Organizational Behavior - Exam #5
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
organizational culture
the set of shared, taken-for granted, implicit assumptions that a group holds and that determines how it perceives, thinks about, and reacts to its various environments
What are the four characteristics of organizational culture?
shared concept
learned over time
influences our behavior at work
impacts outcomes at multiple levels
What are the three levels of organizational culture?
observable artifacts
espoused versus enacted values
basic underlying assumptions
observable artifacts
the physical manifestation of an organization’s culture
espoused values
explicitly stated values and norms that are preferred by an organization
enacted values
values and norms that are actually exhibited or converted into employee behavior
basic underlying assumptions
organizational values that have become taken for granted
What are the four functions of organizational culture?
establish organizational identity
encourage collective commitment
ensure social system stability
act as sense-making device
clan (collaborate) values
internal focus, flexibility valued rather than stability & control
achieving effectiveness by encouraging collaboration, trust & support
employee-focused
means: cohesion, participation, communication, & empowerment
ends: morale, people, development, & commitment
adhocracy (create) values
external focus and flexibility valued
creation of new products and services
culture adaptable, creative, and fast to respond to the marketplace
means: adaptability, creativity, & agility
ends: innovation, growth, & cutting-edge output
hierarchy (control) values
internal focus, formalized and structured work environment
stability and control valued over flexibility
efficiency, timeliness, and reliability
means: capable processes, consistency, process control, & measurement
ends: efficiency, timeliness, and smooth functioning
market (compete) values
strong external focus and stability and control valued
competition
strong desire to deliver results and accomplish goals
means: customer focus, productivity, & enhancing competitiveness
ends: market share, profitability, & goal achievement
What are the four types of organizational culture?
adhocracy
market
clan
hierarchy
What are the outcomes that are associated with organizational culture?
is related to measures of organizational effectiveness
employees are more satisfied and committed to organizations with clan cultures
clan and market cultures are more likely to deliver higher customer satisfaction and market share
innovation and quality can be increased by building characteristics associated with clan, adhocracy, and market cultures
financial performance is not strongly related to organizational culture
market cultures tend to have more positive organizational outcomes
subcultures
often not a single homogeneous culture
multiple of these that either intensify the existing cultural understanding and practices or diverge from them
What are the five main things that subcultures form around?
functional or occupational groups or work roles
divisions or departments
geographical areas
products, markets, & technology
levels of management
What are the four truths of culture change?
leaders are the architects and developers of organizational change
changing culture starts with one of the three levels of organizational culture: artifacts, espoused vales, & basic underlying assumptions
consider how closely the current change aligns with the organization’s vision and strategic plan
use a structure approach when implementing culture change
vision
a long-term goal that describes what an organization wants to become
strategic plan
outlines the organization’s long-term goals and the actions necessary to achieve them
What are the 11 mechanisms for creating culture change?
formal statements (ex. mission, vision, values, etc.)
design of physical space (ex. among people and buildings, location of furniture, etc.)
slogans, language, acronyms, and sayings (easy to remember)
explicit rewards or status symbols (strong impact to embed culture)
role modeling, training, or coaching
stories, legends, or myths
organizational activity and processes (leaders pay attention to those activities they can measure and control)
leader reactions to critical incidents (people learn by watching the leaders)
rites and rituals (used to celebrate important events)
workflow and organizational structure (reducing organizational layers)
organizational systems and procedures and goals (reflect values)
organizational socialization
the process by which a person learns the values, norms, and required behaviors that permit them to participate as a member of an organization
effective onboarding programs result in increased retention, productivity, and rates of task completion for new hires
managers need to help new hires integrate with the culture to overcome stress associated with a new environment
What are the three phases of the organizational socialization process?
anticipatory socialization
encounter
change and acquisition
Phase 1: Anticipatory Socialization
occurs before an individual actually joins an organization
information learned about careers and organizations
learned from: current employees, social media, & internet
offers a realistic job preview
Phase 2: Encounter
employees come to learn what the organization is really like
organizations use onboarding programs to help employees integrate, assimilate, and transition to new jobs by making them familar with corporate policies, procedures, etc
Phase 3: Change & Acquisition
employees master important tasks and roles and adjust to their group’s values and norms
mentoring
the process of forming and maintaining intensive and lasting developmental relationships between a variety of developers and a junior person
coaching
a process that focuses on improving an individual’s behavior and performance to resolve work issues or handle specific aspects of the job and may be short term
What are the four phases of mentoring and embedding organizational culture?
initiation
cultivation
separation
redefinition
What are the two general functions of the mentoring process?
career related: sponsorship, exposure, coaching, protection, etc.
psycho-social related: role modeling, acceptance and confirmation, friendship, etc.
human capital
the productive potential of an individual’s knowledge, skills, and experiences
social capital
the productive potential resulting from relationships, goodwill, trust, and cooperative effort
What are the four steps to developing a mentoring plan?
make it goal driven
seek out those experienced in the areas in which you want to improve
what value will you bring to the relationship?
know when to move on
organization
a system of consciously coordinated activities or forces of two or more persons
common among all organizations: coordination of effort, division of labor, aligned goal, and hierarchy of authority
What are the four basic dimensions reflected in organizational charts?
hierachy of authority
division of labor
span of control
line-staff positions
hierarchy of authority (unity of command principle)
specifies that each employee should report to only one manager
division of labor
what each person’s role is in the organization
span of control
the number of people reporting directly to a given manager
staff employees
do background research and provide technical advice and recommendations to their line managers
line managers
generally have the authority to make decisions for their units
What are the subsystems of an organization in an open system?
goals and values
technical
structural
psychosocial
learning organization
proactively creates, acquires, and transfers knowledge and changes its behavior on the basis of new knowledge and insights
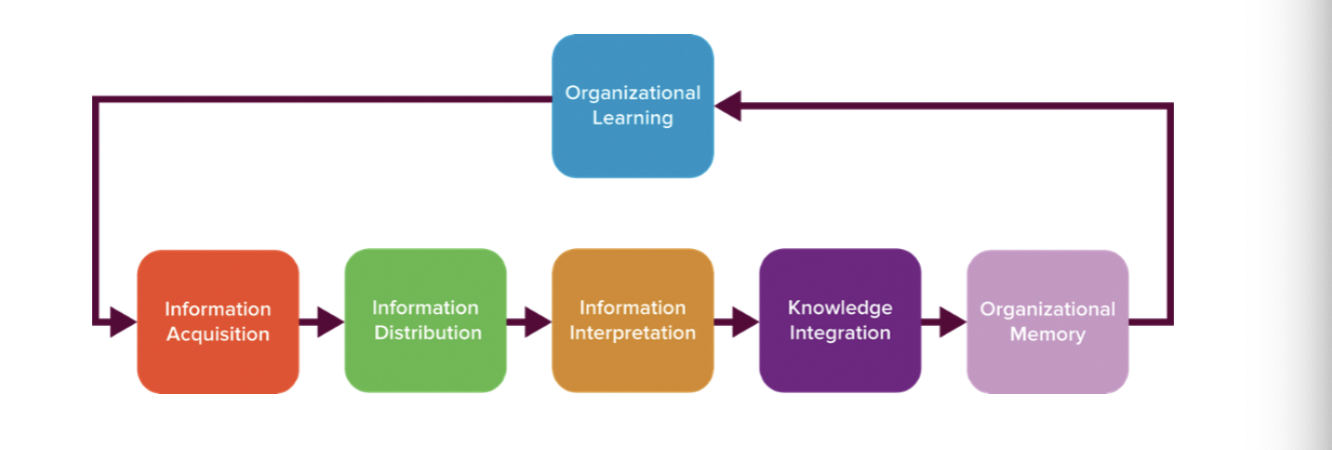
organizational design
sets the structures of accountability and responsibility used to develop and implement strategies, and the HR practices and information and business processes that activate those structures
What are the three categories of organizational design?
traditional
horizontal
open
traditional
mid-1800s through 1970s
focus was self-contrained within organization’s boundaries
type: functional, divisional, and matrix
horizontal
1980s
focus on team- and process-oriented
open
mid-1990s
focus on opened beyond organization’s boundaries
types: hollow, modular, and virtual
What are the seven types of organizational structures?
functional
divisional
matrix
horizontal
hollow or network
modular
virtual
functional structure
employees grouped according to the business functions they perform
pros: saves money, easy to apply
cons: works best in a stable environment
divisional structure
employees grouped based on similar products or services, customers, or clients, or geographic regions
pros: increased focus on customers and products & flexibility in decisions
cons: tend to focus on their own customer groups or products
matrix structure
combines a vertical structure with an equally strong horizontal overlay
generally combines functional and divisional chains of command to form a grid with two command structures
pros: combines advantages of functional and divisional
cons: violates unity of command, decision making is slow, political behavior is common, and requires a lot of communication
horizontal structure
teams or workgroups, either temporary or permanent, created to improve collaboration and work on common projects
pros: improves communication, more creative solutions, knowledge sharing, and faster product development
cons: lines of authority are not clear, requires employees to rise to challenges of empowerment
hollow or network structure
designed around a central core of key functions and outsources other functions to other companies or individuals who can do them cheaper or faster
pros: generate superior returns, focus on what they do best
cons: give up expertise and control when outsourced and have to get results from people without authority
modular structure
the company assembles product parts, components, or modules provided by external contractors
pros: cost savings, greater responsiveness, ability to switch vendors
cons: poor interfaces, poor quality collaboration
virtual structure
members geographically separated, usually working with email and other forms of IT
generally appears to customers as a single, unified organization with a real physical location
can be either: internal or networked external
pros: ability to respond quickly, ability to provide product extension, low exit costs
cons: high level of communication needed, low trust, failure to promote strong employees
contingency approach (to designing organizations)
organizations are often more effective when they are structured to fit the demands of the situation
no one way is best
key issues: strategy and goals, market uncertainty, decision making, size, etc.
mechanistic: rigid bureaucracies with strict rules, narrowly defined tasks, and top-down communication, centralized decision making, and works best when environment is stable and certain
organic: flexible networks of multitalented individuals who perform a variety of tasks, decentralized decision making, and works best when environment is unstable and uncertain
innovation
the creation of something new that makes money; it finds a pathway to the consumer
What are the two types of innovation?
product innovation
process innovation
product innovation
a change in the appearance of functionality/performance of a product or a service or the creation of a new one
process innovation
a change in the way a product or a service is conceived, manufactured, or distributed
What are the two focuses of innovation?
improvement innovations
new direction innovations
improvement innovations
target existing products, services, or processes
new direction innovations
create new markets and customers and rely on developing breakthroughs and inventing things that don’t currently exist
innovation system
a coherent set of interdependent processes and structures that dictates how the company searches for novel problems and solutions, synthesizes ideas into a business concept and product designs, and selects which projects get funded
assessing organizational effectiveness
translating organizational vision, strategy, and goals into comprehensible performance metrics
balanced scorecards (BSC) and other organizational dashboards (financial, custom, internal business process, and learning growth and development processes)
What are the external forces for change?
can apply to the organization, competitors, or the entire industry
dramatically affects why an organization exists and which markets it will participate in and how
key forces: demographics, technological advancements, shareholder/customer/market changes, and social/political pressures
What are the internal forces for change?
may be subtle (ex. low levels of job satisfaction)
may manifest in outward signs: low productivity, increased conflict, or strikes
key forces: HR issues & managerial behavior and decisions
What are the three general types of change?
adaptive change
innovative change
radically innovative change
adaptive change
reintroducing a familar practice
innovative change
introducing a practice new to the organization
radically innovative change
introducing a practice new to the industry
Lewin’s Change Model
unfreezing: create the motivation to change
changing: introduce new information, models, & procedures
refreezing: support & reinforce the change
What are the four systems model of change and what is the system?
assumes that any changes have a cascading effect throughout an organization
inputs: must align with mission & vision
outputs: represent the desired end results or goals
strategic plans: outlines long-term direction & action steps
target elements of change: used to diagnose problems & find solutions
Kotter’s Steps for Leading Organizational Change
provides specific recommendations about behaviors and activities needed to lead organizational change
What are the eight Kotter’s Steps?
establish a sense of urgency
create the guiding coalitation
develop a vision and strategy
communicate the change vision
empower the broad-based action
generate short-term wins
consolidate gains and produce more change
anchor new approaches in the culture
organizational development (OD)
planned change aimed at solving a specific issues
steps: 1. diagnosis 2. intervention 3. evaluation 4. feedback
resistance to change
any thought, emotion, or behavior tha does not align with real or potential changes to existing routines
one of three possible influence outcomes including compliance and commitment
recipient characteristics of resistance to change
dispositional resistance to change
surprise and fear of the unknown
fear of failure
loss of status or job security
peer pressure
past success
change agent characteristics of resistance to change
decisions that disrupt cultural traditions or group relationships
personality conflicts
lack of tact or poor timing
leadership style
failing to legitimize change
change agent-recipient relationship
resistance reduced when there is a positive, trusting relationship
stress
an adaptive response to environmental demands, referred to as stressors that produce adaptive responses: physical, emotional, and behavioral reactions
job stress
the harmful physical and emotional responses that occur when the requirements of the job do not match the capabilities, resources, or needs of the worker
eustress
stress assoicated with positive emotions and outcomes
cognitive appraisals
primary appraisals are perceptions of whether a stressor is irrelevant, positive, or negative
secondary appraisals are perceptions of how able you are to deal or cope with a given demand
coping strategies
control strategy consists of behaviors and cognitions that directly anticipate or solve problems
escape strategies are those in which you avoid or ignore stressors
symptom management strategies focus on reducing the symptoms of stress and include relaxation, meditation, medication, and exercise
overcoming resistance to change
employees are more likely to resist when they perceive that the personal costs of change outweigh the benefits, so managers should provide as much info as possible, inform employees about their reasons, conduct meetings to address questions, and provide employees with opportunities to discuss
this also helps build trust and improves the agent-recipient relationship
organizational process and practices: avoid the assumption that people are cosciously resisting change, obtain employee feedback about their obstacles, and consider modifying the elements of change
contingency approach to resistance to change
inspire
recognize progress
expect mistakes
model, measure, and reward collaboration
positivity
goals and time
cognitive restructuring
can help you stop thinking pessimistically about an event or problem
name the problem
list your beliefs
identify consequences
formulate counterargument
describe how energized and empowered you feel