Bootcamp.com - Photosynthesis
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
_____ are organisms (like humans) that obtain chemical energy from the food they eat
heterotrophs
_____ organisms are capable of making their own food
autotrophic
_____ (like plants) capture solar energy and convert it to chemical energy by photosynthesis
photoautotrophs
_____ creates chemical energy which is passed up the food web to all organisms
photosynthesis
photosynthesis releases _____, which is crucial for aerobic cellular respiration
oxygen
photosynthesis reduces _____ from the atmosphere
carbon dioxide
photosynthesis uses _____ to make _____
photons (light energy); sugars (glucose)
_____ occurs when inorganic carbon is incorporated into an organic molecule (like a sugar molecule)
carbon fixation
write the overall chemical equation for photosynthesis:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
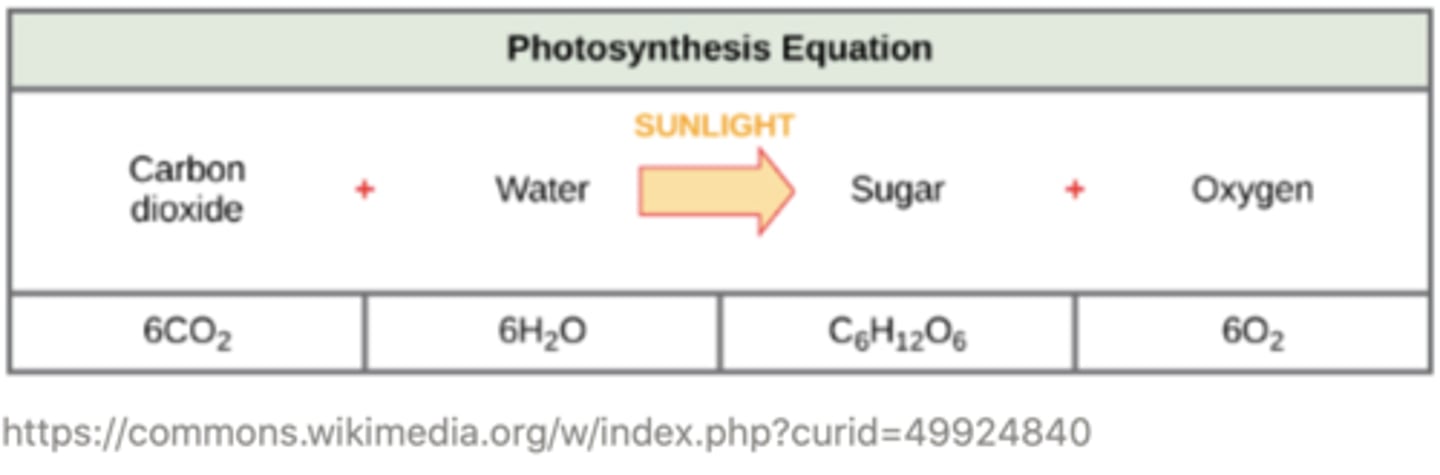
The two stages of photosynthesis are the _________ and the ____________
light dependent reactions; Calvin cycle
light dependent reactions produce _____ and _____
ATP; NADPH
the Calvin cycle (or light independent reaction) uses energy stored in _____ and _____
ATP; NADPH
photosynthesis stores solar energy in glucose chemical bonds - how do plants then use that energy?
aerobic cellular respiration
photosynthesis has a positive Gibbs free energy (+ ΔG), so it is _____ and _____
non-spontaneous; endergonic
the overall reactions of aerobic cellular respiration and photosynthesis are ______
opposites
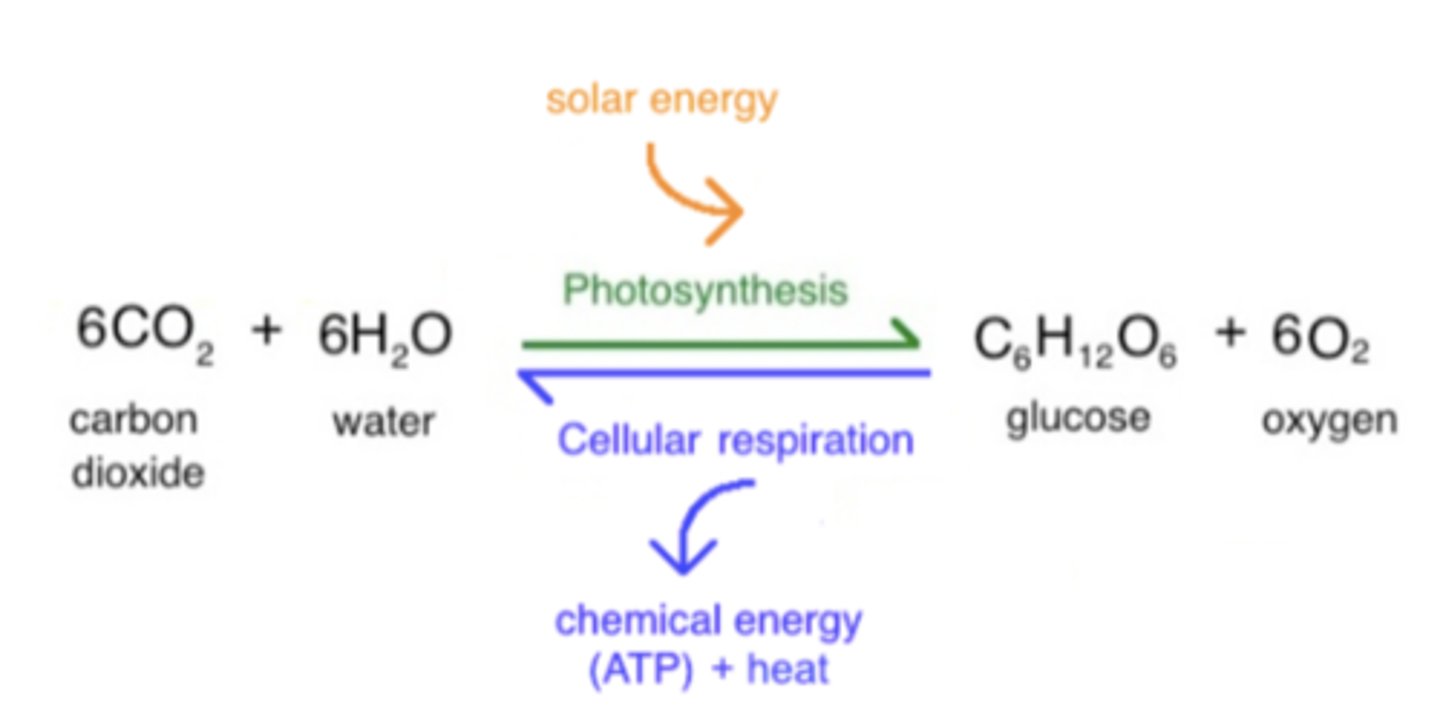
solar energy is input to photosynthesis to convert 6 _____ & 6 _____ to 1 _____ and 6 _____
CO2; H2O; Glucose; O2
chemical energy is released as heat and ATP during aerobic cellular respiration, where 1 _____ and 6 _____ convert to 6 _____ & 6 _____
glucose; O2; CO2; H2O
ATP from the light dependent reactions is not used to _____
power the cell
ATP from the light dependent reactions is consumed to power the _____, which makes glucose
Calvin cycle
_____ tissue is the outer layer of cells - what is its function?
epidermis; it provides protection and prevents water loss
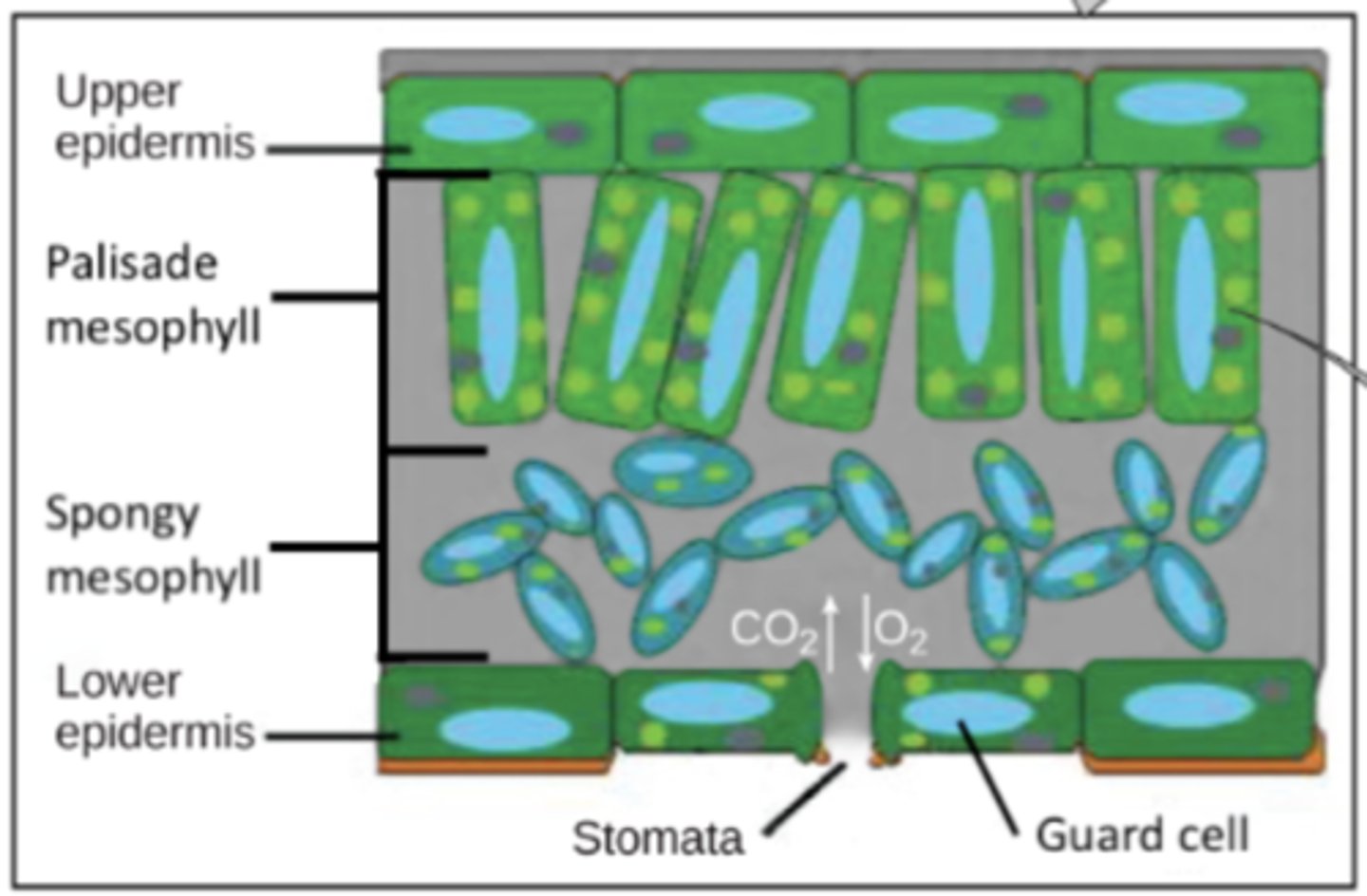
_____ mesophyll cells conduct most photosynthesis
palisade
palisade mesophyll cells contain many _____, and are well organized as a single layer below the _____
chloroplasts; upper epidermis
spongy mesophyll cells conduct some photosynthesis, but not as much as the _____ cells
palisade mesophyll
spongy mesophyll cells have few _____
chloroplasts
spongy mesophyll cells are found toward the _____
bottom of the leaf
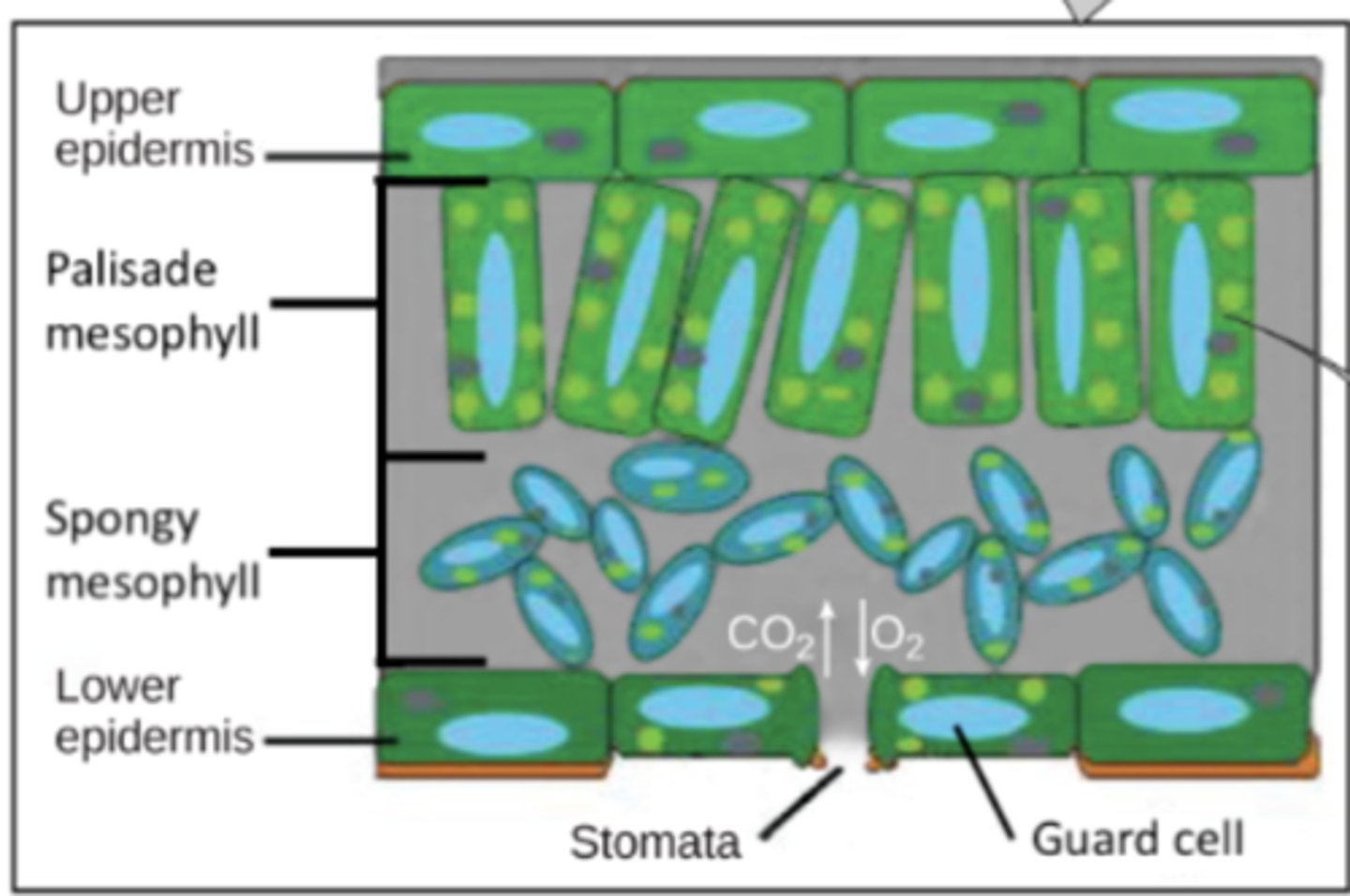
gaps between spongy mesophyll cells facilitate the movement of _____
gases
stomata are pores mainly found in the _____ of leaves and they are the site of _____
bottoms; atmospheric gas exchange
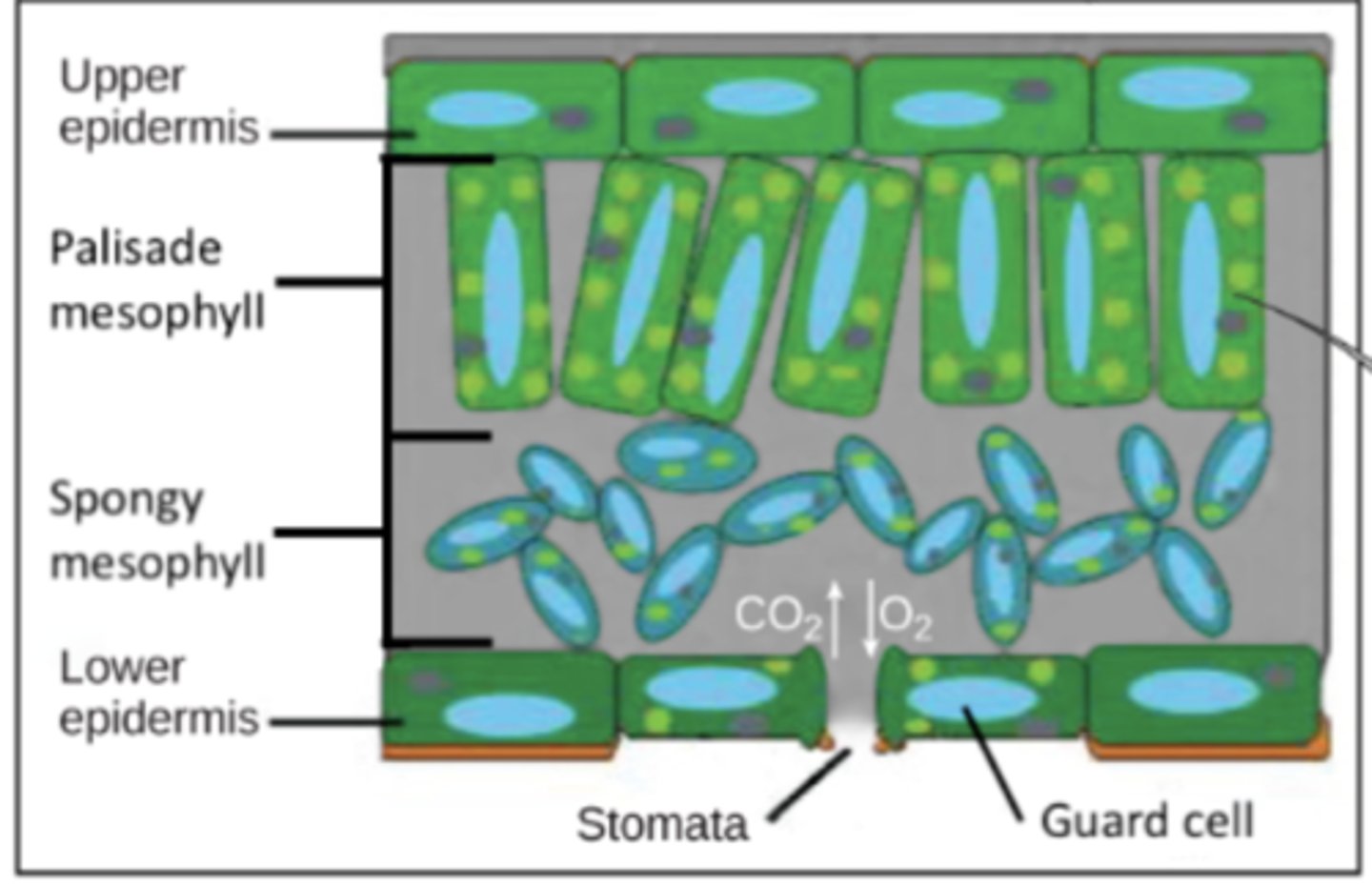
_____ surround stomata, and they control whether the stomata are open or closed
guard cells
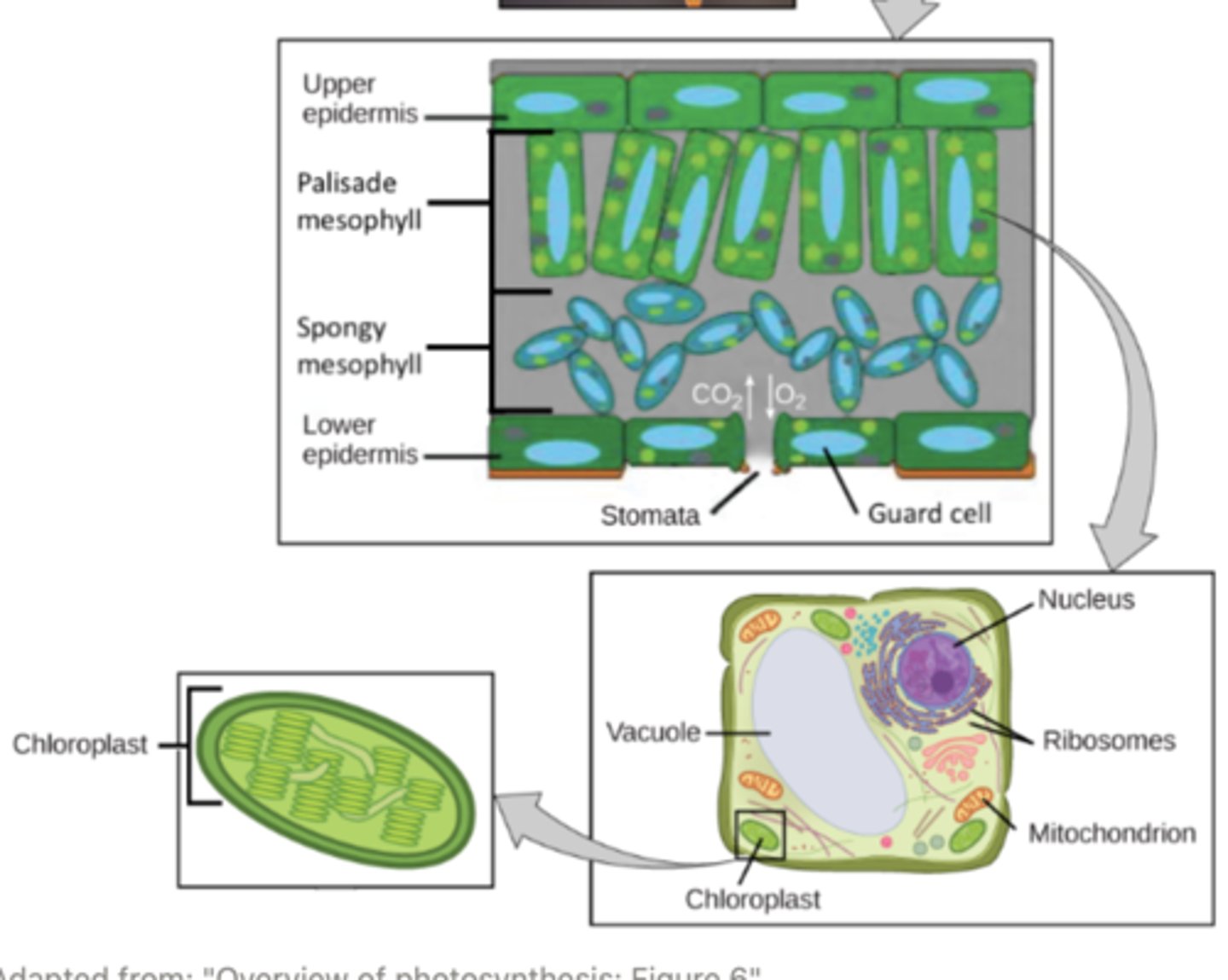
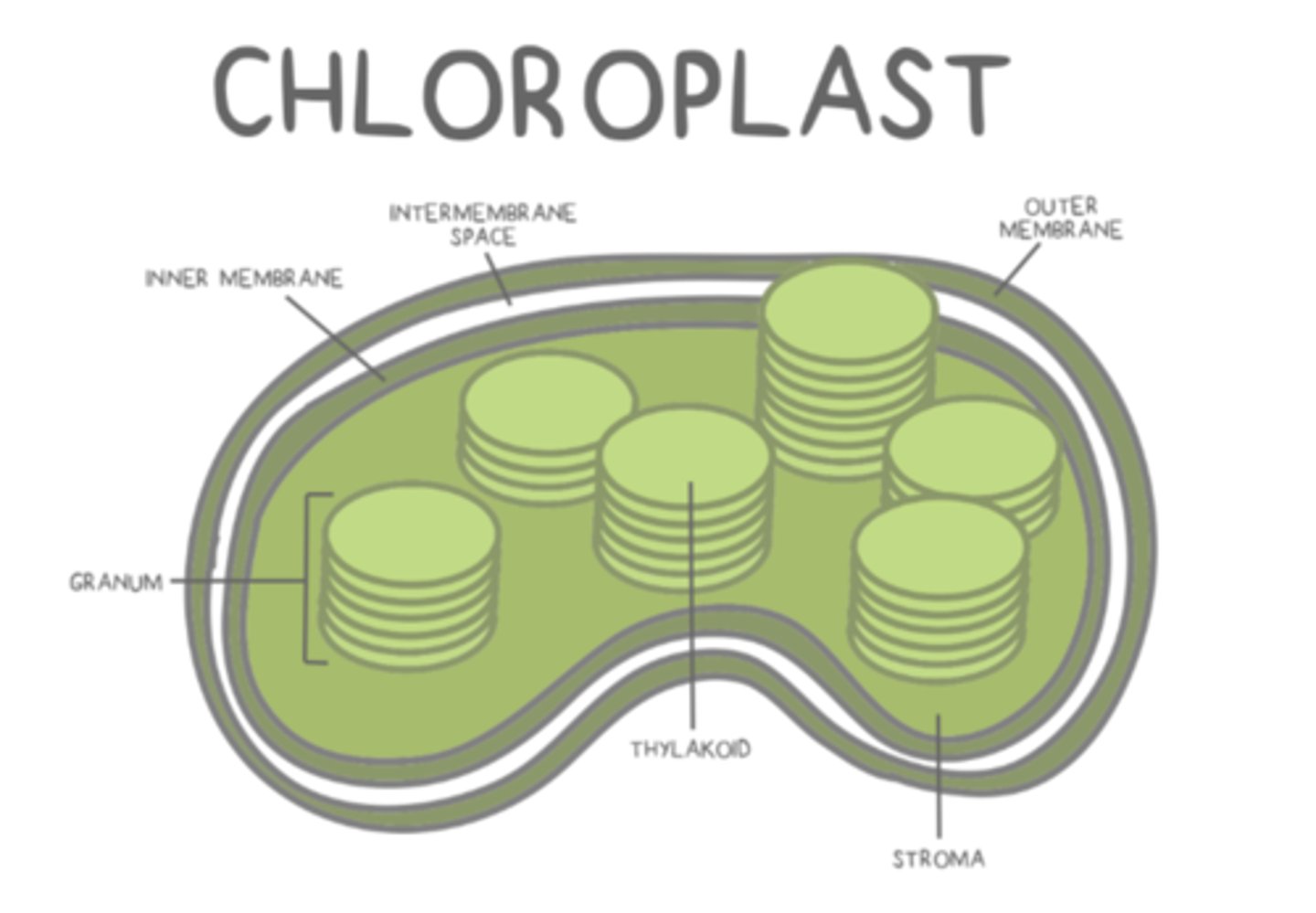
_____ are dual membrane organelles found in plants and photosynthetic algae
chloroplasts
organisms with chloroplasts for photosynthesis will have _____ for cellular respiration too
mitochondria
chloroplasts contain thylakoids, where _____ occur
light dependent reactions
both stages of photosynthesis occur within _____
chloroplasts
_____ are photosynthetic organisms that do not have a chloroplast
cyanobacteria
the _____ is the fluid material that fills area inside the inner membrane of a chloroplast
stroma
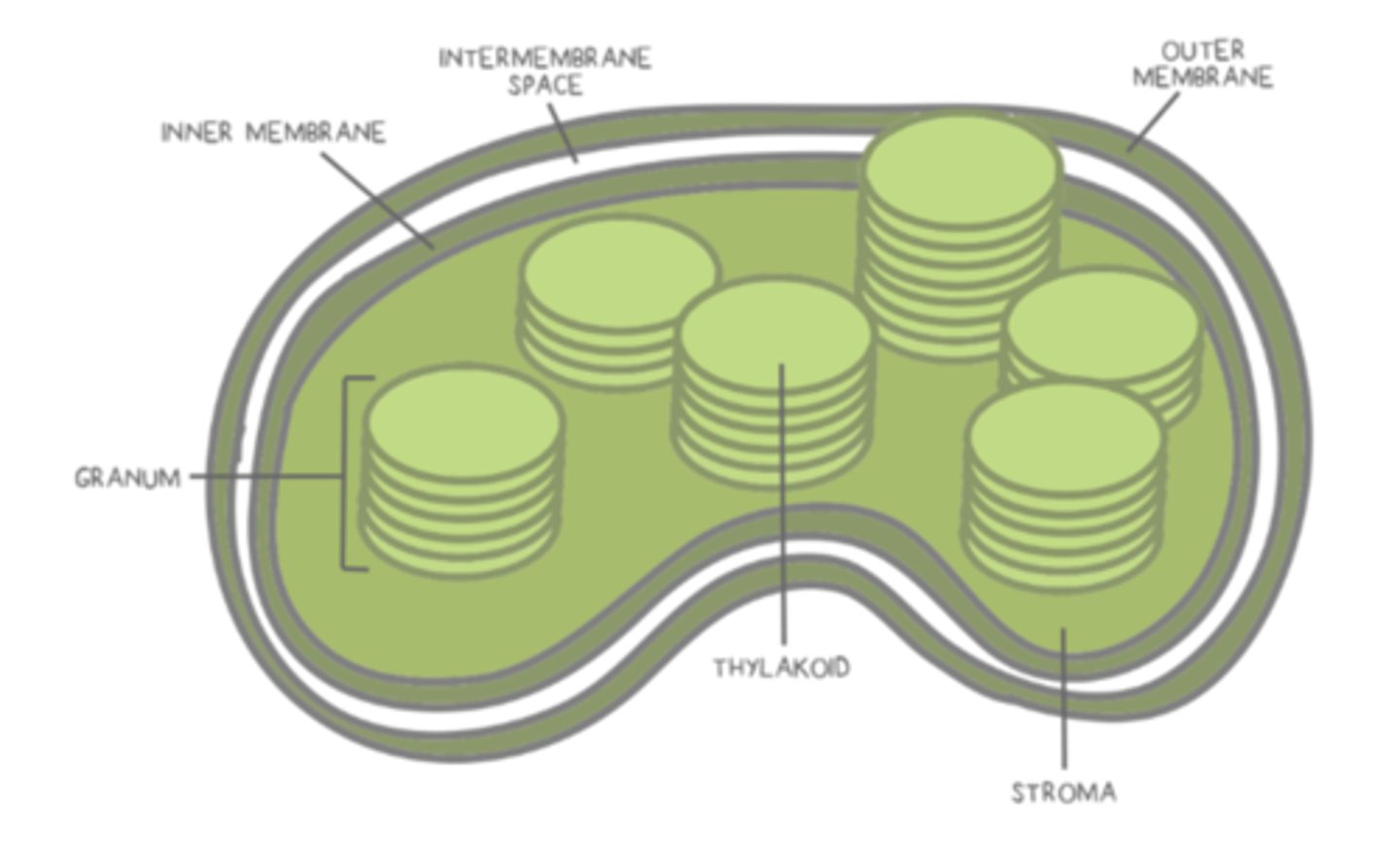
the Calvin cycle occurs in the _____ of the chloroplast
stroma
_____ are phospholipid bilayer structured organelles that are suspended within the stroma
thylakoids
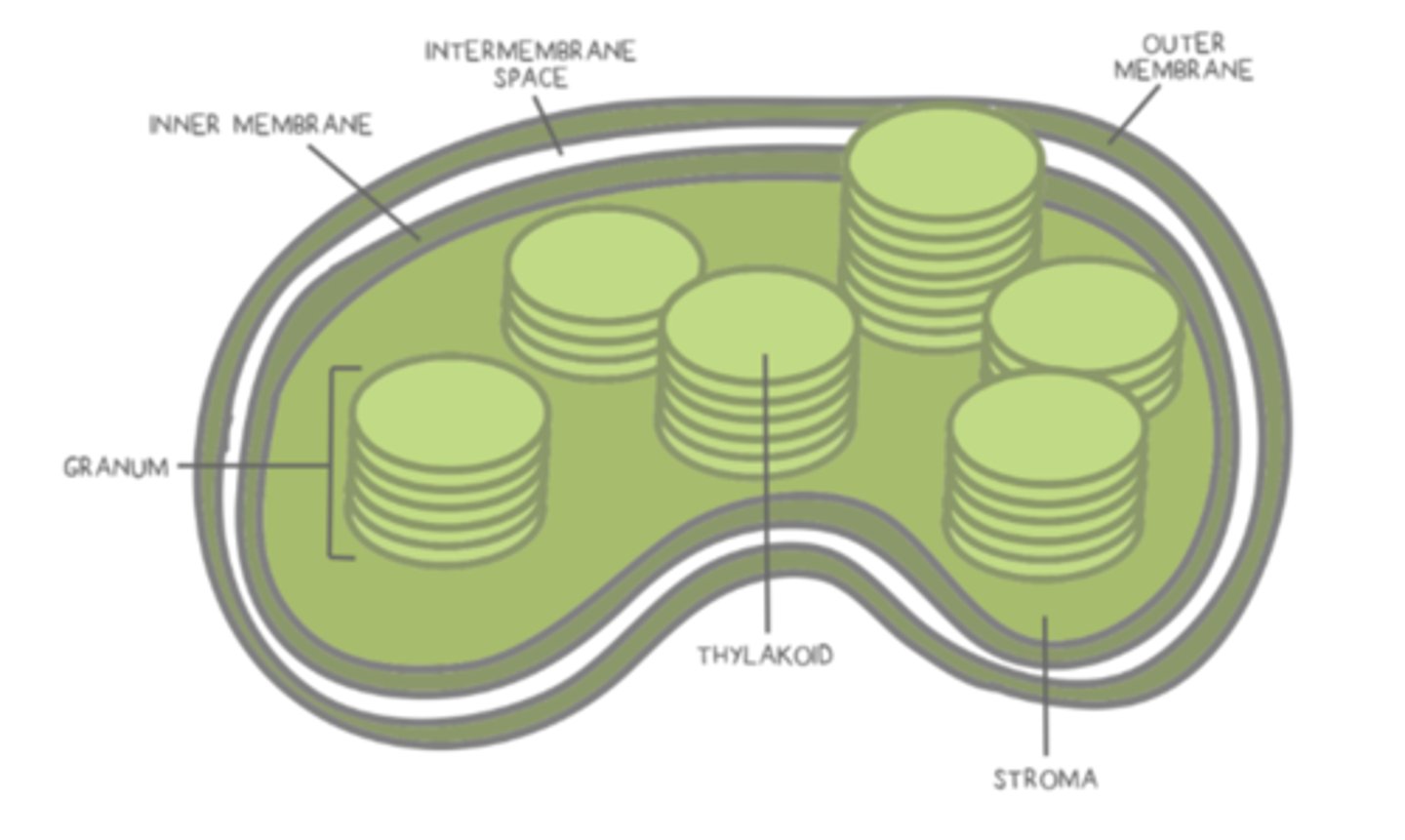
Light dependent reactions occur in the _______ of chloroplasts
thylakoid membranes
an entire stack of thylakoids is called a _____
granum
a junction between two grana is called a _____
lamella
protons (H⁺) for chloroplast chemiosmosis accumulate in the _____
thylakoid lumen
ATP synthesis in the chloroplast occurs as protons (H⁺) flow from the _____ to the _____
thylakoid lumen; stroma
thylakoid membranes have _____ to capture photons
photosystems
photosystems contain special _____, including chlorophylls and carotenoids
pigments
photosystem _____ are directly responsible for absorbing photons
pigments
what are the 2 important photosystems for photosynthesis?
photosystem I and II
photosystems I and II each have a _____ of chlorophyll molecules located in the center of the protein. This is known as the _____
special pair; reaction center
the special pair of chlorophyll molecules in photosystem I is known as _____
P700
the special pair of chlorophyll molecules in photosystem II is known as _____
P680
_____ of water involves the splitting of H₂O molecules into electrons (e⁻), protons (H⁺), and oxygen gas (O₂)
photolysis
where do the electrons (e⁻) from photolysis travel to in photosystem II?
they travel to the special pair at P680 of photosystem II (the reaction center)
When photons reach photosystem II, they will excite electrons (e⁻) at the _______. This causes the electrons (e⁻) to be passed to a primary __________
reaction center; electron accepter
as electrons (e⁻) travel down the primary electron transport chain (ETC) of the thylakoid membrane, they release energy that is used for _____ into the _____ from the stroma.
pumping protons (H⁺); thylakoid lumen
after traveling down the primary electron transport chain (ETC) of the thylakoid membrane, electrons (e⁻) will reach _____
photosystem I (P700 special pair - reaction center)
what is the purpose of the secondary ETC (following PSI) in the light-dependent reactions?
to reduce NADP+ --> NADPH using NADP+ reductase
describe the general pathway of non-cyclic photophosphorylation:
photolysis → Photosystem II (P680) → primary ETC→ Photosystem I (P700) → secondary ETC → NADP+ reductase to make NADPH
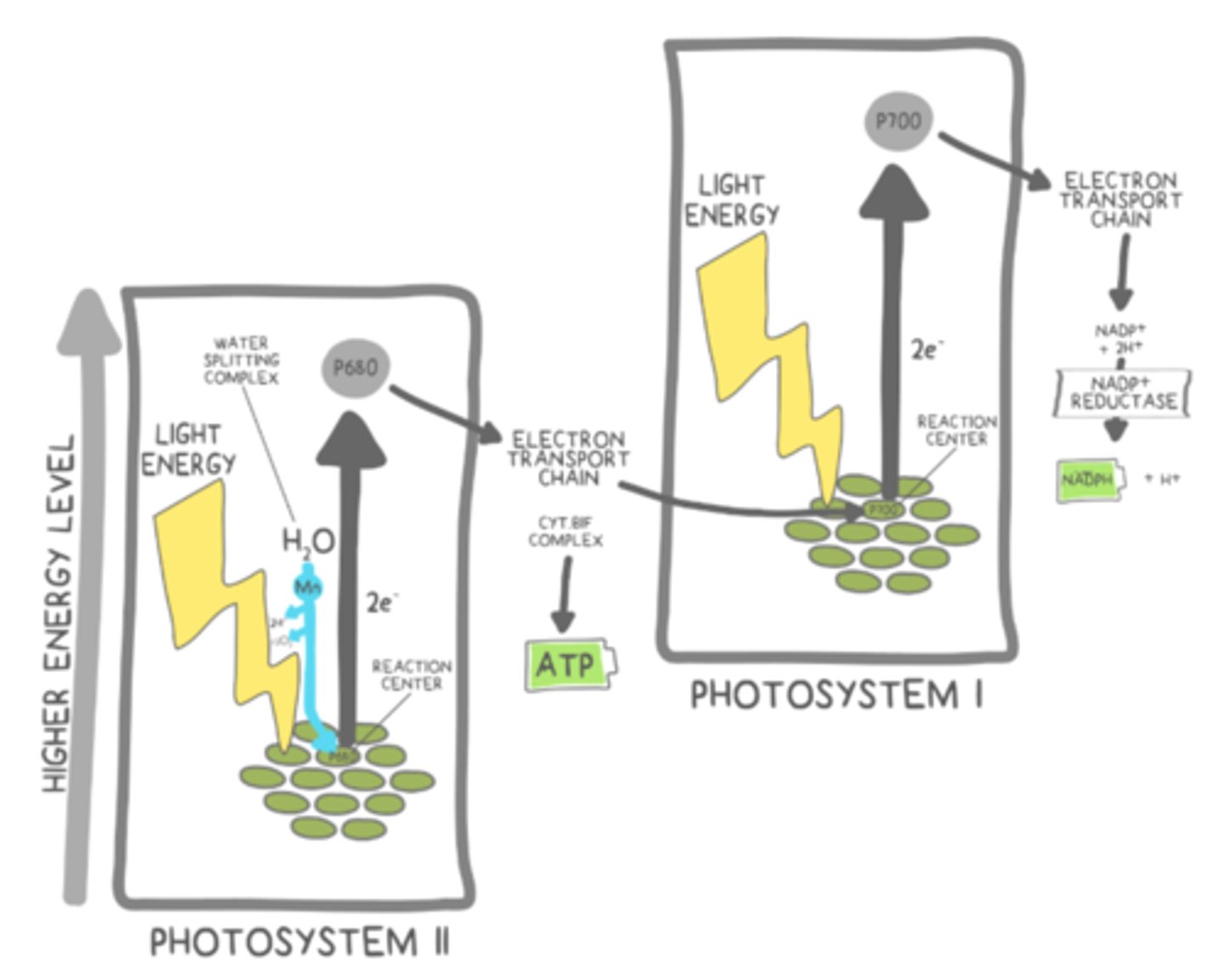
non-cyclic photophosphorylation requires light (photons) to be absorbed _____ - one time at each photosystem
twice
electrons (e⁻) do not travel to the _____ in cyclic photophosphorylation, thus _____ is not produced
second ETC; NADPH
describe the general pathway for cyclic photophosphorylation:
photolysis → Photosystem II (P680) → primary ETC → Photosystem I (P700) → primary ETC → Photosystem I (P700) → etc.
what are the products of the light dependent reactions?
ATP and NADPH, O₂ (waste product)
'normal' photosynthesis can also be called _____ because the carbon fixation step of the Calvin cycle produces three-carbon molecules
C3 photosynthesis
what are the products of the Calvin cycle?
Glucose, ADP, NADP+
the Calvin cycle is sometimes referred to as the _____ because it does not use light energy directly
light independent reactions
the _____ cannot occur without light because it is dependent on the high energy molecules produced from the light reaction (ATP and NADPH)
Calvin cycle
the Calvin cycle fixes _____ into _____
inorganic carbon dioxide; organic glucose sugars
the Calvin cycle must accept _____ CO₂ molecules to synthesize _____ glucose molecule.
6 CO₂; 1 C₆H₁₂O₆ (glucose)
list the 4 steps of the Calvin cycle in order:
carbon fixation; reduction of a 3-carbon intermediate; regeneration of RuBP; carbohydrate synthesis
describe the carbon fixation step (step 1) of the Calvin cycle with an equation and in words:
6 CO₂ + 6 RuBP → 12 PGA
catalyzed by RuBisCo
CO₂ (one-carbon) combines with RuBP (five-carbons) to produce a six-carbon molecule that splits into 2 PGA molecules (three-carbons per PGA molecule)
describe the reduction step (step 2) of the Calvin cycle with an equation and in words:
12 ATP + 12 NADPH converts 12 PGA → 12 G-3-P
ATP from the light dependent reactions will phosphorylate the PGA from carbon fixation to produce another three-carbon intermediate.
NADPH from the light dependent reactions reduces the three-carbon intermediate to produce G3P sugars
describe the regeneration step (step 3) of the Calvin cycle with an equation and in words:
6 ATP converts 10 (of the 12) G-3-P → 6 RuBP
Some G3P will be used to regenerate RuBP so that the cycle can continue. This requires ATP from the light dependent reactions.
Alternatively, some G3P will be saved for step 4 of the Calvin cycle.
describe the carbohydrate (glucose) synthesis step (step 4) of the Calvin cycle with an equation and in words:
2 G3P → 1 glucose
The 2 remaining G3P (three-carbon molecule) that were leftover from step 3 are used to build glucose (six-carbon molecule).
RuBisCo can also bind _____ in a process called _____
oxygen; photorespiration
plants in hot and dry environments ____ their stomata to minimize _____. This results in ____ not being able to leave and ____ not being able to enter the leaf.
close; water loss; oxygen; carbon dioxide
when plants in hot and dry environments _____ their stomata, RuBisCo is encouraged to bind _____ and photorespiration starts to occur
close; oxygen
the byproducts of photorespiration are metabolized by _____ & _____
peroxisomes; mitochondria
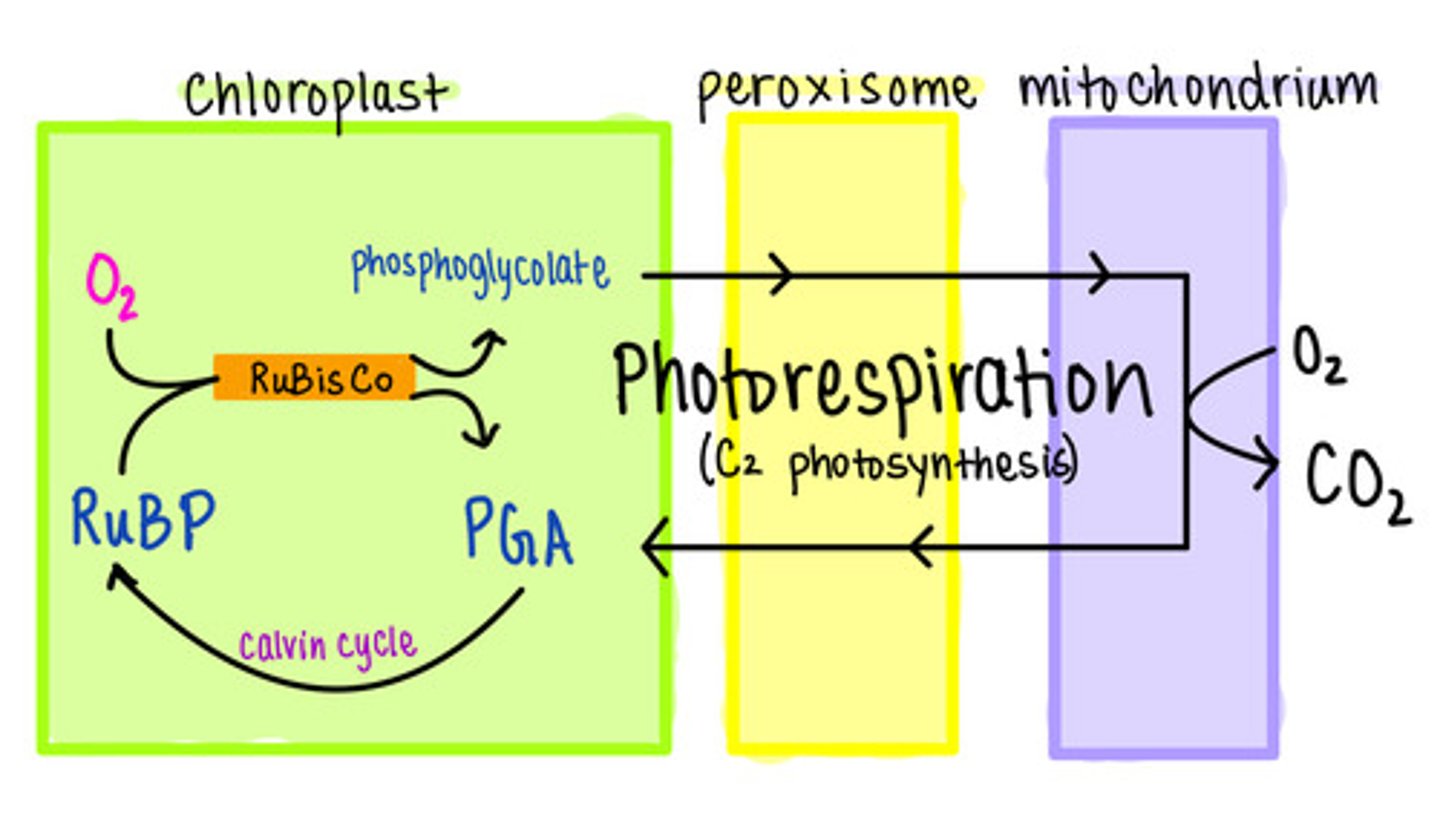
what are 2 mechanisms plants have evolved to minimize photorespiration?
C4 photosynthesis and CAM (crassulacean acid metabolism) photosynthesis
In the mesophyll cell, C4 photosynthesis uses an enzyme called _____, which fixes CO₂ into a three-carbon molecule called _____
PEP carboxylase; PEP
in C4 photosynthesis, CO2 + PEP in the presence of PEP carboxylase makes _____ at the mesophyll cell
oxaloacetate
in C4 photosynthesis, oxaloacetate quickly converts to _____ at the mesophyll cell
malate
C4 photosynthesis is called C4 because..?
both oxaloacetate and malate are 4 carbon compounds
in C4 photosynthesis, malate is transported from _____ cells to _____ cells
mesophyll; bundle sheath
the CO₂ released at the bundle sheath cell of C4 photosynthesis can undergo carbon fixation using _____
RuBisCo
what is the advantage of bundle sheath cells in C4 photosynthesis?
they do not contain as much O₂, so photorespiration is less likely to occur
what happens to the three-carbon pyruvate at the bundle sheath cell of C4 photosynthesis?
it is shuttled back to the mesophyll cell alongside the hydrolysis of ATP → AMP
what does pyruvate convert into when back at the mesophyll cell of C4 photosynthesis?
PEP
C4 photosynthesis occurs in a small percentage of plants living in _____ environments
hot
C4 photosynthesis prevents photorespiration through the _____ of carbon dioxide
spatial isolation
_____ means that inorganic carbon is transported to a different location to prevent photorespiration
spatial isolation
CAM plants use _____, which prevents photorespiration through timing
temporal isolation
CAM plants close their stomata during the ___ to prevent transpiration
day
At ____, CAM plants have their stomata open, allowing carbon dioxide to enter the leaf
night
after CO₂ diffuses into the mesophyll of CAM plants (at night), what happens?
PEP carboxylase will take
CO₂ (one-carbon) + PEP (three-carbon) to produce oxaloacetate (four-carbon), which converts to malate (four-carbon)
what happens to the four-carbon malate molecule produced in CAM photosynthesis?
it is stored in the vacuole of the mesophyll cell for later use
in CAM photosynthesis, during the next day when the stomata are ______, malate will convert back into ________
closed; oxaloacetate
the overall advantage is that CAM photosynthesis can proceed during the day while stomata are _____ (reducing _____ loss)
closed; water (H₂O)