chapter 21: the proton motive force
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
chemiosmotic theory
proposal that electron transport and ATP synthesis are coupled by a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane
matrix, intermembrane space
there is a low H+ concentration in the ____________ and high H+ concentration in the ________________
intermembrane space, matrix
protons are being pumped from __________ to ____________
proton motive force
the energy-rich and unequal distribution of protons is called _______________
chemical and charge gradient
two components of the proton-motive force
downhill, uphill
membrane must contain proteins that couple the __________ flow of electrons in the ETC with the __________ flow of protons across the membrane
F0 subunit
subunit of ATP synthase that acts as a proton channel, allowing H+ to flow back into the mitochondrial matrix
F1 subunit
subunit of ATP synthase that is the catalytic site where ATP is synthesized
embedded in inner mitochondrial membrane
where is F0 subunit located?
resides in the matrix
where is the F1 subunit located?
matrix
protons exit into the ______ through ATP synthase
-
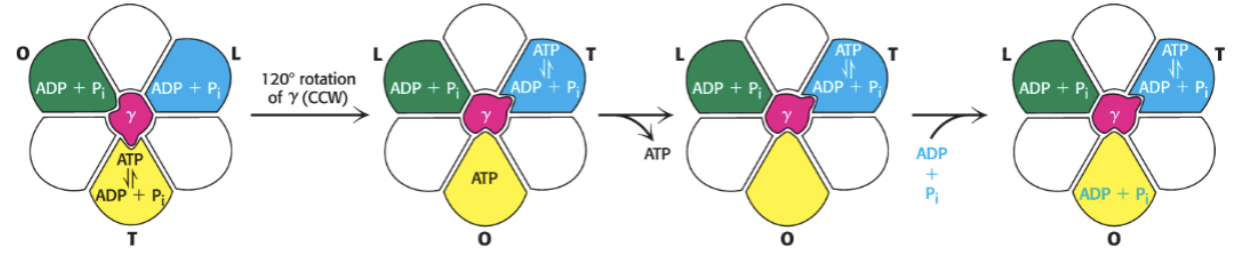
write out mechanism of ATP synthesis using the O, L, and T forms
gamma, beta
the rotation of the ______ unit interconverts the ______ subunits
a, c ring
the __ unit remains stationary as the ______ rotates
intermembrane space, cytoplasmic half, glutamine, asparate, c
matrix half
matrix
A proton enters from the ___________ into the _____________ channel to neutralize the charge on a ___________ or ___________ residue in a __ subunit
with this charge neutralized, the c ring can rotate clockwise by one subunit, moving the amino acid residue out of the membrane into the ___________ channel
this proton can move into the _________, resetting the system to its initial state
-
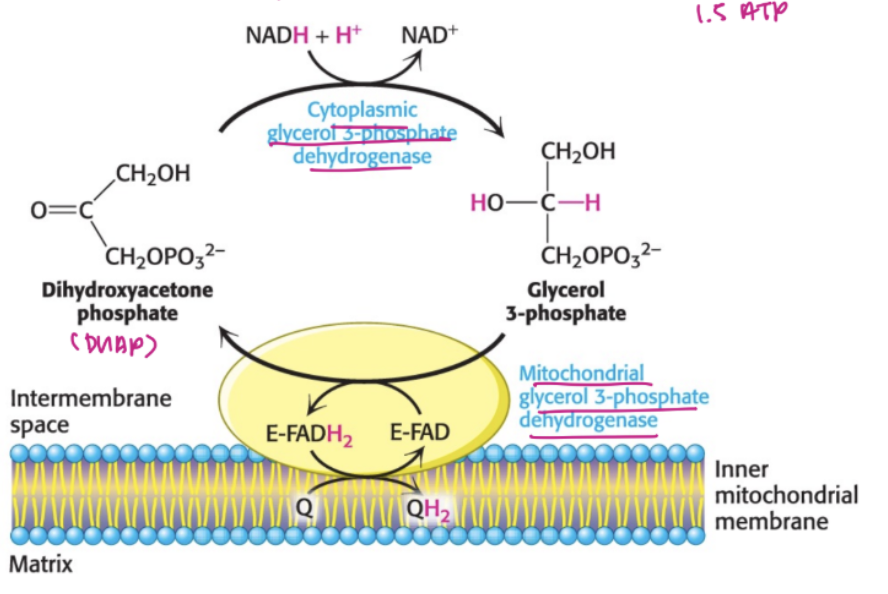
draw out G3P shuttle mechanism
-
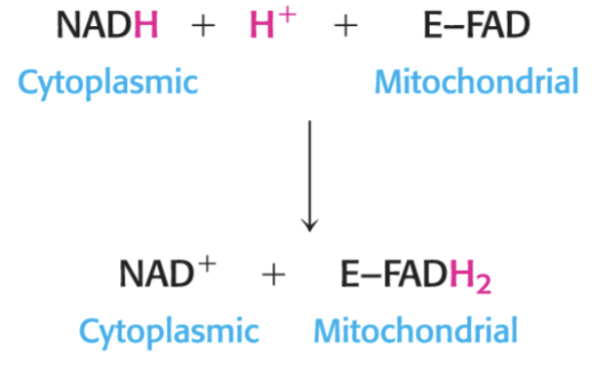
write out equation for G3P shuttle reaction
1.5
cytoplasmic NADH transported by G3P shuttle yields ___ ATP
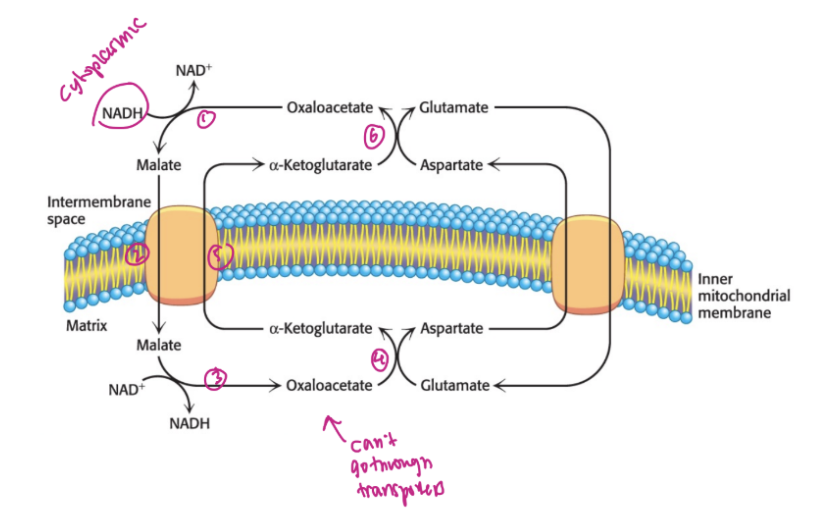
malate-asparate shuttle
in the heart and liver, electrons from cytoplasmic NADH are used to generate mitochondrial NADH through the _________________
-
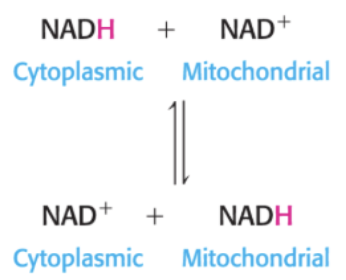
write out equation for malate-asparate shuttle reaction
-
draw out mechanism for malate-asparate shuttle
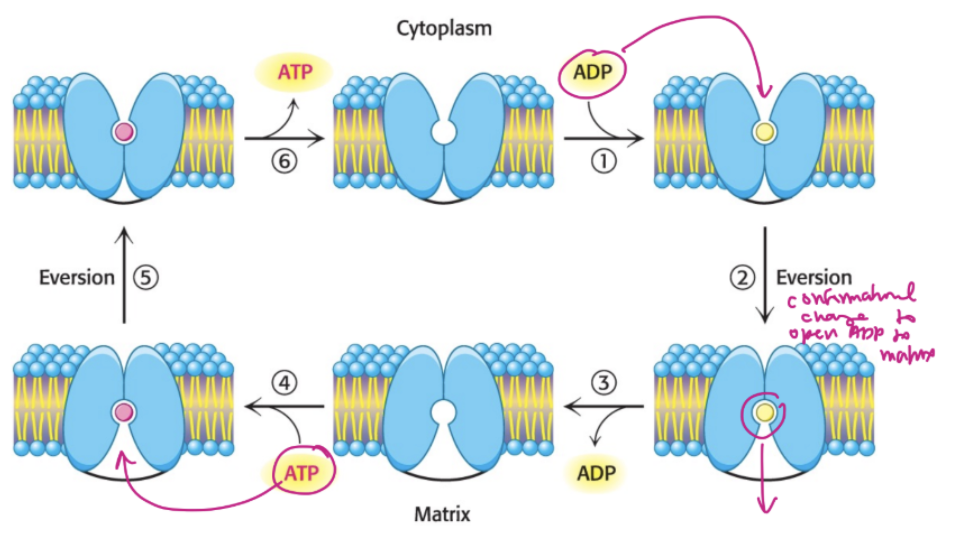
ATP-ADP translocase
enables the exchange of cytoplasmic ADP for mitochondrial ATP
-
write out mechanism of mitochondrial ATP-ADP translocase
26
how many molecules of ATP made in oxidative phosphorylation
~30
number of ATP molecules generated by the complete combustion of glucose
respiratory control/acceptor control
regulation of the rate of oxidative phosphorylation by the ADP level is called __________________