resolving legal disputes
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is the magistrates court?
Court that deals with summary offences (petty offences that can only be tried by the magistrates) or offences triable either way / hybrid offences
Offences triable either way / hybrid offences
A criminal offence that can either be tried in the magistrates court or crown court
How is the venue of a hybrid offence trial decided?
The choice of the defendant
What are the justice of the peace (JPs)
Lay (not legally qualified) magistrates
Who hears bail and legal applications in magistrates court?
By the magistrates
What is the maximum sentence and or fine the magistrate court can sentence?
Imprisonment for up to 12 months as of 2 may 2022 and a fine of up to 5000 pounds
What are some of the additional ppwers that the magistrate court has?
License payments for alcohol and provide betting services
Enforce the payment of council tax, business rates, and bills
who primarily staffs the crown court
high court judge
circuit judges
recorders
in what instances does the crown court have criminal jurisdiction?
indictable offences
sentencing cases from the magistrates court
legal aid and bail applications
appeals
who hears an appeal
a recorder sitting with a bench of justices of the peace
who staffs the county court
circuit judges and district judges
what is ithe jurisdiction of the county court
it purely civil, with examples including:
contract
tort
recovery of land
trusts
mortgages and partnerships
contested wills
divorce
bankruptcy
company insolvency
what act made it allowable for a high court case to be tried in the county court
The Courts and Services Legal Act 1990 (CLSA 1990)
What cases are allowed to be tried in county court
all actions worth up to £25000 and any personal injury case worth under £50000; unless its specialist nature or complexity makes trial in the high court appropriate
what is the high courts principal venue?
Royal Courts of Justice London
what are the 3 divisions of the high court
the Queen’s Bench
chancery
family
what isthe Queen’s Bench division concerned with
trial of cases in contract and tort, also contains the commercial court
what is the chancery division concerned with
tries cases in copyright, patent and design rights, bankruptcy, dissolution of partnerships, sales of land, trusts, mortgages and disputed wills
who is the court off appeal staffed by
lord and lady justices of appeal, and cases are heard by. a bench of 3-5 judges
what jurisdiction does the civil division of the court of appeal have?
to hear appeals against the decisions of the county and high court. it also hears tribunals.
what jurisdiction does the criminal division of the court of appeal have?
The Criminal Division of the Court of Appeal has jurisdiction to hear appeals from Crown Court trials. (Note that the Court of Appeal cannot hear an appeal from the Crown Court where that court has itself been exercising its own appeals jurisdiction regarding cases from the Magistrates’ Court. The only further avenue for such appeals is the Queen’s Bench Divisional Court.)
under what act did the Supreme Court replace the House of Lords and when?
the constitutional reform act 2005
what is the leap frog procedure
enables a case tried in the High Court to bypass the Court of Appeal and go straight to the Supreme Court for the appeal hearing.
what is the first step of the civil litigation procedure?
issuing a letter of claim
what’s the second step of the litigation process
issue of claim, only happens if both parties fail to settle the issue. the claimant fills in a claim form and particulars of claim setting out the details of the claim
state and explain the 3rd step in the civil litigation process
the defendant either accepts or denies the claim
On receipt of a claim form with the particulars of a claim, a
defendant must acknowledge receipt within 14 days and
either admits the claim or puts in a defence within 28 days.
The defence must state which of the allegations in the
particulars of the claim the defendant denies, giving reasons,
and which allegations the defendant admits.
Should a defendant receive a claim form and ignore it, after
14 days the claimant can enter judgment against the
defendant for the sum specified in the claim form.
state and explain the 4th stage of the civil litigation process
the case is allocated to the relevant track
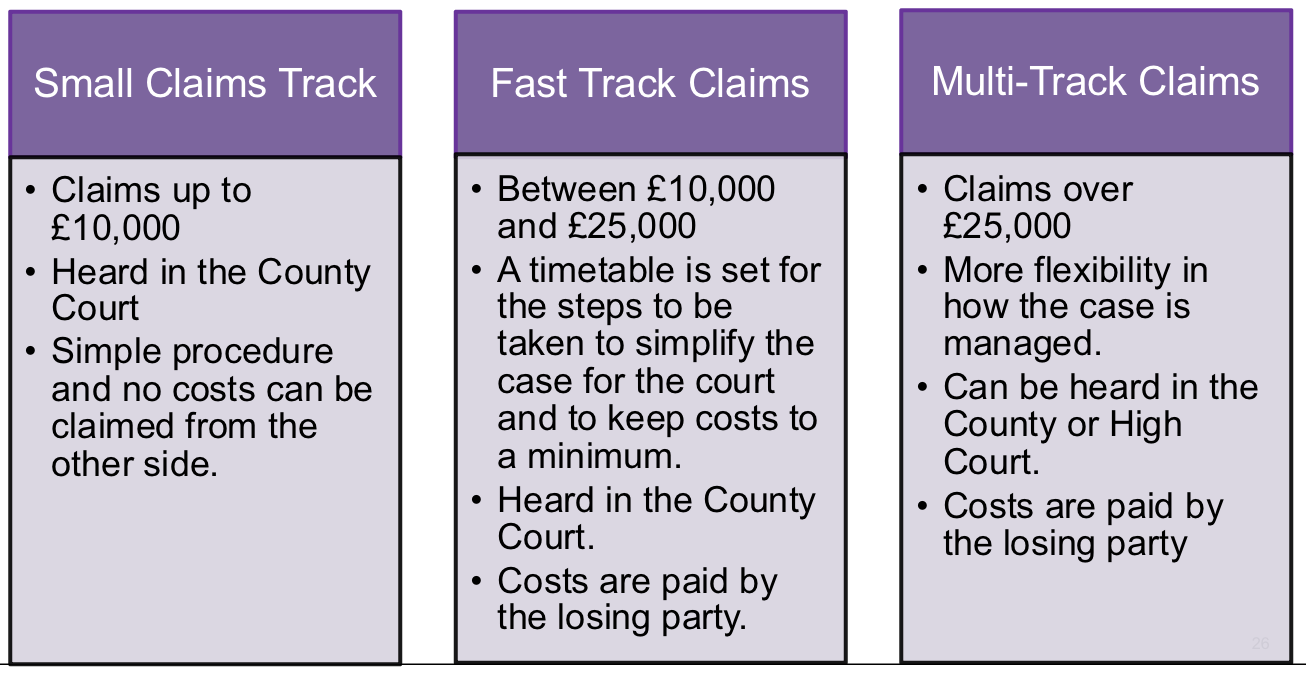
what are the relevant tracks concerning the 4th stage of the civil litigation process
small claims track
fast track claims
multi track claims
explain each track
state and explain the 5th stage of civil litigation
the interlocutory stages, These stages are the pre-trial stages.
The judge may give each party directions as to the steps to
be taken to prepare for the trial.
what is the 6th stage of the civil litigation process
the trial
state and explain the 7th stage of the civil litigation process
executing the judgment - The losing party will be expected to pay the sums due by a
date set by the court.
If the defendant does not pay then the winning side may
have to apply to the court to enforce the judgment.
the court has powers to award which set of orders
distraint order (siezing a companies assets)
a charging order ( debt is secured by taking away property)
attachment of earnings
3rd part debt order (freezes money held by a 3rd party and then the money is paid directly to the winner)
insolvency proceedings
what is commercial arbitration
Arbitration is the procedure by which the parties refer their
disputes to a third party or parties to be resolved, rather than
taking their dispute to a court.
The parties agree to be bound by the decision of the arbitrator
When drafting legal contracts an arbitration clause is often
included. This states that in the event of a dispute the parties
will refer the matter to arbitration to find a solution.
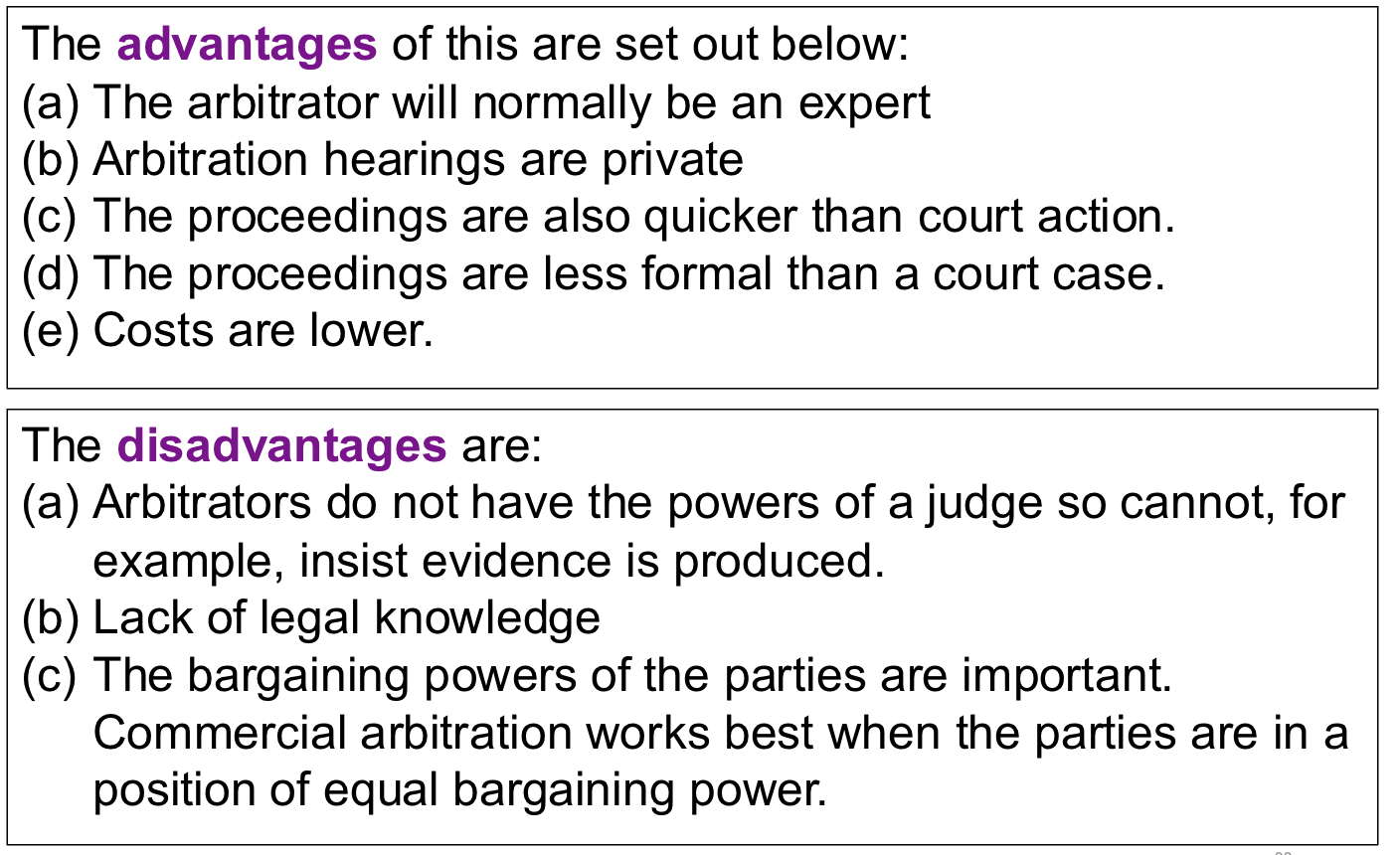
list the advantages and disadvantages of commercial arbitration
what principles does section 1 of the arbitration act 1996 say it was founded on

what are the Ombudsmen Services
if the dispute falls into either the legal, banking, insurance or
financial services then the ombudsmen service can
investigate and resolve problems
what is conciliation
Conciliation is less formal than mediation. The conciliator
assists the parties to explore all possible solutions for settling
the dispute and points out the positive and negative
consequences of the different solutions
what is mediation
Mediation is conducted in private at a time and place to suit
the parties.
The mediator is appointed by the parties and is trained as a
mediator.
He may or may not be legally qualified. The mediator acts as
a facilitator through which the disputing parties can
communicate and negotiate.
Mediators can move between the parties without the parties
meeting—they just communicate through the mediator.
Alternatively, the mediator can operate in the presence of the
parties
differences between conciliation and mediation
In mediation, it is the parties themselves who determine their
own solution; however, in conciliation, the conciliator can
suggest different options to the parties. If conciliation fails the
parties may bring their dispute before a court
advantages of tribunals
cheaper than court
informal
quick
flexible
persons sitting on tribunals have expert knowledge in the subject area
disadvantages of tribunals
can be difficult to get legal aid which may result in an imbalance of power
become more formal over time
urgent cases aren’t resolved quickly enough
little publicity meaning it may be harder to find the outcomes of similar cases
what is overruling
when an appeal court believes that a
precedent no longer represents the law, in this case the
precedent is overruled with a new precedent
what is distinguishing
it allows a court to avoid following a previous
decision by declaring the facts before it as significantly
different enough for it not to be followed. If they distinguish
their case from a previous case it means they do not have to
follow a particular precedent
advantages and disadvantages of stare decisis
