Biology - key things from past papers
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
size of cells
eukaryotic - up to 40 micrometers
prokaryotic - 1-5 micrometers
virus components
dna or rna
protein capsid
only some have an outer phospholipid layer
test for sugars
add benedicts, colour change from blue to yellow to brick red
non-reducing sugars test
non reducing sugars (sucrose) have to be broken down by HCl before benedicts
alpha glucose
amylose, amylopectin, glycogen
only 1,4 glycosidic bonds
amylose, cellulose
1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
amylopecting, glycogen
higher enzyme affinity
lower Km
competitive inhibitor
binds to active site
tunica media (middle layer) contains
collagen fibres, elastic fibres and smooth muscle
systolic blood pressure
maximum blood pressure in arteries
diastolic blood pressure
minimum blood pressure in arteries
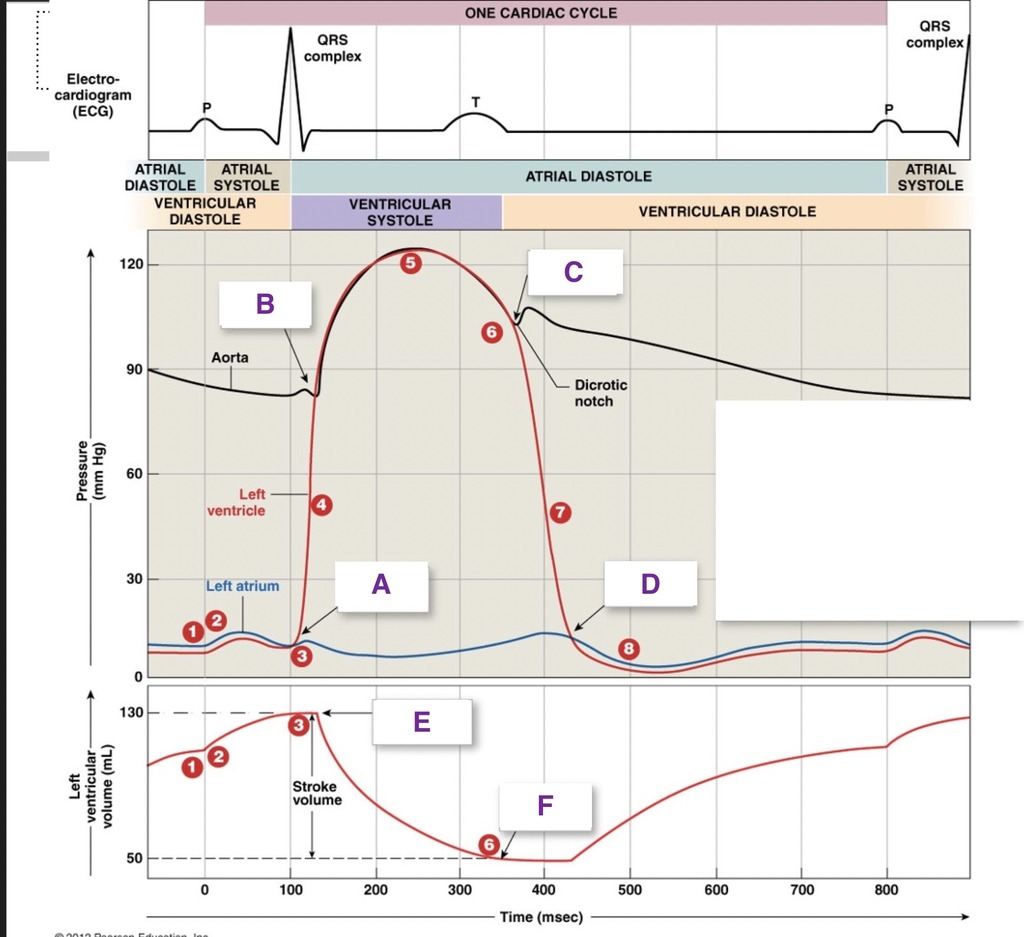
A
AV valve closes
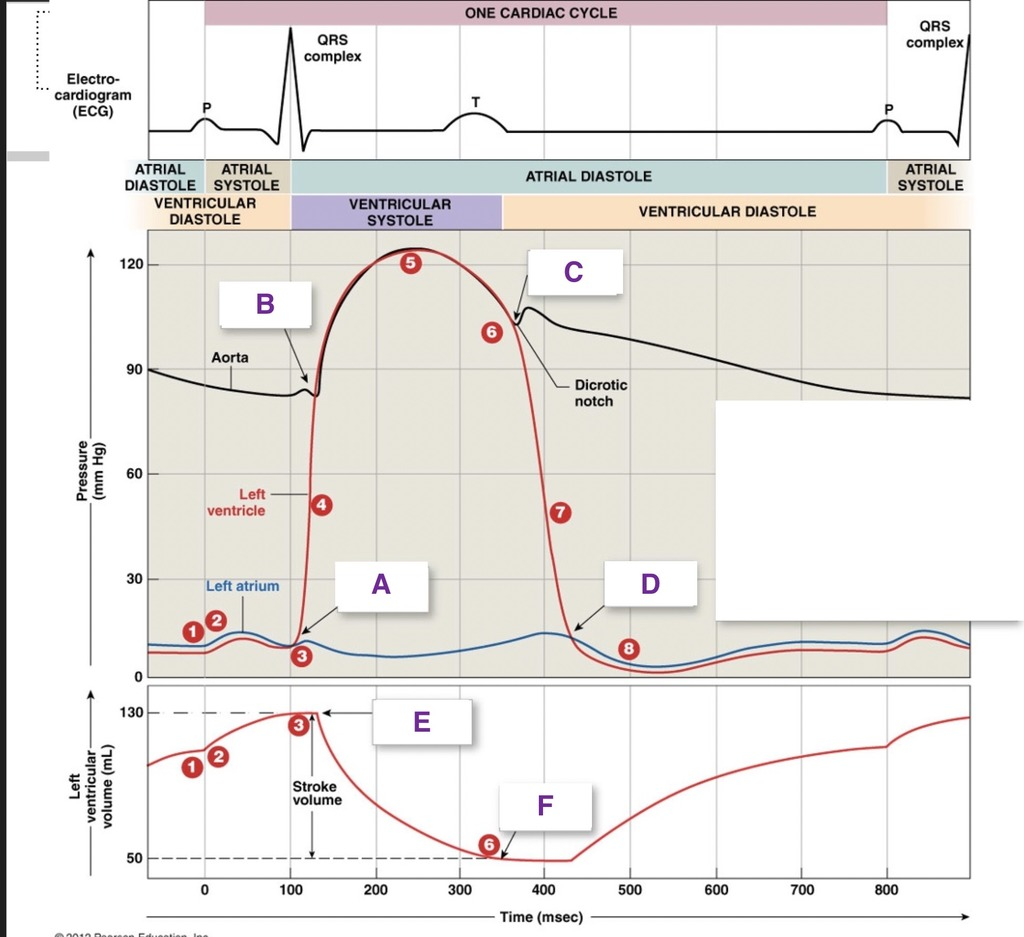
B
SL valve opens
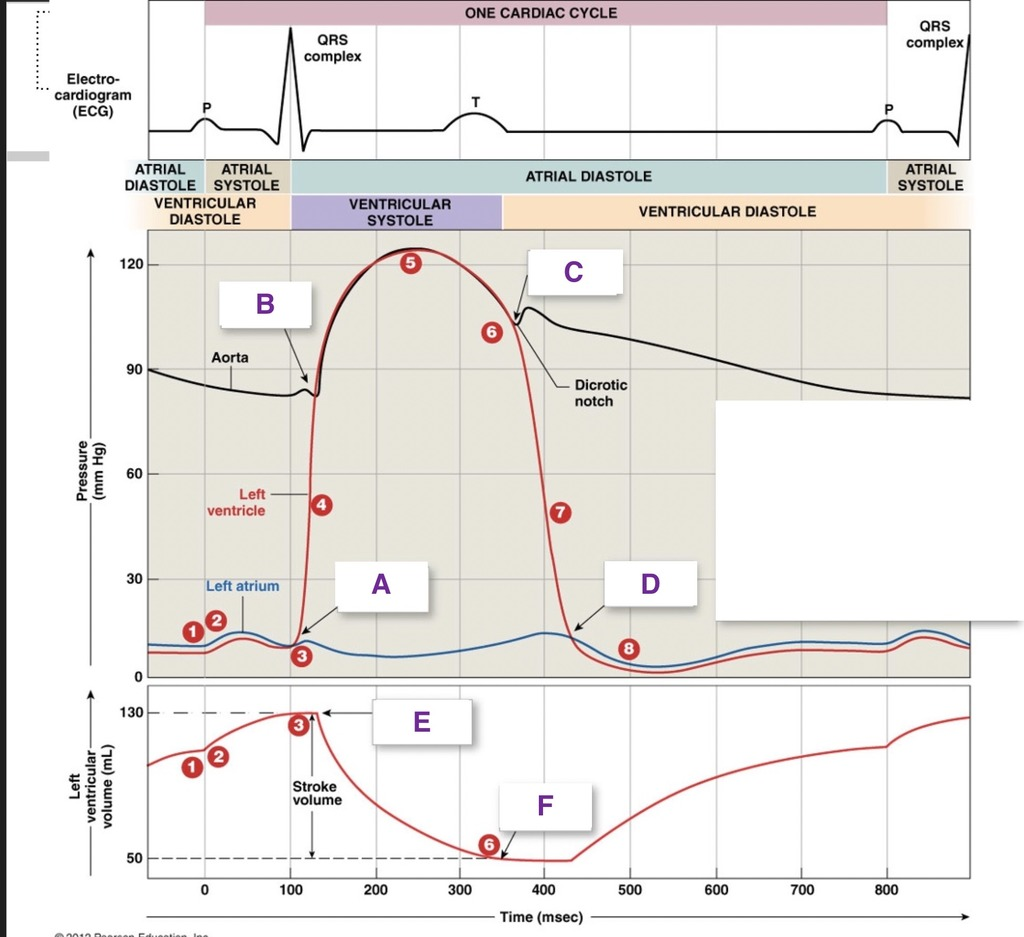
C
SL valve close
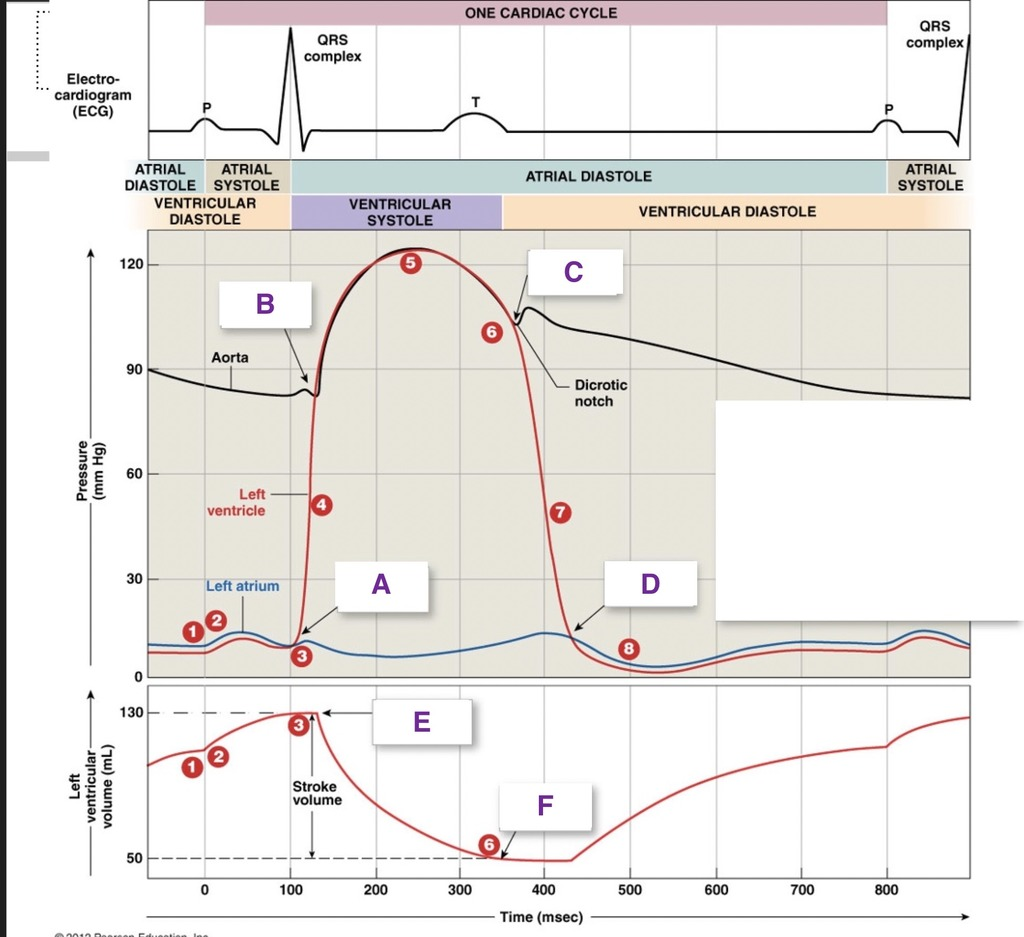
D
AV valves open
factors resulting in the bohr shift
high CO2 concentration, increasing temperature, high acidity
Cholera pathogen
Bacterium - Vibrio Cholerae
Malaria pathogen
Protoctist - Plasmodium
Malaria vector
Female anopheles mosquito
AIDS pathogen
Virus - HIV
Tuberculosis pathogen
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
glucose + glucose
maltose
alpha glucose and fructose
sucrose
galactose and glucose
lactose
test for starch
add iodine - colour change orange → dark blue/black
state with saturated fatty acids
solid at room temp
lipid bond
ester
carbohydrate bond
glycosidic
protein bond
peptide
dna bond
phosphodiester