Pharmacodynamics
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Chronic use of a drug may cause an increase in enzymes used to metabolize it, need to take more of the drug to get the same effect
Enzyme induction
Some drugs may inhibit some enzymes, which might be beneficial for some health concerns but may have adverse interactions with other drugs
Enzyme Inhibition
MAO-Is inhibit monoamines to treat depression usually, but alcohol could affect the body more now that this inhibition is occuring (so doctors will advise people to not drink alcohol on MAO-Is) What is this an example of?
Enzyme Inhibition
Taking more than one drug that could compete for the same enzyme to be broken down, both drugs can build up in the system more than they individually would affect the body
Competition
Time it takes for ½ the drug to be removed from the system (time to get to steady plasma level, blood concentration)
Half Life of Drugs
Early on in the half-life time there is _____ drug in the system and _____ clearance rate.
more, faster
The more often you take a drug the more ______ the plasma levels and blood concentration
steady
Removal of drug by it’s half-life, when the enzymes are not saturated by the drug
First-order kinetics
Which form of decay is exponential, first-order kinetics or zero-order kinetics?
First-order kinetics
When there is more drug in your system than enzymes that can break it down
Zero-order kinetics
Which form of decay has a steady clearance rate and is non-concentration dependent, first-order kinetics or zero-order kinetics?
Zero-order kinetics
Which form of decay is alcohol and example of? First-order kinetics or zero-order kinetics
Zero-order kinetics
Most drugs that enter the kidneys to be broken down get _____________
reabsorbed into the blood
Since most drugs that enter the kidneys get reabsorbed into the blood, they must be _________________ that is not as likely to be reabsorbed
broken down into a form by the liver
When the liver converts drugs into a form that can be excreted, it makes the drug _____________
less lipid soluble
What are the three measured effects of drugs?
Therapeutic effects
Side effects
Toxicity effects
How well a drug binds to the receptor
Affinity
____ affinity in agonists and _____ affinity in antagonists
high, low
To what degree a drug elicits the response
Efficacy
How much of a drug is needed to elicit a response, based on affinity
Potency
On a dose response curve what is the Y-axis?
% response
On a dose response curve what is the X-axis?
Dose
On a dose response curve what does lower dose mean in terms of the response?
Lower response
On a dose response curve what does higher dose mean in terms of the response?
Higher response
On a dose response curve, how can someone identify the efficacy?
The plateau at the max response
Which side of the dose response curve has higher potency?
Left
Which side of the dose response curve has higher potency?
Left
Which side of the dose response curve has higher affinity?
Left
Different pain relievers have the same response, but one might work better than another is an example of which concept?
Efficacy
Different pain relievers may all relieve pain, but some require a larger amount than others is an example of which concept?
Potency
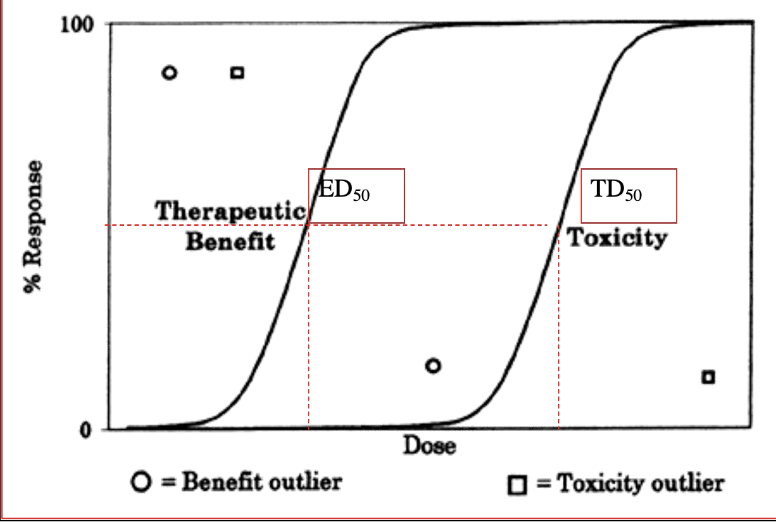
Dose where 50% of subjects respond with the desired response
ED50
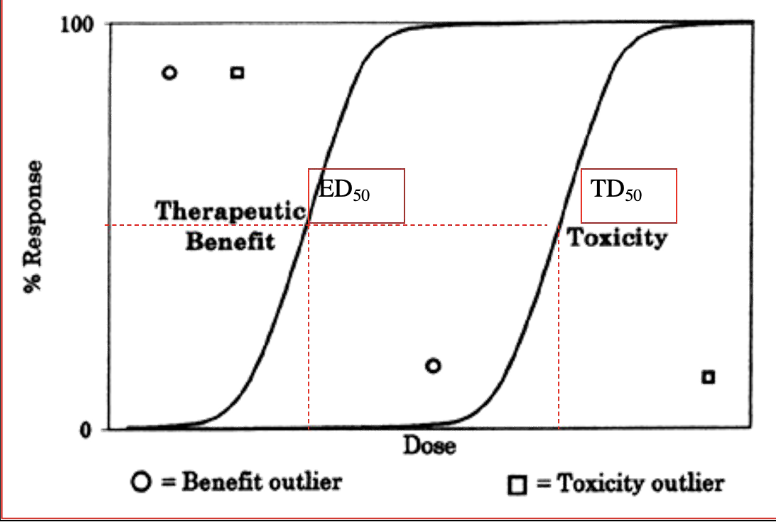
Dose where 50% of subjects respond with an undesired, toxic response
TD50
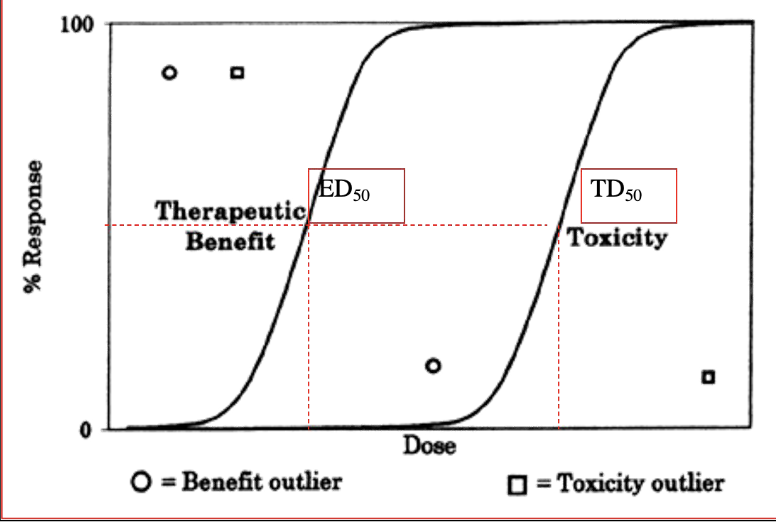
Dose where 50% of subjects die
LD50
What is the formula for the therapeutic index?
TD50/ED50=LD50
The ______________ is the amount of a drug it is ok to take to get an effect until the toxic effect starts
margin of safety
What is an example of a drug that would cause a non-typical dose-response curve (one that is an inverted U and has both rising and falling phases)?
Melatonin
If we pretreat a drug with a competitive antagonist, _______ potency and need _____ drug to get desired effect.
lower, more
If we pretreat a drug with a non-competitive antagonists, _____ efficacy and ____ of a maximum response.
lower, less
Drugs and antagonists are not competing for binding spots so the drug has a ______ affinity and the more drug you take will just get broken down
lower
Drug interactions reduce each others effectiveness but are not competing on the same receptor
Physiological Antagonism
Drug A + Drug B = larger response than each drug individually
Addictive Effects
Drug A (higher efficacy) + Drug B (lower efficacy) = greater response than what you would expect
Potentiation
How much drug is available
Pharmacokinetics
What does ADME stand for in pharmacokinetics?
Absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion
How much is active and excreted
Pharmacodynamics
Need more of a drug to get the desired effect
Tolerance
Tolerance is ______ when drug-use stops (drunk faster when you haven’t drank in awhile)
reversible
What are the 3 things tolerance depends on?
Dose
Context
Frequency
Tolerance could occur _____ or after ____ use
rapidly, chronic
Not all _____ of a drug show tolerance
effects
Increasing enzymes in the liver to break down a drug
Metabolic Tolerance
Changing receptors that bind with the drug
Pharmacodynamic Tolerance
Increase receptors
Up-regulation
If an antagonist is blocking receptors for a NT, ________ will help
Up-regulation
Decrease receptors
Down-regulation
If an agonist has an overload of NT trying to bind to a receptor, ___________ will help
Down-regulation
Classical Conditioning
Behavioral Tolerance
Environment determines tolerance, ____ environment = no tolerance
New