Chemistry - Unit 14 - Redox Reactions
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
How to complete a redox reaction
1) Assign oxidation numbers. Use this to figure out what is oxidized and what is reduced.
2) Split the equation into two half equations
3) Balance equations in terms of mass
4) Balance equations in terms of charge/electrons
Find the charge and add electrons to one side to neutralize this charge (for both half reactions)
5) Make both half reactions have the same number of electrons (added to one side) by multiplying and finding least common multiple.
6) Electrons now cancel (one on products side, one on reactants side) so half equations can be added with their new coefficents
Spectator
Ion or particle that does not lose/gain e- from reactants or products in a reaction
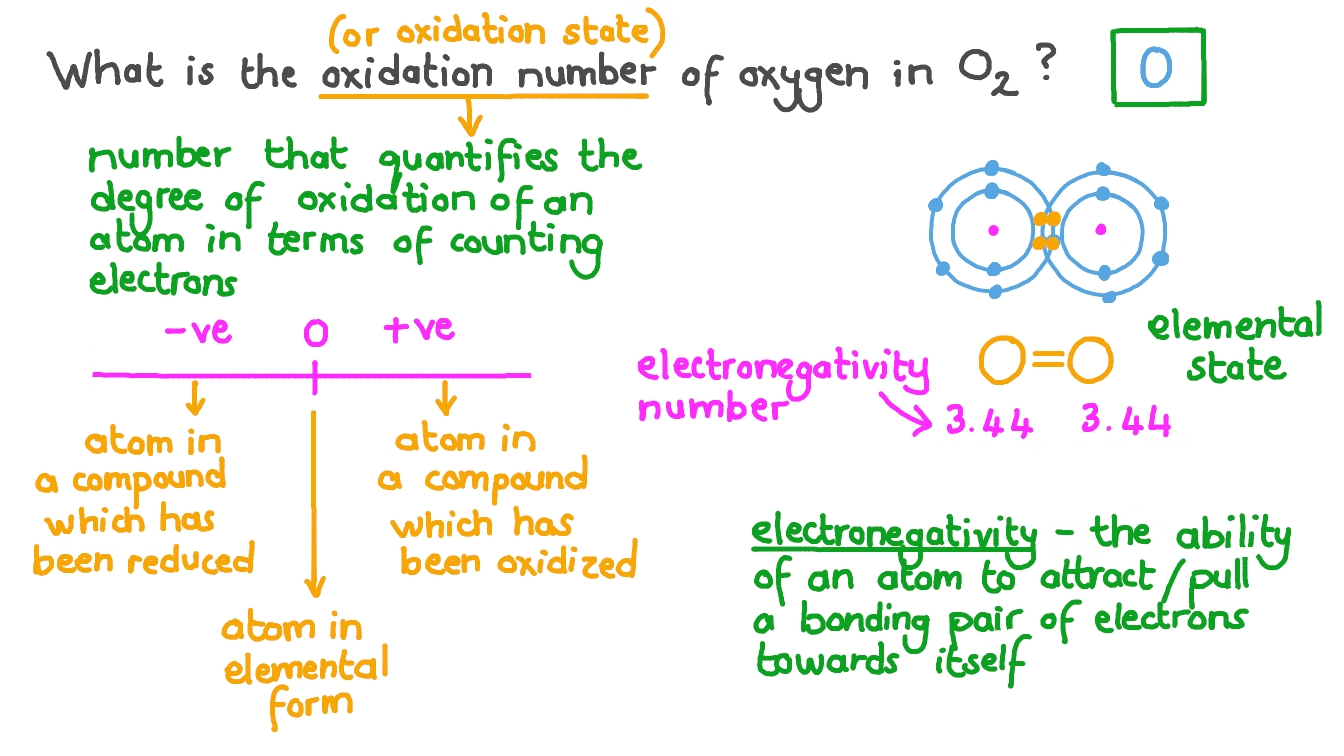
What is oxidation state (in terms of electrons)
Oxidation state, also known as oxidation number, describes the hypothetical charge an atom would have if all its bonds were fully ionic. In simpler terms, it represents the degree of oxidation, or the number of electrons an atom has effectively lost or gained in forming a chemical bond. A positive oxidation state indicates a loss of electrons (oxidation), while a negative oxidation state indicates a gain of electrons (reduction).
What process involves the transfer of electrons?
The process that involves the transfer of electrons is called an oxidation-reduction reaction (also known as a redox reaction). In these reactions, one substance loses electrons (oxidation) while another substance gains electrons (reduction
The substance that is being oxidized is also the _________
The substance that is being reduced is also the ________
The substance that is being oxidized is also the reducing agent
The substance that is being reduced is also the oxidation agent
Reduction
Electrons are gained
Oxidation number decreases
Also the oxidizing agent
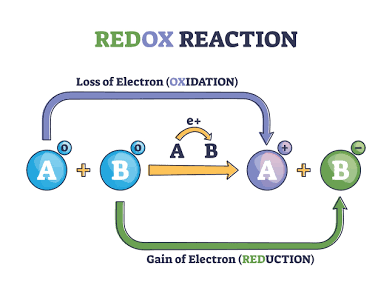
Oxidation
Electrons are lost
Oxidation number increases
Also the reducing agent the thing that gets oxidized is doing the reduction
If something has goes from low oxidation number to high oxidation number is it being reduced or oxidized? What about the opposite?
Low —> high = oxidized (electrons lost)
High —> low = reduction (electrons gained)
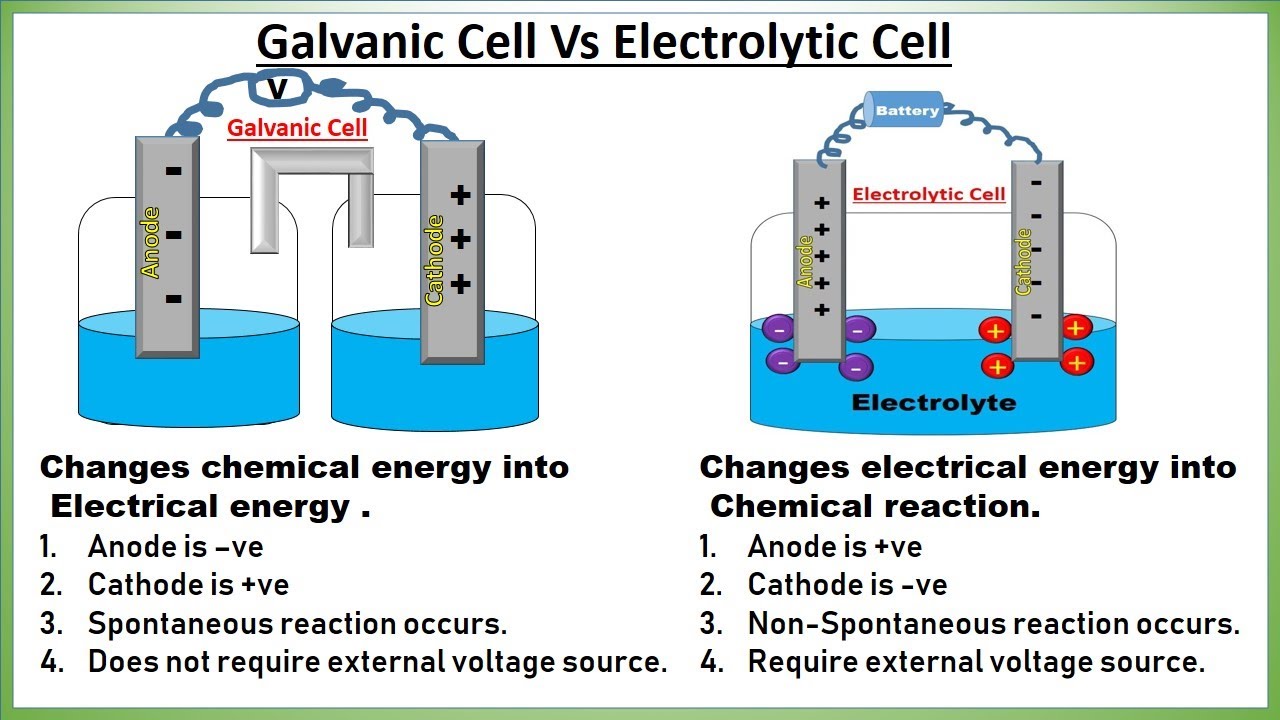
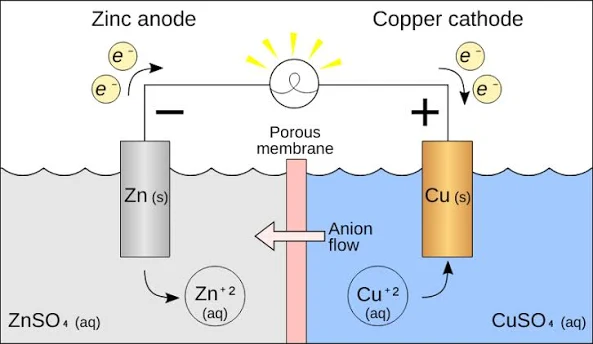
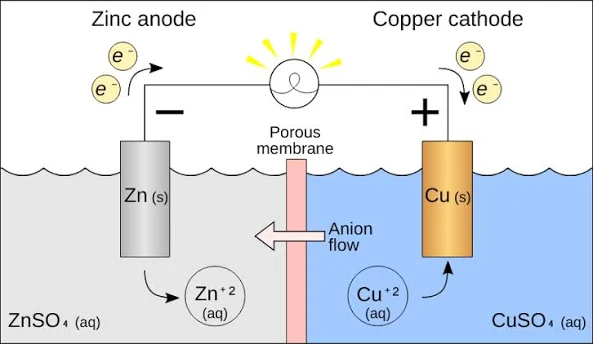
Voltaic Cell / Galvanic Cell (cathode/anode, mass)
An electrochemical cell that uses a spontaneous redox reaction to convert chemical energy to electrical energy
Negative anode
Positive cathode
2 chambers
Salt bridge
Anode decreases in mass (electrons leaving), concentration of ions increases
MORE active metal —> ready to loose electrons = ready to oxidize = AnOx
Cathode mass increase (electrons added), ion concentration decreases
LESS active metal
Spontaneous Reactions (and how to tell they are spontaneous)
A reaction that does not require an external energy force in order to happen (happens on its own)
ex: when a solid metal is more active than another metal in ionic compound (single replacement)
How to tell —> Table J, if the metal that is replacing the other metal is higher up on the table (AKA: MORE reactive then what its replacing)
All Rules:
Element in elemental form
Monoatomic ion
Metals of group 1
Group 2
Fluorine and other Halogens
Hydrogen
Oxygen
The sum
Element in elemental form = 0
Monoatomic ion = charge
Metals of group 1 = +1
Group 2 = +2
Fluorine is always -1, the other halogens are also -1 when they are the most electronegative element in the compound
Hydrogen +1 w/ nonmetals but -1 w/ metals
Oxygen is -2 exception; with flourine and w: peroxide
The sum: sum must be zero, the sum of the oxidation number in Polyatomic ions must equal the charge of the ion
Electrolysis
When electricity is used to force a chemical reaction to occur.
—> Can be used to decompose compounds to obtain pure reactive elements
Ex: group 1,2,H2
Electrolytic Cell
Non spontaneous reaction that uses electricity to convert electrical energy to chemical energy.
used a battery
Anode is positive (lose electrons)
Cathode is negative (gain electrons)
NO salt bridge
1 chambers Salt
Anode (positive), looses e-
decreases mass
Cathode (negative), gains e-
Increase mass
Electroplating
USING ELECTROLYTIC CELLS TO COAT A LAYER of metal on an object
—> object being plated is always the cathode
—> only covers the metal, nothing else
—> used in jewelry
Oxidation State:
The hypothetical charge that an atom would have in a molecule if bonds were 100% ionic
Used to track how many electrons are lost or gained during a reaction
Identifying redox reactions
1) oxidation numbers for both sides, if change it is redox
Hints:
1) synthesis, decomposition, single replacement ALL REDOX
2) elemental form on one side and compound on the other side
OIL RIG
OIL RIG
Oxidation Is Losing e
Reduction is Gaining e
THINK ABOUT THIS WHEN WRITING HALF EQUATIONS —> OXIDATION MEANS ELECTRONS ARE IN PRODUCTS AND VICE VERSA FOR REDUCTION
Oxidizing and reducing agent
Oxidizing Agent: COMPOUND that reduces another element (also the element that is being oxidized)
Must be on the left side (reactants)
Reducing Agent: COMPOUND that oxidizes another element (also the element that is being reduced)
Must be on the left side (reactants)
Half reactions, what are they? (difference)
Every redox reaction is made up of two half-reactions: in one, electrons are lost (oxidation) and in the other, those electrons are gained (reduction process)
LOST ELECTRONS = Oxidation Half = electrons are in products
GAIN ELECTRONS = Reduction Half = electrons are in reactants
Redox Half Reaction Steps
Process of Balancing charge in Redox reactions.
1 - Assign oxidation numbers. What is oxidized? What is reduced?
2- Split the whole equation into two half equations: red half + ox half
ox half = electrons as products
red half = electrons as reactants
3- Balance equations in terms of mass. Balance in terms of charge using electrons.
4 - Find least common multiple for electrons and multiple each half reaction so electrons equal least common multiple
5 - add the equations (electrons cancel but coefficents stay)
Half reactions Location of electrons
Oxidation:
Reduction :
Oxidation: electrons are a reactant
Reduction: electrons are a product
What metals are easiest to oxidize and why
Easiest to oxidize: Metals in group 1 and group 2 because they are easily giving away electrons, making them strong reducing agents. If they are good reducing agents they are good at oxidizing.
Spectator
Spectator: Ion or particle that does not loose/gain electrons from reactant to products in a reaction
Can be omitted from half reactions and net equation
Electrochemical cell:
Electrochemical cell: involves a chemical reaction (redox, single replacement) and a flow of electrons. Parts of an electrochemical cell include: two metal electrodes (anode and cathode), ion solutions, wires connecting the electrodes.
Voltaic Cell/Galvanic Cell
Voltaic Cell/Galvanic Cell
An electrochemical cell that uses a spontaneous redox reaction to convert chemical energy to electrical energy
Has a salt bridge, positive electrode is a cathode, negative electrode is anode, NO BATTERY because its spontaneous reaction
Forces electrons through a specific path (wire) to use the flow of electrons as electricity
AnOx RedCat (applies to both)
AnOx (applies to both)
Anode = Oxidation = Losing electrons = oxidation state is more positive (losing electrons)
RedCat (applies to both)
Reduction = Cathode = Gaining electrons = oxidation state is more negative (gaining electrons)
What is the purpose of the salt bridge
Provide mobile ions that can move between two half cells to keep the charge of the solution neutral (Ex: NaCl can split into ions Na and Cl, when and ion travels to the other half cell then on of the ions will replace it so its neutral)
The electrons always flow from:
ANODE → CATHODE
Anode = oxidation half cell
Cathode = reduction half cell
In Voltaic/Galvanic… Why two half cells:
In a negative electrode you have the oxidation half equation, the products are the ion and the electrons, these electrons are pulled to the cathode because…
The product is the oxidized element but with a charge (lost electrons), the concentration of this thus increases
As oxidized the mass of metal anode decreases because its dissolving (the strip) into electrons and ions
In positive electrode you have the the reduction half equation which have electrons as a reactant (thus why the electrons are pulled to cathode)
The ions (what is being reduced) are being used (reactants) so the concentration of them decreases
As reduction happens the mass of the cathode increases because gaining of electrons means it turn into a solid metal, adhering to the cathode, increasing mass
Electrolytic
Electrolytic Cell: nonspontaneous reaction that uses electricity (uses battery b/c not spontaneous) to convert electrical energy to chemical energy
Electroplating:
Electroplating: using electrolytic cell to coat a layer of metal on an object using an electrolytic cell, object being plated is always the cathode
Battery pushes electrons to the cathode where they attach to
What is the battery’s purpose?
What is the battery’s purpose?
Pulling electrons from anode to cathode
This makes the neutral metal particles on the anode now ions which can dissolve in water
Neutral → ion
Electrons are being pushed into the cathode. This side has electrons so the floating ions that came from the anode (metal we are plating that lost an electron to the battery who stole it) want electrons to become neutral, they go over to the cathode, take an electron, and now they are neutral and solid.
What is added to the water to facilitate electroplating?
Chemicals that dissipate into positive and negative ions
Balance
Work as electrolytes → make the water conductive so the circuit is completed and the battery works.
Cathode and Anode (electroyltic) —> talk about mass
Cathode: RedCat = reduction at cathode, mass increases cathode
Negative electrode = Cathode
Where the metal we are plating goes (going to be covered in the other metal)
Mass increase
Anode: AnOx = oxidation at anode, mass decreases
Positive electrode = Anode
Where the used metal is (in electroplating what we are transferring to random metal to plate)
Mass decreases
Cathode and anode in voltaic v electrolytic
Voltaic cell - Anode is negative, cathode positive
Electrolytic cell - Anode is positive, cathode negative
NEUTRAL ATOMS MAKE UP SOLID METAL. METAL IONS USUALLY DISSOLVE IN WATER
THUS —> Electolytic cell works and elctorplating works
Electrolysis:
When electricity is used to force a chemical reaction to occur. Can be used to decompose compounds to obtain pure elements.
On table J the replacement metal is lower in reactivity then what it is replacing
Electroplating is a type of electrolysis
Difference between Galvanic cell and electrolytic cell:
Galvanic cell is spontaneous and thus doesn't need a battery
Electrolytic is non spontaneous and thus needs a battery
Galvanic cell has positive electrode of the cathode and negative electrode of the anode
Electrolytic Cell has positive electrode as the anode and the negative electrode as the cathode
Biggest difference: Galvanic = Chemical → electrical, Electrolytic = Electrical → Chemical
Salt bridge and two different chambers in voltaic V
No salt bridge and connection to battery with one chamber for electrolytic