instrumental chap 20
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
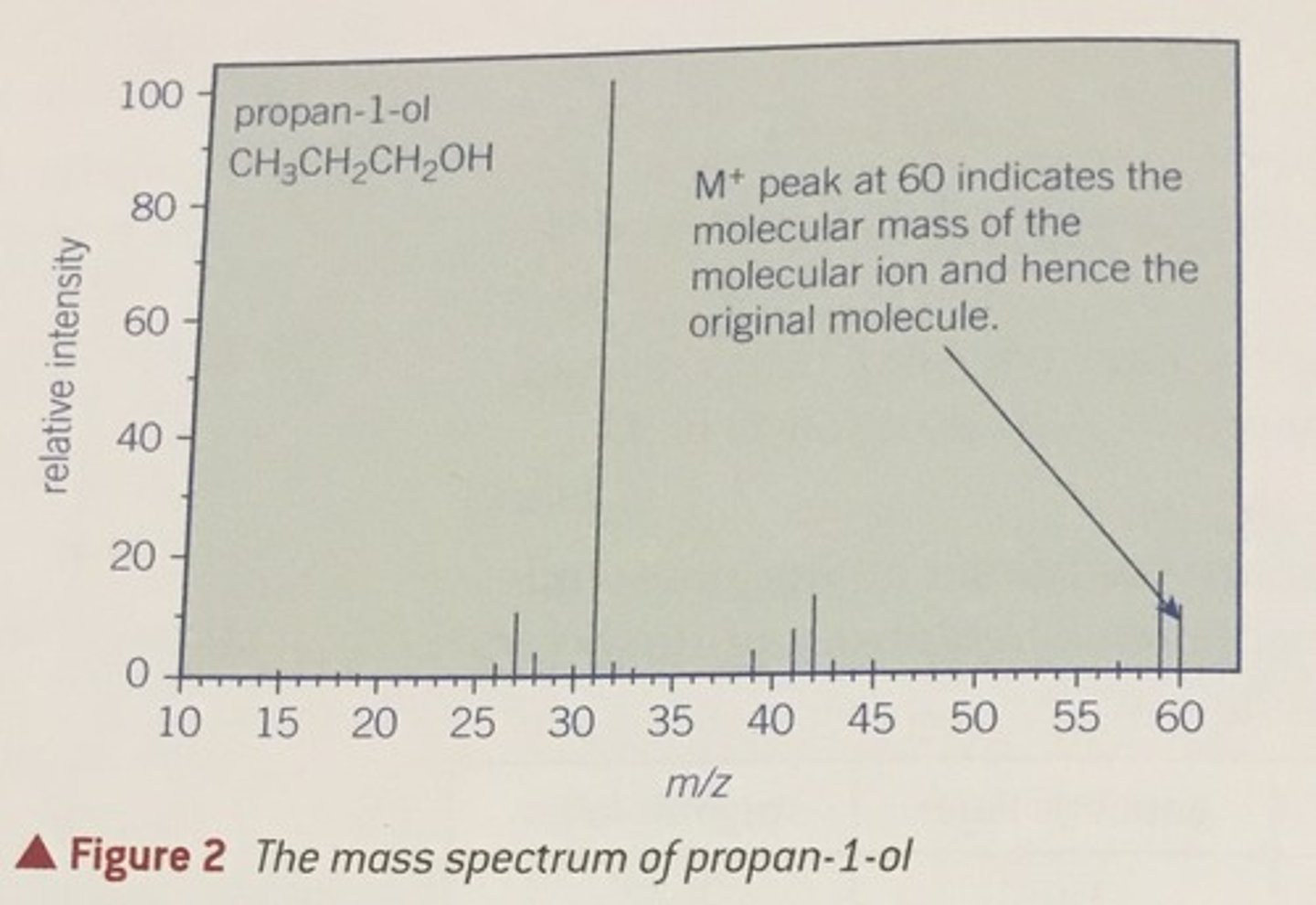
molecular mass spectrometry
capable of providing information about the structures of inorganic, organic and biological molecules and about the qualitative and quantitative composition of complex mixtures.
hard source destroys structure and looks at fragmentation, soft source is mild, fragmentation not as visible
ion sources for molecular mass spectrometry
electron ionization
method used to create ions from gaseous molecules in the inlet of a mass spectrometer by bombardment of the gas with high-energy electrons
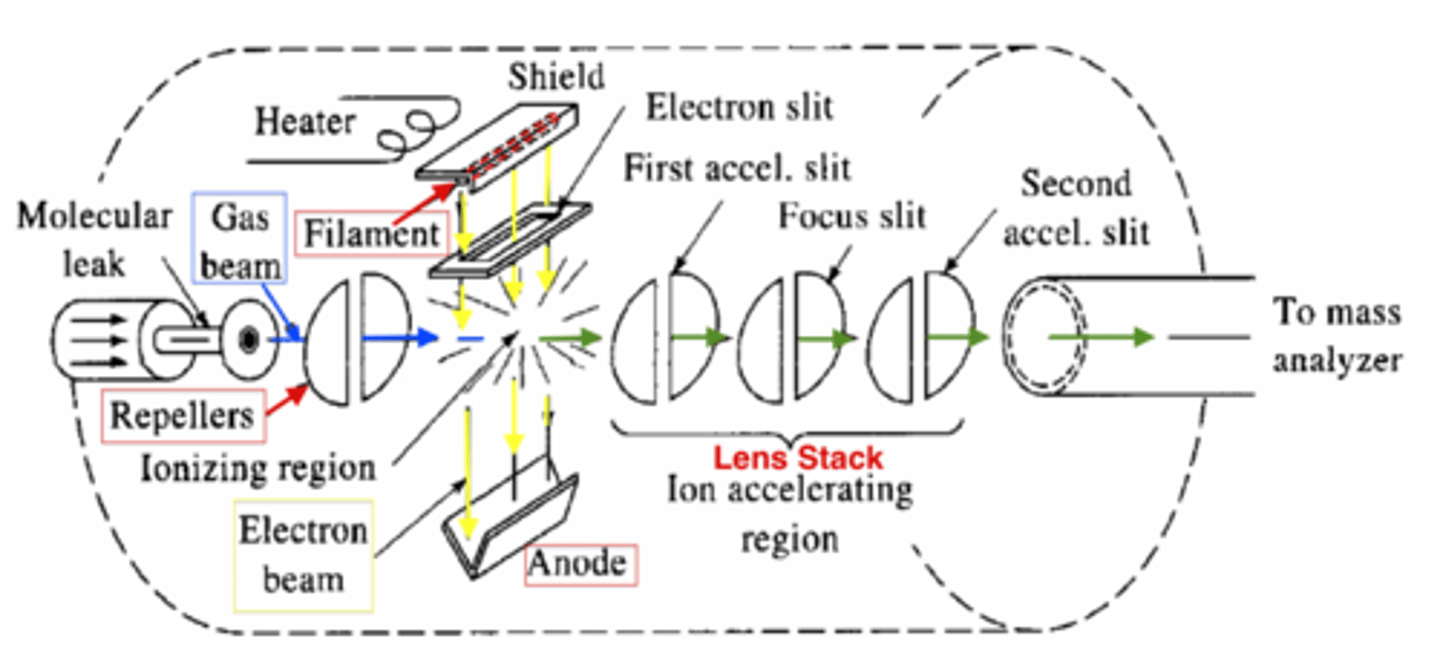
convenient, produces high ion currents, extensive fragmentation
advatnges of electron ionization
disappearance of molecular ion peak, need to volatilize sample, good for analytes with certain mass
disadvantages of electron ionization
chemical ionization
a type of mass spectrometry in which a molecule reacts under relatively low energy with a reagent gas rather than fragmenting extensively
gaseous atoms of the sample are ionized by collision with ions produced by electron bombardment of a reagent gas
Chemical inoization
matrix assisted laser desorption ionization
-is a soft ionization technique used in mass spectrometry
-allowing the analysis of biomolecules (biopolymers such as DNA, proteins, peptides and sugars) and large organic molecules (such as polymers, dendrimers and other macromolecules), which tend to be fragile and fragment when ionized by more conventional ionization methods
mixes a sample with a UV-absorbing matrix material, uses a pulsed laser to desorb and ionize the sample, causing it to form ions for analysis
MAlDI
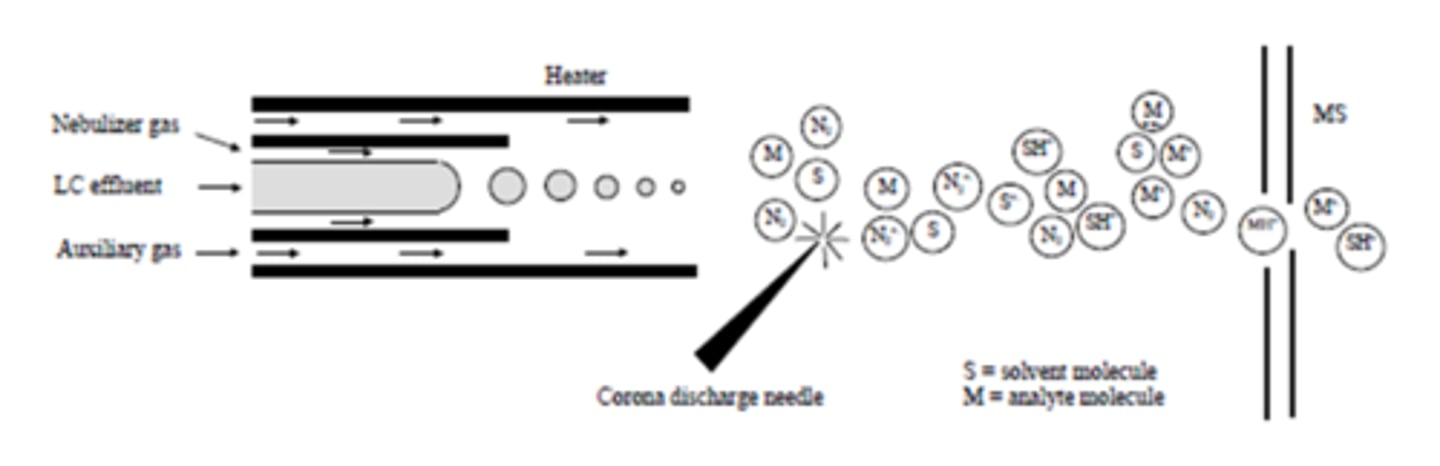
electrospray ionization
Sample dissolved in volatile solvent then injected through needle to give fine mist which is attached to positive end of high voltage power supply, particles gain proton
NB- Mr of substance is actually one less than shown due to extra H+
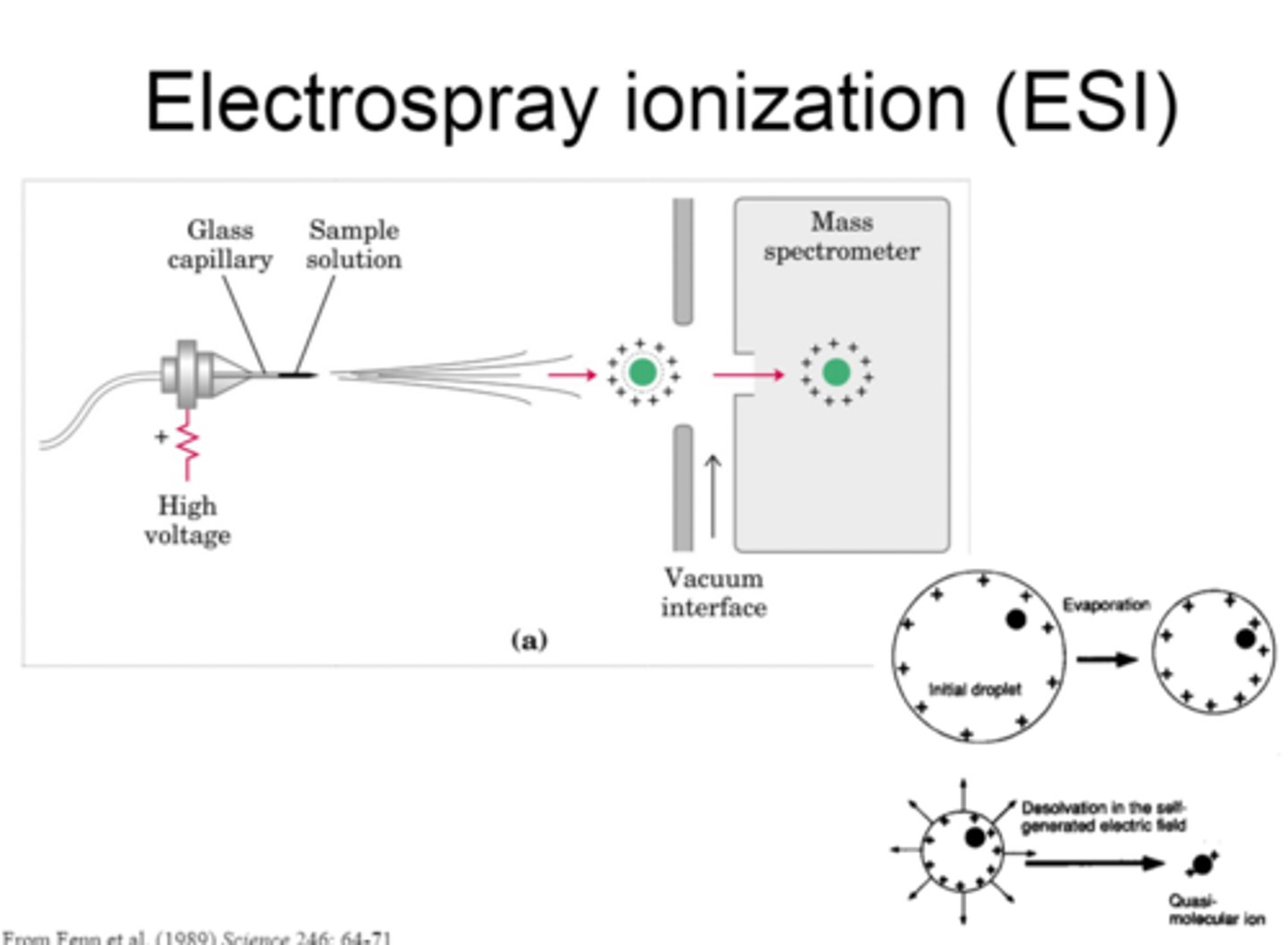
applies high voltage to liquid sample, forcing it through a capillary to create fine mist of highly charged droplets
ESI
double focusing mass spectrometer
A spectrometer that uses electric and magnetic sectors in series to obtain high resolution.
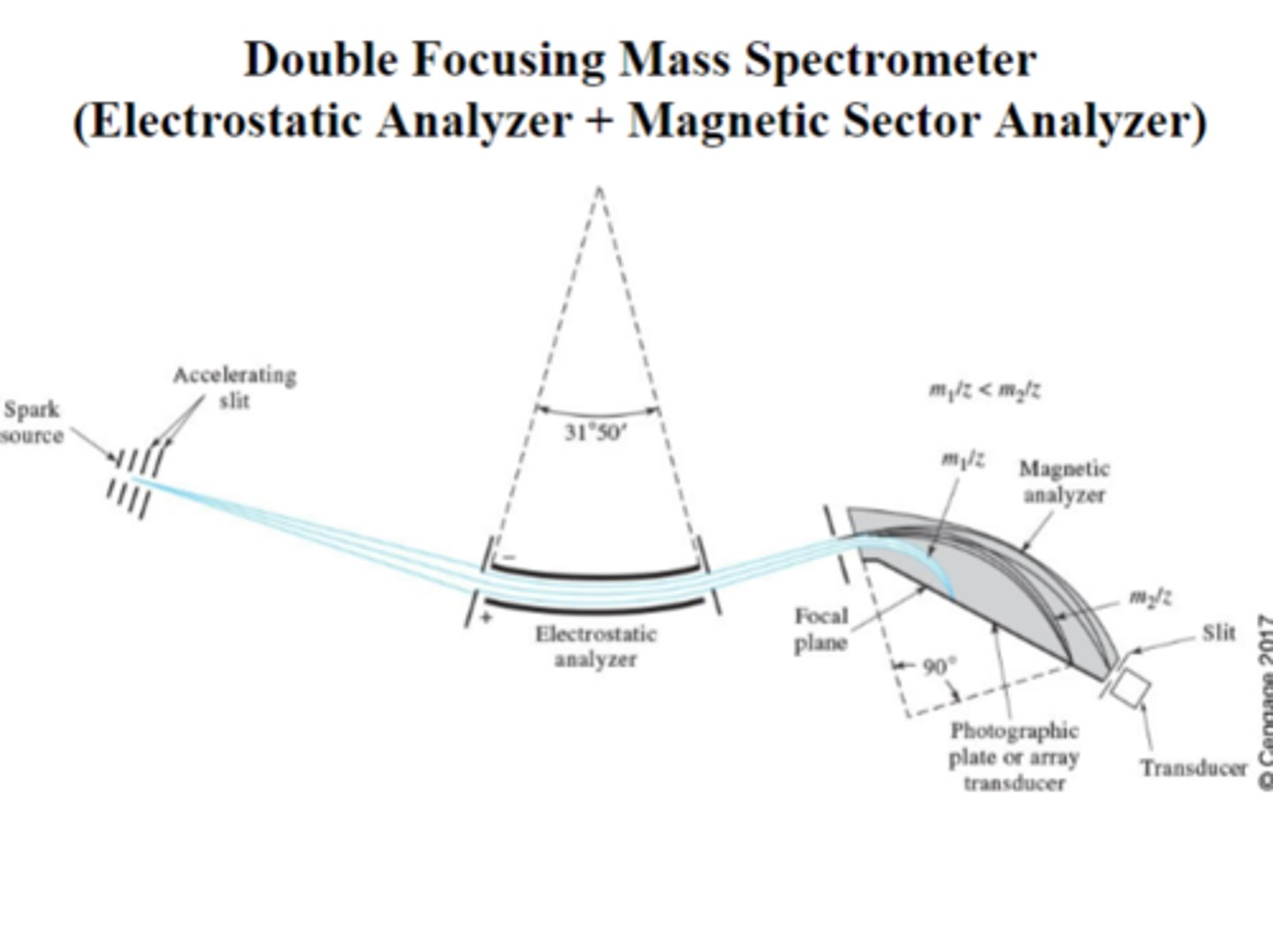
electrostatic analyzer
Focuses ions in terms of kinetic energy often used in conjunction with a magnetic sector mass analyzer
ESA corrects energy distribution of ions, magnetic corrects directional distribution of ions
ESA vs magnetic analyzer
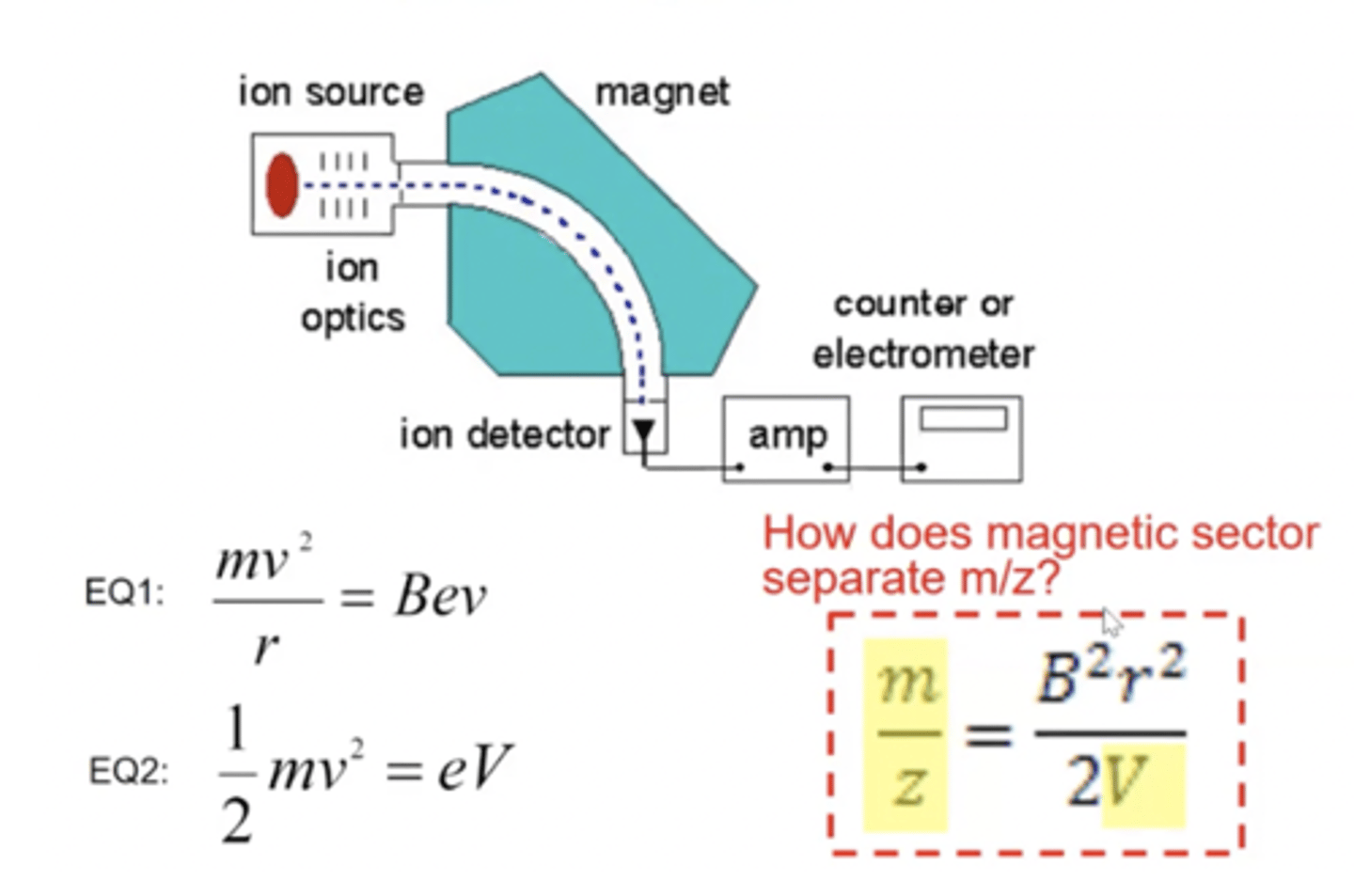
ion trap mass spectrometer
Three electrodes, in a ring shape and two end caps, produce ions in the cavity until selectively ejected to the ion detector
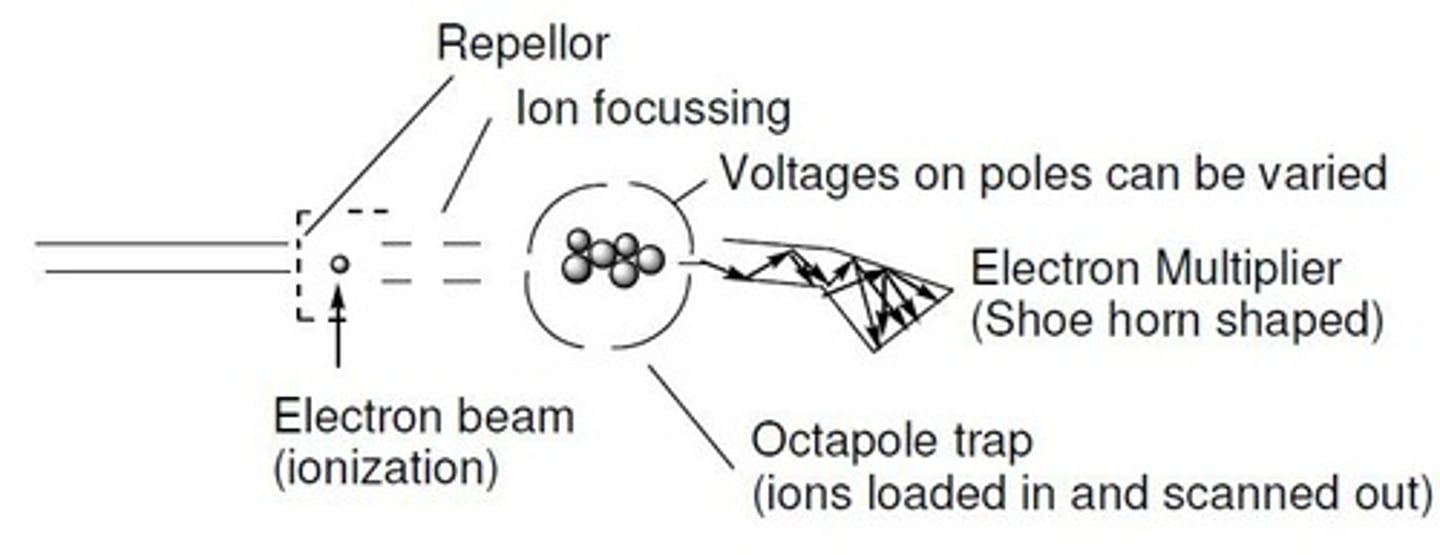
traps ions using RF and DC fields, isolates specific ions, inducing fragmentation, scans them out to a detector
ion trap
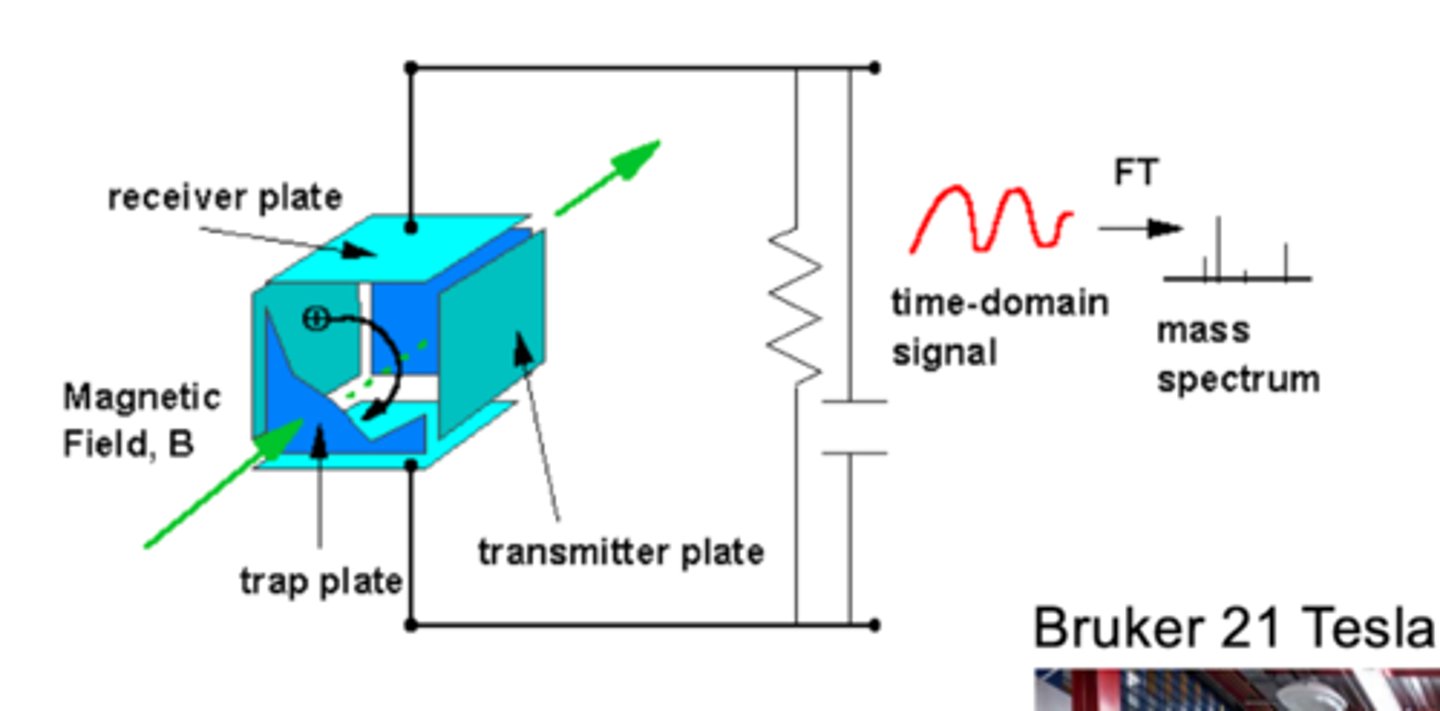
Ion cyclotron Resonance
Trapping of ions in cubic cell under the influence of trapping voltage and magnetic field