DENT Fun. I - Collagen & Hemoglobin
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
____ is the most abundant protein in animals.
Collagen
Collagen
Fibrous protein that gives the skin form and strength
Collagen is formed by ____.
fibroblasts; deposited in the ECM
Over 90% of collagen in the body is ____.
Type I Collagen; skin, bones, tendons
Collagen Primary Structure
Repeating amino sequence: Gly-X-Y where "X" and "Y" can be Proline or Hydroxyproline
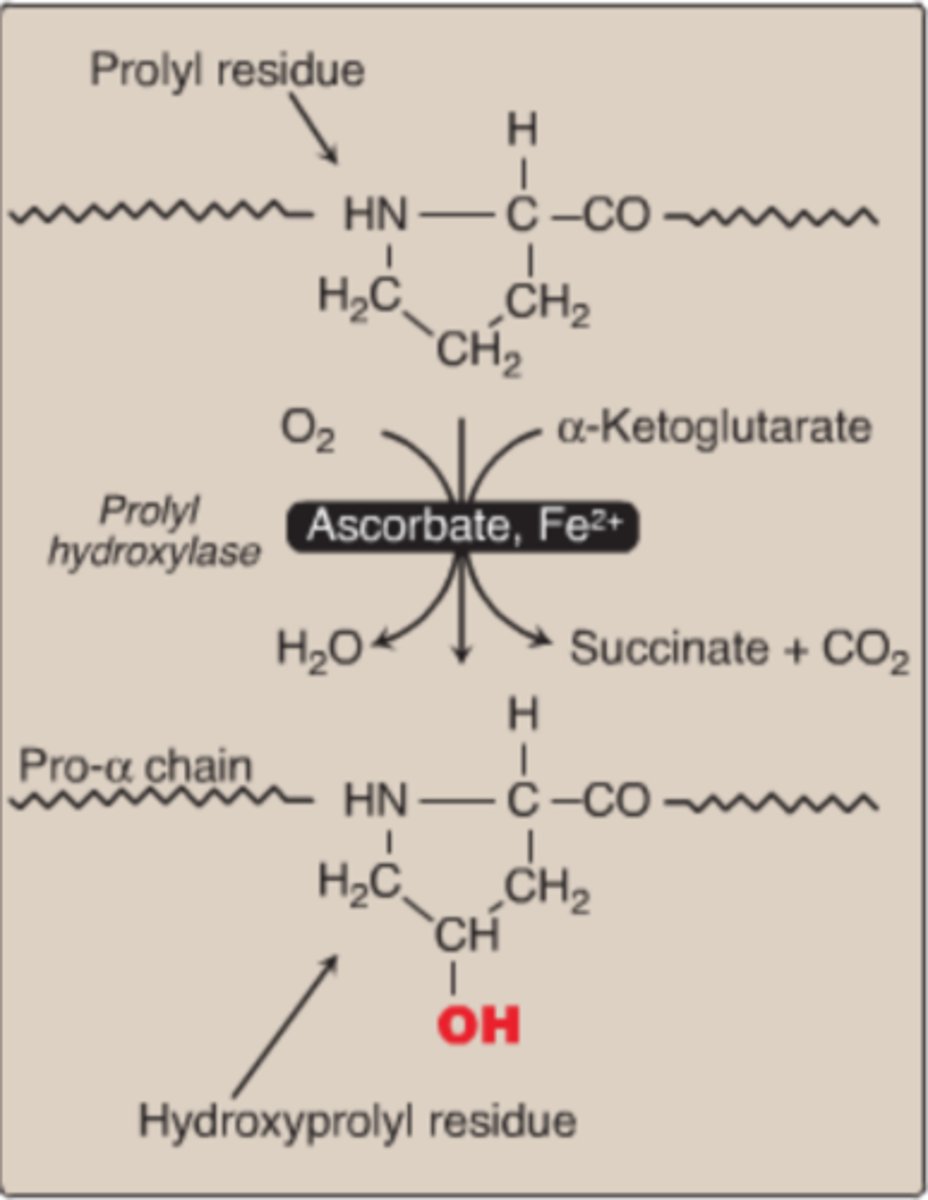
Hydroxylation of Proline
Proline + O2 + Ascorbic Acid (Vit. C) + a-Ketoglutarate
Hydroxylation of Lysine
Lysine + O2 + Ascorbic Acid (Vit. C) + a-Ketoglutarate
via the enzyme, Lysyl Hydroxylase
Scurvy
Vitamin C deficiency that causes collagen malformation
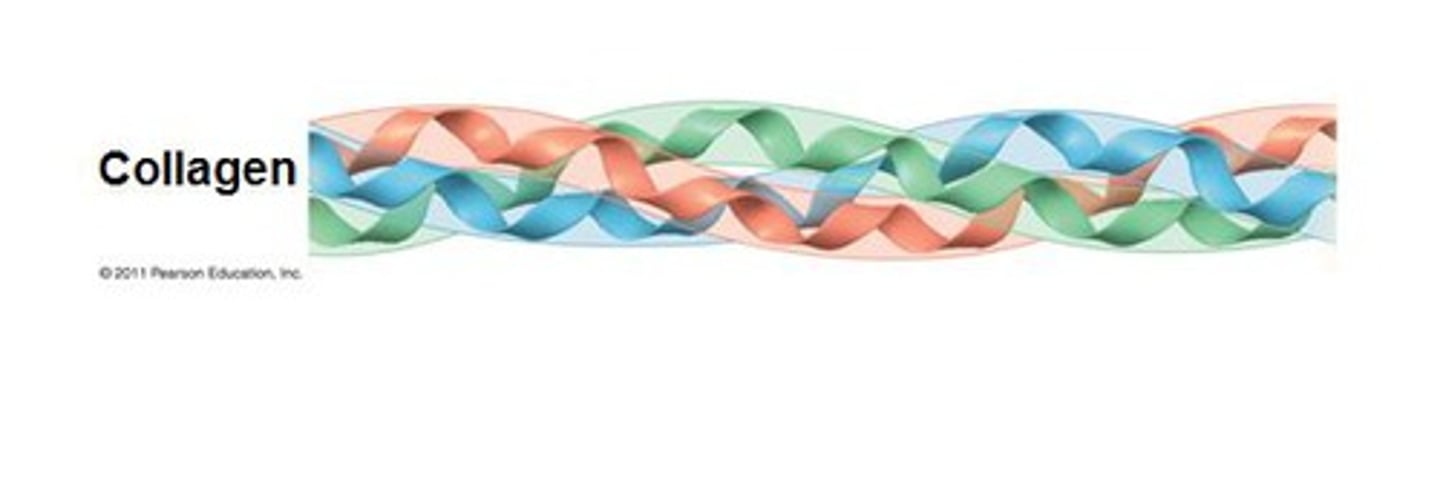
Collagen Secondary Structure
Left-Handed Helix
3.3 amino acids/turn
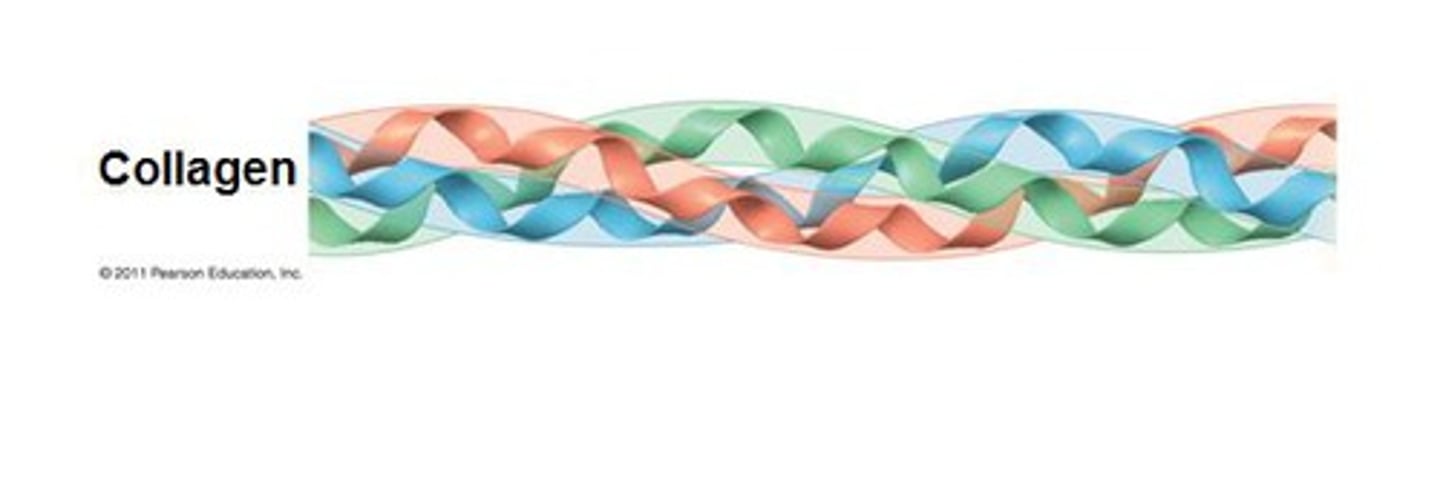
In collagen, every third amino acid is Glycine. Because of this there is a ____ on the Left-Handed Helix.
strip of Glycine
Collagen Tertiary Structure
- Triple Helix of Left-Handed Helices intertwined to form a Right-Handed Triple Helix called Tropocollagen
- Glycine is in the middle of the triple helix
What is the basic structural component of Collagen?
Tropocollagen
Tropocollagen
RH Helix of intertwined LH Polypeptide Chains
Collagen Quaternary Structure
Alpha Triple Helix: 3 bands of Tropocollagen "super-coiled" together

5-Hydroxylysine is an attachment site for ____.
sugars
Galactose and Glucose are frequently covalently bonded to 5-Hydroxylsine via ____ and ____.
galactosyltransferase/glucosyltransferase
What do sugars attached to Hydroxylysine do?
- Organize collagen fibrils
- Act as sites of nucleation for bone mineralization
What happens in the gaps of Collagen's Quaternary Structure?
Mineralization of bone
Collagen Fibers are ____.
cross-linked
What is the major class of Collagen?
Fiber-Forming (Types I, II, and III)
Work to convert Procollagen to Collagen in the ECM
What are the 6 other classes of Collagen?
- Fiber-Associated
- Network
- Filament
- Anchoring Fibril
- Transmembrane
- Multiplexins
Fiber-Forming Collagens are ____, while other classes of Collagen are associated ____.
parallel/anti-parallel
The other Collagen classes seldom convert Procollagen to Collagen (T/F)
True
Collagen Synthesis
(1) Synthesis in the Rough ER
(2) Peptide chains form into trimers (Procollagen)
(3) Procollagen further folds and is secreted into the ECM
(4) Proteases in the ECM cleave the carboxy and amino ends, creating Tropocollagen
(5) Tropocollagens cross-link to form Collagen
____% of total body heme is located in RBCs
85
Hemoglobin (Hb)
Tetramer composed of 2 Alpha Chains & 2 Beta Chains
Myoglobin
Monomeric O2 storing protein in Muscle
Myoglobin has a Quaternary Structure (T/F)
False; it is Monomeric, so it does not associate with other protiens
Allosteric Regulation
The binding of a regulatory molecule to a protein at one site affects the function of the protein at a different site
Fe2+ is coordinated by ____.
His F8
Iron interacts with ____ ligands in Hb and Mb.
6
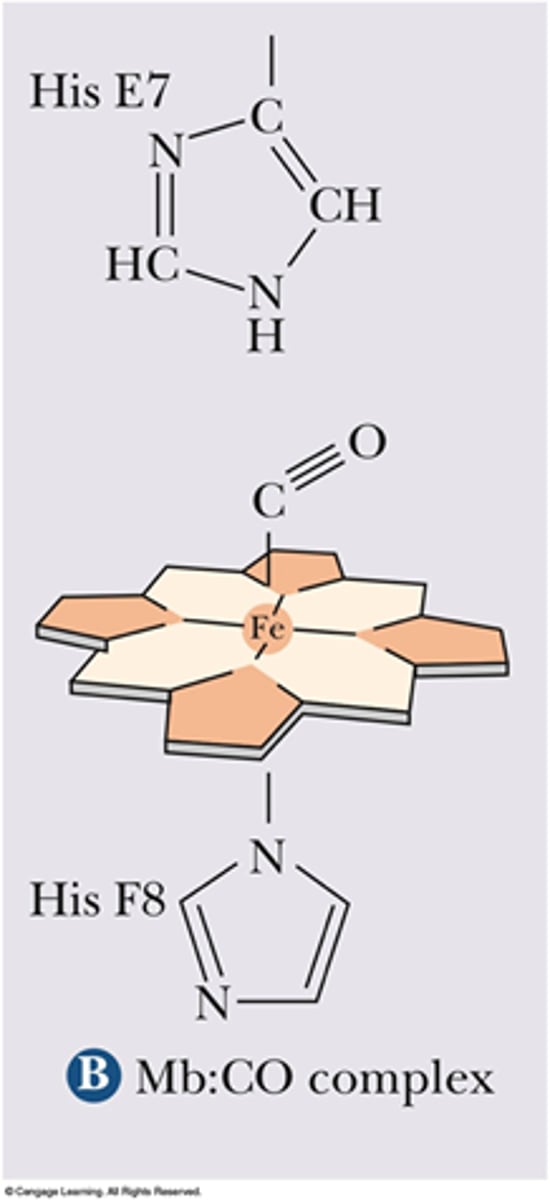
What are the 6 ligands Iron binds with in Heme?
- 4 Nitrogens from Porphyrin
- The Imidazole Ring of His F8
- O2
O2 binding to the Heme group causes ____.
conformational change, pulling His F8 and Fe2+ into the plane of Heme
Fe2+ moves less than ____ nm when conformational change occurs.
0.04
O2-Binding Curve
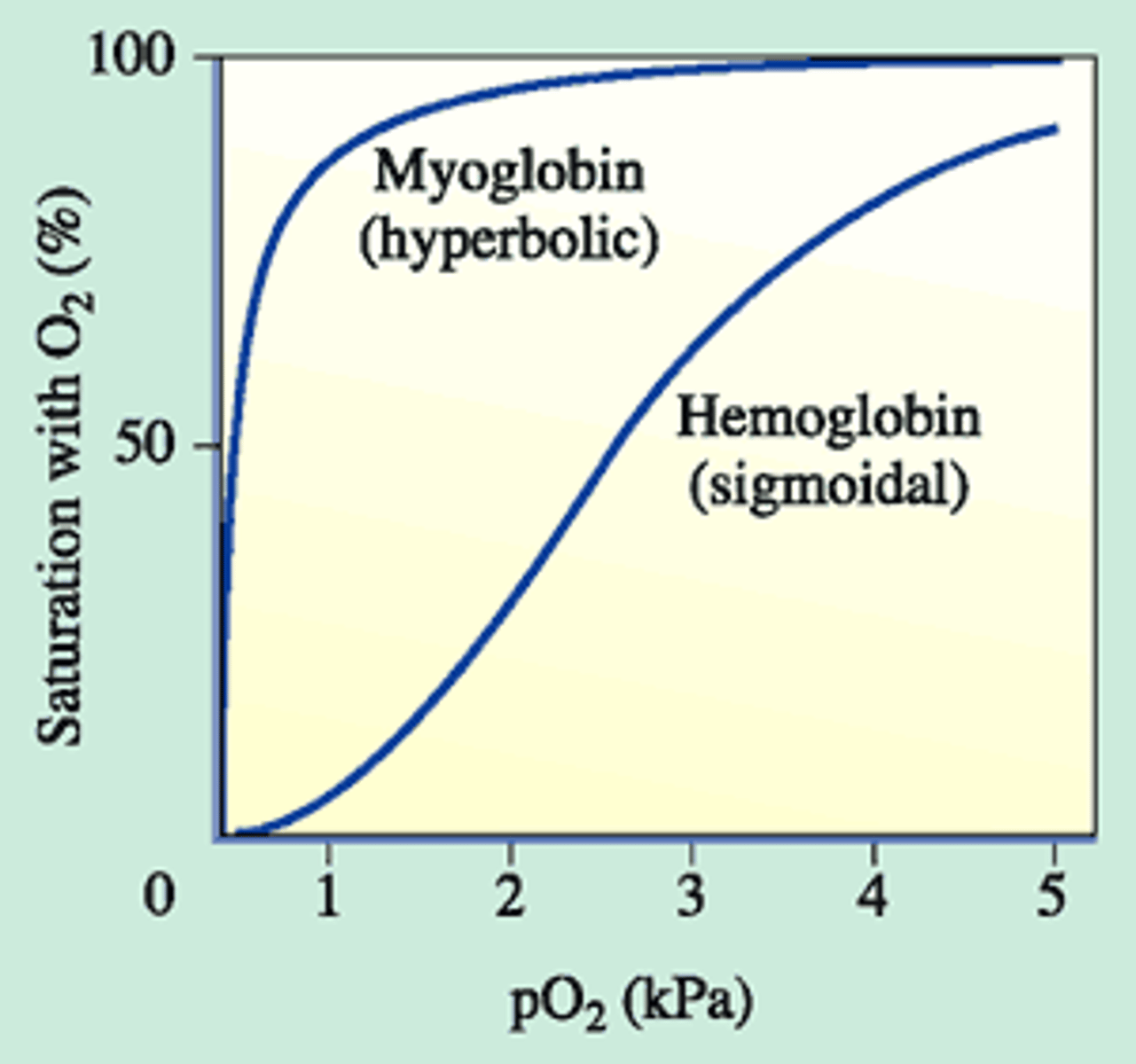
Hb has a higher affinity for O2 than Mb (T/F)
False; Mb stores O2 more readily at all O2 pressures
Cooperative Binding
The tendency of the protein subunits of Hb to affect each other's O2 binding such that each bound O2 increases the likelihood of further O2 binding
Hb binds O2 in the lungs, where the pO2 is about ____.
100 torr
Hb releases O2 in the capillaries, where the pO2 is about ____.
40 torr
O2 Binding by Hb induces a ____ structure change.
quaternary
When O2 binds, an Alpha-Beta Hb subunit moves ____ in relation to the other.
15*
R Conformational State of Hb
"Relaxed" Oxyhemoglobin
T Conformational State of Hb
"Tense" Deoxyhemoglobin
p50
The pO2 when hemoglobin is 50% saturated
P50 of Hb = ____
26 torr/mmHg
The p50 is inversely proportional to ____.
O2 affinity
ie. High p50 = Low O2 Affinity
What agents can affect Hb-O2 Binding?
- H+
- CO2
- Cl-
- 2,3-BPG
Bohr Effect
Decrease in the amount of O2 associated with Hb in response to lowered blood pH resulting from an increased [CO2] in the blood
Dissociation of O2 from Hb increases as pH decreases
Lower pH will ____ the p50 of Hb.
increase
H+ Effect on Hb
Bind directly to Hb, decreasing O2 affinity
CO2 Effect on Hb
CO2 + H2O <-> H+ + HCO3-
Increase in [CO2] = Increase in [H+]
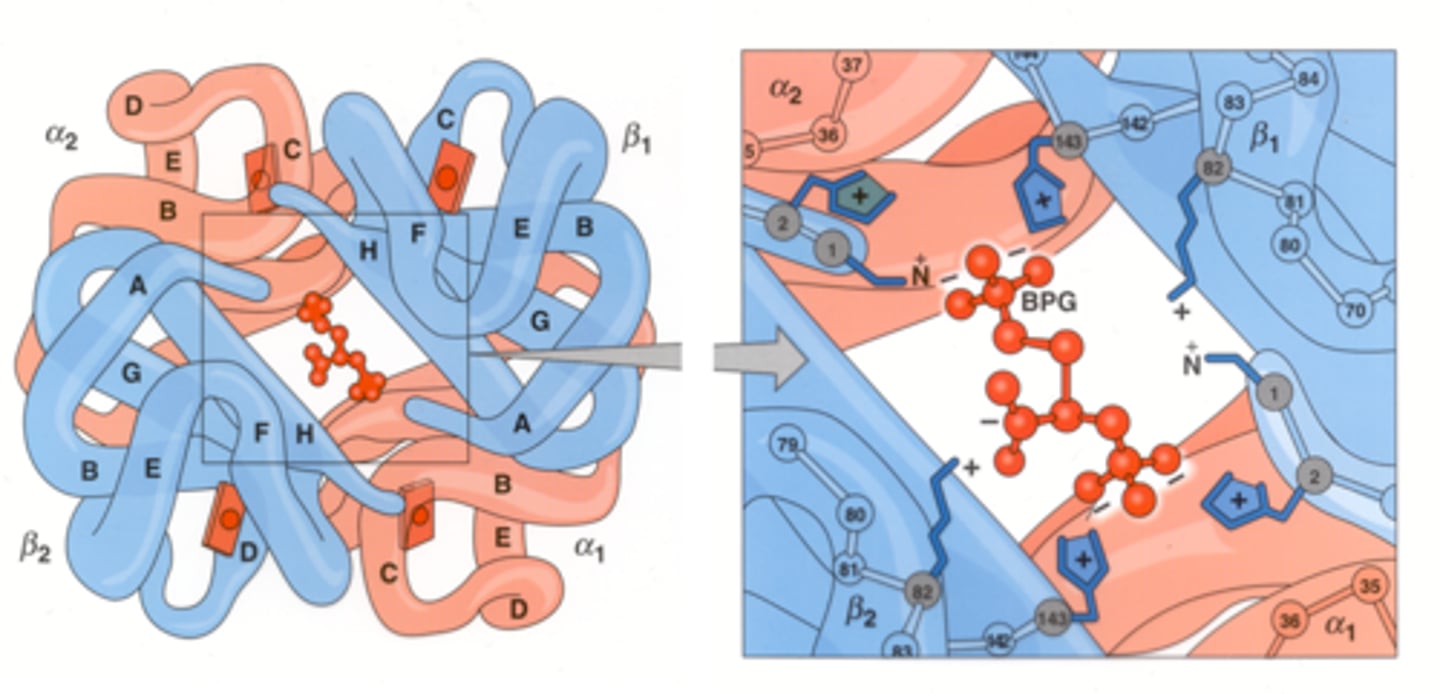
2,3-BPG Effect on Hb
Allosteric Effector of Hb that binds a site distanced from the Heme Iron, decreasing O2 affinity
Where does 2,3-BPG bind Hb?
In a pocket formed by the 2 β chains in the center of Hb; 2,3-BPG is very electronegative so it binds the positive charges of Deoxyhemoglobin, stabilizing it
Fetal Hb has a ____ O2 affinity.
higher
Why does Fetal Hb have a higher affinity for O2?
It has a lower affinity for 2,3 BPG
Why does Fetal Hb have a lower affinity for 2,3-BPG?
Instead of 2 Beta-Chains it has 2 Gamma-Chains, which has Ser instead of His at position 143. This creates less positive charge in the pocket for 2,3-BPG to bind.
Fetal Hb
2 Alpha and 2 Gamma chains
Sickle Cell Anemia is caused by ____.
a single mutation in Beta-Globin
Creates misfolding of Hb and formation of a hydrophobic pocket in DeoxyHb. The malformed DeoxyHb will aggregate and form fibers that shape the RBCs into a sickle-shape.
Cooley's Anemia is caused by ____.
the absence of Beta-Globin chains