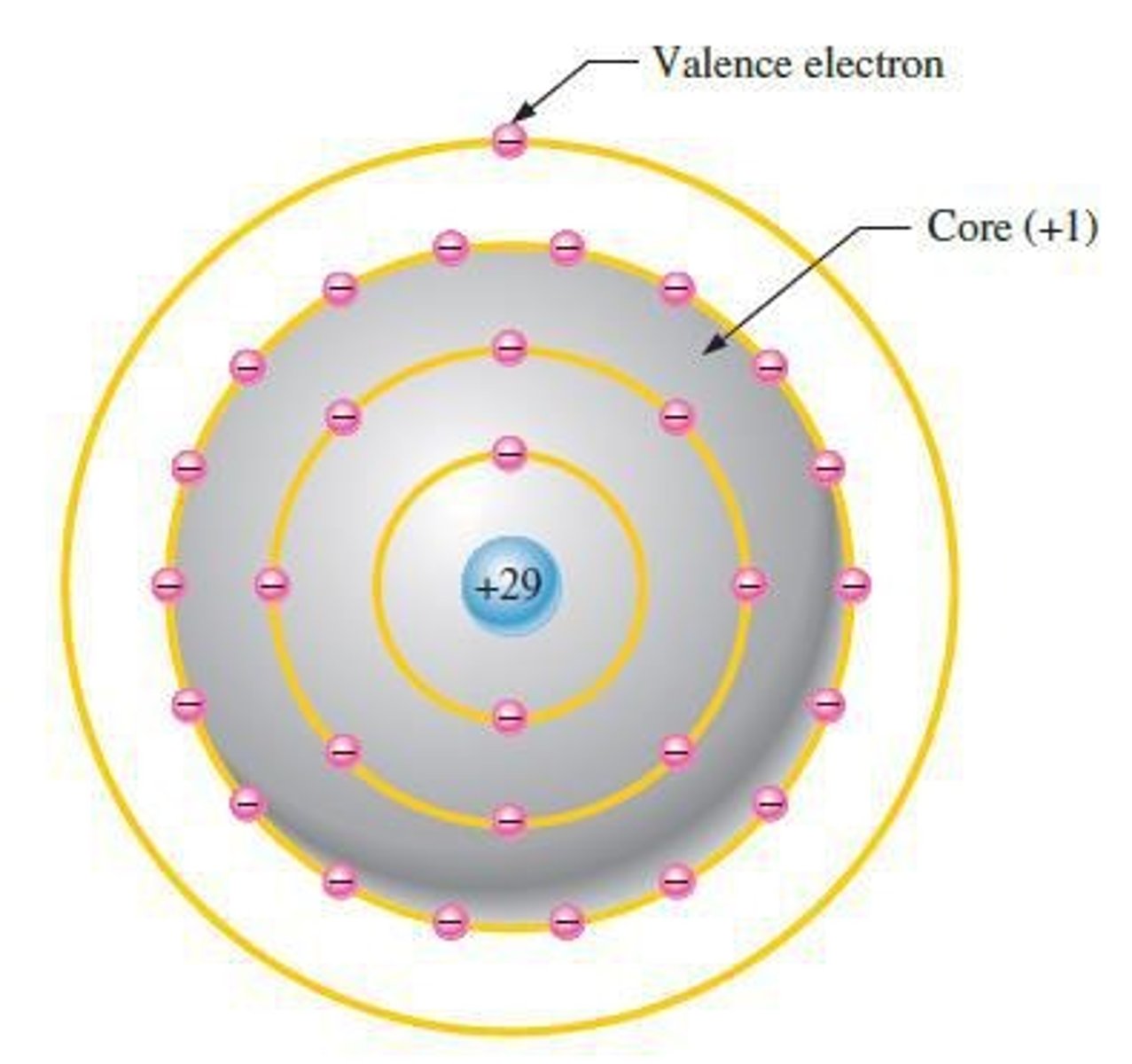
Electrons
Electrons are negatively charged and in discrete shells.
Atomic number
The atomic number is the number of protons and determines the particular element.
Neutral atom
In the neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons.
Valence shell
The outer shell is called the valence shell; electrons in this shell are involved in chemical reactions and account for electrical and thermal conductivity in metals.
Silicon (Si)
Si is classified as a semiconductor.
Sodium atom (Na)
The sodium atom has only one electron in its outer shell and is highly reactive.
Non-metals
Non-metals have either complete or nearly complete outer shells, making them poor electrical conductors.
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the most outermost shell orbit.
Free Electrons
When an electron absorbs a photon of sufficient energy, it escapes from the atom and becomes a free electron.
Ions
An atom that either lost or gained an electron.
Positive Ion
An atom that loses an electron.
Negative Ion
An atom that gains an electron.
Conductors
Conductors are materials that readily allow current and have a large number of free electrons, characterized by one to three valence electrons in their structure.
Insulators
Insulators are nonmetallic materials that are poor conductors of electric current; they are used to prevent current where it is not wanted and have no free electrons in their structure.
Semiconductors
Semiconductors are classed below conductors in their ability to carry current because they have fewer free electrons than conductors and have four valence electrons in their atomic structures.
Electrical charge
There is a force (F) between electrical charges; like charges repel, and unlike charges attract.
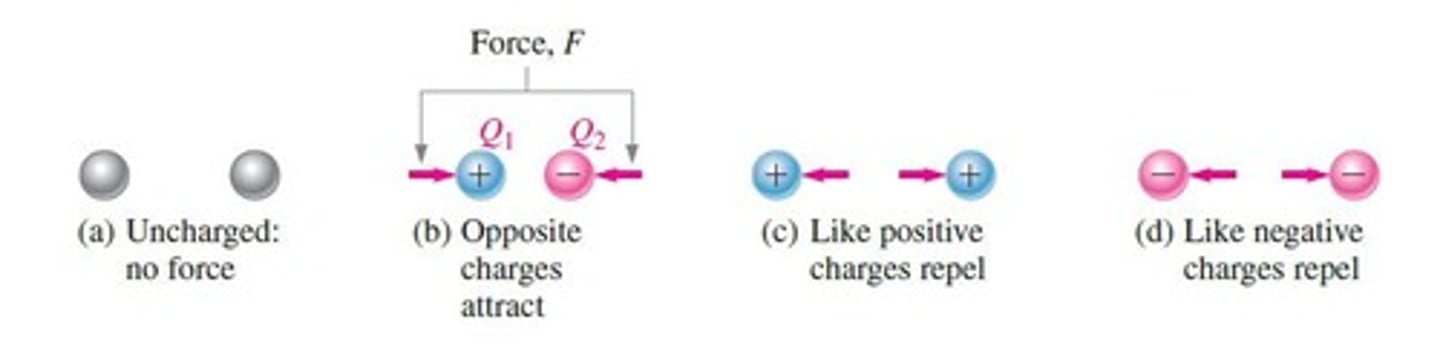
Force between charges
The force is directly proportional to charge and inversely proportional to the square of distance.
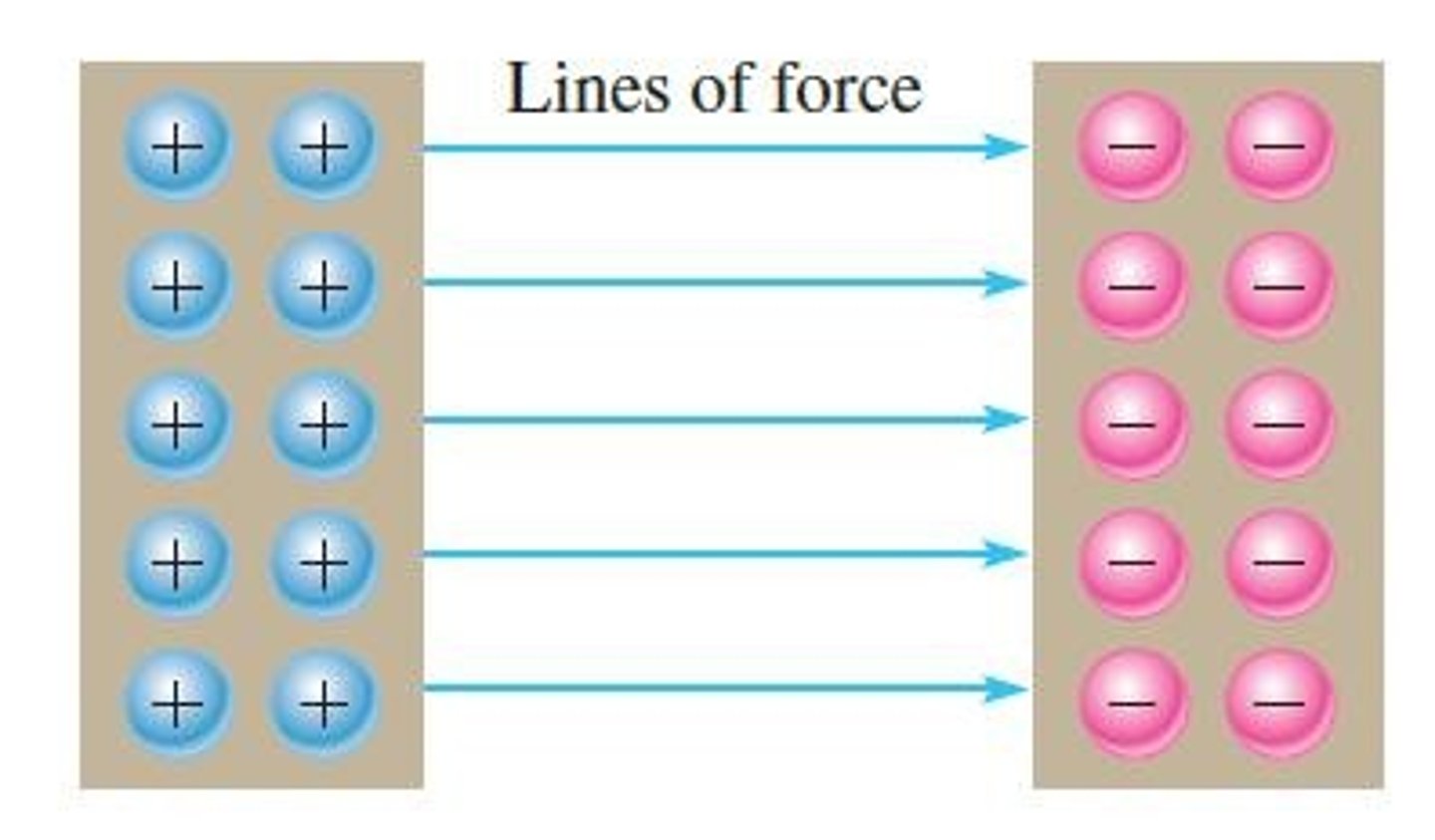
Coulomb's law
A force (F) exists between two point-source charges (Q1, Q2) that is directly proportional to the product of the two charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d) between the charges.
Coulomb
The Unit of Charge.

Voltage
Voltage is the work per charge done against the electric field.
Conventional Flow
By convention, current flows from the positive to negative terminals (many technical texts).
Electron Flow
Current follows electron flow, from the negative to positive terminals (scientifically correct texts).
Defining equation for voltage
The defining equation for voltage is W/V = Q.
One volt
One volt is the potential difference (voltage) between two points when one joule of energy is used to move one coulomb of charge from one point to the other.
Sources of voltage
Sources of voltage include batteries, solar cells, fuel cells, and generators.
Single cell battery
A Cu-Zn battery, such as you might construct in a chemistry class, is shown.
Automobile battery
An automobile battery is an example of a multiple cell battery.
Battery
Like all batteries, the automotive battery does not store charge - it stores chemical energy that can be converted to current when an external path is provided to allow the chemical reaction to proceed.
Charging a battery
Rather than saying 'charging' a battery, it is more accurate to say 'reversing the chemical reaction' in a battery.
Fuel cell
A fuel cell is a device that converts chemical energy into dc voltage directly by combining a fuel (usually hydrogen) with an oxidizing agent (usually oxygen).
Chemical reaction in fuel cells
The hydrogen and oxygen react to form water.
Difference between batteries and fuel cells
The process differs from batteries in that the reactants constantly flow into the cell where they combine and produce electricity.
Work done in moving a charge
Work done in moving a charge against the electric field leads to the definition of voltage.
Electric field
Electric field exists between two oppositely charged surfaces.
Work per charge
Voltage is defined as the work per charge done against the electric field.
Chemical energy in batteries
Batteries store chemical energy that can be converted to current.
Current
Voltage is responsible for establishing current.
Zinc (anode)
In a Cu-Zn battery, zinc acts as the anode.
Copper (cathode)
In a Cu-Zn battery, copper acts as the cathode.
Salt bridge
A salt bridge is used in electrochemical cells to maintain electrical neutrality.
Reaction in Cu-Zn battery
Zn + 2e- → Zn2+ at the anode and Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu at the cathode.
Solar cells
The operation of solar cells is based on the photovoltaic effect, which is the process whereby light energy is converted directly into electrical energy.
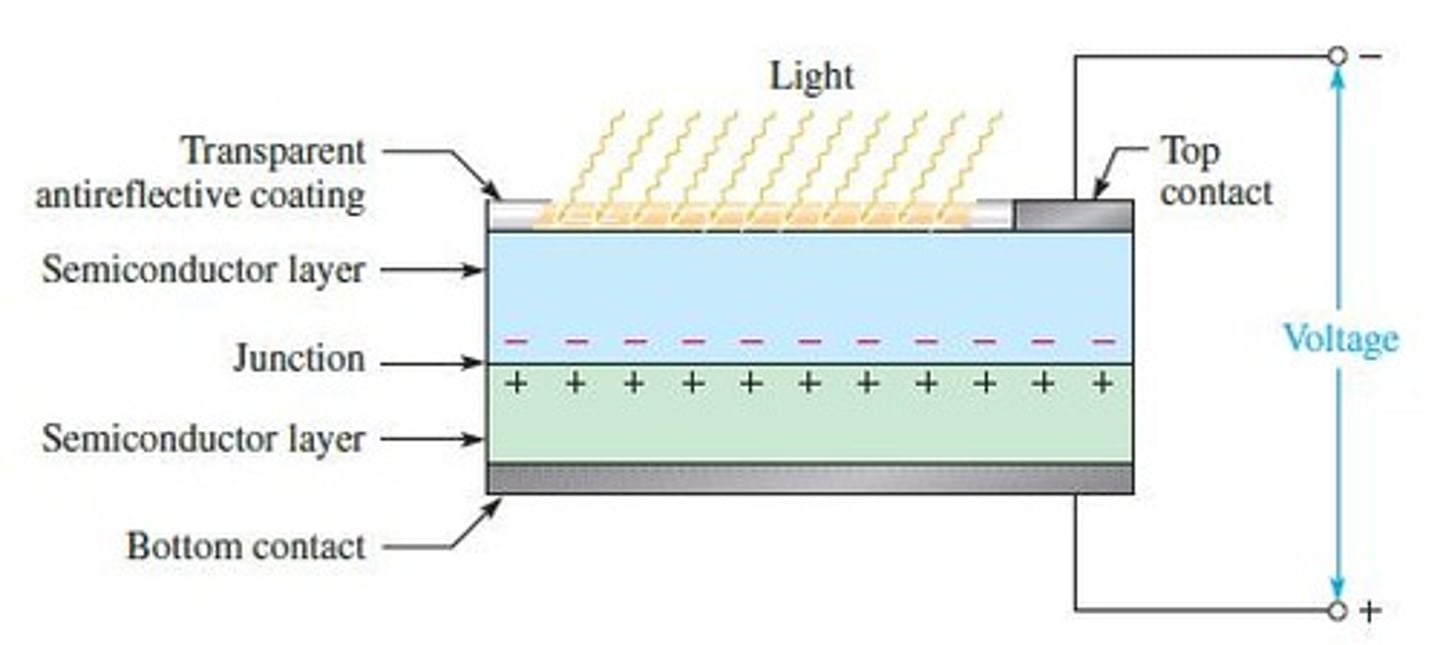
Generator
Electrical generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy using a principle called electromagnetic induction.
Power Supply
Power supplies convert the ac voltage from the wall outlet to a constant (dc) voltage that is available across two terminals.
Thermocouples
The thermocouple is a thermoelectric type of voltage source that is commonly used to sense temperature.
Piezoelectric Sensors
These sensors act as voltage sources and are based on the piezoelectric effect where a voltage is generated when a piezoelectric material is mechanically deformed by an external force.
One ampere
One ampere is a number of electrons having a total charge of 1 C moving through a given cross section in 1 s.
Current Source
Ideally, a current source can provide a constant current for any load.
Resistance
Resistance is the opposition to current.
One ohm
One ohm (1 Ω) is the resistance if one ampere (1 A) is in a material when one volt (1 V) is applied.
Conductance
Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance.
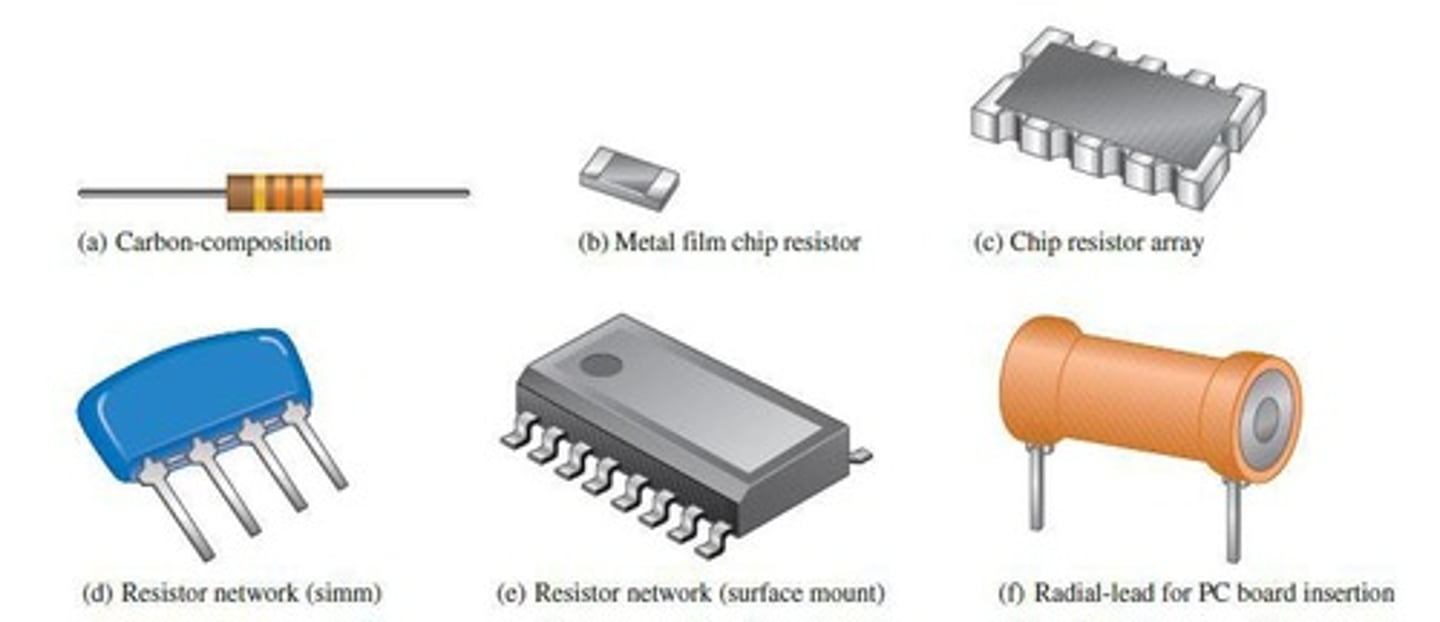
Resistors
Components designed to have a specific amount of resistance are called resistors.
Color bands
Color bands are used to indicate the resistance value of resistors.
Resistance material
Resistance material can include carbon composition.
Insulation coating
Insulation coating is used to cover resistors to prevent short circuits.
Leads
Leads are the metal wires that connect resistors to a circuit.
IV curve for an ideal voltage source
The IV curve for an ideal voltage source has a constant voltage for all current.
IV curve for an ideal current source
The IV curve for an ideal current source has a constant current as indicated by the straight line.
Current sources
Current sources are not as common as voltage sources, but they are useful for production testing.
Mechanical energy
Mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy in generators.
Electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic induction is the principle used by generators to produce voltage.
Voltage across a conductor
A voltage is produced across the conductor when it is rotated through a magnetic field.
Constant (dc) voltage
Constant (dc) voltage is the output of power supplies from ac voltage.
Color
A code used to indicate resistance values in resistors.
Digit
A numerical symbol used to represent values.
Multiplier
A factor that indicates how many zeros follow the second digit in a resistance value.
Tolerance
The acceptable deviation from the specified resistance value.
color-code
A system of colored bands used to indicate resistor values.
Black
Represents the digit 0 in color coding.
Brown
Represents the digit 1 in color coding.
Red
Represents the digit 2 in color coding.
Orange
Represents the digit 3 in color coding.
Yellow
Represents the digit 4 in color coding.
Green
Represents the digit 5 in color coding.
Blue
Represents the digit 6 in color coding.
Violet
Represents the digit 7 in color coding.
Gray
Represents the digit 8 in color coding.
White
Represents the digit 9 in color coding.
Gold
Indicates a tolerance of ±5%.
Silver
Indicates a tolerance of ±10%.
No band
Indicates a tolerance of ±20%.
Variable resistors
Components that allow resistance to be adjusted, including potentiometers and rheostats.
Wire resistance
The resistance of a wire, calculated using the equation R = ρ(l/A).
The electric circuit
A basic setup consisting of a voltage source, a path, and a load.
Switches
Devices used to control circuits by either mechanical or electronic means.
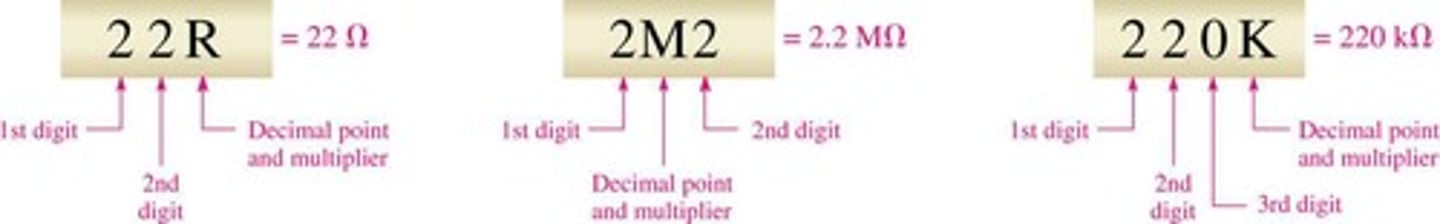
Alphanumeric Labeling
A method of identifying resistance values using digits and letters R, K, or M.
Throw
The number of contacts that are affected by a single switch action.
SPST
Single Pole Single Throw switch.
SPDT
Single Pole Double Throw switch.
DPST
Double Pole Single Throw switch.
DPDT
Double Pole Double Throw switch.
Fuse
A protective device that interrupts the circuit when excessive current flows.
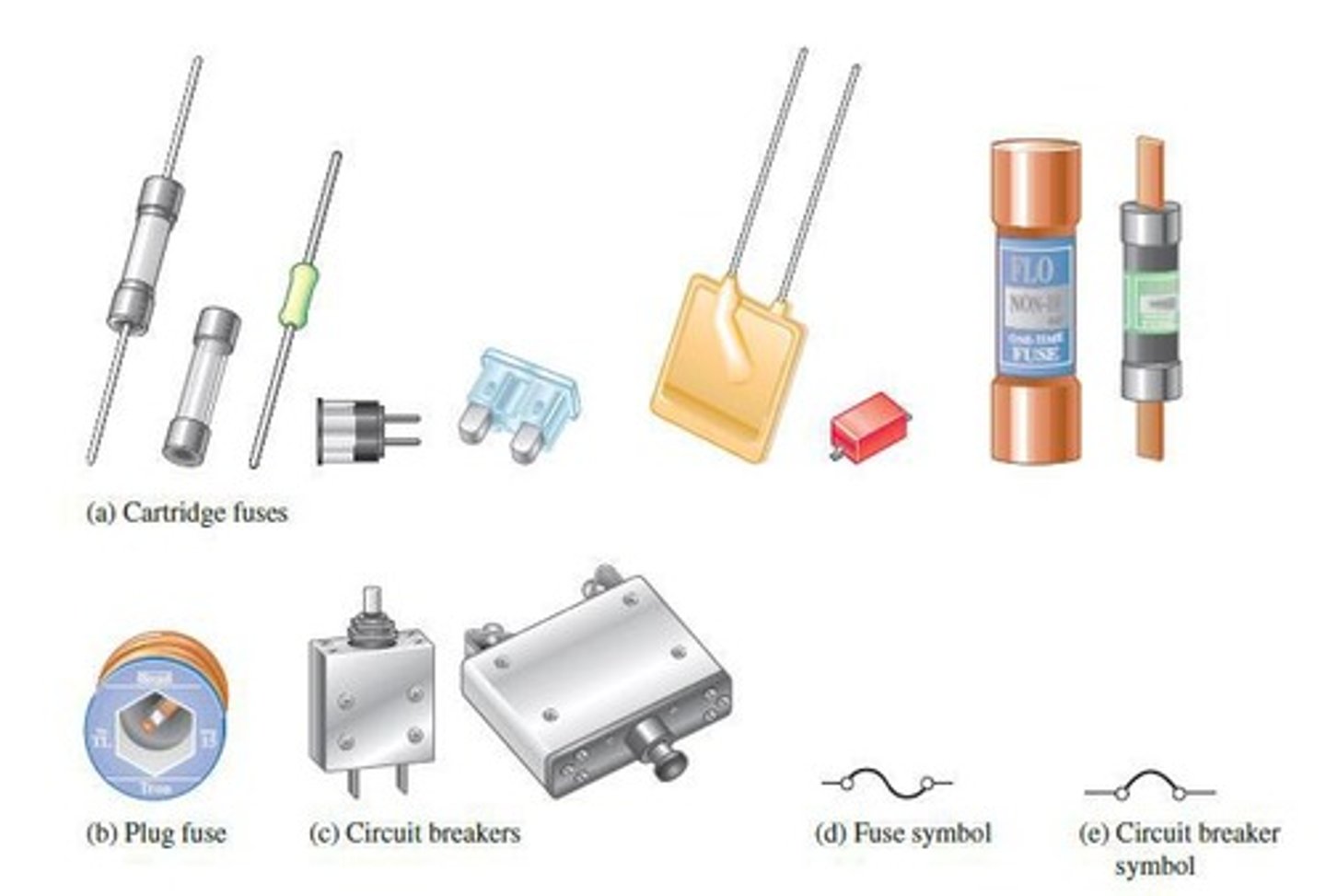
Circuit Breaker
A protective device that interrupts the circuit when excessive current flows, can be reset.
Ground
The reference point in an electric circuit, typically connected with an 8-foot long metal rod driven into the earth.
DMM
Digital Multimeter, an important multipurpose instrument which can measure voltage, current, and resistance.
Analog Meter
Also called a VOM (volt-ohm-milliammeter), measures voltage, current, and resistance.
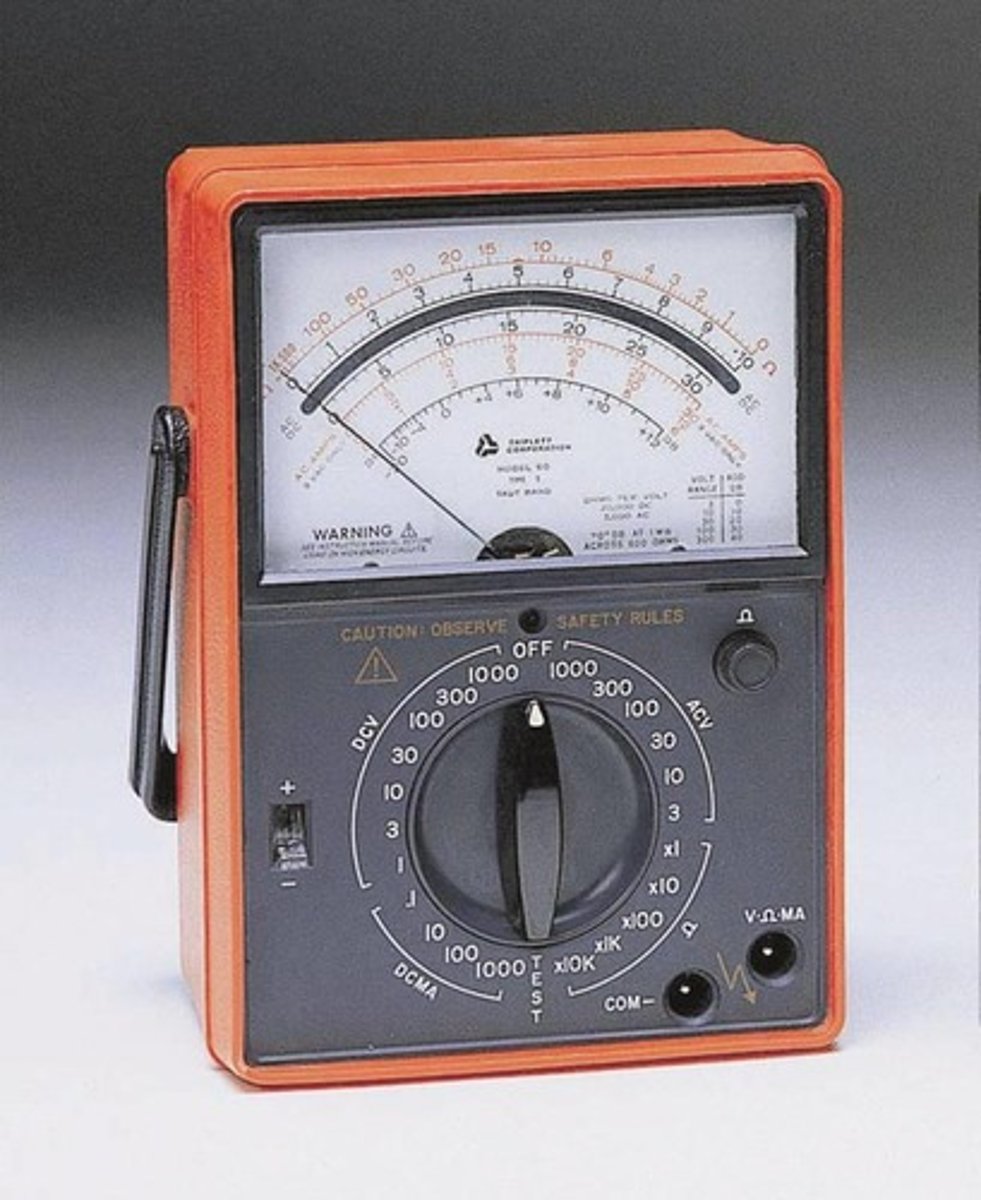

Measuring Current
The process of determining the flow of electric charge in a circuit.
Measuring Voltage
The process of determining the electric potential difference between two points.