Chapter 25, Lesson 5: The Small Intestine
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 25, Lesson 5 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Tenth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Small intestine
The site of nearly all chemical digestion and nutrient absorption, it is the longest part of the digestive tract as a coiled tube filling most of the abdominal cavity
5 to 8 meters
The small intestine’s length — longer in cadavers without muscle tone — “small” refers to the diameter (2.5 cm), not length
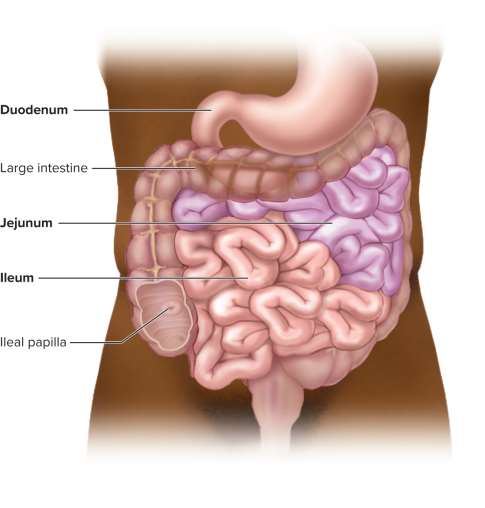
Small intestine regions
Three regions:
Duodenum (first 25 cm)
Jejunum (next 40%)
Ileum (last 60%)
Duodenum
The first 25 cm of the small intestine starting at the pyloric valve and curving around the pancreas; it neutralizes stomach acid, emulsifies fats, and aids digestion with enzymes, bile, and pancreatic juice
Jejunum
The first 40% (1 to 1.7 meters) of the post-duodenal small intestine, it has a thick and muscular wall and rich blood supply for most digestion and nutrient absorption
Ileum
The last 60% (1.6 to 2.7 meters) of the post-duodenal small intestine, it forms a thinner, paler, and less muscular wall and connects to the ileocecal junction
Ileocecal junction
The end of the small intestine where the ileum joins the cecum of the large intestine
Superior mesenteric artery
The artery from which the small intestine receives nearly all of its blood supply
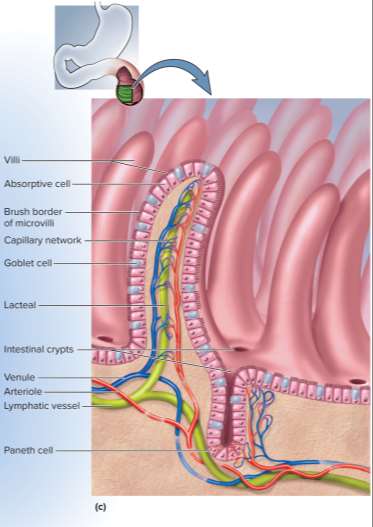
Villi
Type of projection in the small intestine for a 10 times increase in surface area to aid nutrient digestion and absorption
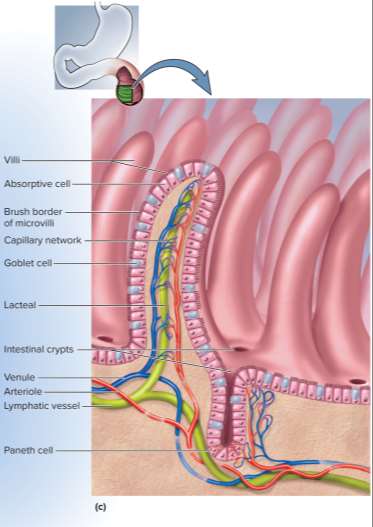
Microvilli
Type of smaller projection in the small intestine for a 20 times increase in surface area to aid nutrient digestion and absorption; forms a fuzzy brush border with supporting enzymes
Sodium bicarbonate
A base used to neutralize stomach acid within the duodenum; secreted by the duodenal glands
Intestinal juice
1 to 2 liters of liquid secreted by the intestine per day in response to acid or intestinal distension; has a pH of 7.4 to 7.8 and mixes with water, mucus, bile, and pancreatic juice
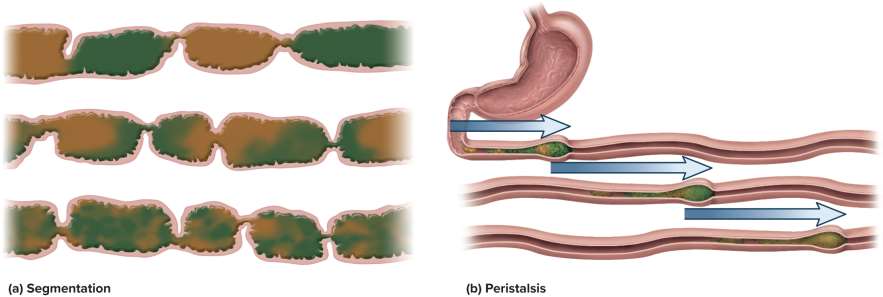
Segmentation
Movement in which stationary ring-like constrictions appear and disappear in several places along the intestine to knead and churn the intestinal contents