Trauma Exam
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
What is the leading cause of death in the first four decades of life in developed countries?
Trauma
This is the period immediately following trauma in which rapid assessment, diagnosis and stabilization must occur
"Golden Hour" of trauma

Trauma death occurs in a _____ death distribution
Trimodal Death Distribution
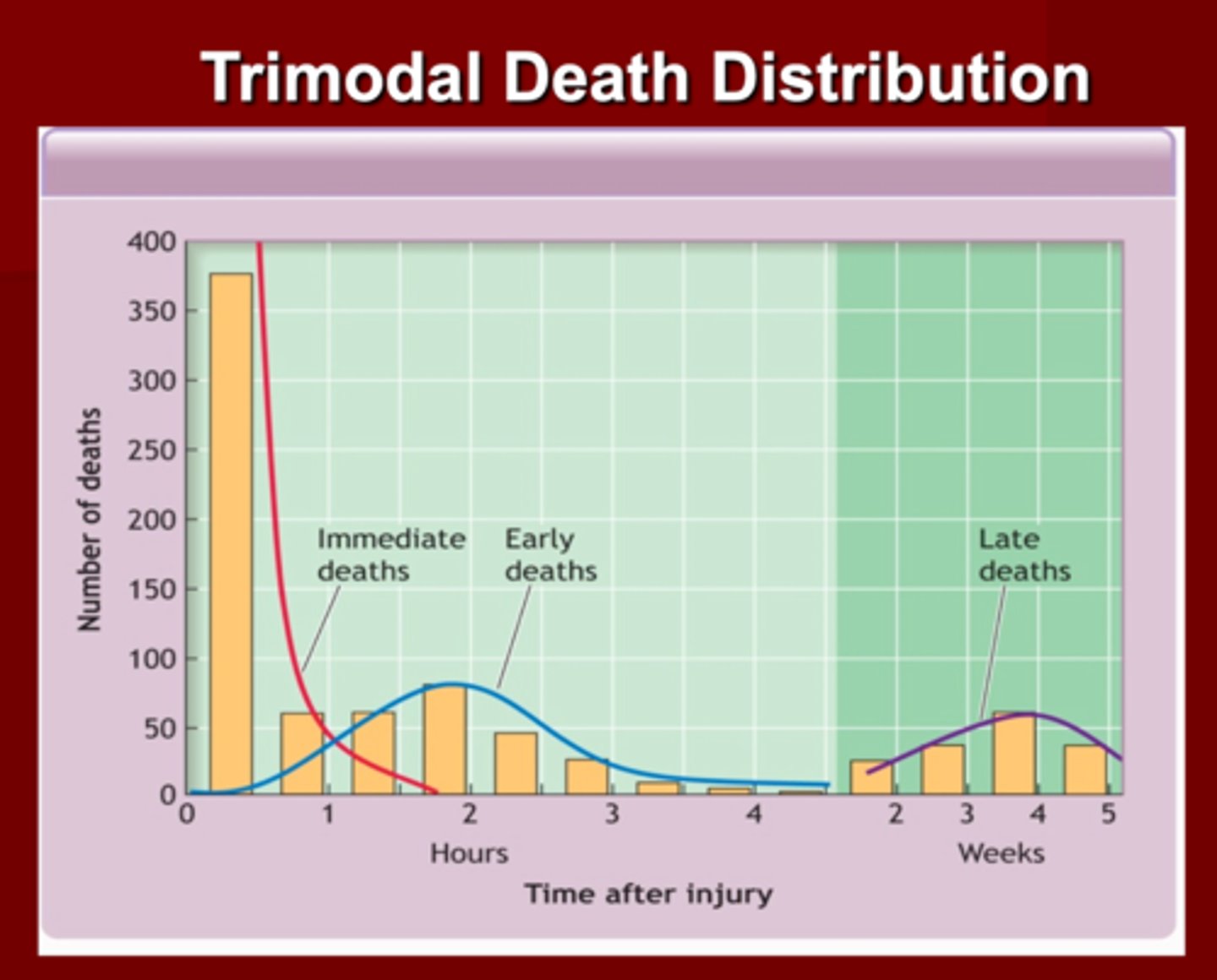
First Peak in Trimodal Death Distribution
1. Occurs ____ to _____ of injury
2. Death is caused by injury/laceration to .....
1. seconds to minutes of injury
2. Brain, brainstem, high spinal cord, aorta large blood vessels
(death is instantaneously)

Second Peak in Trimodal Death Distribution
1. Occurs ____ to _____ of injury
2. Time for ______ intervention
3. What kind of injuries would you suspect?
1. Minutes to hours of injury
2. ATLS (Advanced Trauma Life Support
3. Sub/epidural hematoma
- Hemopneumothorax
- Ruptured organs
- Pelvic Fractures
- Blood loss

Third Peak in Trimodal Death Distribution
1. Occurs ____ to _____ of injury
2. Death usually occurs due to ?
1. Days to weeks after injury
2. Sepsis
- Multiple organ failure
- Injury complications
(This is where we stabilize patients and send them to the ICU--> and they die anyway)

What are the Trauma Basics?
1. _________ approach to evaluation & treatment
2. What should be treated FIRST?
3. What is NOT immediately important to do at this time ?
4. ______ is of the essence
5. Do no further harm!!
Trauma Basics
1. ABCDE
2. Greatest threat to life should be TX first
3. Definitive diagnosis NOT important
4. Time is of the essence

Trauma History
1. Whenever possible take AMPLE History. What does AMPLE stand for?
1. Allergies
2. Medications (-/+ inotropic effect)
3. Past medical hx
4. Last Meal (for intubation to protect the airway)
5. Events leading up to injury

What is the most important information in trauma history?
Events leading up to the injury (MOA)
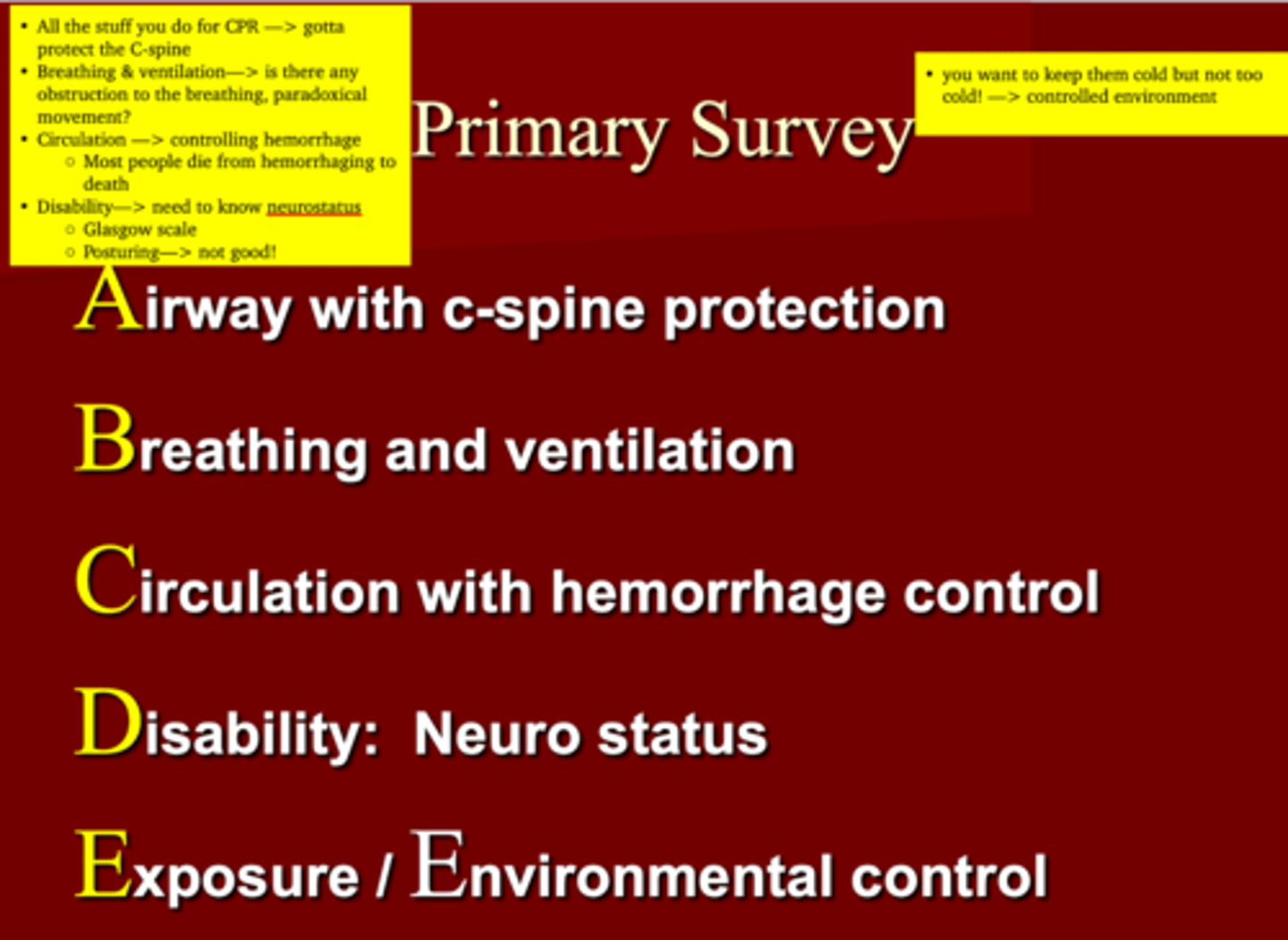
What are the ABCDE's of the Primary survey in trauma?
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
5. E
1. Airway with c-spine protection***
2. Breathing & Ventilation (obstructions, paradoxic movement?)
3. Circulation with hemorrhage control (
4. Disability: Neuro status (GCS)
5. Exposure/Environmental control
(Expose the body to assess any other injuries)
What are the initial assessment and management steps ?
1. Preparation, Primary survey (resuscitation adjuncts), Revaluation
2. Detailed secondary survey (resuscitation adjuncts)
3. Reevaluation & definitive care

During the initial assessment of a trauma patient, the _______ and _______ of viral functions are done simultaneously using a ____ approach
1. Primary survey
2. Resuscitation
3. Team approach

What is the saying that must be done during the initial assessment?
2 tube and a finger
Intubation tube
NG tube
Finger to check rectal sphincter tone
What is a quick, simple way to assess a patient in 10 seconds?
Ask the patient
1. His/her name
2. What happened

An appropriate response to a quick assessment confirms ?
ABCD
1. Patent airways
2. Sufficient air reserve to permit speech
3. Sufficient perfusion
4. Clear Sensorium

What should be done when assessing the Airway & C-spine during a trauma?
1. Assess _____ of airway
2. Use _____ or _____ to open air way
3. All _____ should be cleared
4. Insert _____ or _____ should be used when necessary
5. ________ is done when unable to intubate**
6. Assumes C-spine injury with all injuries above _______******
1. Patency of airway
2. Jaw thrust or Chin lift
3. Foreign bodies (don't put fingers in mouth)
4. Oral or Nasal airway
5. Surgical airway ***
6. Clavicle

When a patient is obtunded/unconscious they should always be ______
intubated

You should assume a C-spine injury with ALL injuries above the ______
Clavicle

How should you asses the breathing & ventilation of a trauma patient to ensure adequate oxygenation & ventilation?
1. Respiratory rate
2. Chest movement
3. Air entry
4. Oxygen saturation
5. Inspect, ascultate & palpate chest

To ensure adequate ventilation you must ID/TX injuries that may immediately impair ventilations such as?
1. Tension pneumothorax
2. Hemothorax
3. Open pneumothorax (shot/stabbed: sucking chest wound)
4. Flail chest

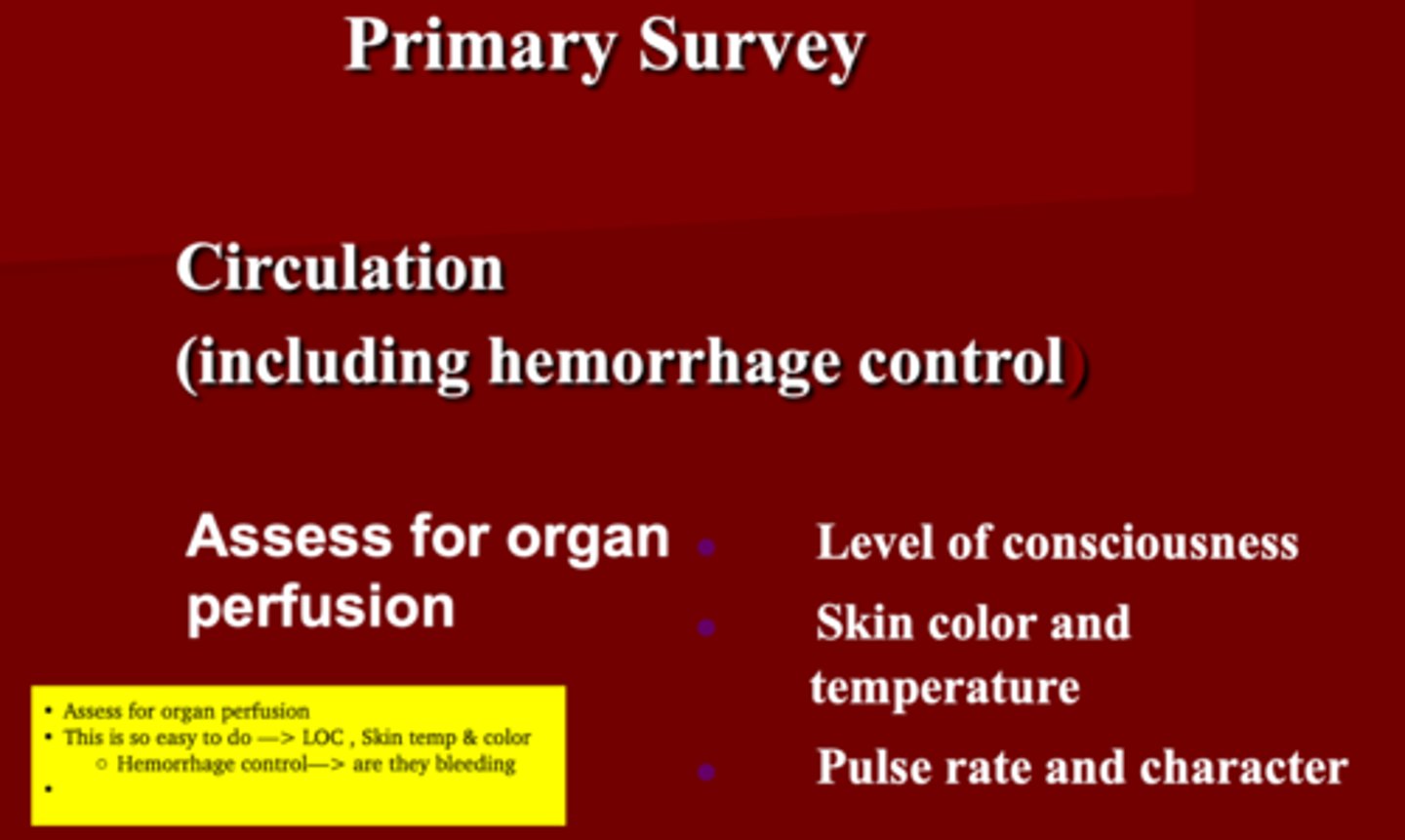
Assessing a patient circulation including hemorrhage control is indirectly assess for _______
organ perfusion
How can you assess circulation when doing the primary survey?
1. Level of consciousness
2. Skin color, temp & cap refill
3. Pulse rate & character
What can be done for circulatory management?
1. Control hemorrhage
2. Restore value
3. Reassess patient
What are the pitfalls to circulatory management ?
1. Elderly (they don't follow rules & don't respond as well)
2. Children (they don't follow rules & they can be fine one minute and bottom out the next minute)
3. Athletes (Known to have lower HR)
4. Medications (some meds have - inotropic effect (BB))
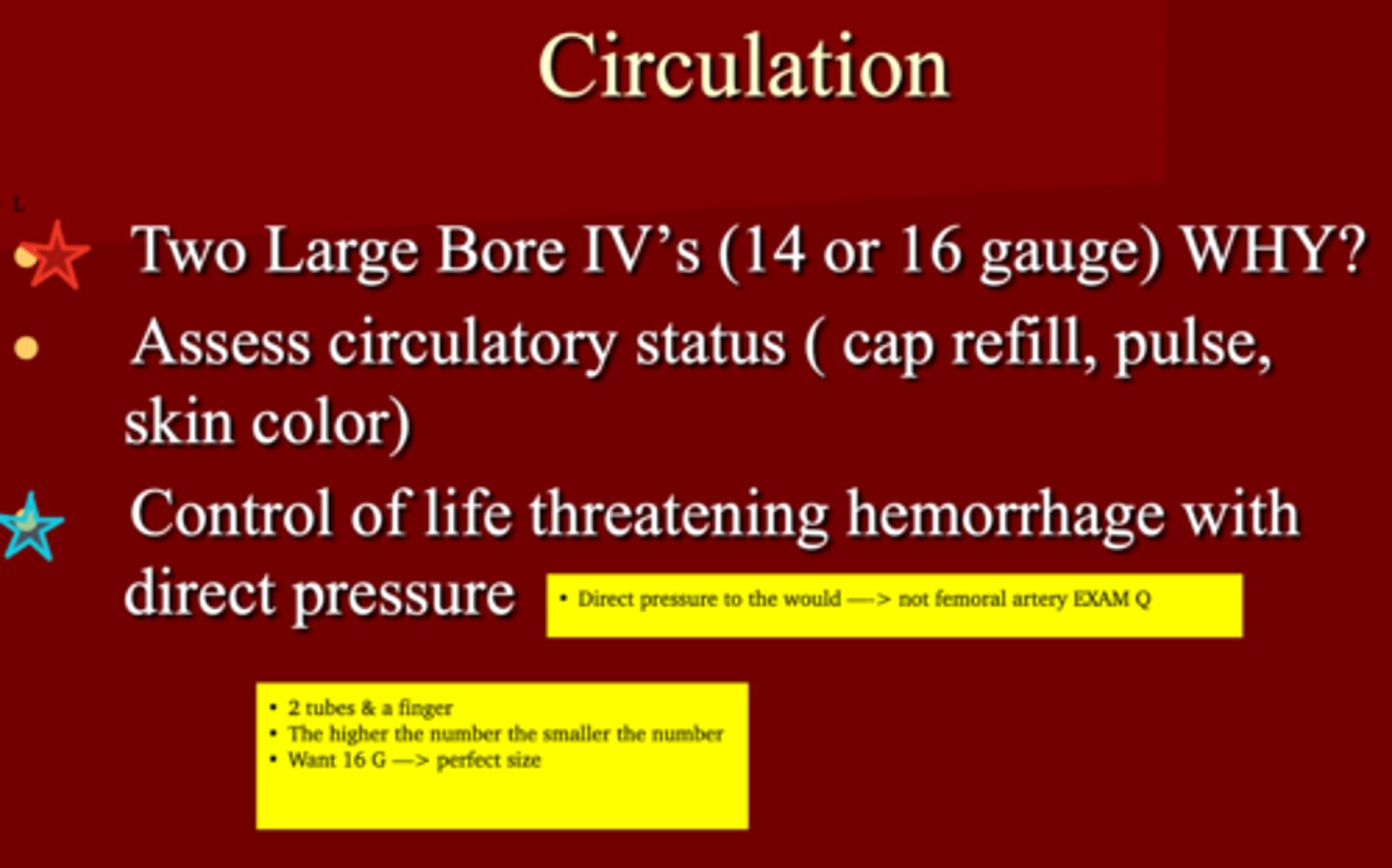
How should you restore volume when managing circulation in a trauma patient?
2 large bore IV's (16G* or 14)
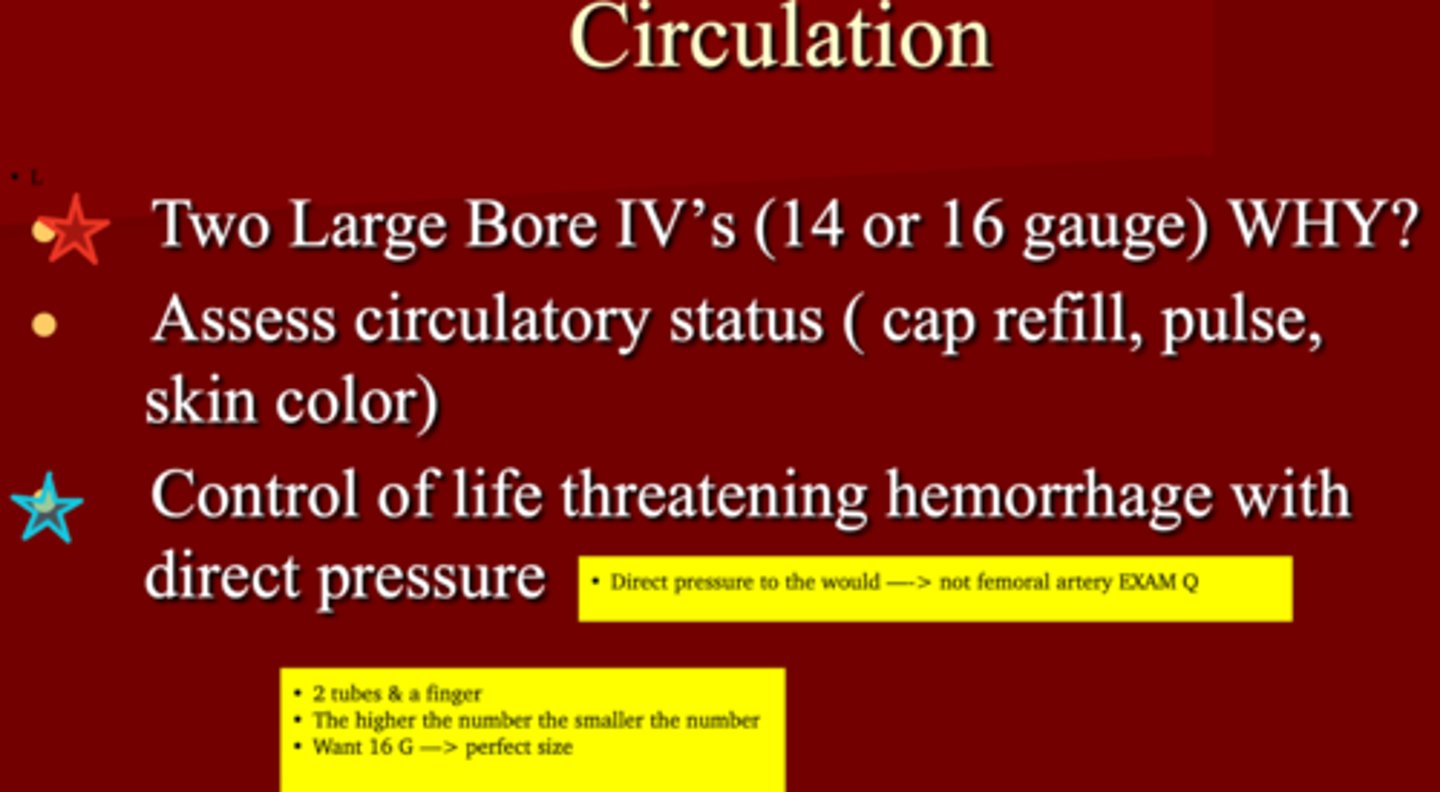
Control of life treating hemorrhage with ________
direct pressure (EXAM Q)
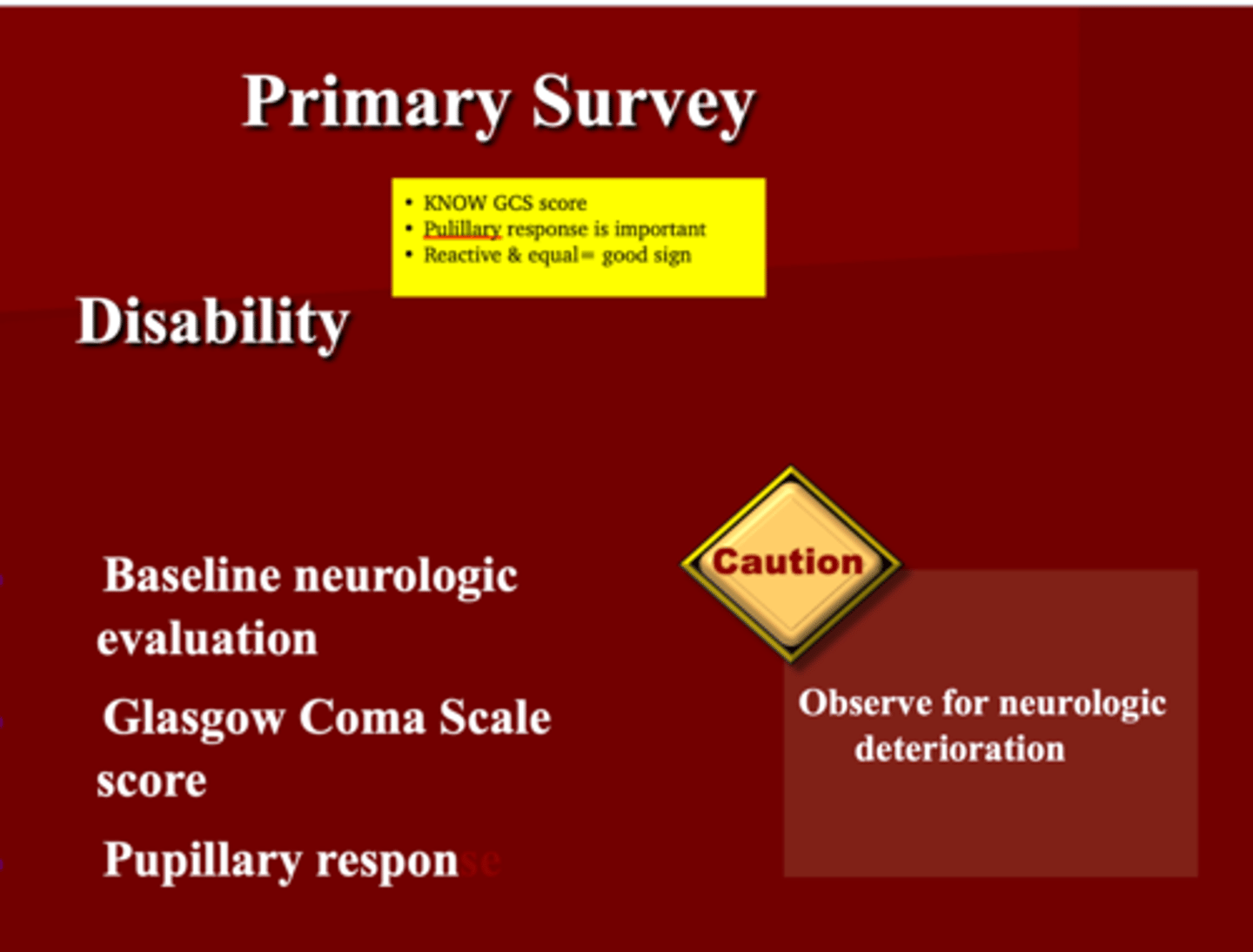
How do you asses disability during the primary survey ?
1. Baseline neurological evaluation
2. Glasgow Coma Scale score (GCS)**
3. Pupillary response

You must be cautious and observe for _____ _____
neurological deterioration
What consists of the Mini Neuro examination ?
AVPU
1. Alert
2. Response to VOCAL stimuli
3. Painful stimuli
4. Unresponsive
*detailed Glasgow Coma Scale

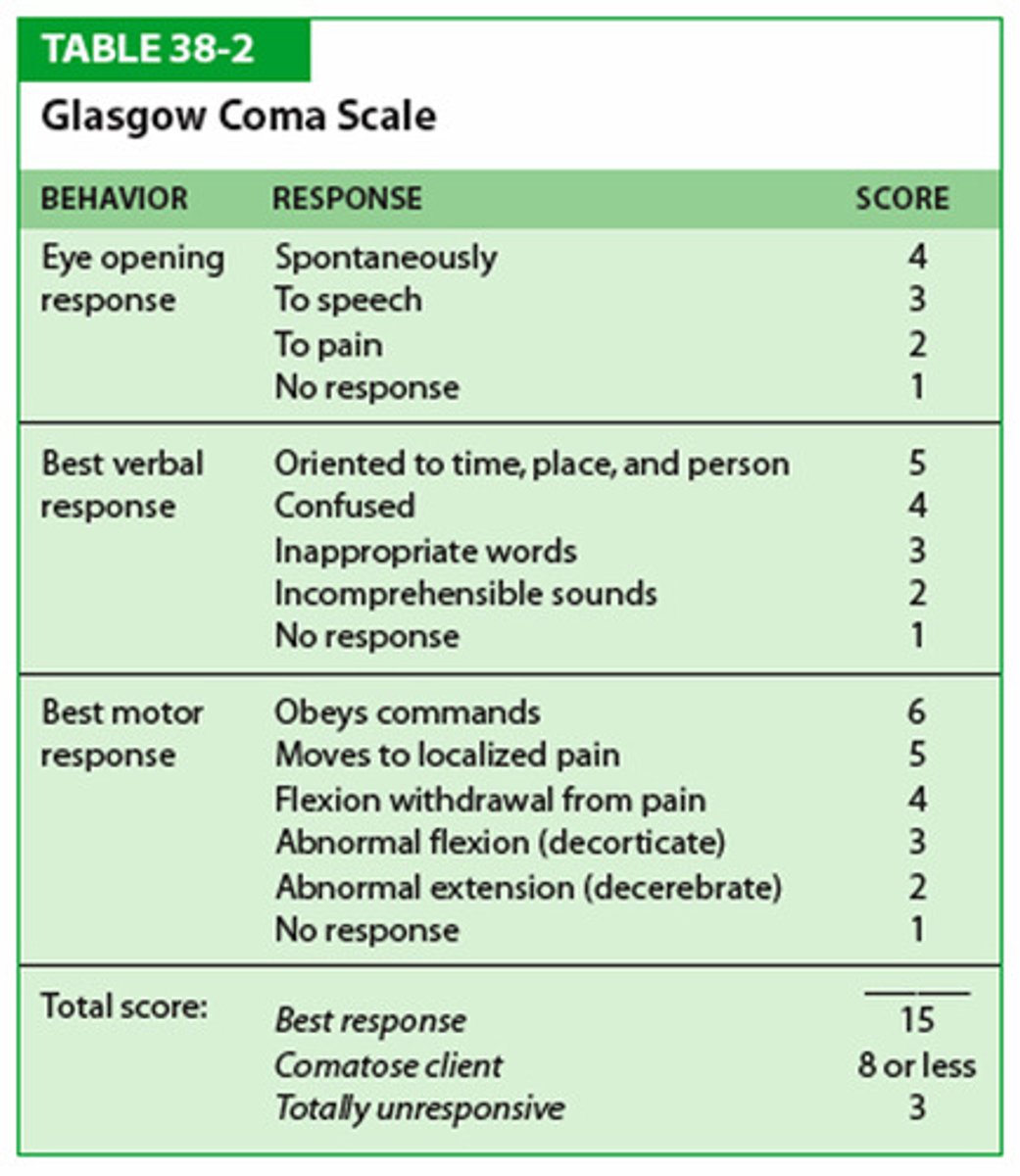
A scoring system used to describe the level of consciousness in a person following a traumatic brain injury
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
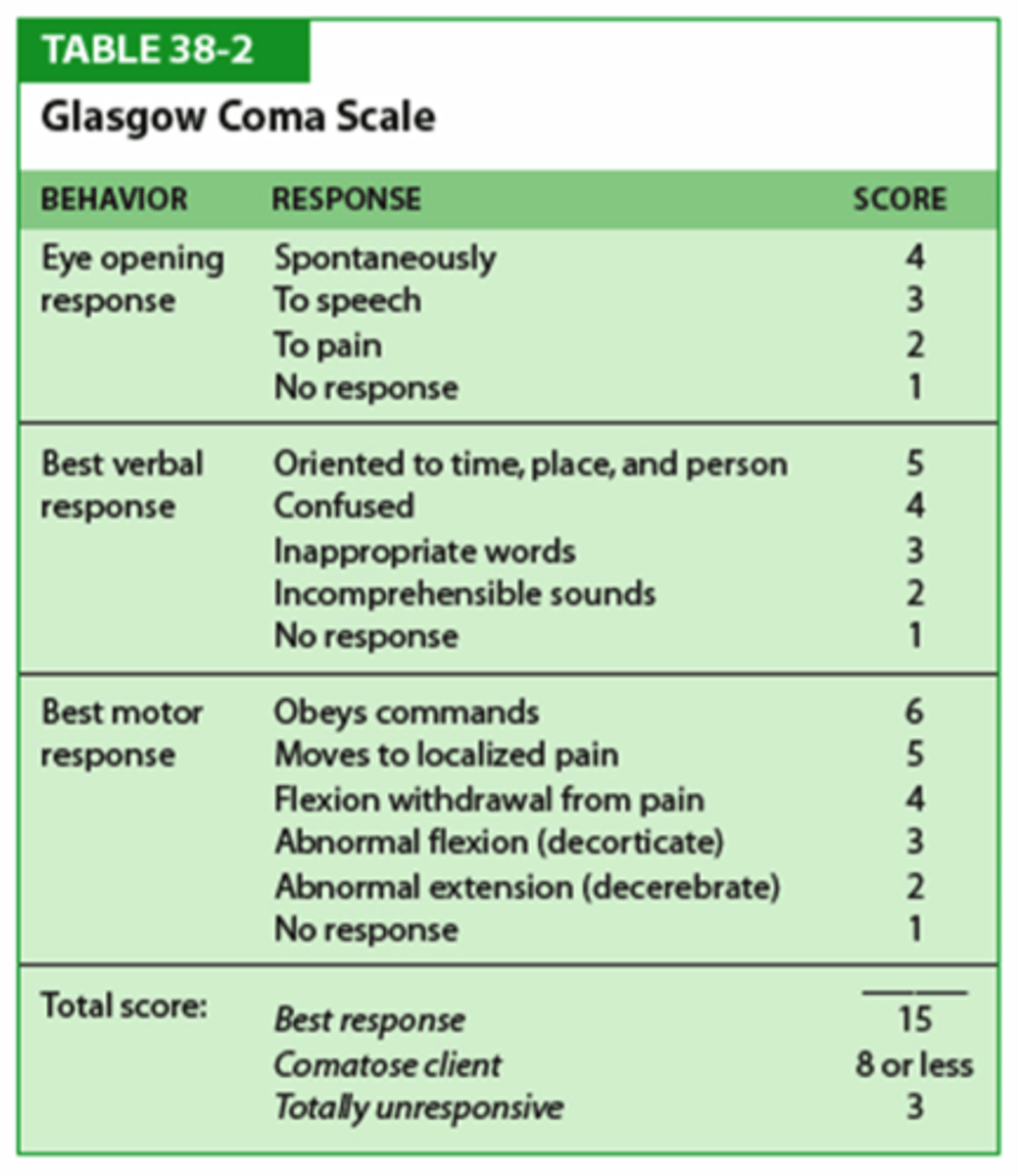
What is the GCS for Eye opening response? (KNOW)
-Spontaneously=4
-Verbal command=3
-To pain=2
- No response=1
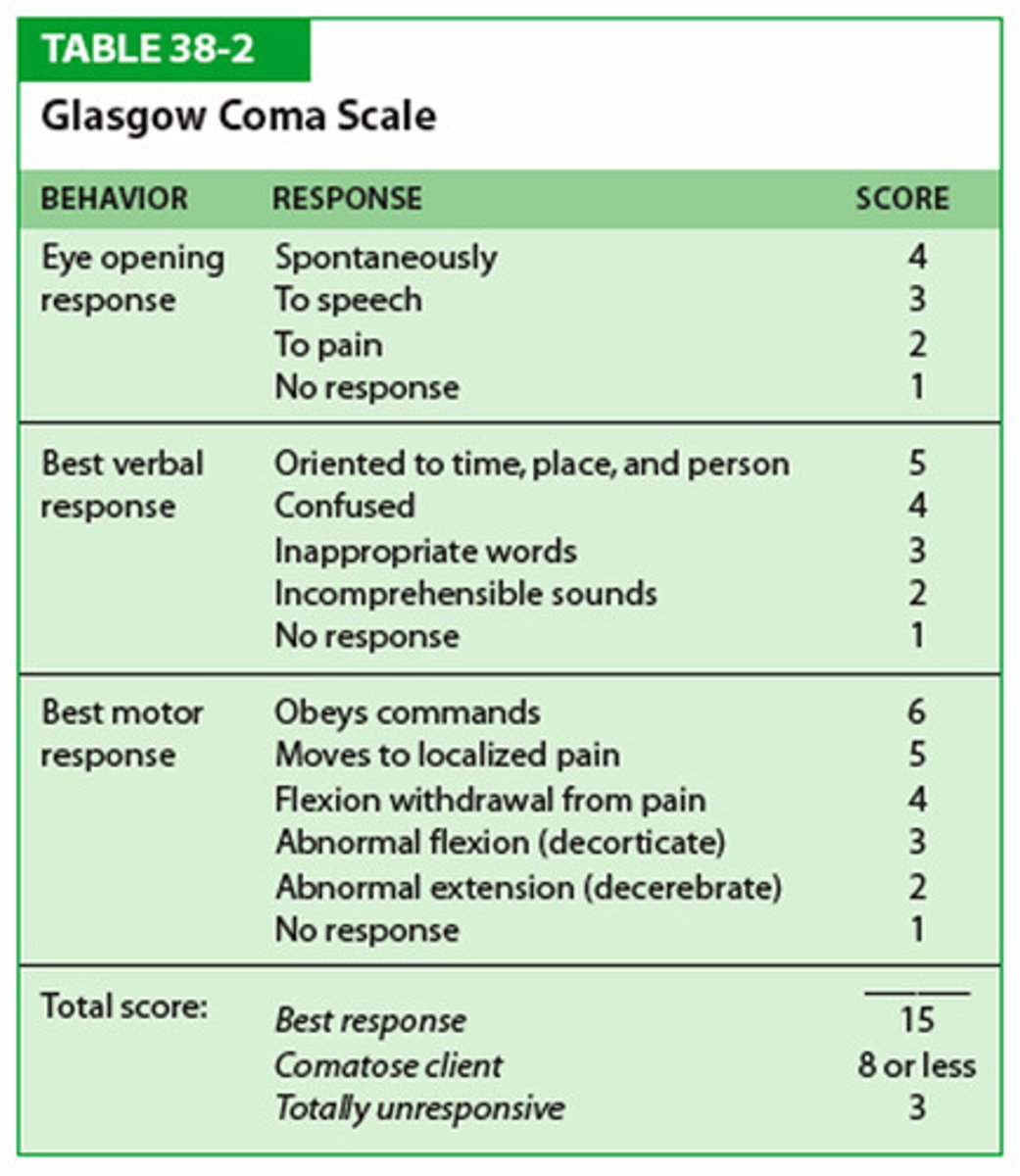
What is the GCS for Verbal Response ? (KNOW)
- Oriented & converses= 5
- Disoriented & converses=4
- Inappropriate words= 3
- Incomprehensible words= 2
- No response= 1
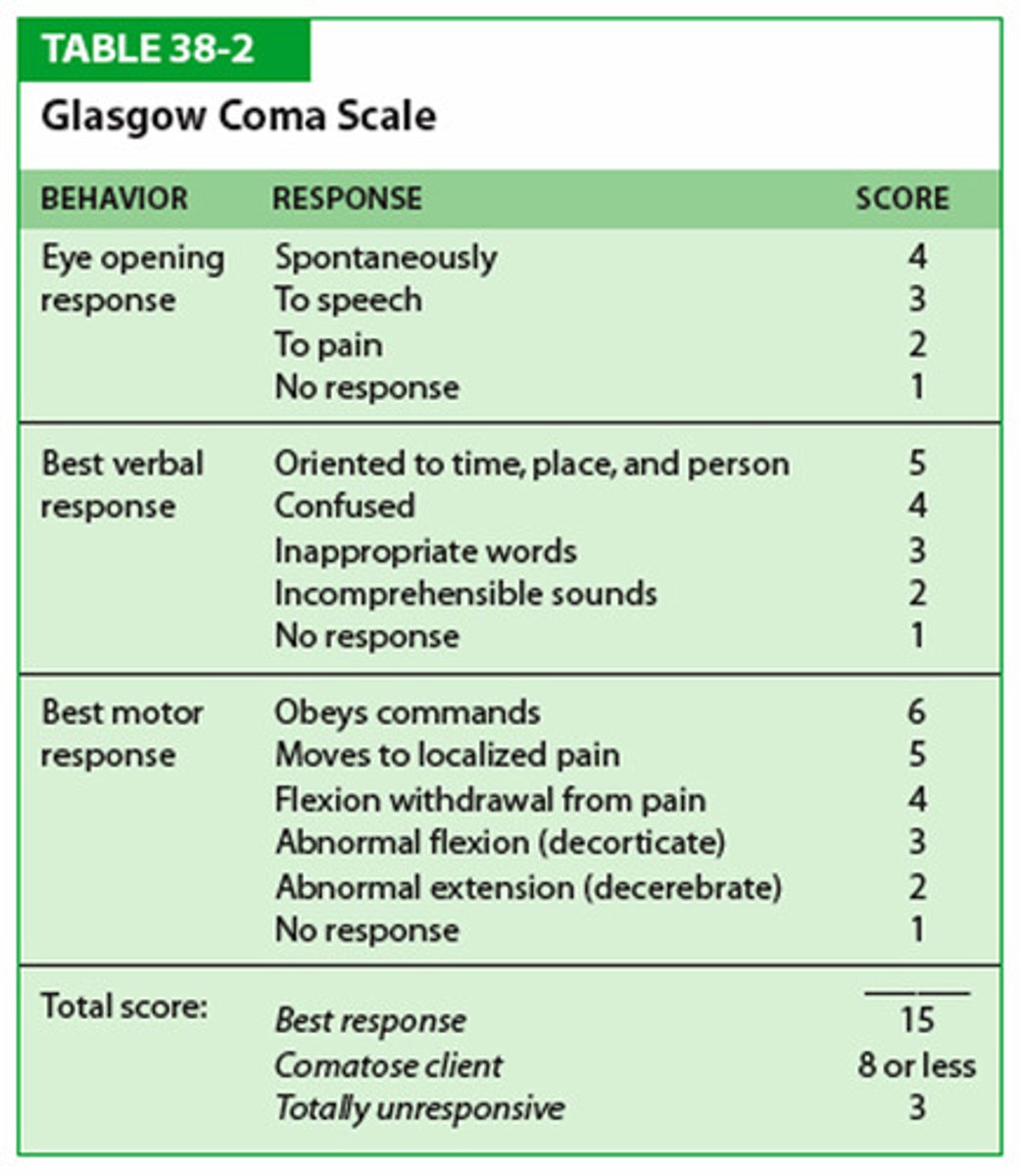
What is the GCS for Motor Response ? (KNOW)
- Obeys verbal commands= 6
- Moves to localized Pain= 5
- Flexion-withdrawal from pain= 4
- Abnormal Flexion= 3
- Abnormal Extension= 2
- No response= 1
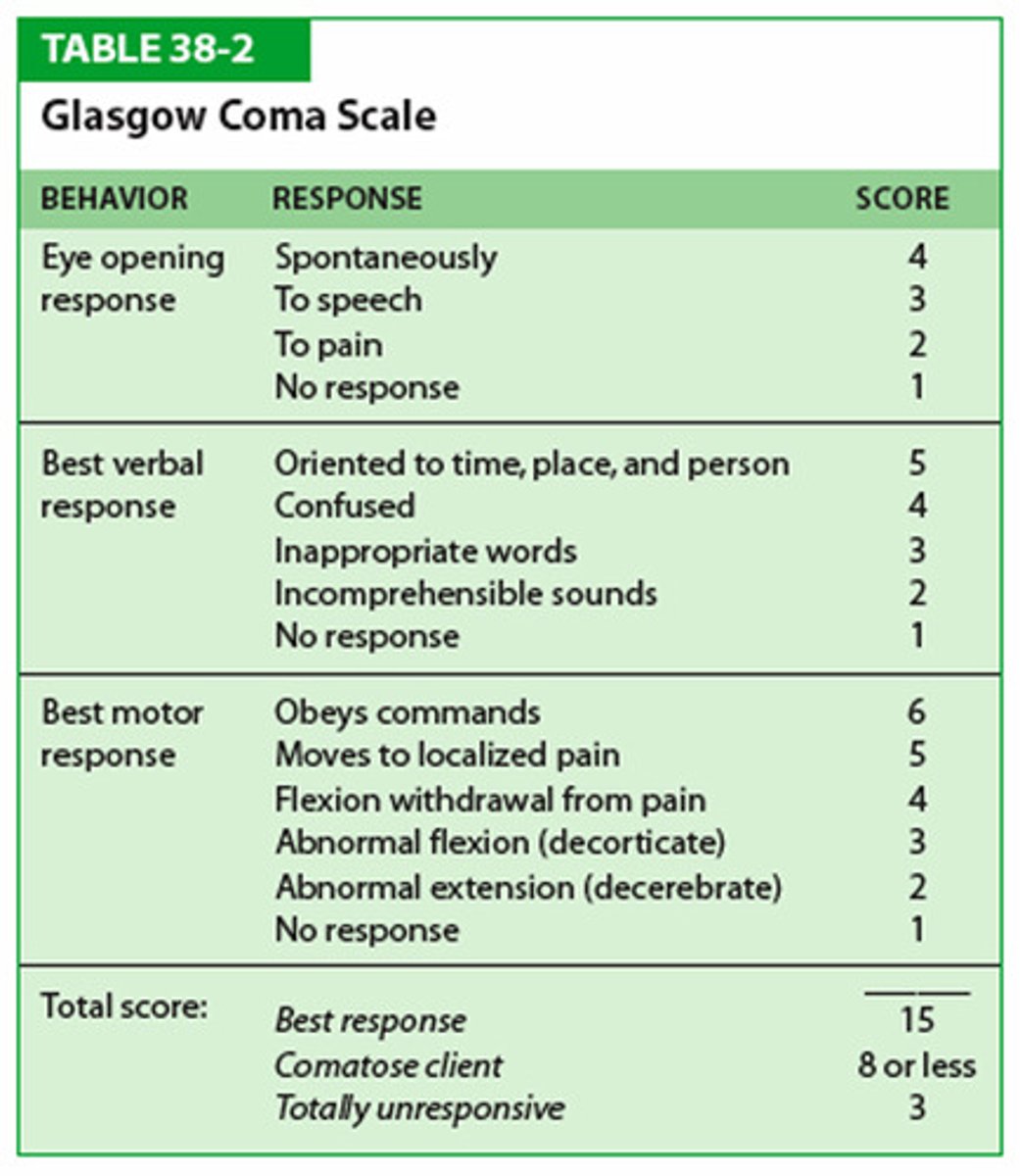
Interpret the score of the GCS.
A. 15-13
B. 9-12
C. 8 or less
A. Minor injury
B. Moderate injury
C. Comatose & severe injury (residual permeant brain deficit)
How are you going to asses exposure and environment during the Primary survey?
1. Completely undress the patient
2. Prevent hypothermia by covering patient with warm blankets ASAP
3. Hook up monitory (EKG, BP, Pulse Ox)
4. Look for missed injuries
What steps are you going to do to resuscitation a trauma patient?
1. Protect & secure airway
2. Ventilate & Oxygenate
3. Stop the bleeding
4. Crystalloid (LR/NS)/blood resuscitation
5. Protect from hypothermia
(Crystalloid= not volume expanders just water with electrolytes)
(Blood= volume expander= losing it , replace it)

What are some adjunct to primary survey?
A. Vital signs, Pulse Ox, CO2
B. ECG & ABGs
C. Urine output
D. Urinary/Gastric catheters unless CI
E. All the above
E. All the above
Why is it important to place a foley in a trauma patient ?
Another way to assess BP because if you're not making any urine that indicates there's not much blood flow through the kidneys
(Normal= 30 cc/hour)
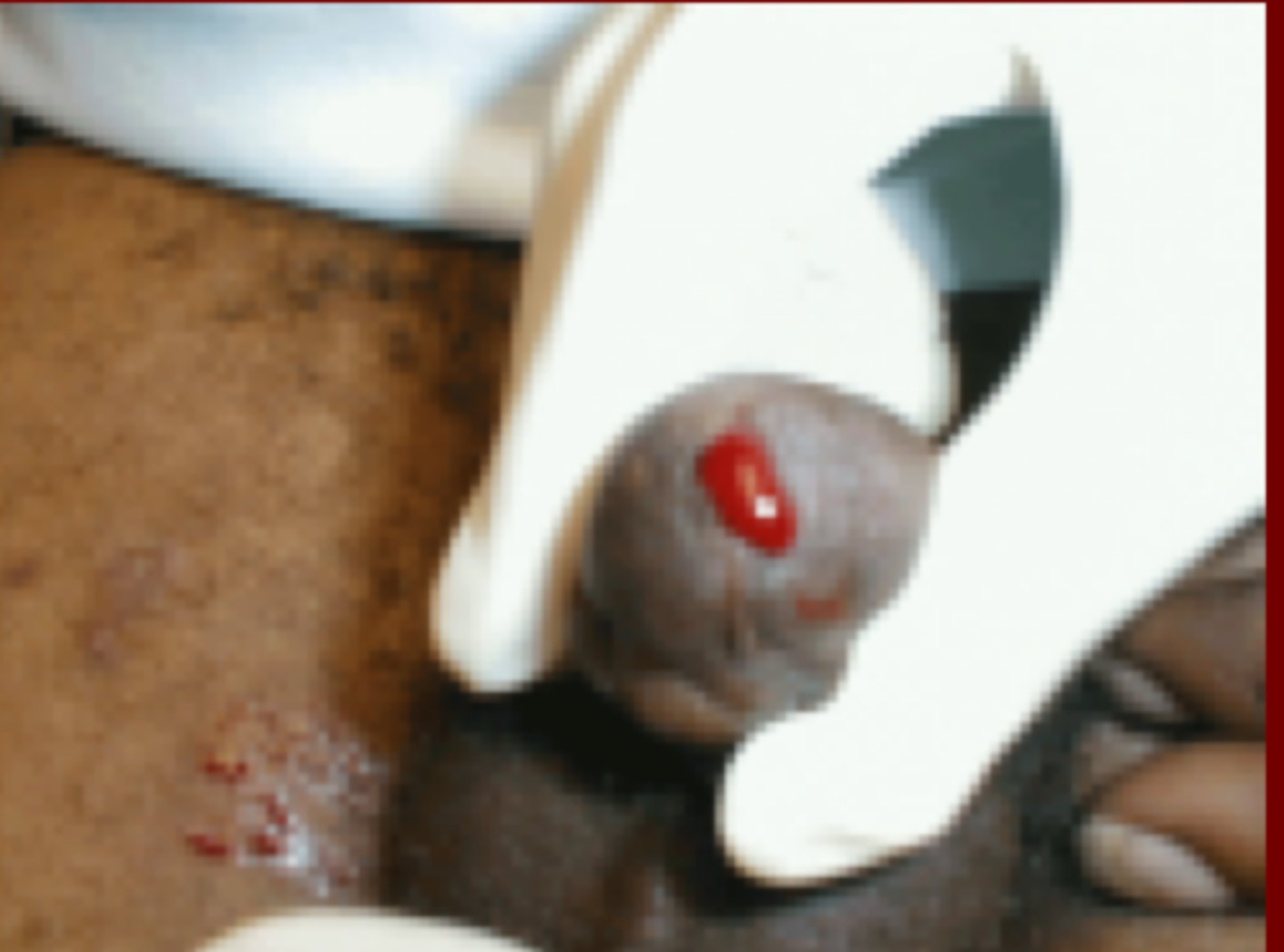
Patient presents with blood at the meatus, "high" riding prostate with a hematoma on the scrotum. What are you worried about ?
Urethral transection
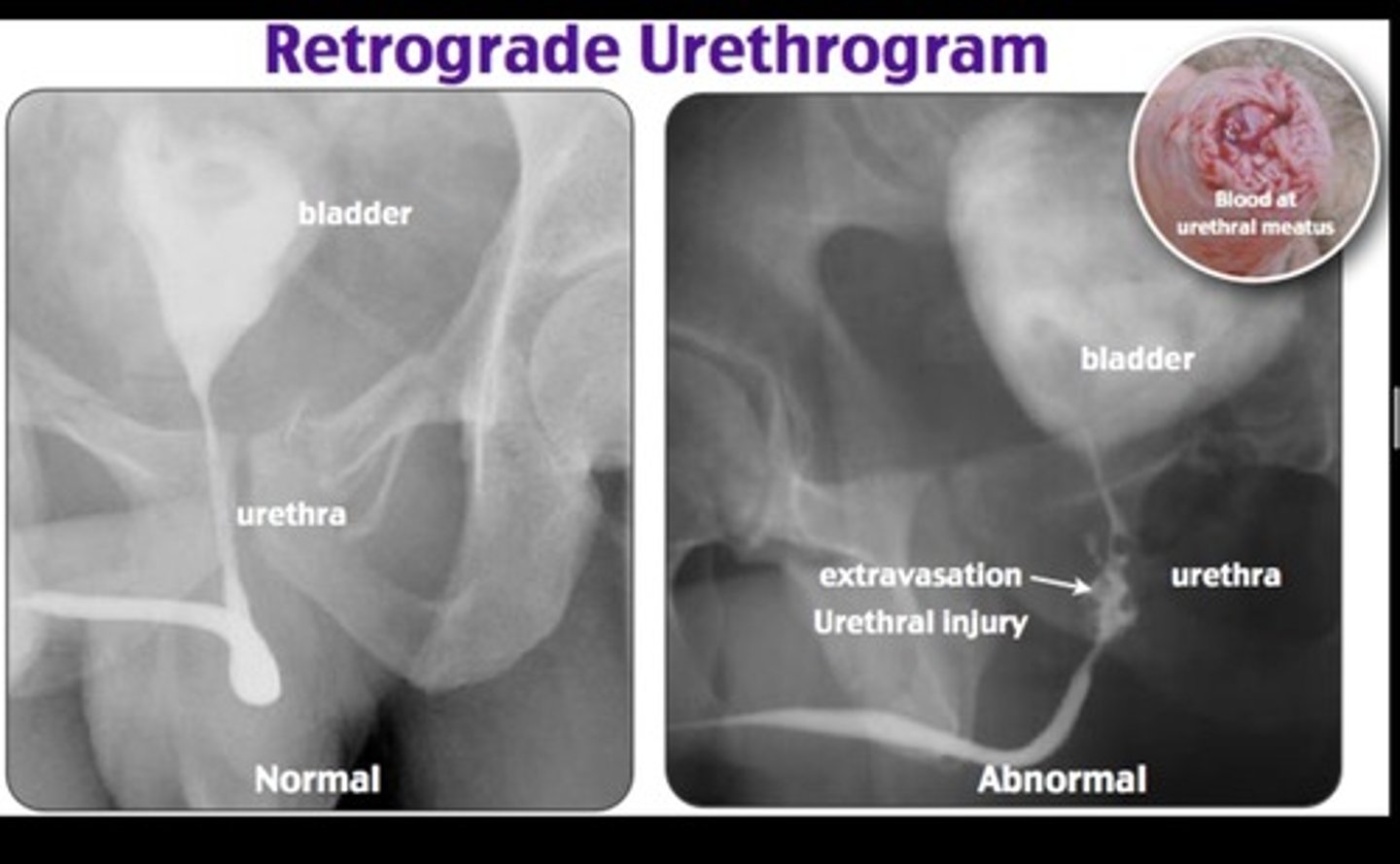
If you are suspicious of a pelvic fracture what should you order?
retrograde urethrogram
If you are a BIOLOGICAL female, the last he has checked they DON'T have a ______
prostate
(HE SAID HAVE TO KNOW THIS lol)
Secondary Survey consists of the inspection of ____ ,____ and _____
1. Perineum
2. Rectum
3. Vagina

What are the pitfalls to secondary survey ?
1. Urethral Injury
2. Pregnancy

What are you asses the perineum for in a trauma pt?
1. Contusions
2. Lacerations
3. Hematomas
4. Urethral blood

What are you asses the Rectum for in a trauma pt?
1. Sphincter tone***
2. High riding prostate
3. Pelvic fracture
4. Rectal wall integrity
5. Blood

You want to asses the vagina for ___ and ___
Blood
Lacerations
What must be avoided if you suspect a urethral injury?
Placement of Foley*
What does a "trauma series" consist of and should be performed concurrently with early resuscitative efforts?
X-Ray of Chest, Pelvis, C-Spine
_______ & _____ are tools used for rapid detection of intra-abdominal bleeding & occurs early in resuscitative process
1. Diagnostic Lavage (DPL)
2. FAST (Focused ABD Sonogram in TRAUMA)

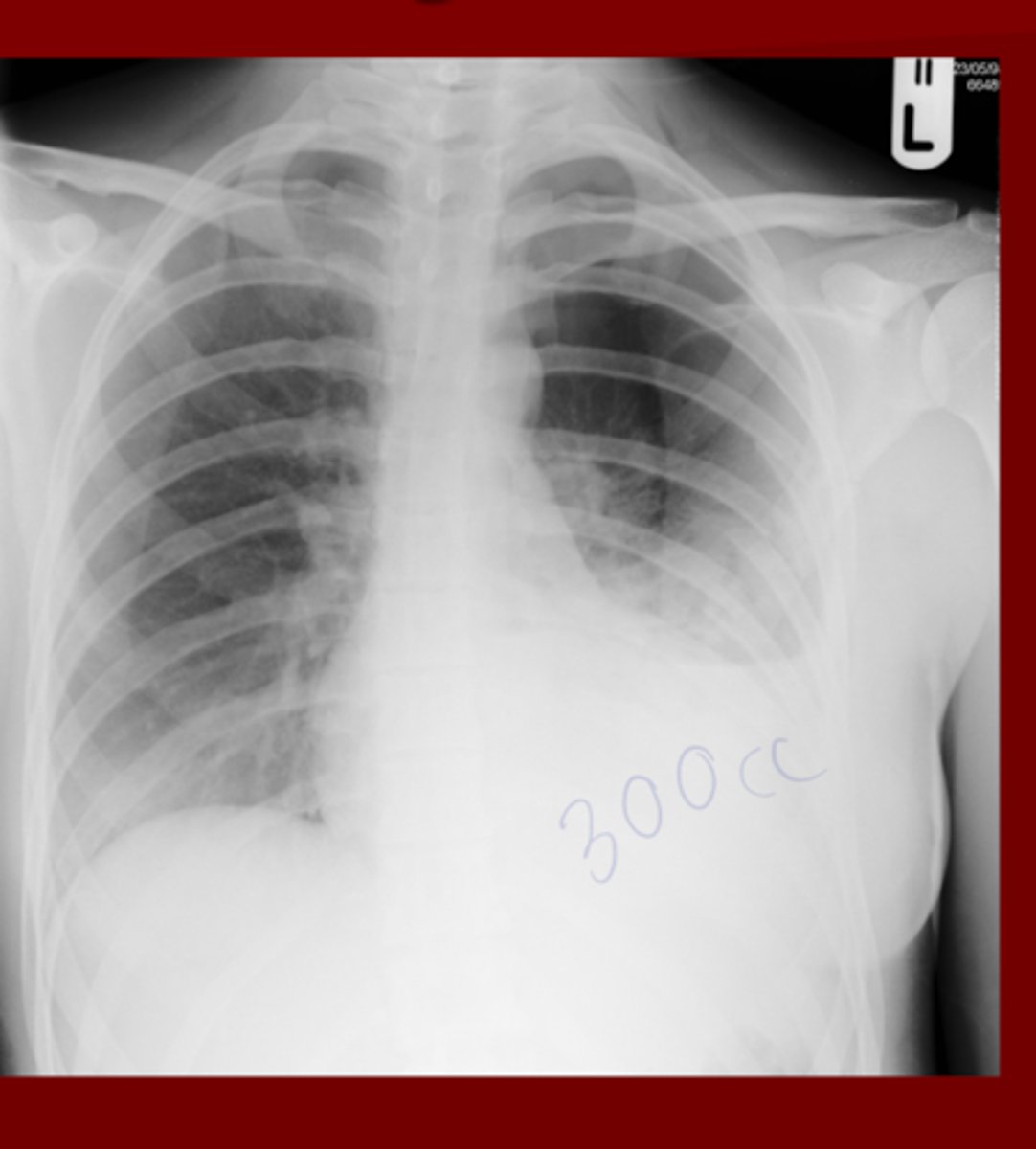
Left Lower Lobe Effusion
(Need Approx. 300cc to see)
What's wrong here?
EXAM Q: The definition of shock is based on clinical recognition of the presence of inadequate _____ _____ & _______
inadequate tissue perfusion & oxygenation

What is the first step in the Initial management of shock?
Recognize it's presence

What are the two classifications to cause shock?
1. Hypovolemic
2. Non-hemorrhagic

Hypovolemic shock can be due to ______ or _____ loss
Blood or Fluid loss

What are some causes for non-hemorrhagic shock?
1. Tension Pneumothorax
2. Cardiac Tamponade
3. Cardiogenic
4. Neurogenic
5. Septic

This type of shock is due to myocardial dysfunction such as a cardiac injury, Cardiac tamponade, MI or Air embolus
Cardiogenic Shock

This causes an impaired venous return and collapsed lung that can cause shock
Tension pneumothorax
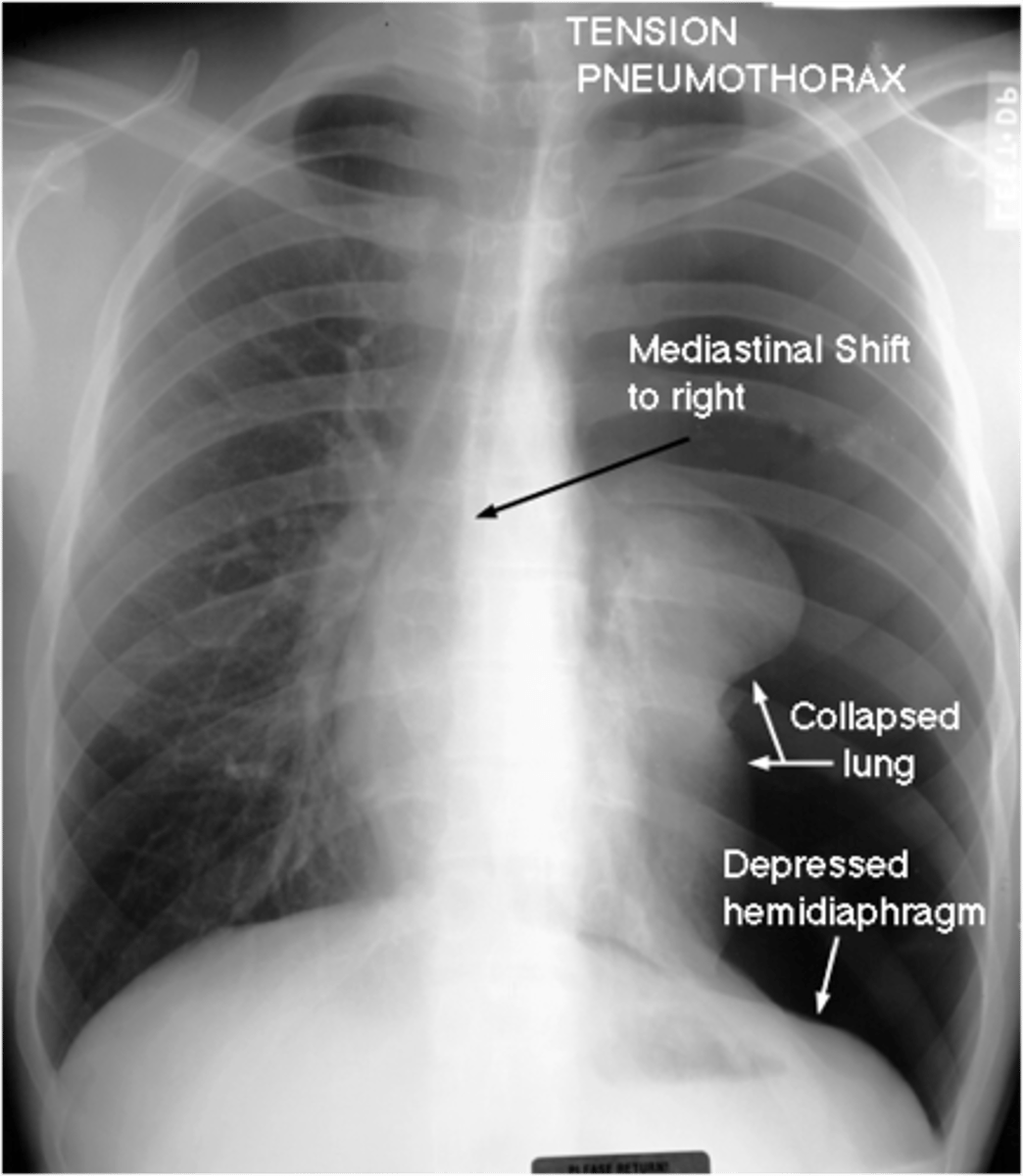
A life-threatening collection of air within the pleural space; the volume and pressure have both collasped the involved lung and caused a shift of the mediastinal structures to the opposite side.
Tension pneumothorax
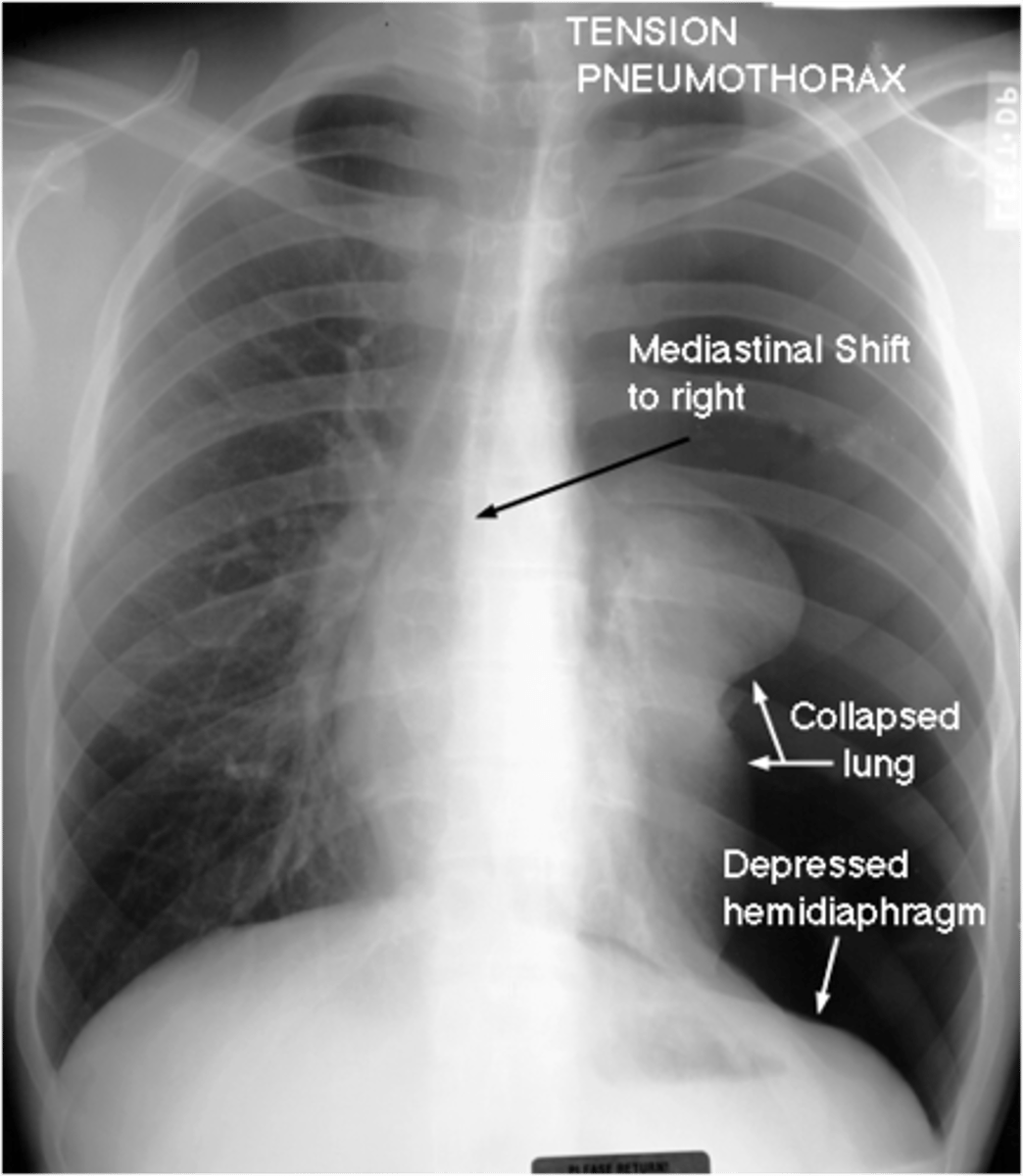
This type of shock causes a loss of sympathetic tone and innervation to the heart
Neurogenic shock
This type of shock causes a circulatory collapse 2/2 to infection
Septic shock
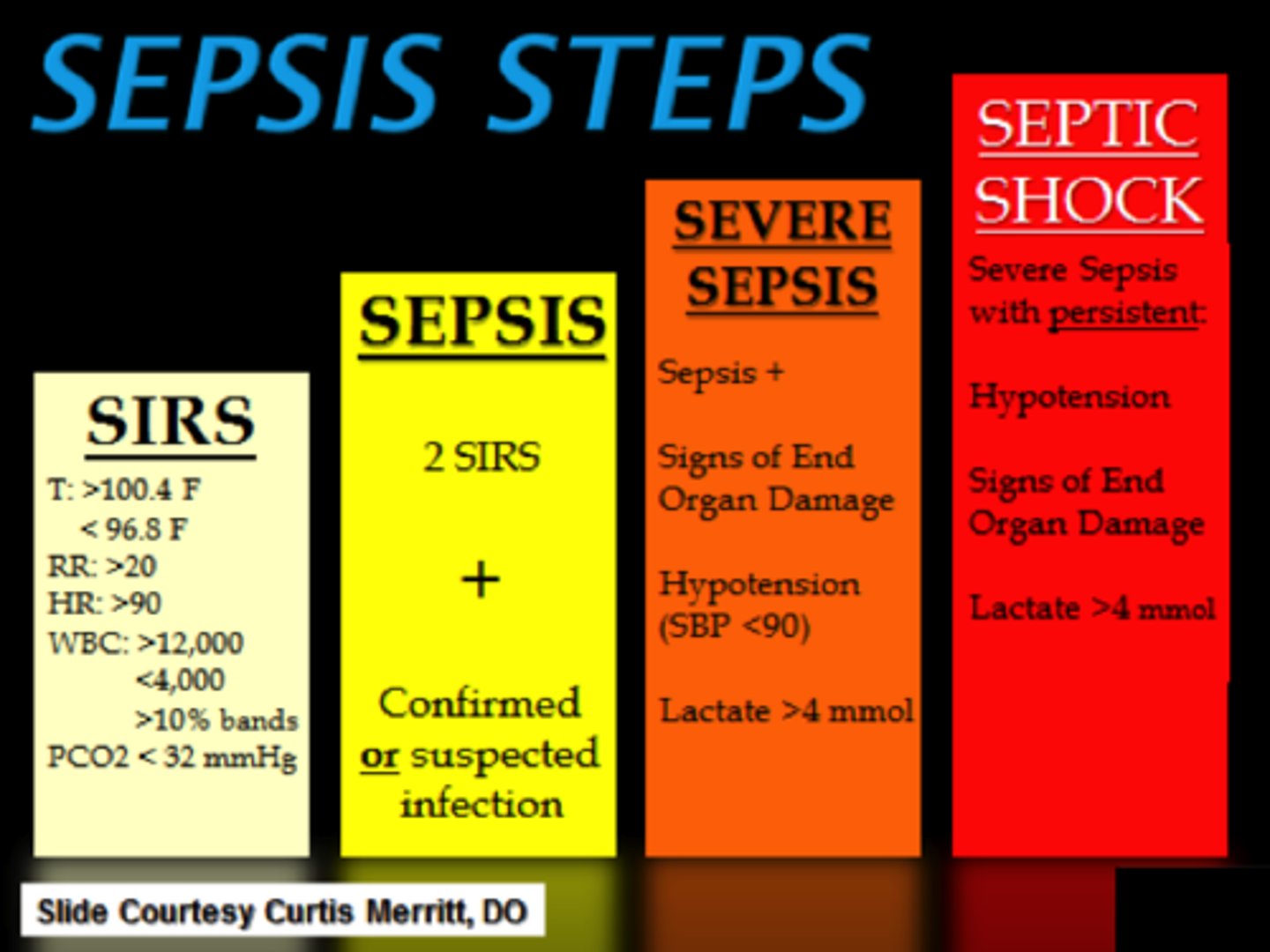
Class 1 Hemorrhage Shock
1. _______ blood volume loss
2. Slightly _______
3. Vital signs: BP ______ , HR _______ , RR ______ , UO _____
4. Administer: _______
1. 750 mL (15%)
2. Anxious
3. BP normal
-HR <100
- RR 14-20
-UO 30 mL/hr
4. Crystalloid

Class 2 Hemorrhage Shock
1. ________ mL blood volume loss
2. How does the patient look?
3. VS: BP_____ , HR ______, _______ pulse pressure, RR _____, UO _______
4. Administer: ______
1. 750-1500 (15-30%)
2. Anxious
3. BP= Normal
- HR > 100
- decreased pulse pressure
- RR= 20-30
- UO= 20-30 mL/hr
4. Crystalloid
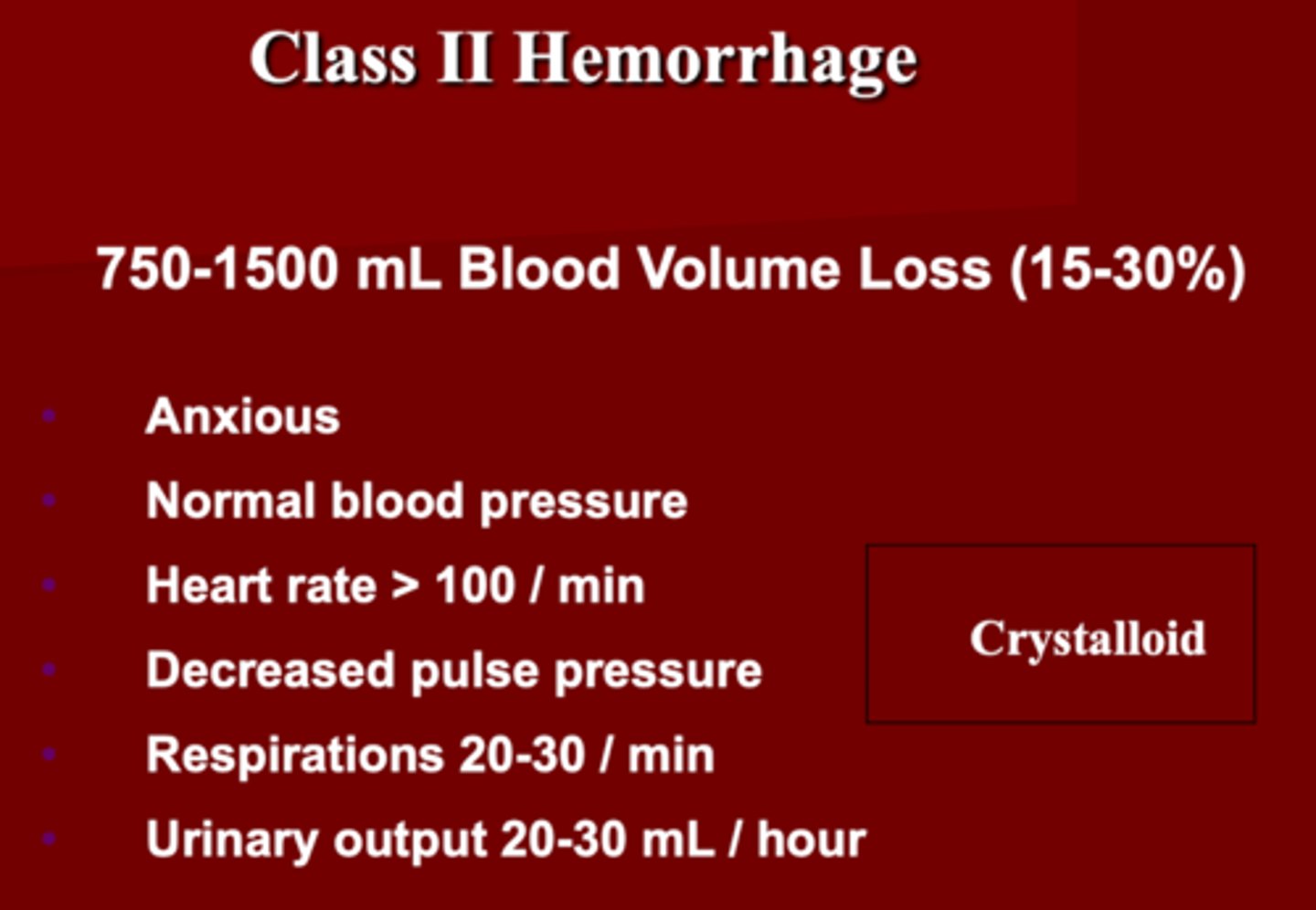
Class 3 Hemorrhage Shock
1. ________ mL blood volume loss (30-40%)
2. How does the patient present?
3. VS: BP _______, HR _____ , ______ pulse pressure, RR ______, UO ______
4. Administer:
1. 1500-2000 (30-40%)
2. Confused, anxious
3. BP decreased
- HR > 120
- decreased pulse pressure
- RR 30-40
- UO 5-15 mL/hr
4. Crystalloid
- blood components
- definitive bleeding control
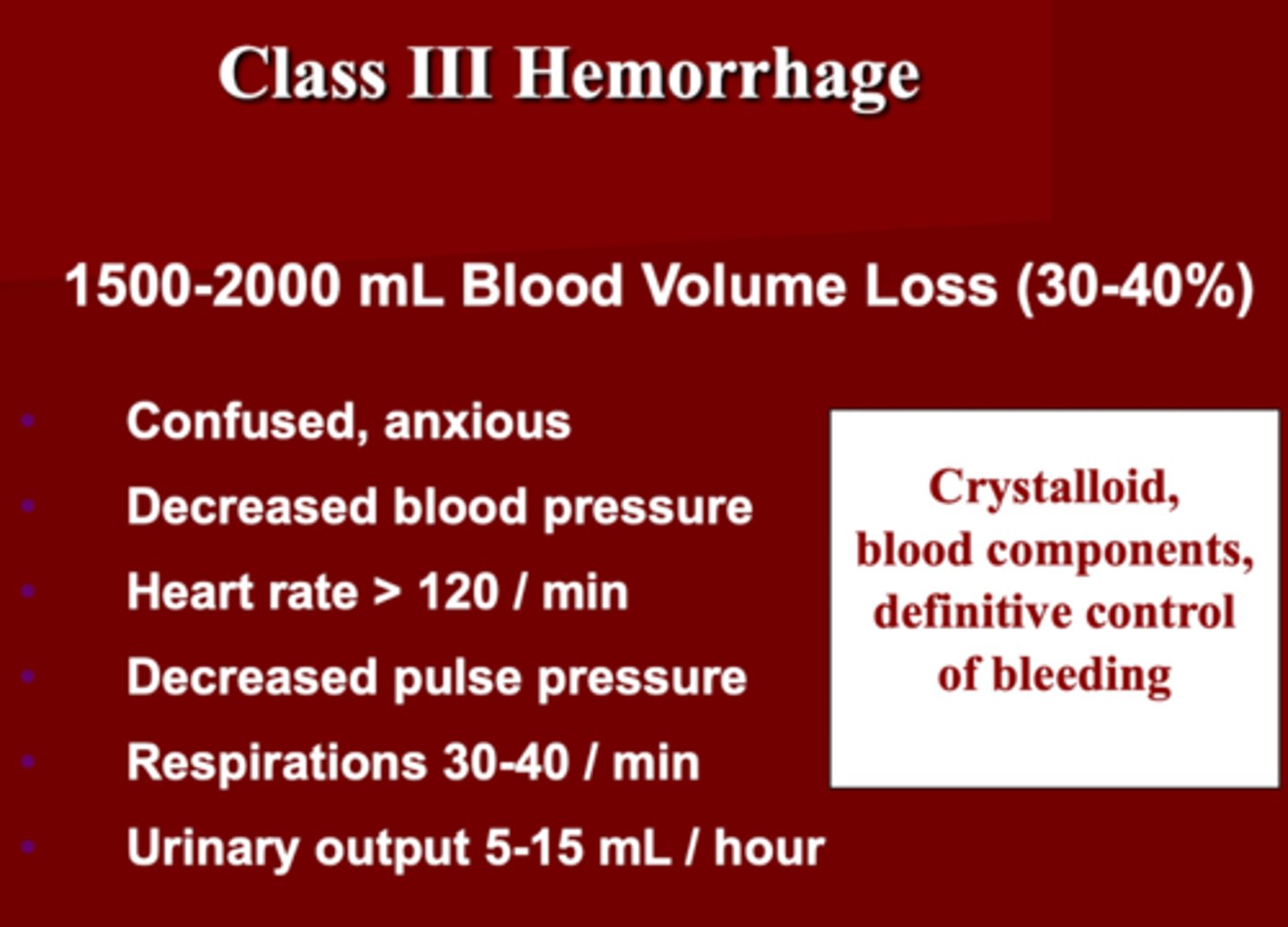
Class 4 Hemorrhage Shock
1. ______ blood volume loss
2. How does the patient present?
3. VS: BP _______, HR_____ , ______ pulse pressure, RR _____, UO _____
4. Administer: Blood components, definitive bleeding control
1. > 2000 mL (> 40%)
2. Confused, lethargic
3. hypotensive
- HR > 140
- decreased pulse pressure
- RR > 35
- UO negligible
4. Blood components
- definitive bleeding control
How do you manage shock?
STOP THE BLEEDING
1. Hemostatic Resuscitation (fluid challenge based on
2. Direct pressure/tourniquet
3. Angio-embolization ***
4. Reduce pelvic volume
5. Hemostatic agents
6. Operation
7. Splint fractures

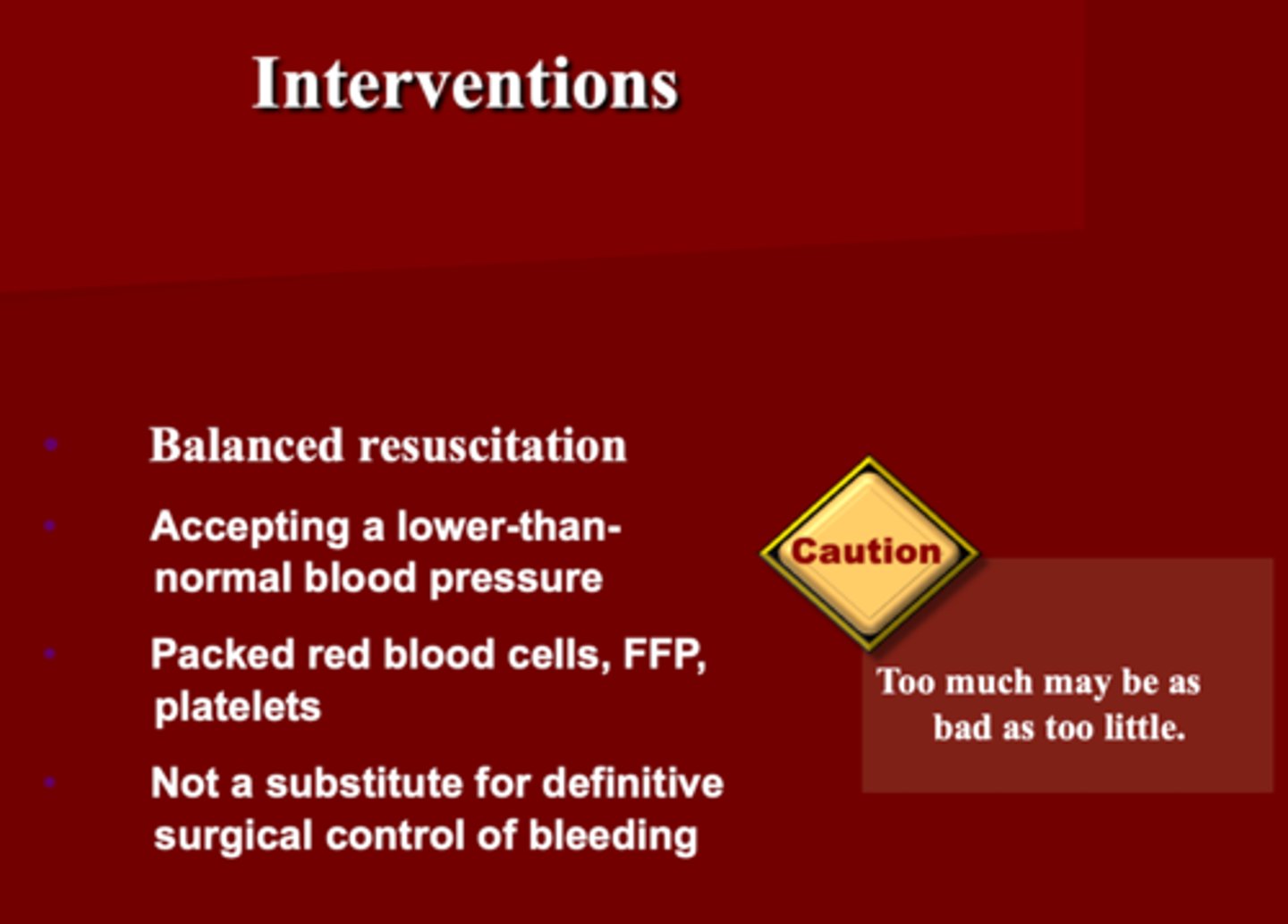
Interventions with Shock
1. Need a _____ resuscitation
2. You can accept a lower than normal _____
3. You want to give _____, ___ and ___
4. This is _____ a substitute for definitive surgical control of bleeding
5. What should you be cautious about?
1. Balance resuscitation
2. BP
3. Packed RBC, FFP and Platelet
4. NOT
5. Too much may be as bad as too little
Resuscitation for Shock
1. What should direct further resuscitative efforts?
2. What should be considered in pt's who fail to respond?
3. How should we fluid challenge the patient ?
4. What is the goal of resuscitation ?
1. Response to initial fluid bolus
2. Early blood transfusion & surgical intervention
3. Healthy= push 200cc & evaluate Cardiac output
4. Perfuse Brain & vital organs

True/false
For fluid resuscitation in a trauma patient, we need to fluid challenge the patient based on their comorbid status.
True
The complete history & physical examination in a trauma patient is known
Secondary Survey
This begins once primary survey is complete and resuscitative efforts are well underway. It is a head-to-toe evaluation of the patient including detailed history with frequent reassessment is key. Neurological exams, procedures, radiological and examination, and lab testing take place at this time if not already accomplished
Secondary Survey

What are the components of the secondary survey?
1. History (MOA)
2. Physical Exam: Head to toe
3. Complete Neurological Exam (not Mini)
4. Special Diagnostic Test
5. Reevaluation

True/False
Secondary survey also consists of history & AMPLE
1. Allergies
2. Medications
3. Past illnesses/pregnancy
4. Last meal
5. Events/environment/ Mechanism
True

True/False
ALL neck injuries are potentially life-threatening**** (above the clavicle)
True

The Neck is divided into ____ and _____
Triangles (Anterior & Posterior)
Zones (1,2,3)
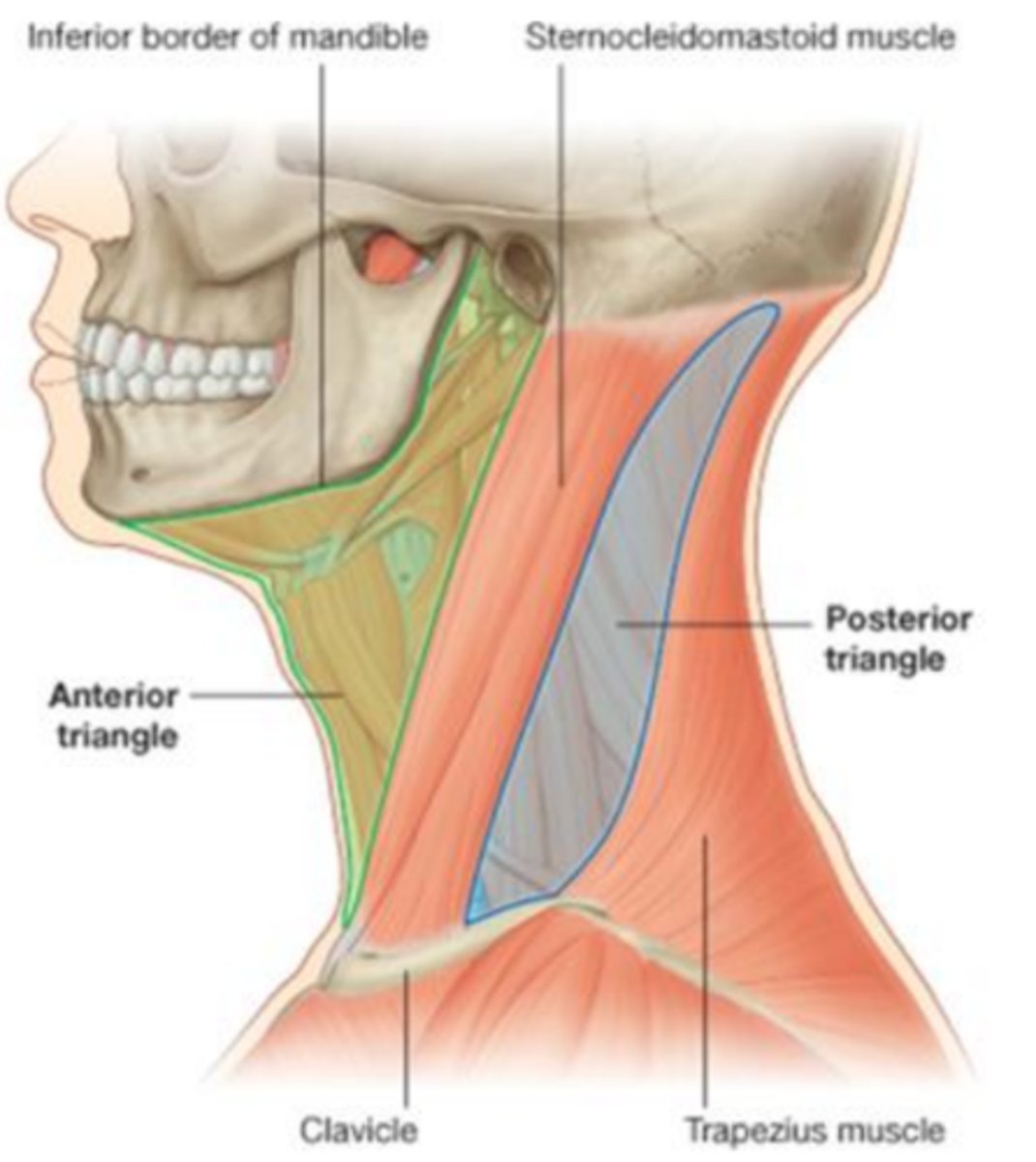
What are the borders of the Anterior Triangle of the neck?
1. Midline
2. Anterior border of SCM
3. Mandible
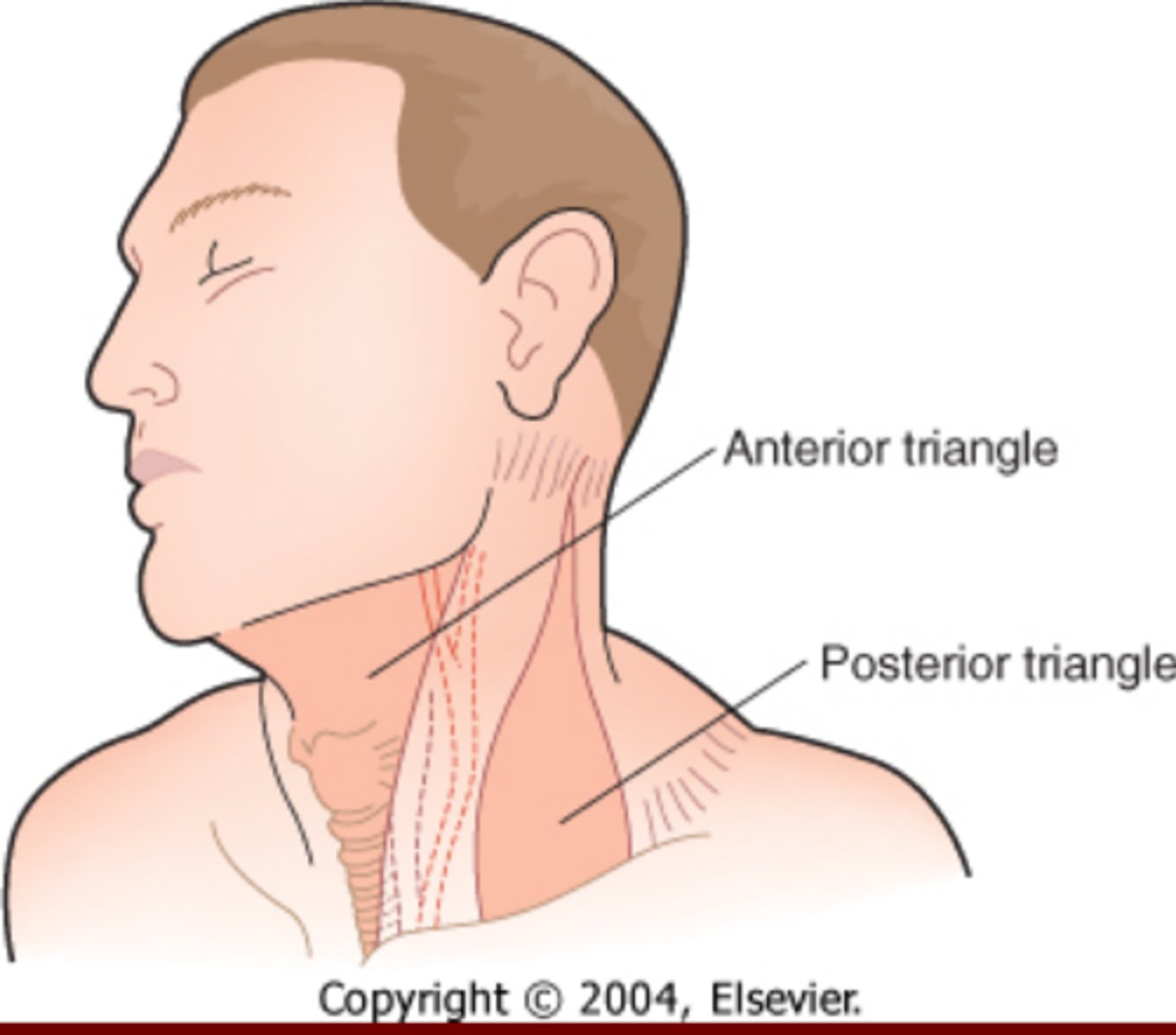
What are the borders of the Posterior Triangles of the Neck?
1. Trapezius
2. Post border SCM
3. Clavicle
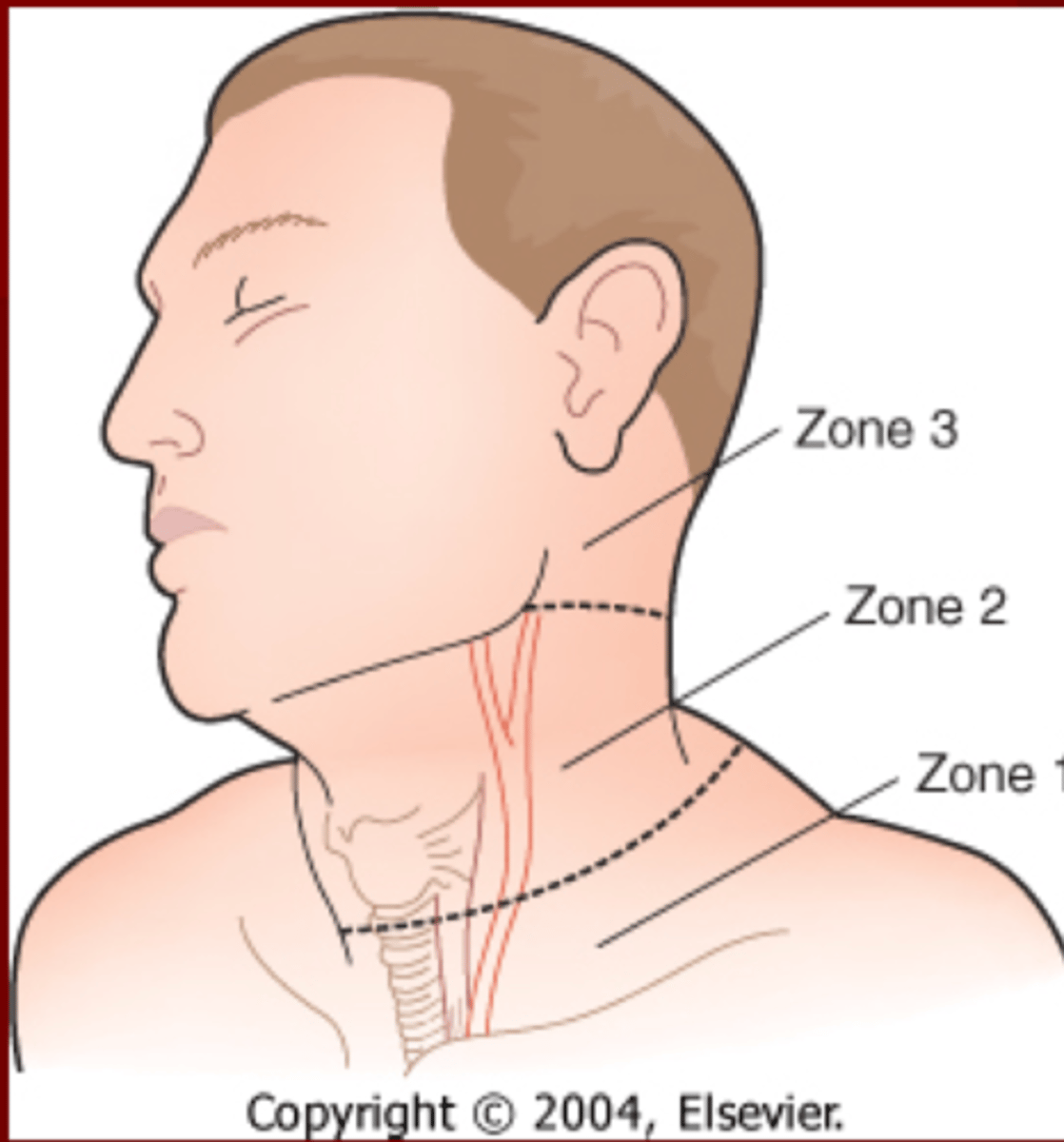
Anatomical Neck Zones
Zone 1 is from _____ to _____
Zone 2 is from ____ to ____
Zone 3 is from _____ to ____
Zone 1= Sternal Notch to Cricoid
Zone 2= Cricoid to Angle of Jaw
Zone 3= Angle of Jaw to Base Skull
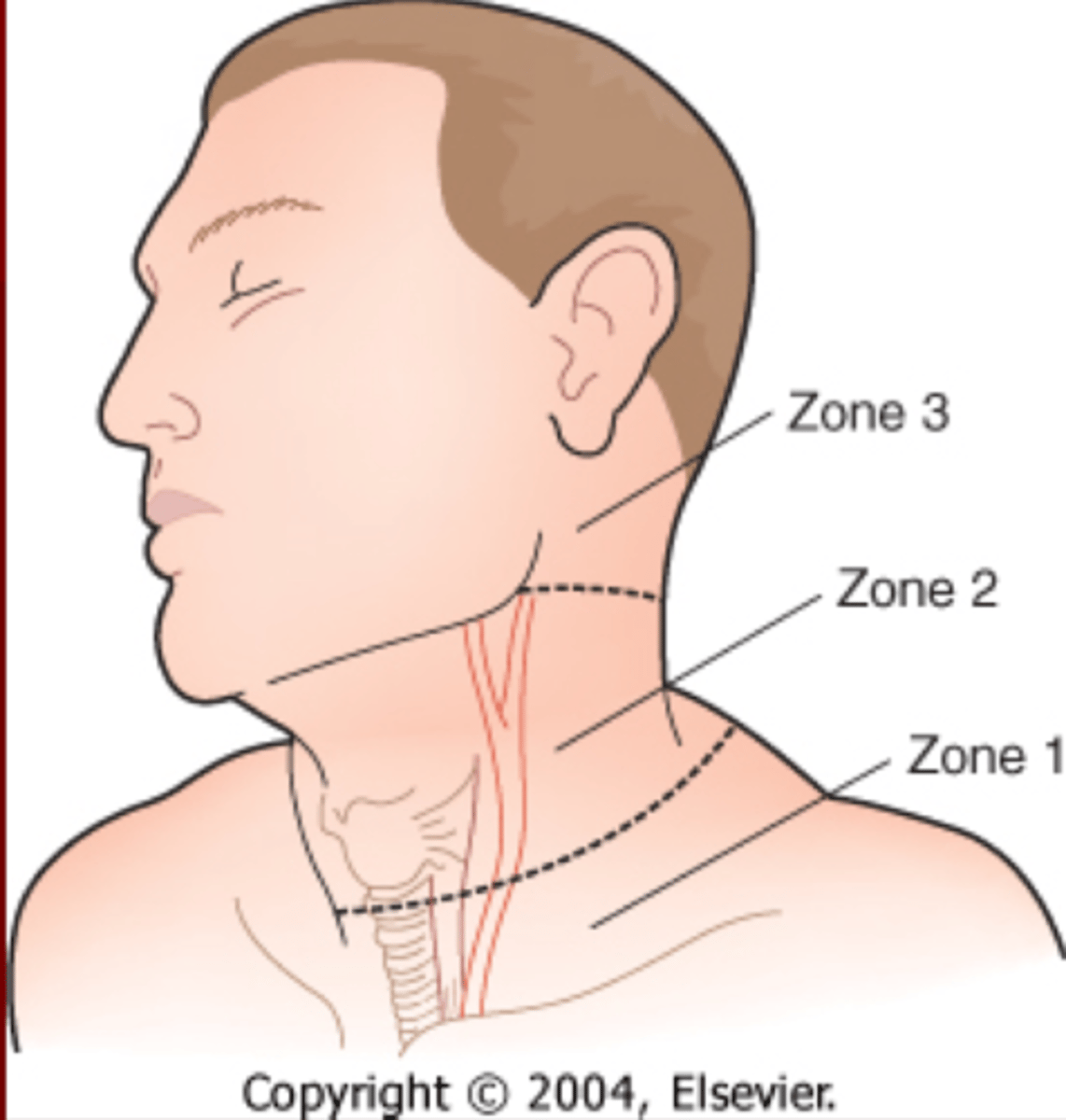
What two zones of the neck are very difficult to assess and why?
1. Zone 1 because the trachea is exposed and esophagus is behind the trachea
2. Zone 3 because of the neuromuscular bundles & arteries are located
(complicated)
These injuries are very common & life threatening. It can lead to exsanguination, hematoma formation with compromise of airway & CVA's
Vascular injuries

Injury to the larynx & trachea including fracture of thyroid cartilage leading to compromise of the airway & a difficult intubation is considered a ______ injury
Non-vascular Injuries

Zone 2 is easy to asses but we are concerned about _____ injuries here. If the ____ muscle is exposed an _______ ______ needs to be done
1. Vascular injuries
2. Platysmal muscle
3. Exploratory Laparotomy
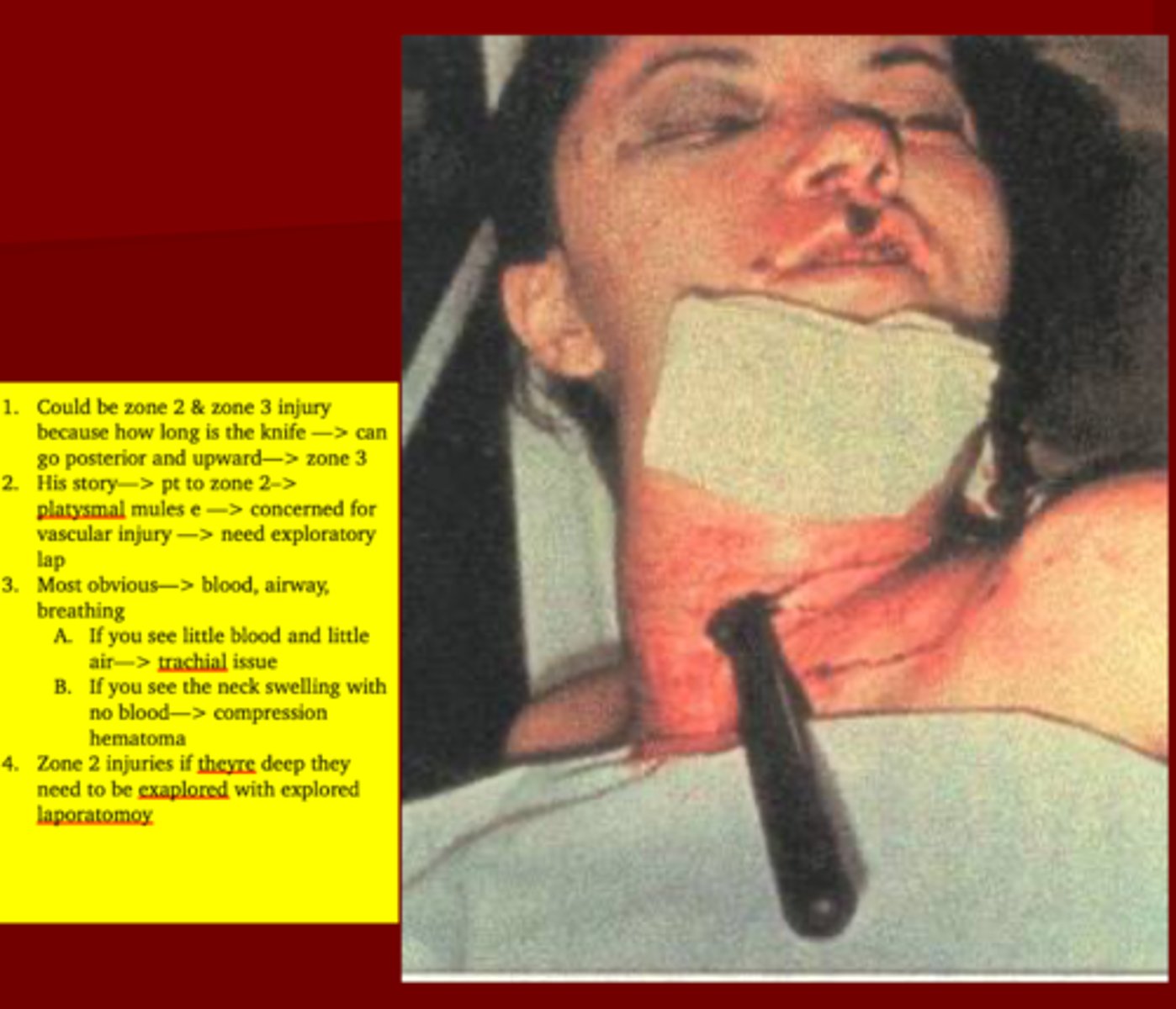
TX for Neck Injuries
1. Always remember your ______
2. Zone 2 with Instability or expanding hematoma need to ______
3. Zones 1 & 3 can be manage conservatively using ?
1. ABCs
2. OR for Exploration*** (just always take them in Zone 2 no matter what)
3. Angiography, bronchoscopy, EGD, barium studies, CT, OR
Spinal Trauma
1. May involve injury to _____, _____ or both
2. 50% injuries occur in the _____
3. _____ is critical ASAP
1. Spinal column or Cord
2. C-spine
3. Immobilization**

True/False
As long as spine is appropriately immobilized, evaluation for spinal injury may be deferred until patient is stabilized
True

This type of spinal cord injury demonstrates no preservation of neurologic function below the level of injury
Complete spinal cord injury
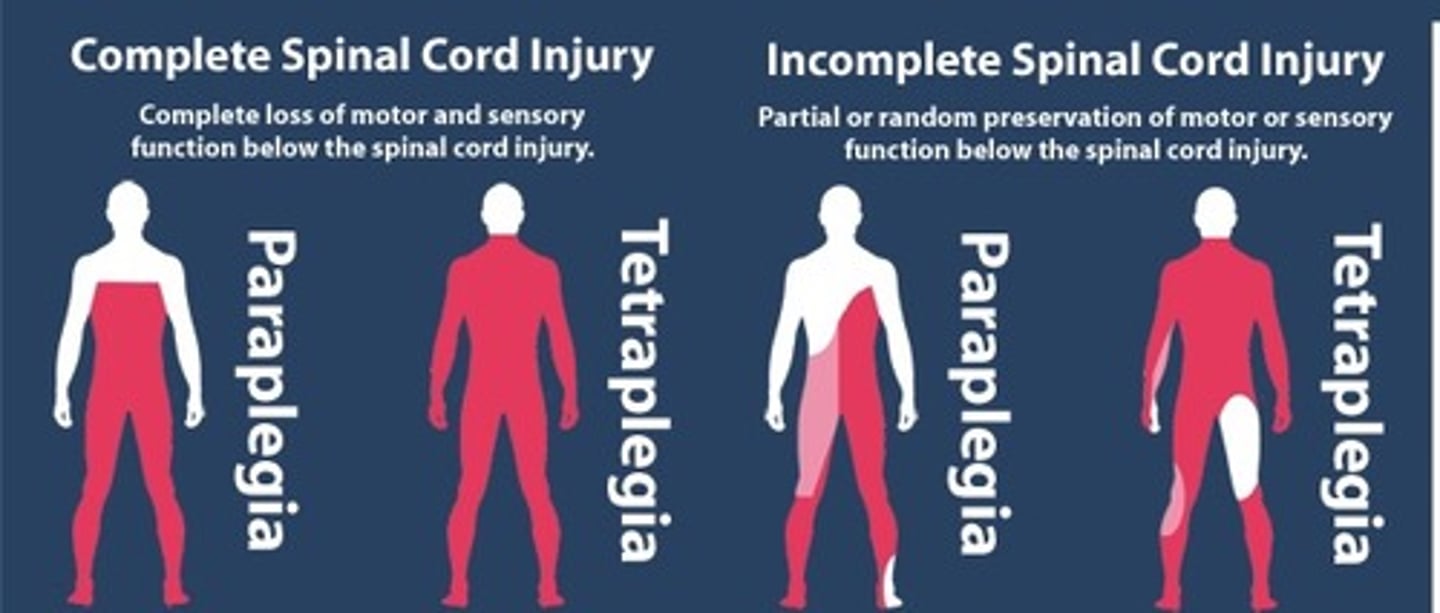
______ sparing refers to _______ sensation, _____ contraction, or voluntary toe ______. These are a signs of ________ spinal cord injury with a better prognosis
1. Sacral sparing
2. Perianal sensation
3. Sphincter contraction
4. Toe Flexion
5. Incomplete spinal cord injury

EXAM Q: Full or partial loss of bilateral pain and temperature sensation and paraplegia with preservation of posterior column function
Anterior Cord Syndrome
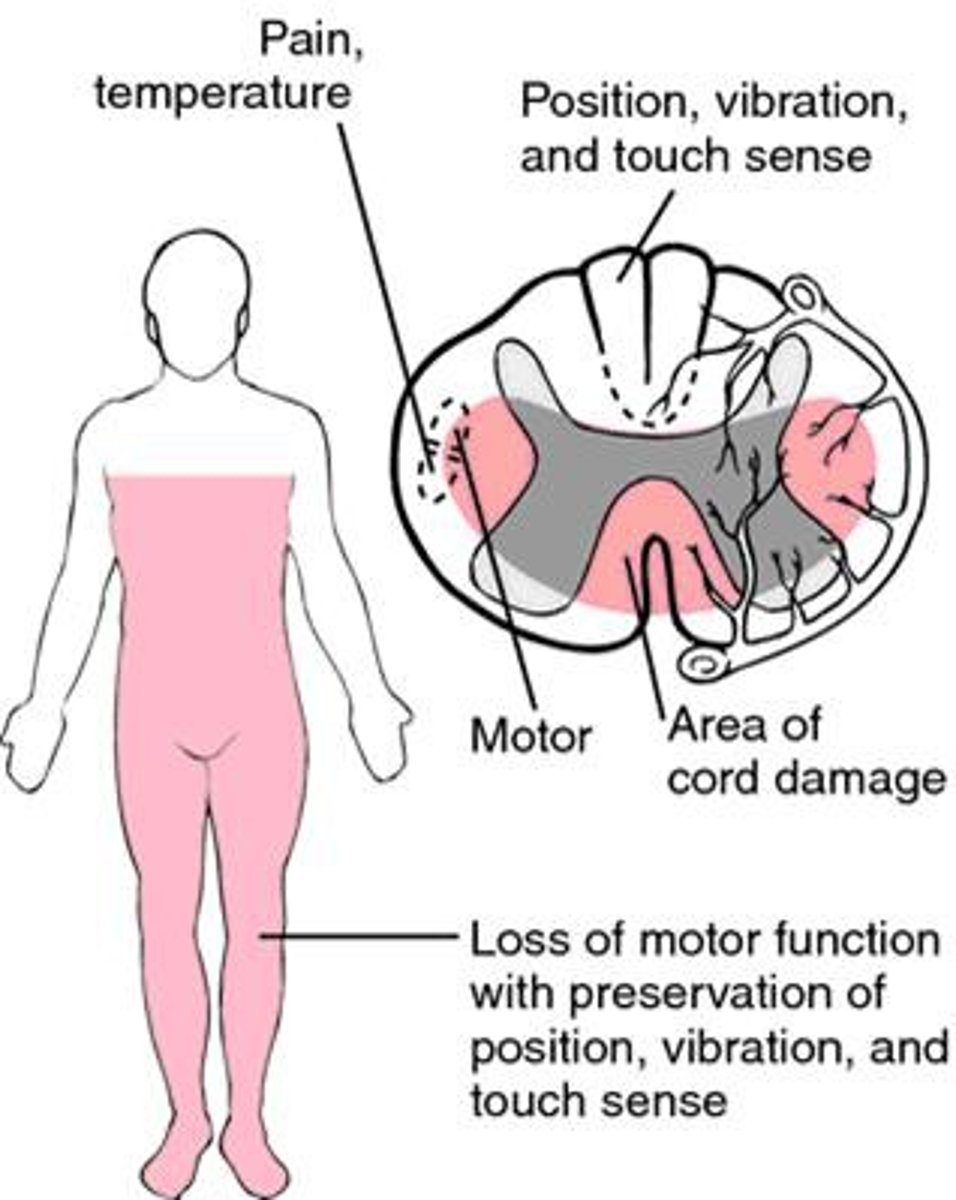
Anterior Cord Syndrome
1. Loss of ____, ___ and ____
2. Seen with ____ injuries
3. Carries a _____ prognosis
1. Loss of pain, temp & is paraplegia
2. Flexion injuries (Forward)
3. Poor Prognosis

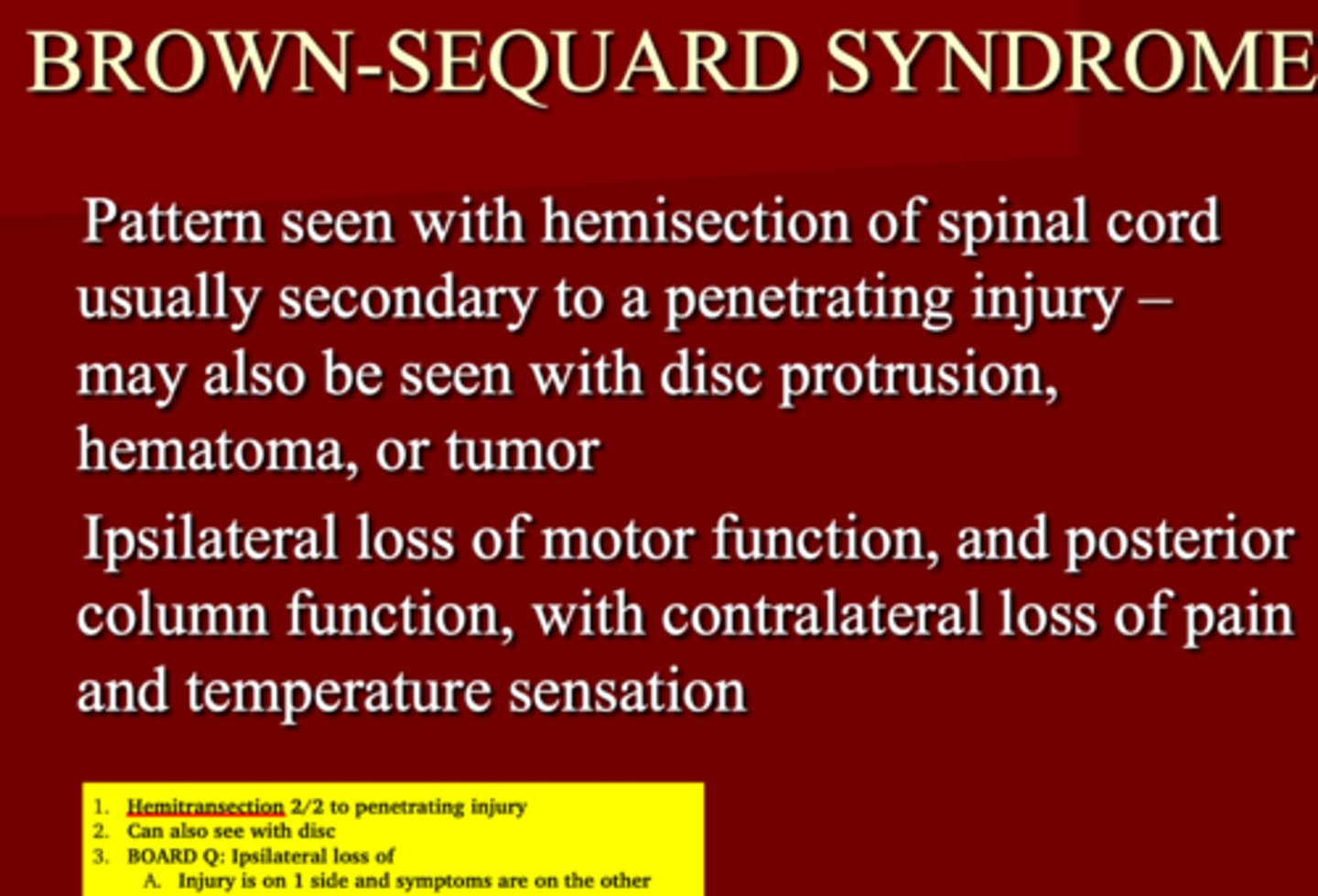
Hemisection of spinal cord causing Ipsilateral loss of motor function & posterior column function with contralateral loss of pain & temperature sensation
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
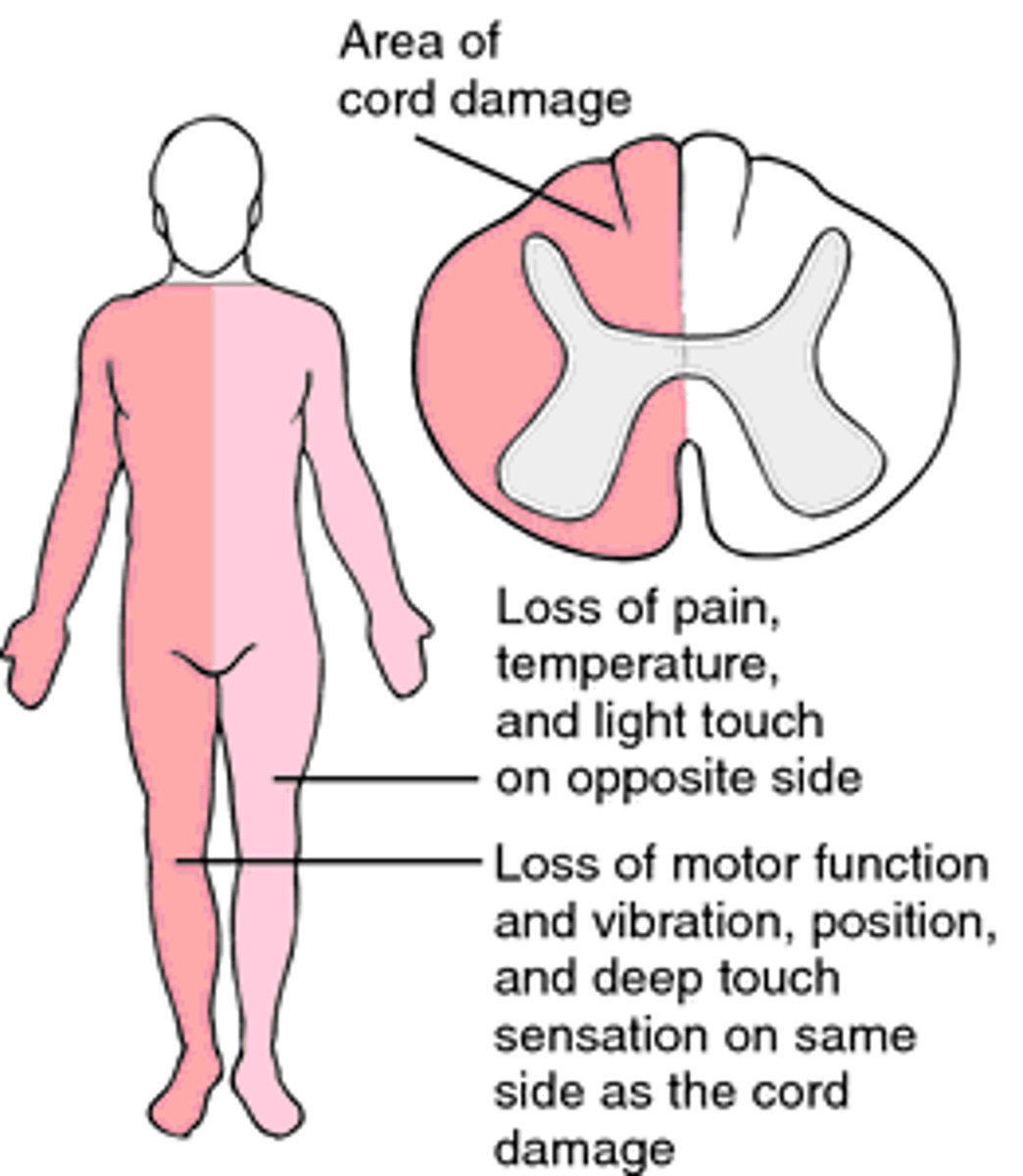
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
1. Pattern seen with _____ of spinal cord
2. MC Secondary to _____ injury
3. Can also be seen with _____ protrusion, ____ or ___
1. Hemisection
2. Penetrating injury
3. Disc protrusion, Hematoma or Tumor
(injury on one side & symptoms on another)
This type of spinal cord injury causes weakness to be greater in the Upper extremities than the LE & distally more than proximally
Central Cord Syndrome
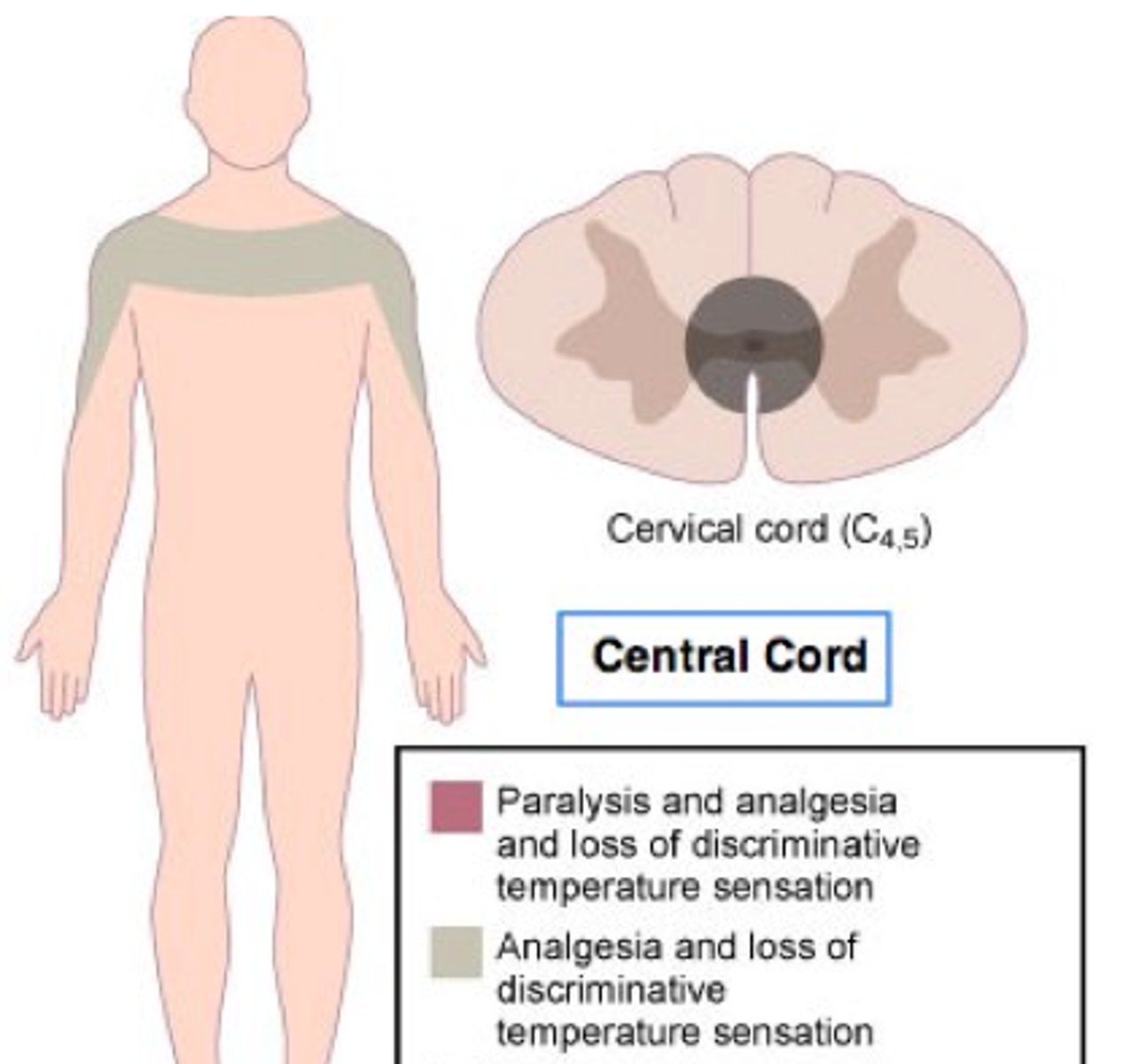
Central Cord Syndrome
1. Seen with ______ injuries
2. Describe sxs?
2. _____ prognosis with characteristic pattern of recovery such as?
1. Hyperextension injuries
2. More Weakness UE & distally
3. Better prognosis with LE recovery progressing upward , then hands recover strength

What is the TX for Spinal Cord Injuries?
Consider early federally to Regional Spinal injury center***
(He said to focus on last bullet)

When is a C-spine film indicated?
**** SUSPICION****
(told to erase everything else)

Reading C-spine film
1. Need to visualize _____
2. Assess alignment of ______ _____ curves
3. Prevertebral Soft Tissue: ______ suggests hematoma w/ fracture
4. Predental Space: _____ suggests transverse ligament tear w/ C1 fracture
5. Space between _______
1. C1-T1
2. 4 lordotic curves
3. > 5 mm
4. > 3 mm
5. spinous processes

Prevertebral Soft Tissue wider than 5 mm suggests ?
Hematoma with fracture
Predental Space wider than 3mm suggests ?
transverse ligament tear w/ C1 fracture
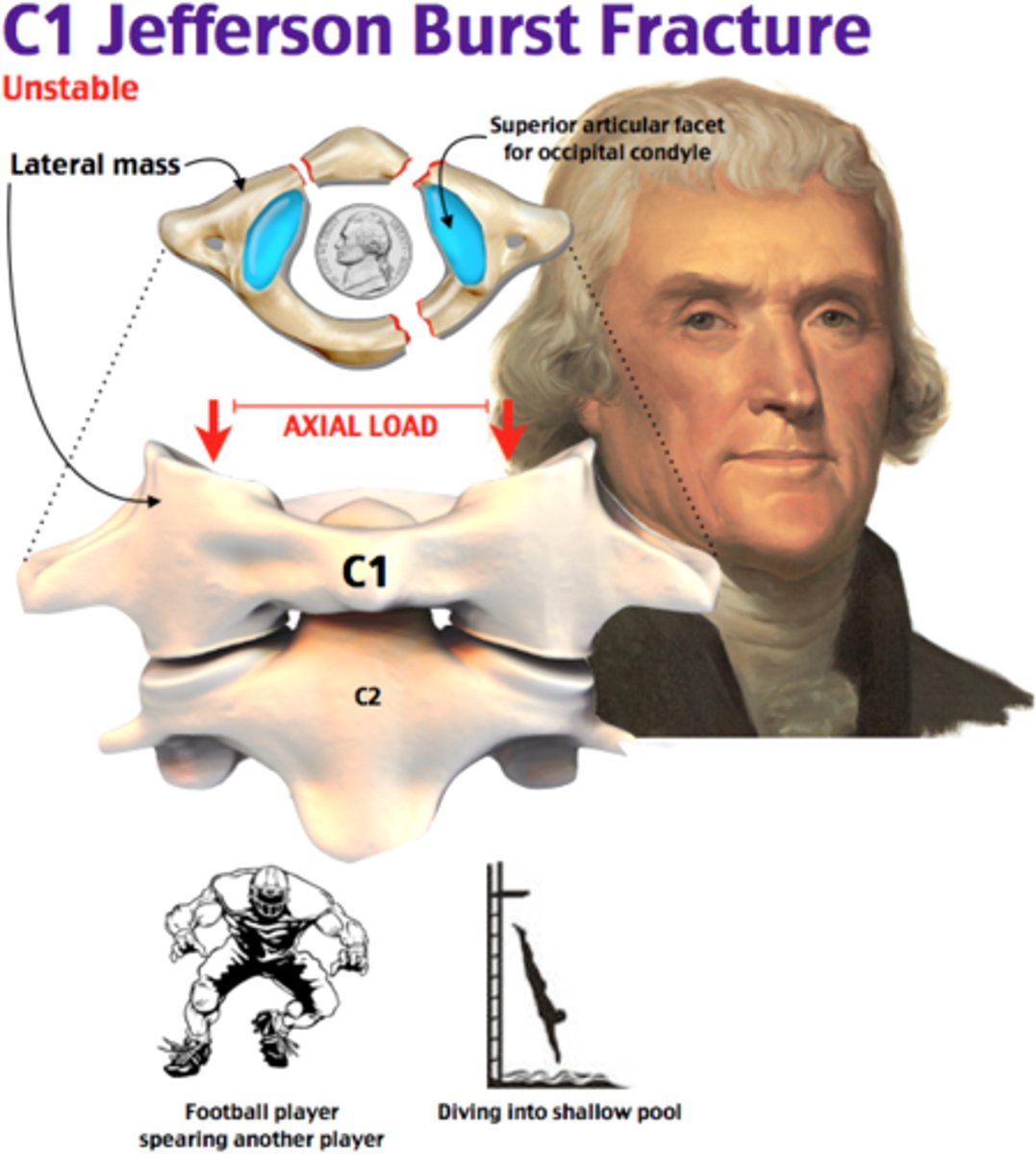
Fracture of both anterior and posterior rings of C1 (atlas) that is caused by Axial loading (i.e. patient falls on head, direct blow to head). Often associated with C2 fractures & is consider unstable even though most do not cause spinal cord injury.
Jefferson fracture (burst fracture)
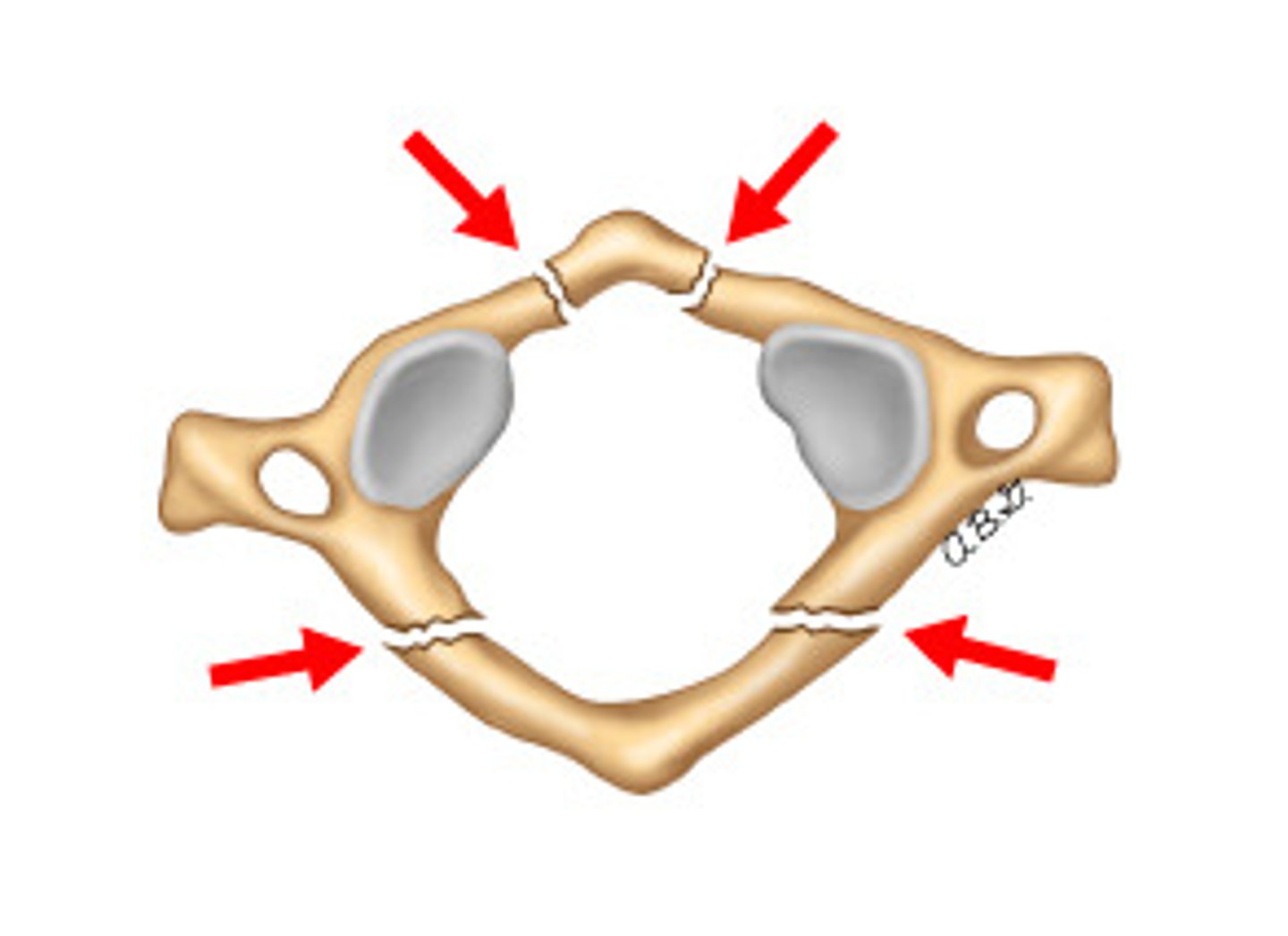
Jefferson fracture
1. Fx of _____ and ____ rings of _____
2. Caused by _____
3. Often associated with _____ fx
4. Considered ______
Jefferson fracture
1. Anterior & Posterior rings of C1 (burst fx)
2. Axial Loading (i.e. patient falls on head, direct blow to head)
3. C2 fx
4. Unstable (even though most do not cause spinal cord injury)
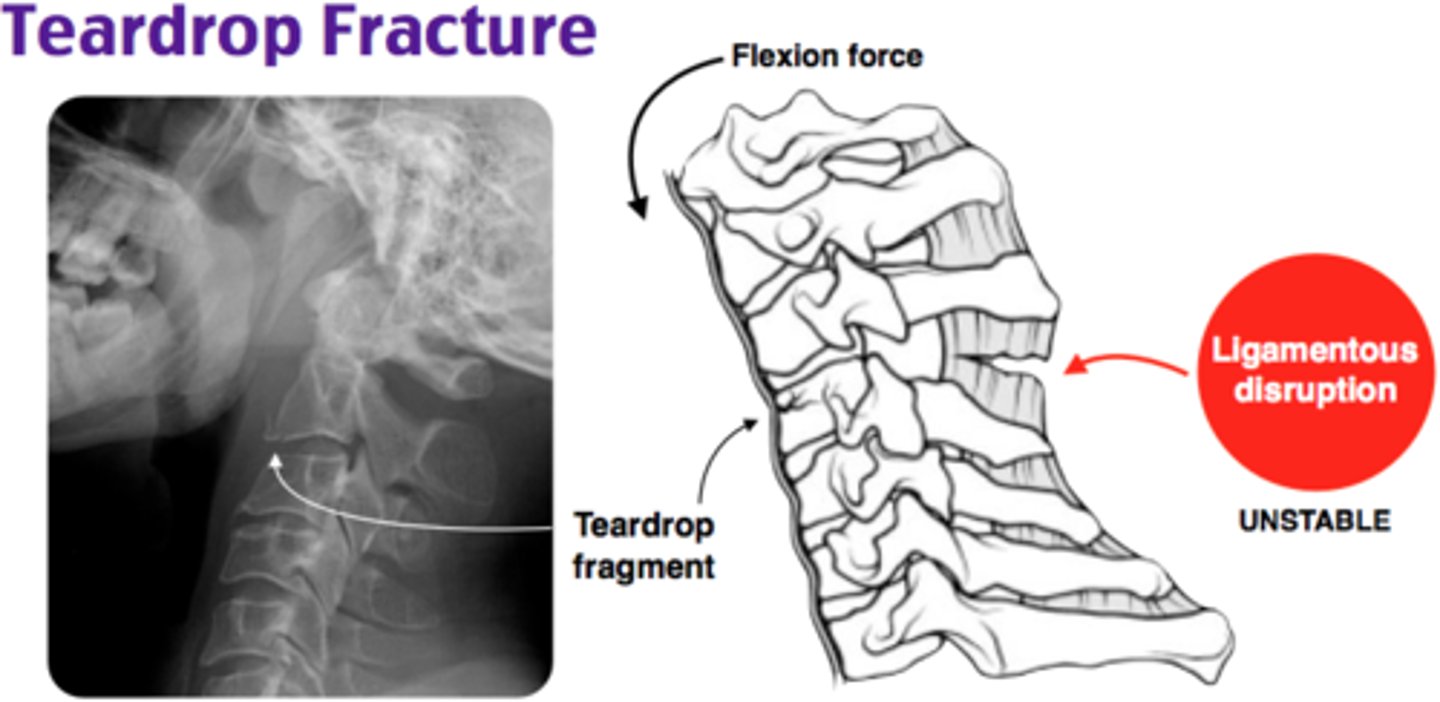
Fracture of anterior inferior portion of vertebral body that is caused by Flexion injury. It appears as teardrop-shaped fragment & considered unstable because it's associated with tearing of posterior ligament and neurologic damage
Flexion Teardrop Fracture