The Respiratory System and Gas Exchange
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Be able to label and draw the structures of the respiratory system.
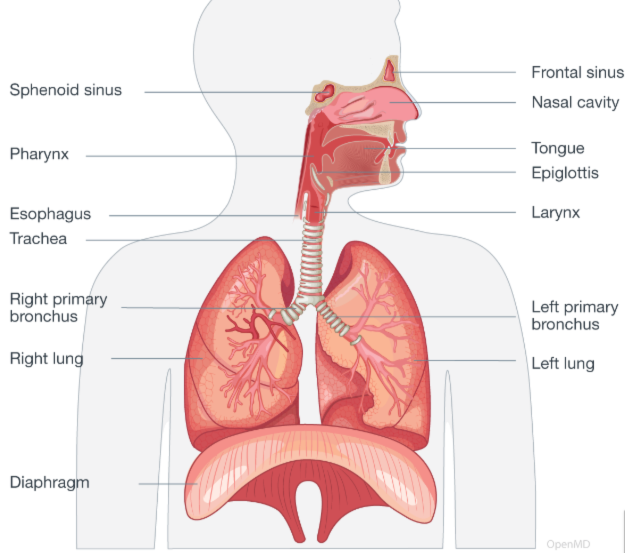
What is a type I pneumocyte? Where is it found and what is its function?
Long cells in alveoli, ideal for gas exchange.
What is a type II pneumocyte? Where is it found and what is its function?
synthesises pulmonary surfactant which converts o2 to liquid o2 to diffuse into capillaries. found in alveoli
What is the role of phagocytes in the alveoli?
Clearing the air of infectous, toxic or allergenic particles.
Describe the action of the intercoastal muscle and the diaphragm during inhalation and exhalation
Inhalation - diaphragm down/contract
- External IM contract
- Internal IM relax
Exhalation - Diaphram up/relax
- External IM relax
- INternal IM contract
describe the causes and consequences of emphysema
Cause - Smoking
Effect - Ruptures alveoli = less area for gas exchange = shortness of breath and lack of oxygen
Describe the Bohr shift (difference between fetal and adult)
fetal haemoglobin is much more saturated with oxygen in comparison to adult
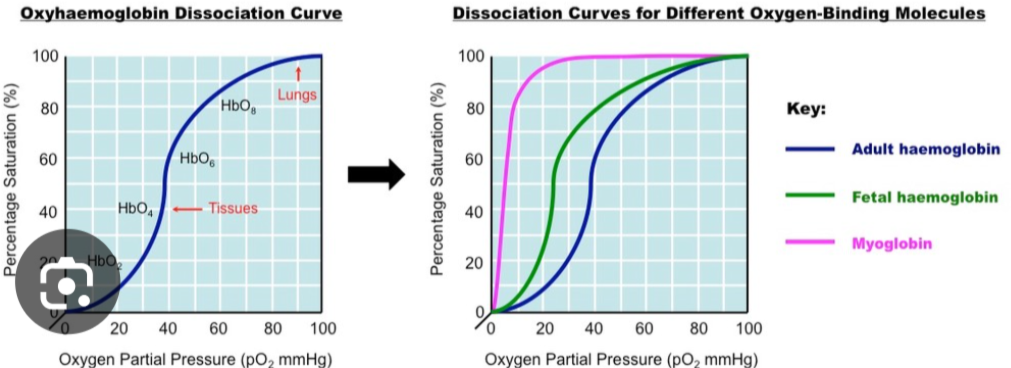
How does hemoglobin have an affinity for oxygen?
binding is cooperative in hemoglobin which means that the more oxygen binds to immigration the more attractive it is to other oxygen molecules. For oxygen molecules can bond to hemoglobin at a time due to it containing four iron molecules in its 4 heme groups
What is the normal range of lung pressure and tissues outside of lung?
Lung pressure - 10-13kpa
other - 5-10kpa