WWII
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:27 AM on 3/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
1
New cards
Which countries were a part of the Axis?
Germany, Japan, Italy
2
New cards
Which countries were a part of the Allies?
Russia, Britain, France, US, China, Canada
3
New cards
Why did Russia change sides?
Germany violated their Non-Agression Pact when they decided to invade them in Operation Barbarossa
4
New cards
When did the war start in Europe?
September 1, 1939
5
New cards
When did the US enter the war?
December 8, 1941
6
New cards
When did the war end in Europe? (V-E Day)
May 8, 1945
7
New cards
When did the war end in the Pacific? (V-J Day)
September 2, 1945
8
New cards
What is fascism?
a political ideology in which everything is controlled by the government
9
New cards
How was press treated under fascism?
full of propaganda, censored, no free press or speech
10
New cards
Why were aircraft carriers important?
they allowed planes to take off from the ocean, which was especially key for fighting in the pacific
11
New cards
What were Kamikaze pilots?
they were suicide bombers; over 1900 were sent by Japan in the Battle of Okinawa (also used in the Battle of Leyte Gulf)
12
New cards
What was island hopping?
instead of capturing each Japanese controlled island, they would capture the weaker ones to cut off access to the stronger ones; it reduced time, money, and lives lost
13
New cards
When and what was the Lend-Lease Act?
March 1941, the US sent aid to the allies for free meaning they were no longer isolationist nor neutral
14
New cards
When and where was the bombing of Pearl Harbor?
December 7, 1941 at the US military base on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii
15
New cards
Why did Japan bomb Pearl Harbor?
it was the heart of the US pacific fleet and it would give them time to attack other islands
16
New cards
How was the Battle of Britain fought?
nearly a year long of continual bombing by the German Air Force; focused on airfields and factories at first, then moved towards cities like London to break morale
17
New cards
When and where was the Battle of Dunkirk?
end of May, 1940 on the beaches of Dunkirk, France
18
New cards
How was the Battle of Dunkirk fought?
allied soldiers were trapped and suffering under heavy fire, Britain sent 850 ships of any kind to rescue them, in 9 days 338,000 were rescued
19
New cards
When and where was Operation Barbarossa?
June 22, 1941 in the Soviet Union
20
New cards
Why did Germany invade Russia?
because of race, to gain territory, and to destroy communism
21
New cards
When and where was D-Day? (aka Operation Overlord)
June 6, 1944 at Normandy, France
22
New cards
Who and what was important about D-Day?
Led by Eisenhower, they leaked fake plans to Germany to get a large portion of Hitler’s army to a wrong location. It was the largest land-sea-air operation in army history; allied victory, allowing them to control part of France
23
New cards
Where and when was the Battle of the Bulge?
December 16, 1944 in Belgium
24
New cards
Why was the Battle of the Bulge fought?
After the allies captured their first German town (Aachen), Hitler ordered one last final attempt and used tanks to advance into allied territory; allied victory, Germans lost 120,000 troops and tons of equipment
25
New cards
What was the purpose of the Doolittle Raid?
16 bombers were sent to raid Tokyo, while there was little physical damage it left a severe psychological impact leaving Japan vulnerable and lifting American spirits
26
New cards
When was the Battle of Midway?
June 3-7, 1942
27
New cards
What was significant about the Battle of Midway?
It was midway between the war, between Japan and the US, and the turning point in the war in favor of the allies; it stopped Japan’s advancement and the US would win most battles after this
28
New cards
What was significant about the Battle of Iwo Jima?
Iwo Jima was one of the most fortified sports on earth with trenches and cave systems, the allies won by a landslide (only 200 Japanese survived) but it wouldn’t have been possible without the Navajo Code Talkers who sent and received 800 messages with no errors
29
New cards
What was the largest camp during the Holocaust?
Auschwitz
30
New cards
How many Jews were killed in the Holocaust?
6 million
31
New cards
What is the first level of the Pyramid of Hate and examples of it?
Biased Attitudes: stereotyping, fear of differences, non-inclusive language, justifying biases by seeking like-minded people, accepting negative of misinformation
32
New cards
What is the second level of the Pyramid of Hate and examples of it?
Acts of Bias: bullying, name calling, slurs, social avoidance, dehumanization, belittling jokes
33
New cards
What is the third level of the Pyramid of Hate and examples of it?
Discrimination: economic, political, educational, employment, segregation, housing, criminal justice
34
New cards
What is the fourth level of the Pyramid of Hate and examples of it?
Bias Motivated Violence: murder, rape, assault, arson, terrorism, vandalism, threats
35
New cards
What is the fifth level of the Pyramid of Hate and examples of it?
Genocide: the act of deliberately and systematically kill an entire group of people
36
New cards
When and where did Japanese incarceration occur?
After the bombing on Pearl Harbor (Dec 1941), anti-Japanese sentiment increased in the US
37
New cards
Why and how were Japanese-Americans incarcerated?
Americans believed them to be disloyal and conspiring against the US in the war, they were a “threat to national security”; they were forcibly removed from their homes and put into concentration camps which were isolated, cheap, fenced in with barbed wire, heavily guarded, and crowded
38
New cards
What was executive order 9066?
Authorized relocation of all people deemed a threat to national security to assembly centers and eventually concentration camps
39
New cards
How did some Japanese Americans resist incarceration?
They used test cases like Ex Parte Endo and Korematsu vs US or they fought in the war for the US to prove loyalty
40
New cards
Who were the “No-No Boys”?
Those who answered no to both questions on the loyalty questionnaire and were kept separate from other incarcerees
41
New cards
Where and when was the Bataan Death March?
April 9, 1942 in the Pacific
42
New cards
Who was involved and why in the Bataan Death March?
Japan forced their prisoners of war (mainly Filipinos) on a 5 day march at gunpoint with little food and water because Japan saw it dishonorable to surrender
43
New cards
Why were the Navajo Code Talkers important?
They had the only unbroken code in military history (Dene) and were the largest group of decoders, especially key in winning Iwo Jima
44
New cards
What was the Manhattan Project?
Building and testing of the atomic bomb; the most ambitious scientific enterprise in history, costing billions of dollars and hundreds of thousands of workers (who usually did not know what they were building) led by Oppenheimer
45
New cards
Why did the US choose Hiroshima and Nagasaki to bomb? (August 6 and 9)
The size and layout made them suitable to bomb, almost every building collapsed in less than a minute
46
New cards
What point was added to international law in the Nuremberg Trials?
Individuals are responsible for their own actions, even in times of war
47
New cards
What was Germany found guilty of in the Nuremberg Trials?
Crimes against Peace (they planned and waged the war), War Crimes (killing hostages and POWs), Crimes against Humanity (genocide)
48
New cards
What was the purpose of the Yalta conference?
Roosevelt, Stalin, and Churchill met in the Soviet Union to discuss post-war Germany. Stalin wants harsh punishments, dividing them into 4 regions and Roosevelt sides with him to get support from such a powerful nation. Stalin promised free elections in Poland and to participate in the UN
49
New cards
How did the US change over the course of the war?
The war ended the great depression, unemployment fell to 1.2%, women were in the workforce while men were away but were fired as they returned, mass migrations, baby boom as men returned home, and the GI Bill of Rights provided education and training for veterans
50
New cards

Who is this?
Winston Churchill; leader of Britain
51
New cards

Who is this?
Tojo Hideki; military leader of Japan
52
New cards
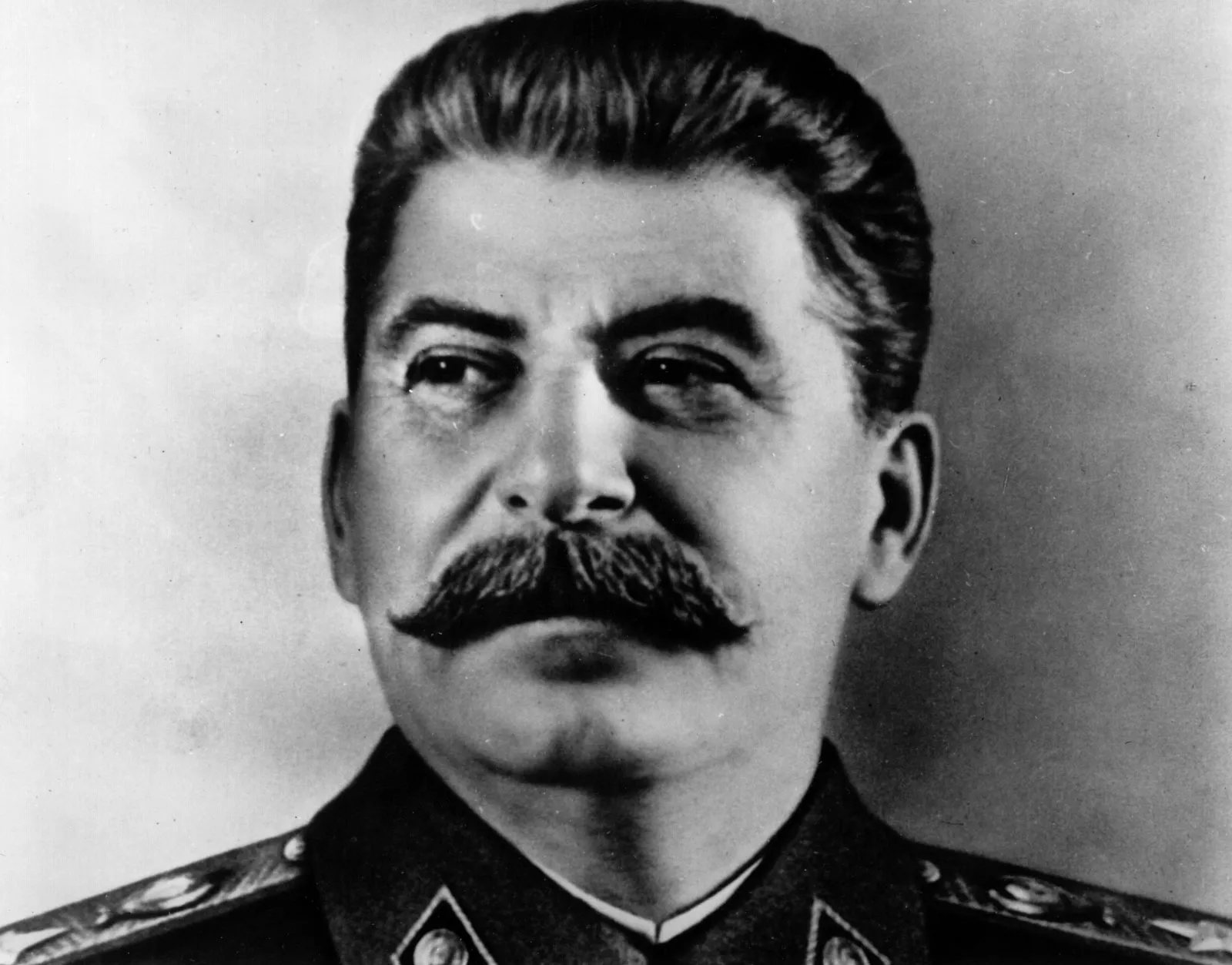

Who is this?
Stalin; leader of the Soviet Union
53
New cards

Who is this?
Mussolini; leader of Italy
54
New cards

Who is this?
Hitler; leader of Germany
55
New cards
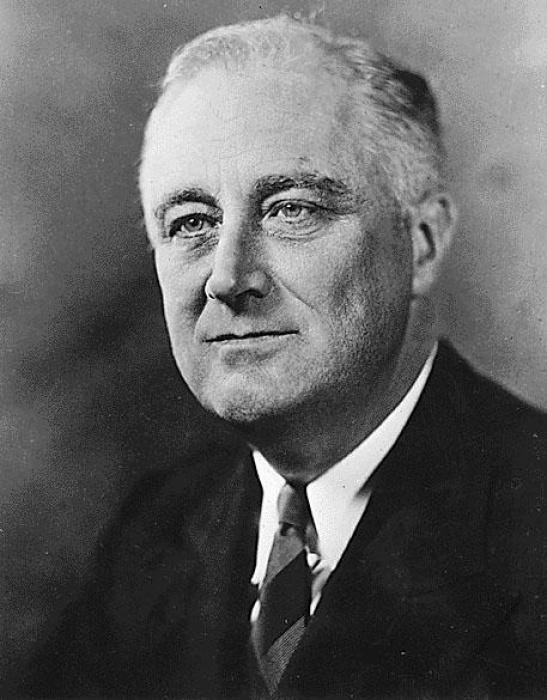

Who is this?
Franklin Roosevelt; leader of US (and president)
56
New cards
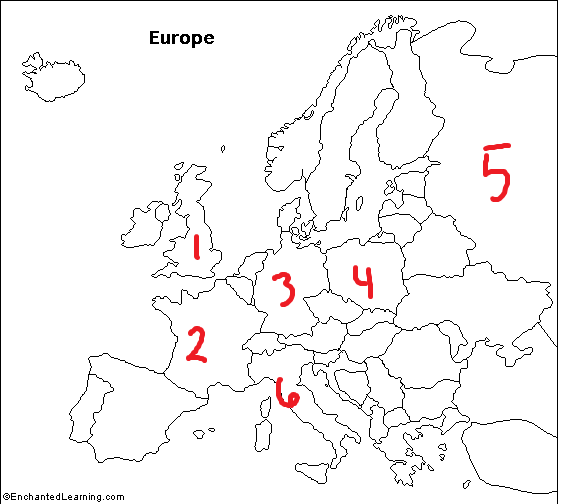
Label the European Countries
1- UK
2- France
3- Germany
4- Poland
5- Russia
6- Italy
2- France
3- Germany
4- Poland
5- Russia
6- Italy
57
New cards
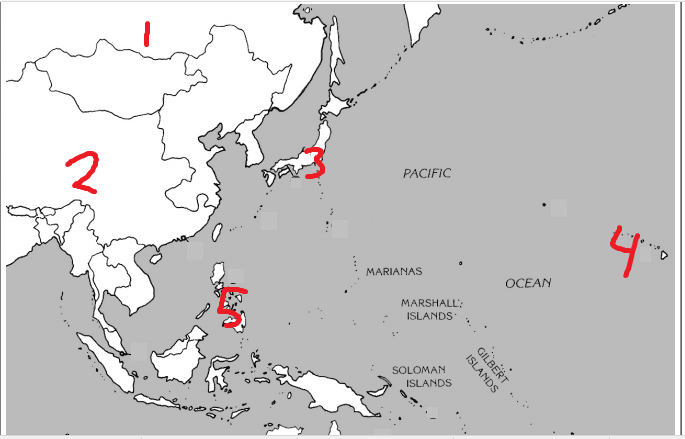
Label the Pacific regions
1- Russia
2- China
3- Japan
4- Hawaii
5- Philippines
2- China
3- Japan
4- Hawaii
5- Philippines