Cellular respiration
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
cellular respiration
the process by which organic molecules, taken in as food, are broken down into the cells to release energy for cellular activities.
can release energy from glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol.
primarily glucose
cellular respiration (chemical and word equation)
Glucose + Oxygen > Carbon Dioxide + Water + 38ATP
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38 ATP
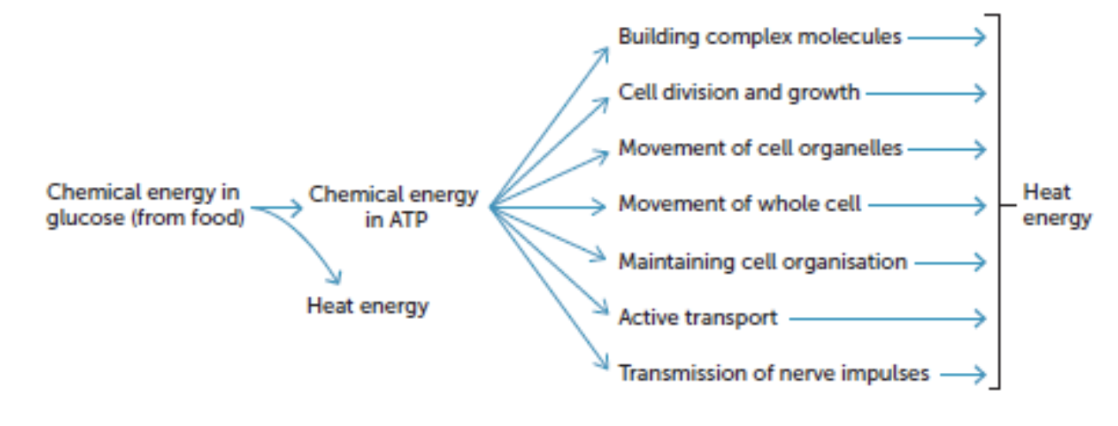
Energy from cellular respiration
around 60% of the available energy is lost to heat. cells cannot use energy but it is important as it keeps the body temperate constant.
the remaining energy is used to form a compound called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Composed of adenosine (a nucleic acid and sugar ribose) and three phosphate grounds.
ATP is used in cellular respiration
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
ATP is the primary energy molecule in cells. This high-energy molecule stores and transports energy within cells. Formed when an inorganic phosphate group is linked to a molecule of adenosine diphosphate (ADP).
Some energy from cellular respiration is stored in the bond between the ADP molecule and the third phosphate group, which is easier to break than the first and second phosphate groups, allowing for energy release when needed. ADP captures the energy released from cellular respiration.
Stages of Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis: takes place in the cytosol
Krebs Cycle: takes place in the mitochondrial matrix
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
NADH: high energy electron carrier used to transport electrons in all three steps.
Glycolysis
glycolysis is an anaerobic process > does not require oxygen
takes place in the cytosol
glucose splits and gets broken down into 2 pyruvate molecules. (pyruvate is a molecule formed from the splitting of glucose)
energy is required for this to occur, but energy is also released
4 energy released, but 2 is used.
Energy net yield is 2 ATP and 2 NADH
Krebs Cycle
Krebs cycle is an aerobic process > requires oxygen
takes place in the mitochondrial matrix
each pyruvate molecule combines with oxygen to form carbon dioxide (the pyruvate molecules are completely oxidised)
each pyruvate molecule releases 1 ATP and 3 NADH when oxidised)
net energy yield from this process is 2 ATP and 6 NADH
total energy yield: 4 ATP and 8 NADH
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
ETC is an aerobic process > that requires oxygen
Electrons are passed between molecules, resulting in oxygen molecules forming water (combining the electrons with the oxygen to create water)
the energy required to do this comes from electrons carried by 8 NADH molecules produced thus far.
estimates ATP produced ranges between 26 and 34 molecules
Total net energy produced: (2 + 2 + 34 = 38 ATP)
aerobic respiration
The complete breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water requires oxygen. The pyruvate produced from glycolysis is completely broken down into carbon dioxide and water. This is respiration requiring oxygen
This occurs in the mitochondria. To complete the breakdown of glucose, the two pyruvate molecules produced in the glycolysis must enter a mitochondrion, where enzymes are available to allow the next series of reactions to occur
Anaerobic Respiration / fermentation
Fermentation
If there is no oxygen available, the pyruvate produced is converted to lactic acid by fermentation. Lactic Acid makes its way to the liver, where oxygen is added and then the lactic acid is returned into pyruvic acid and eventually back into glucose.
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration is very important during vigorous physical activity when the respiratory and circulatory systems are unable to supply muscle cells with enough oxygen to meet all the energy demands of contracting muscles
energy used by the cell
Why oxygen?
Kreb’s Cycle & Electron Transport Chain
Oxygen is required by any organism that has mitochondria because it is used to keep the electron transport chain running