Structural Kins: Kinesiology Fundamentals
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
superior
the head is ______ to the abdomen.
inferior
the abdomen is ______ to the head.
posterior
the spine is ______ to the sternum.
anterior
the sternum is _____ to the spine.
proximal
the elbow is ______ to the wrist.
distal
the wrist is ______ to the elbow.
medial
the big toe is ______ to the last toe.
lateral
the last toe is ______ to the big toe.
superfical
The pectoralis major muscle is ______ to the ribs.
deep
The ribs are ______ to the peactoralis major muscle.
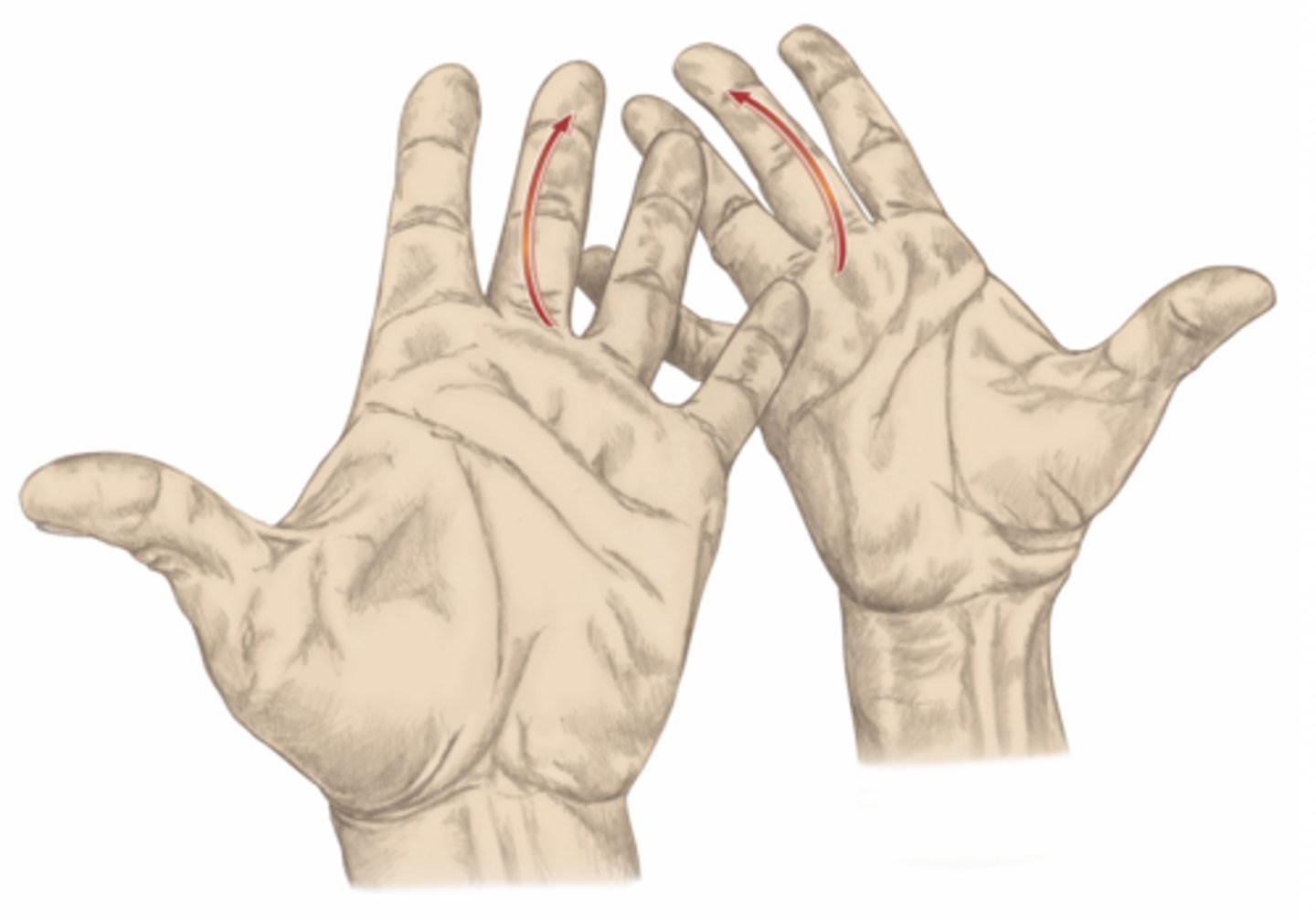
extension of the fingers
please identify the movement and its location
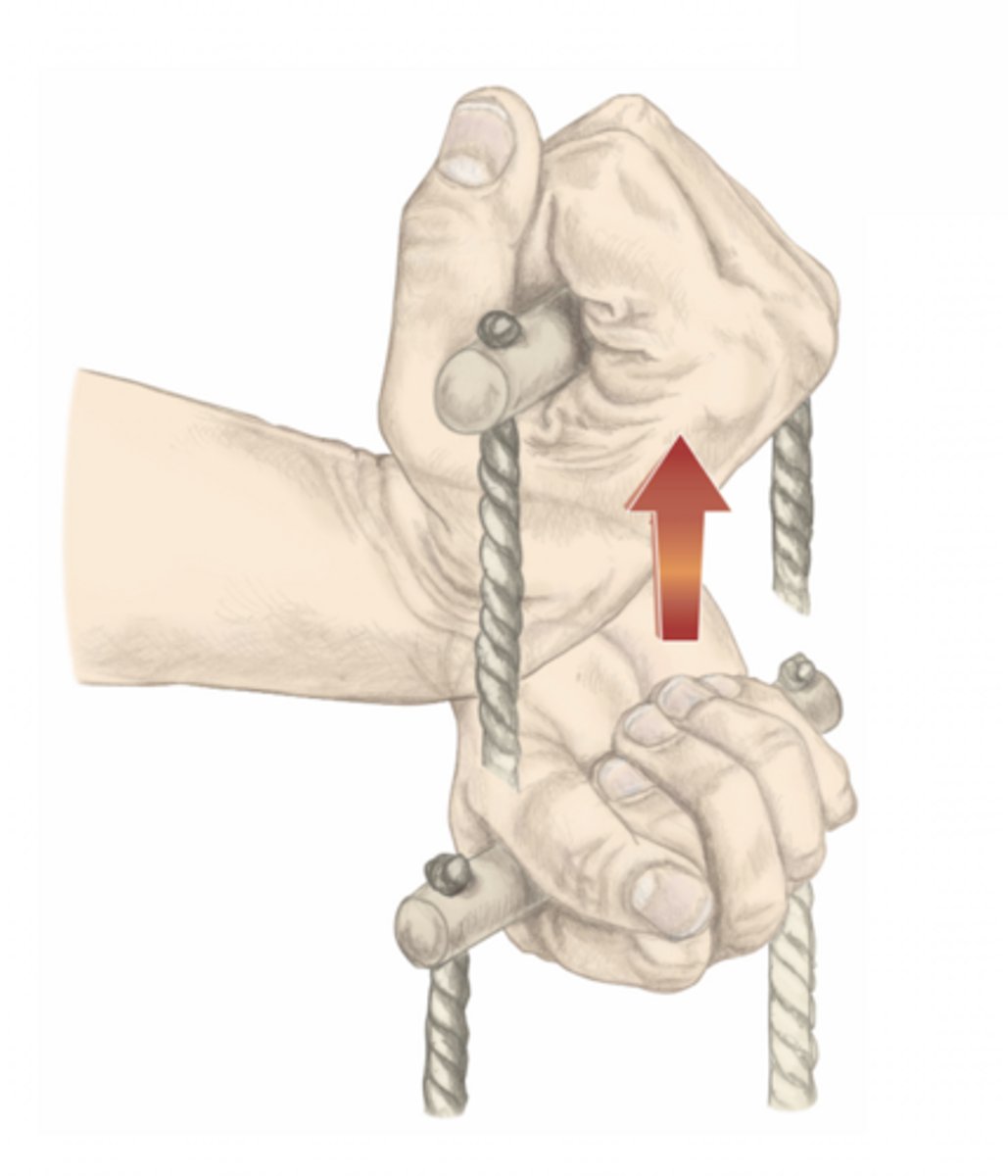
flexion of the wrist
please identify the movement and its location
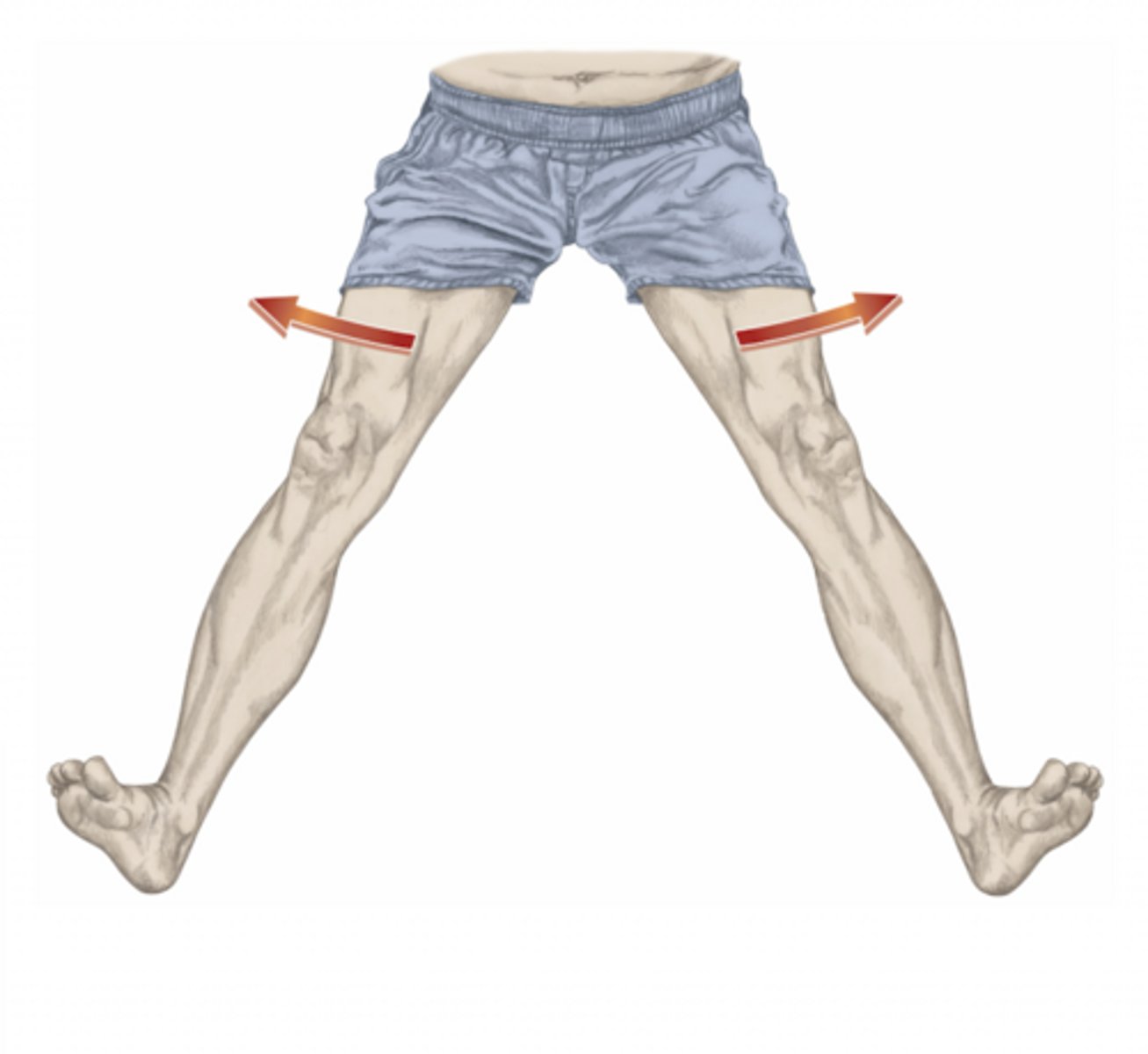
abduction of the hips
please identify the movement and its location
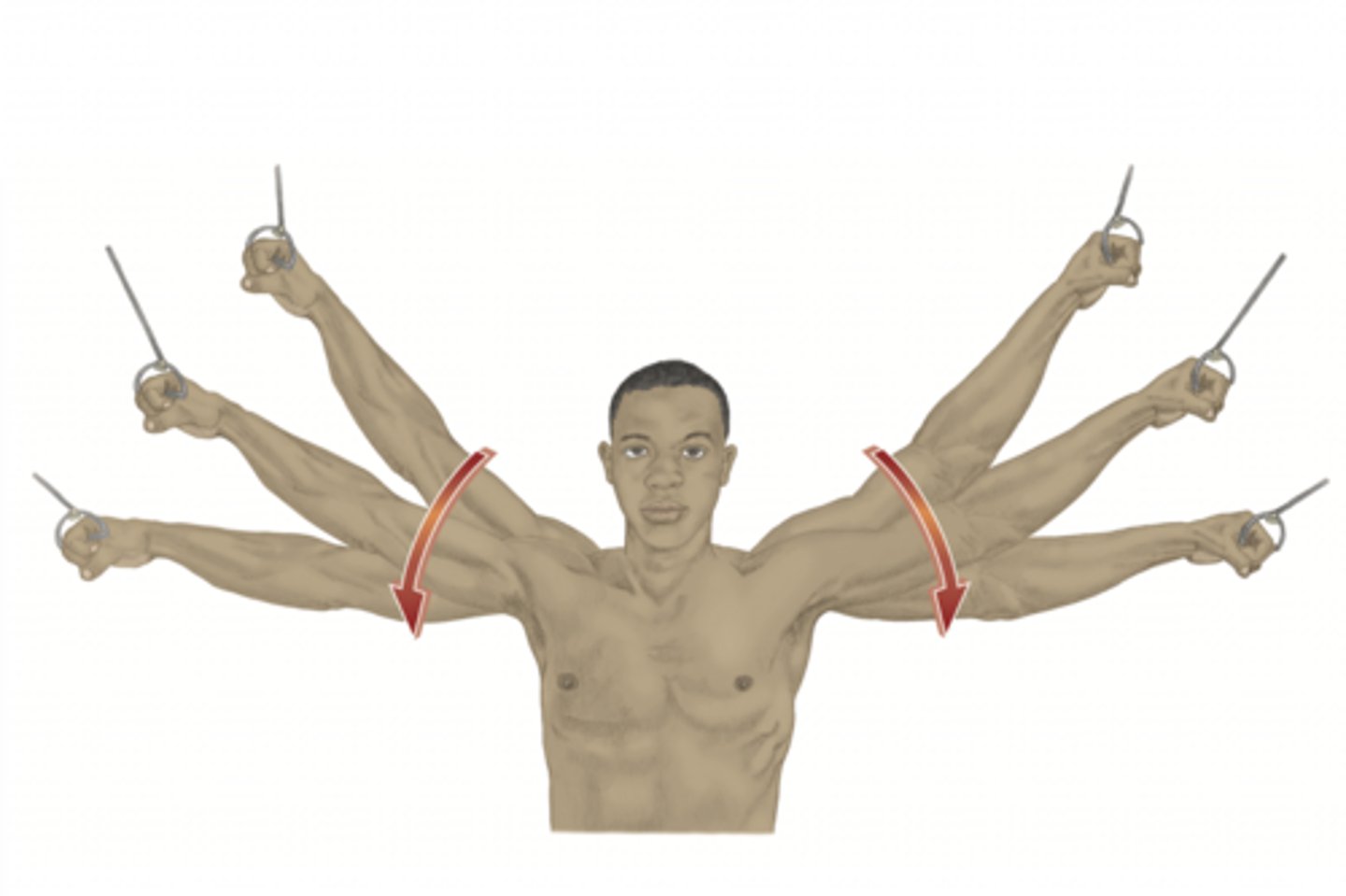
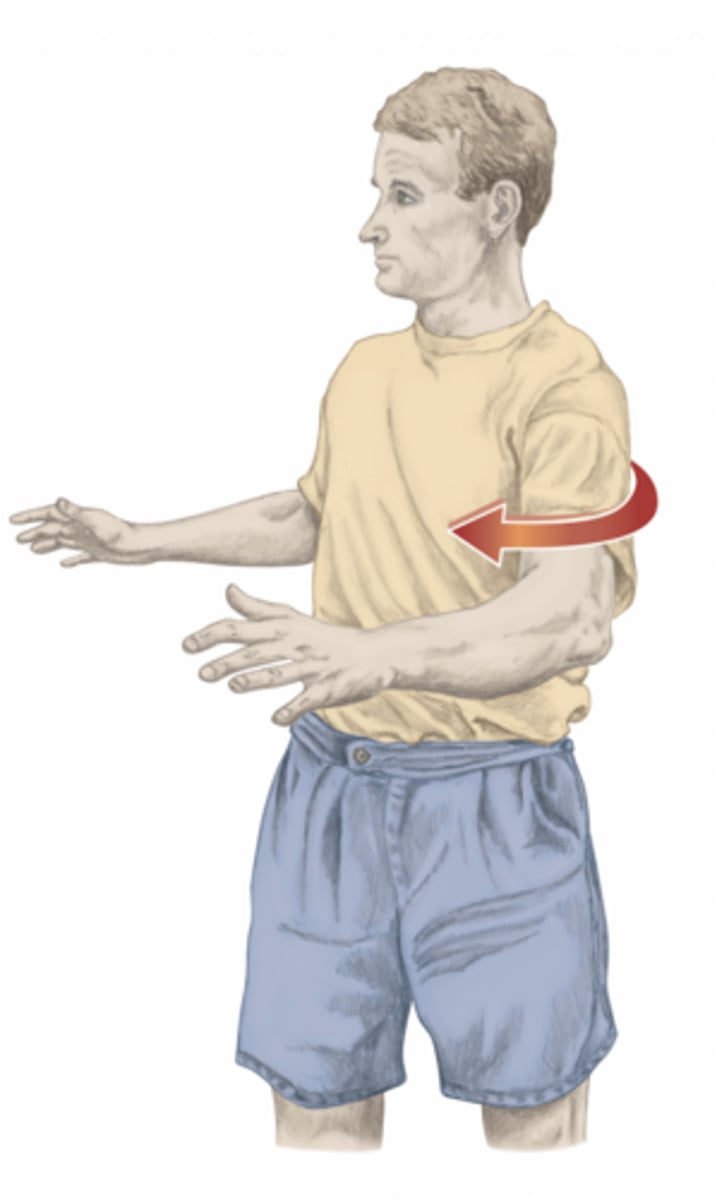
adduction of the shoulder
please identify the movement and its location
medial rotation of the hip
please identify the movement and its location
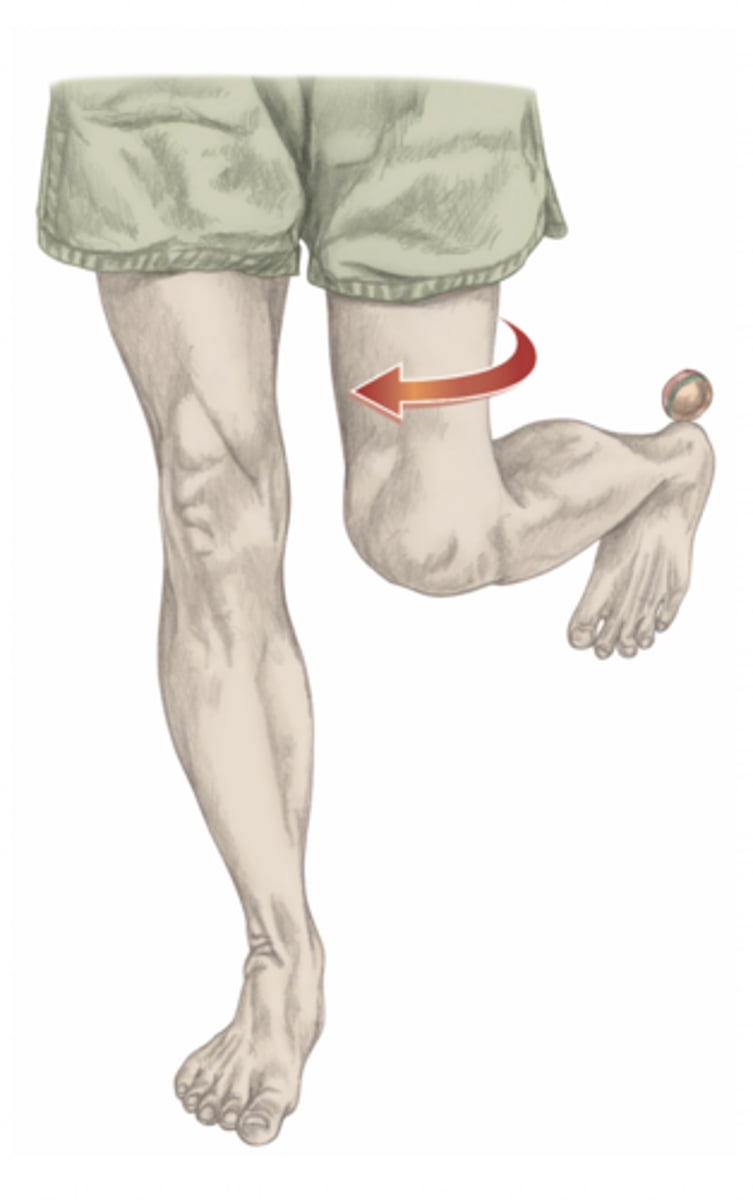
lateral rotation of the hip
please identify the movement and its location
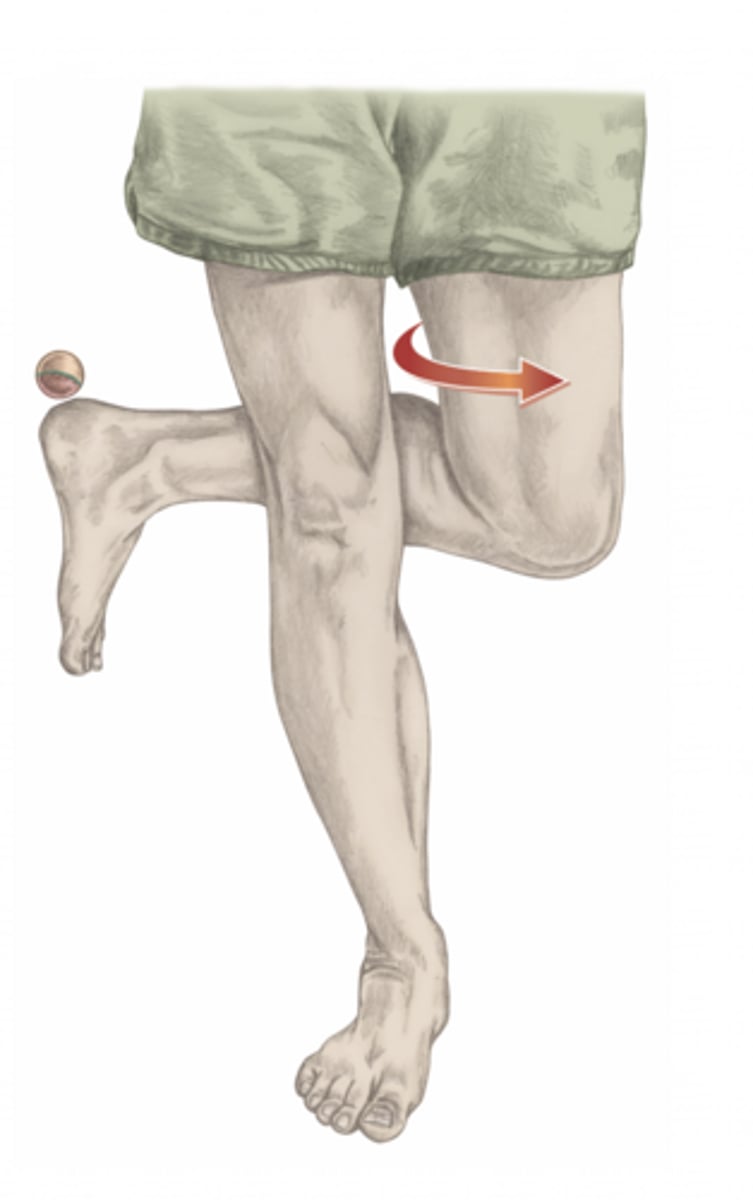
internal rotation of the shoulder
please identify the movement and its location
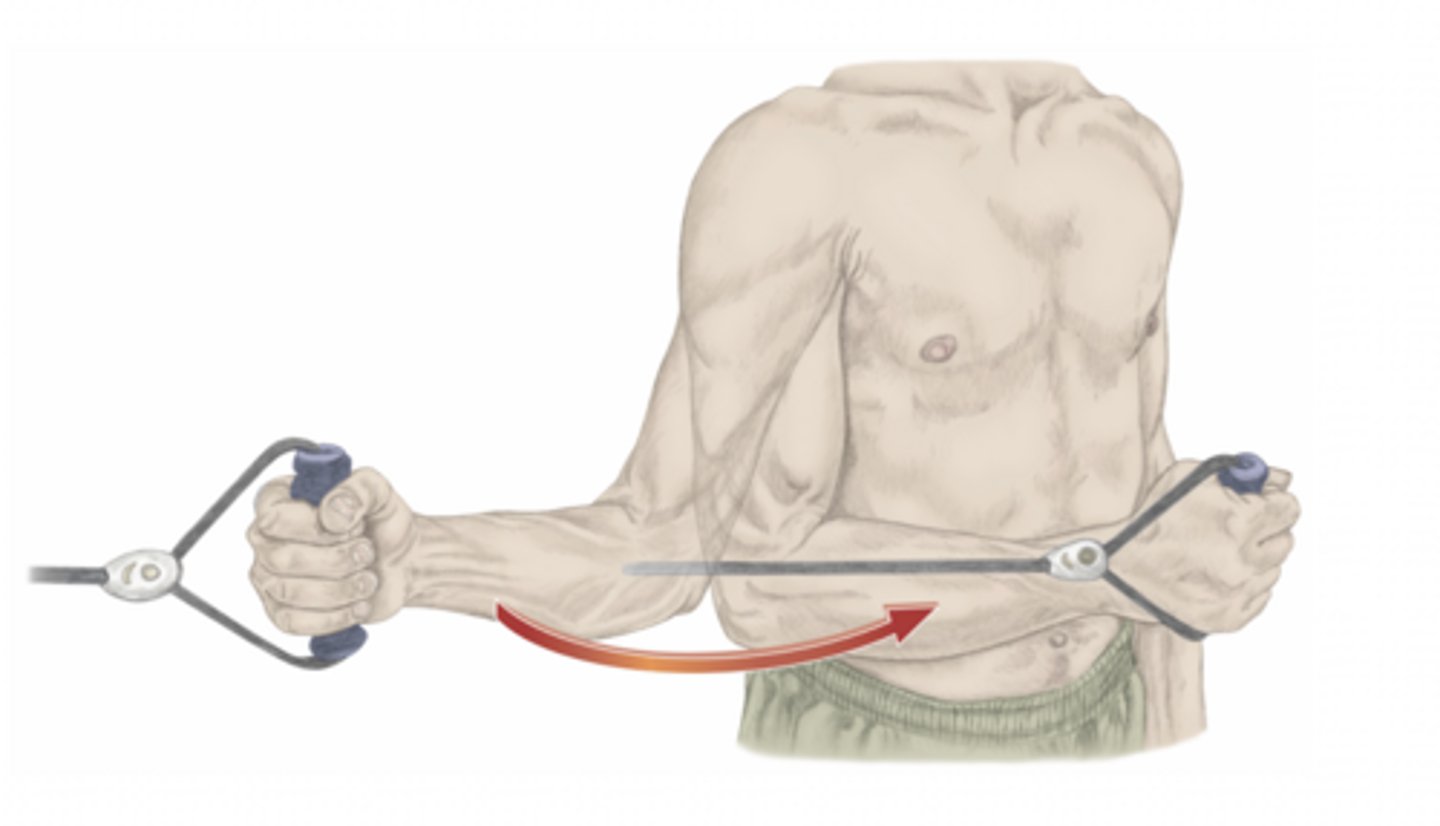
external rotation of the shoulder
please identify the movement and its location
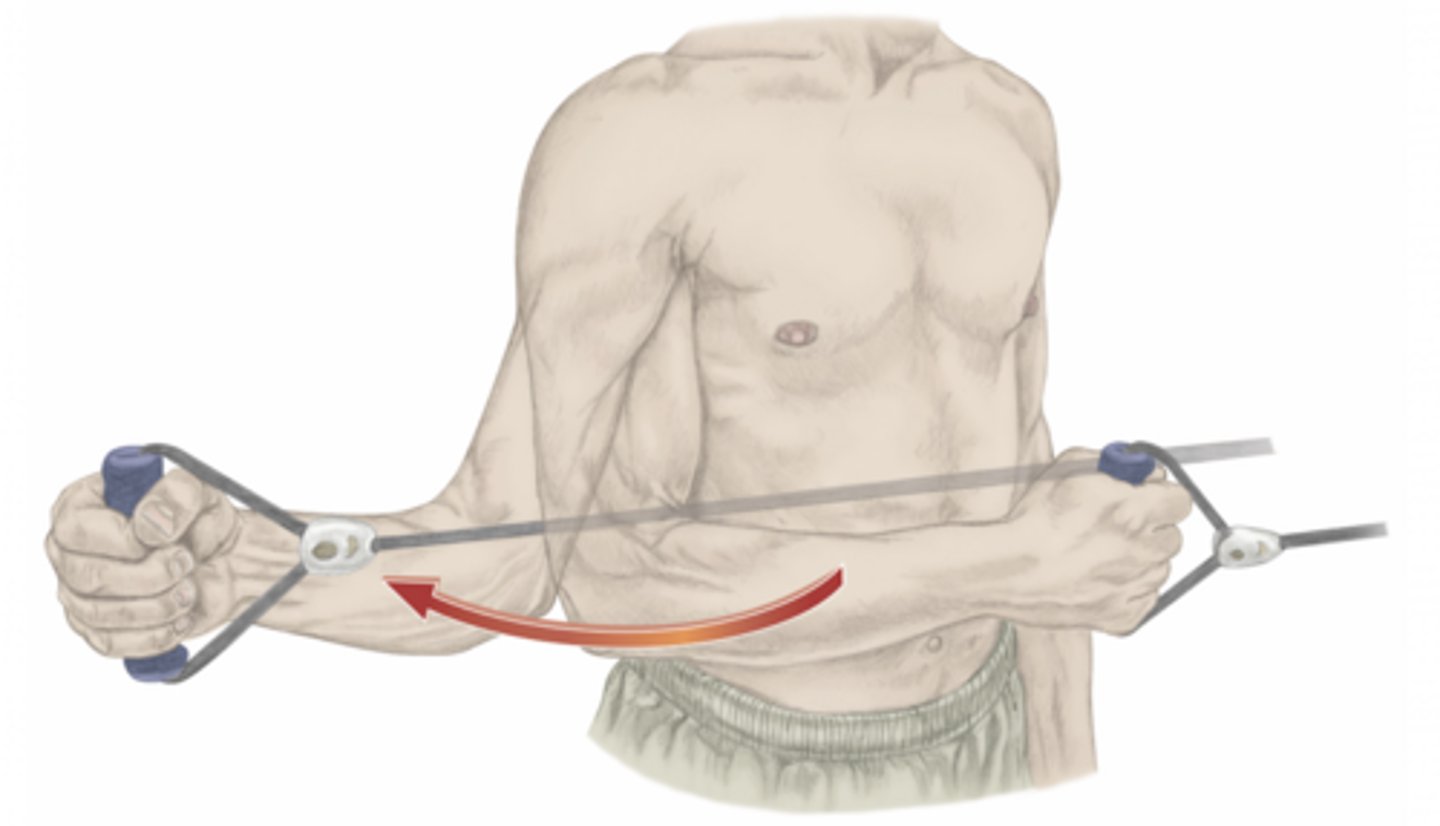
rotation of the spine
please identify the movement and its location
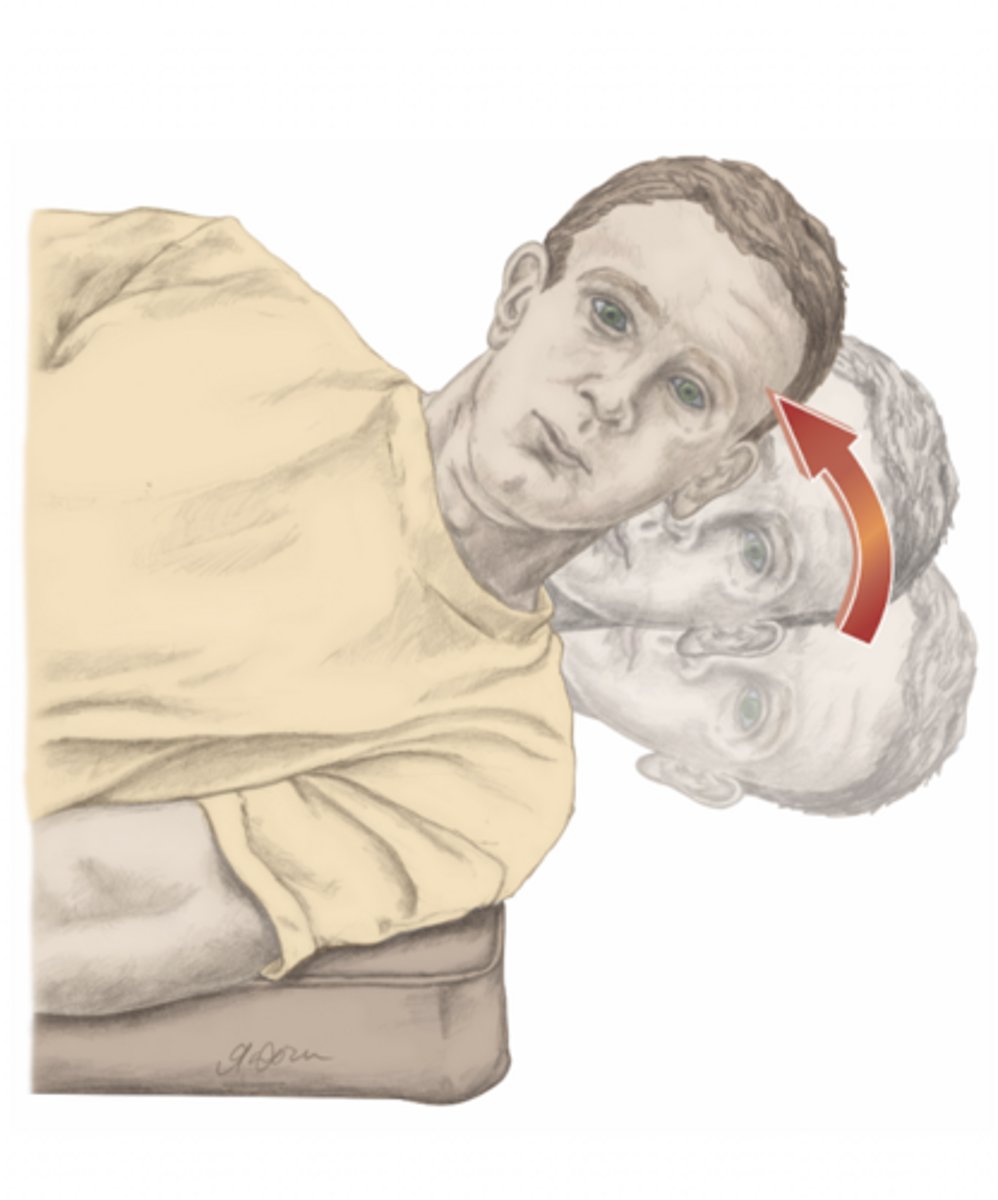
lateral flexion of the neck
please identify the movement and its location
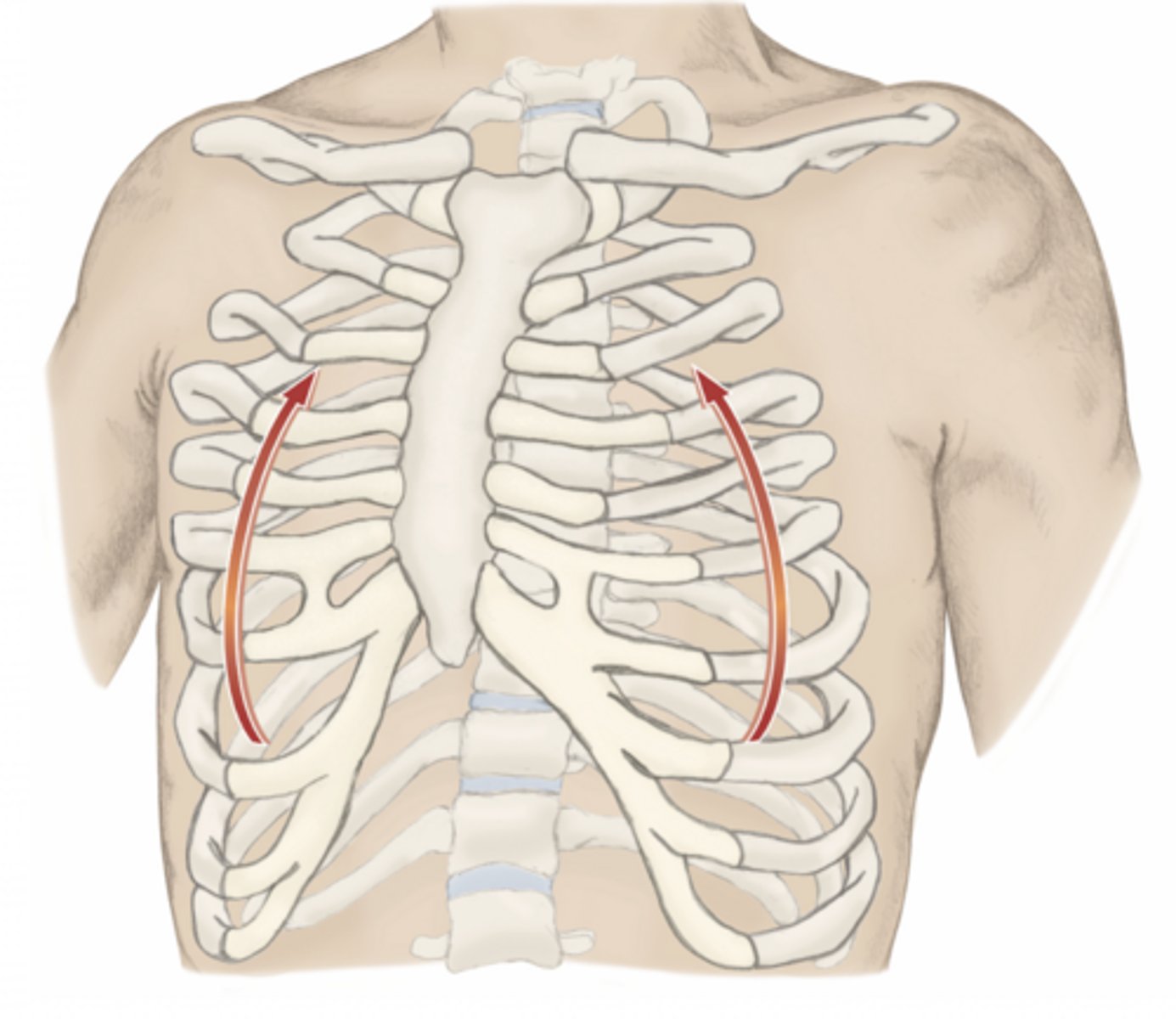
elevation of the ribs
please identify the movement and its location
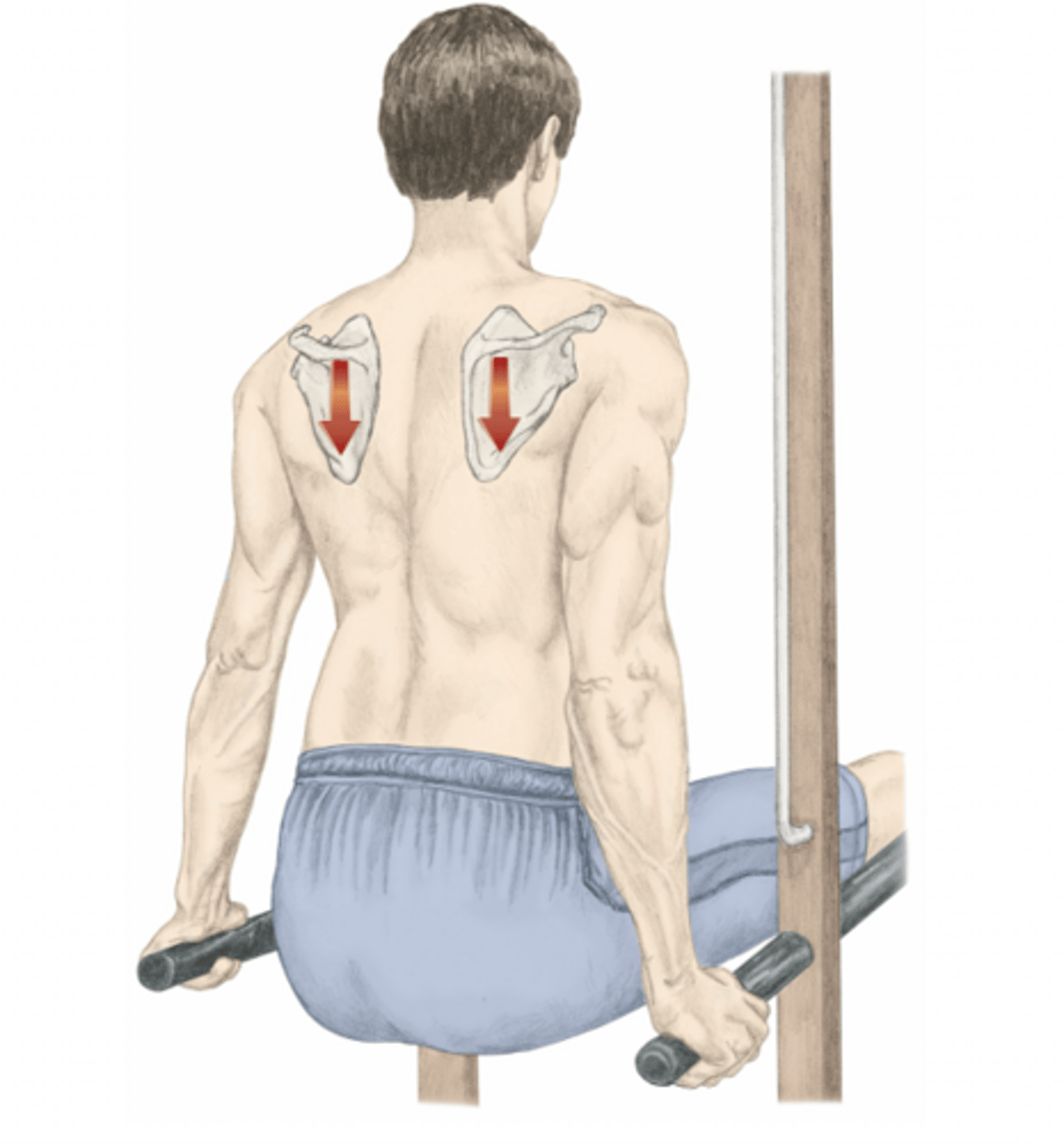
depression of the scapula
please identify the movement and its location
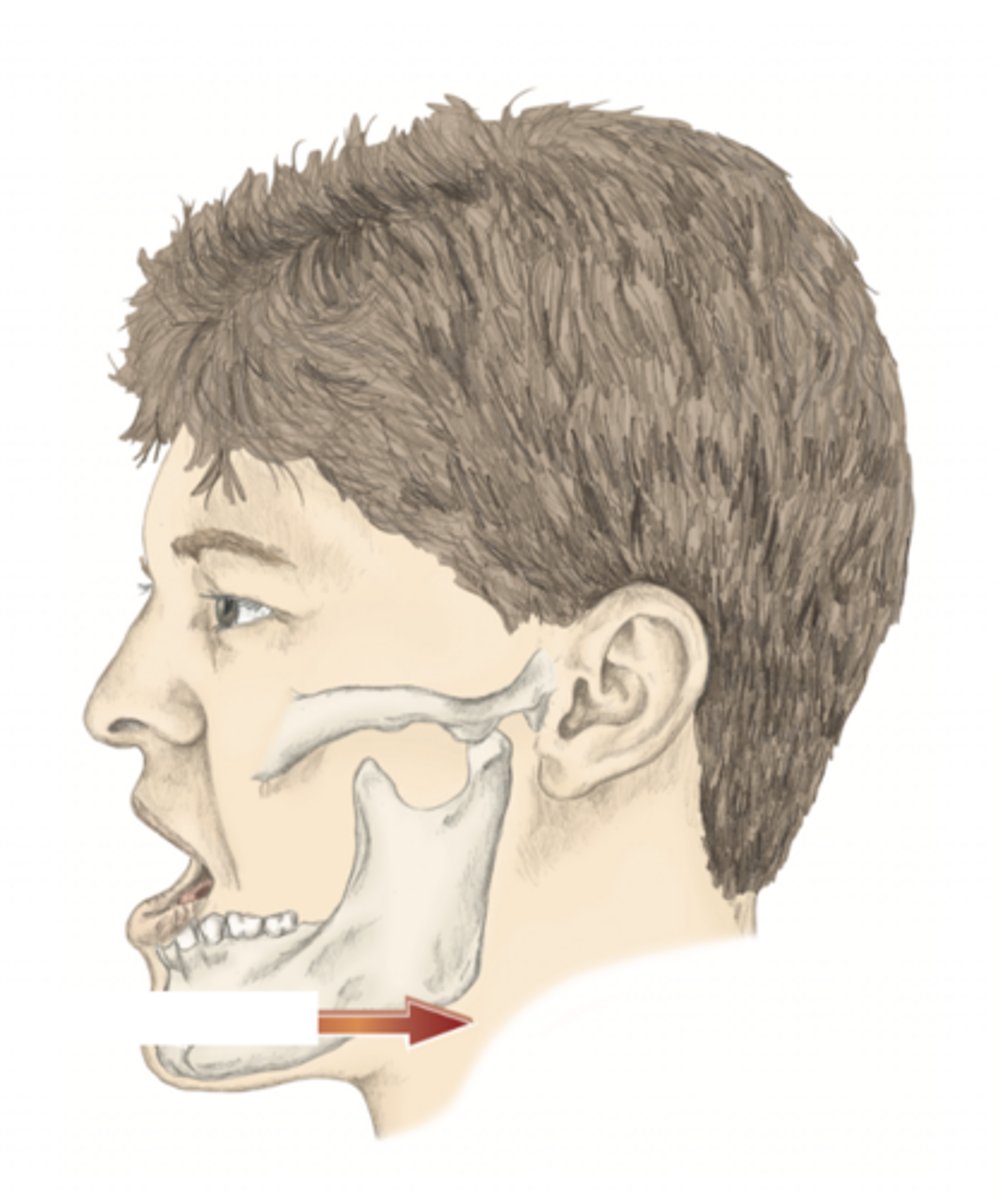
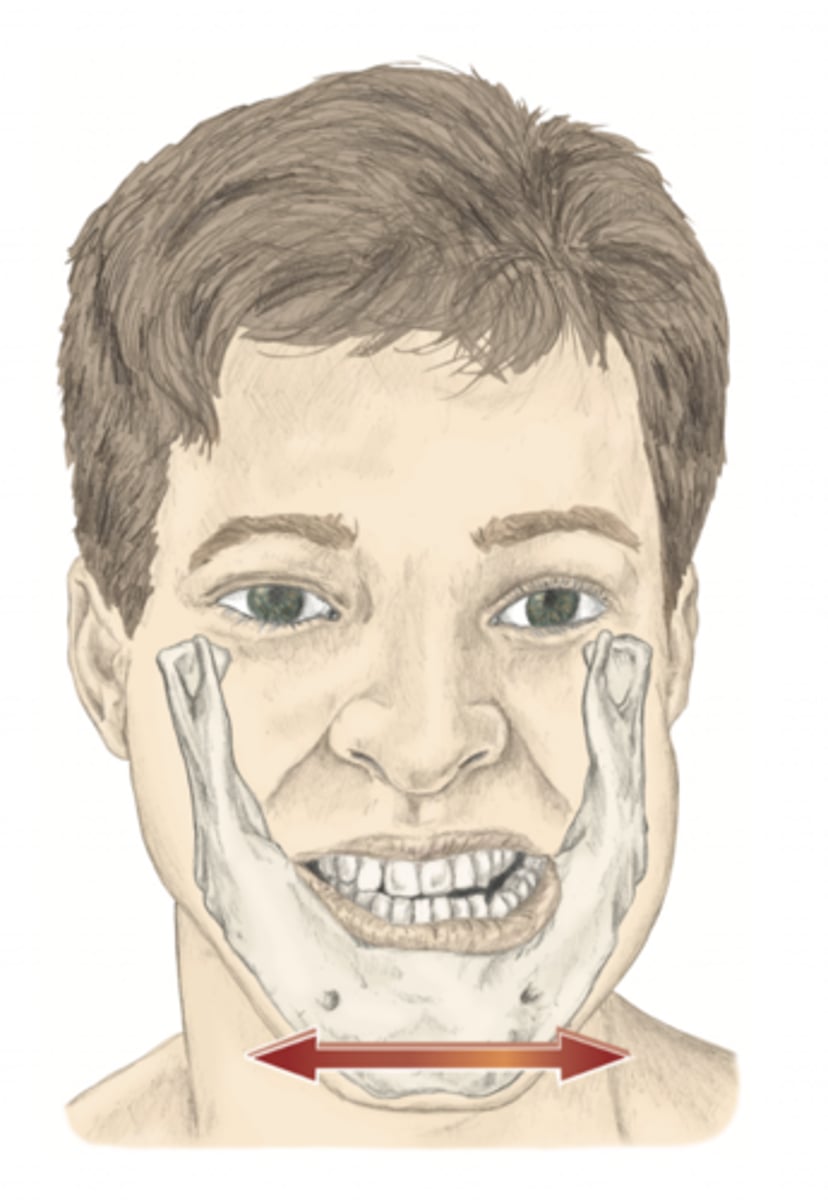
protraction of the mandible
please identify the movement and its location
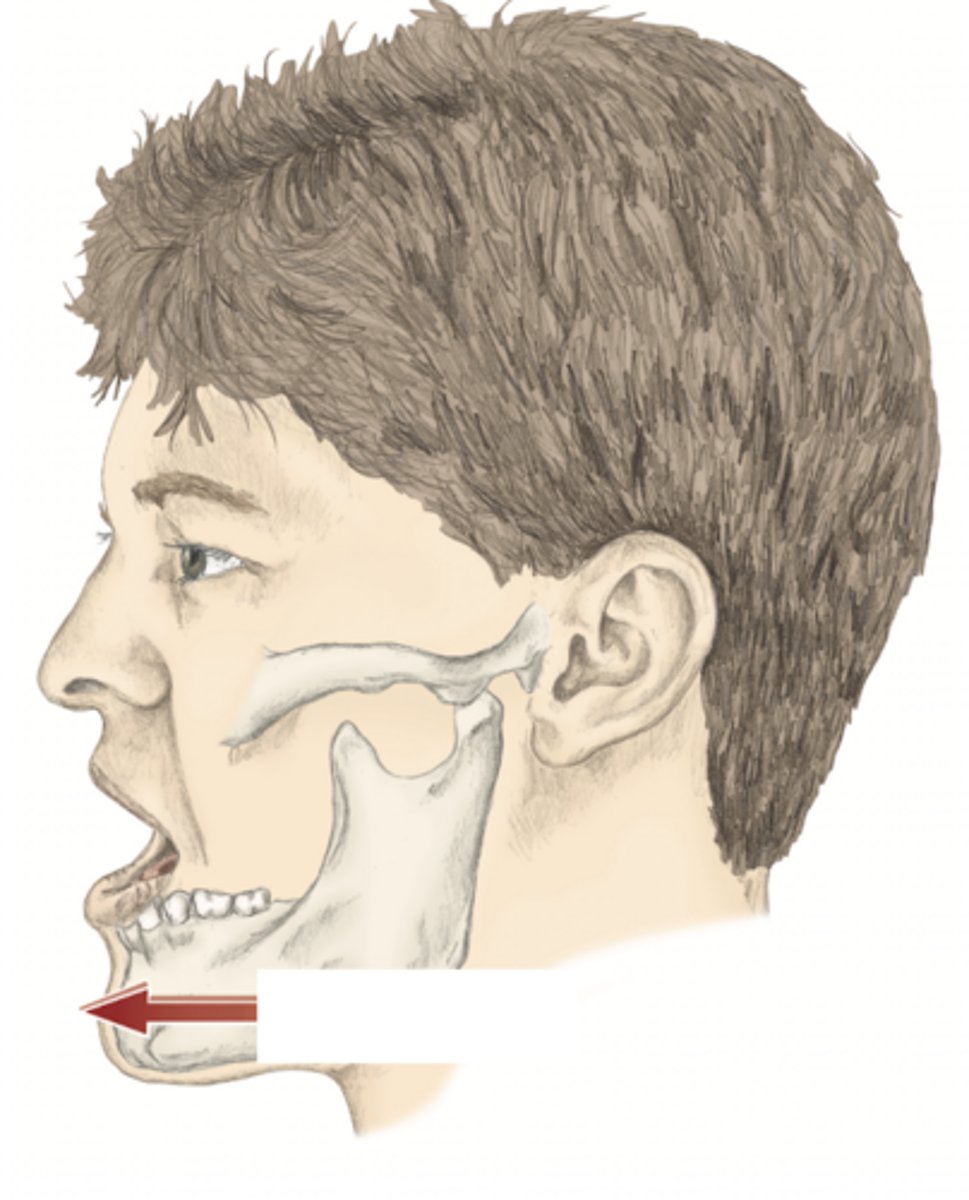
retraction of the mandible
please identify the movement and its location
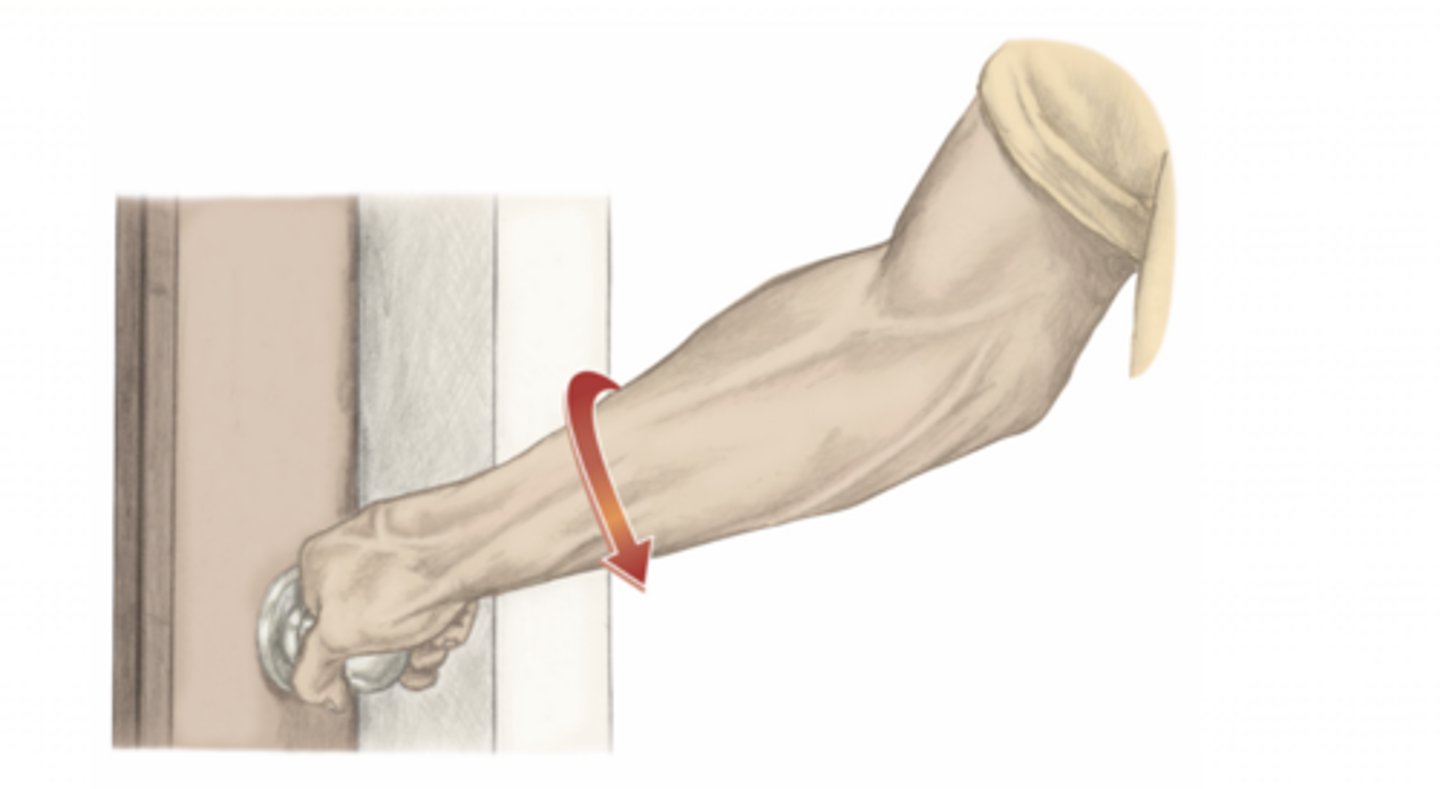
pronation of the forearm
please identify the movement and its location
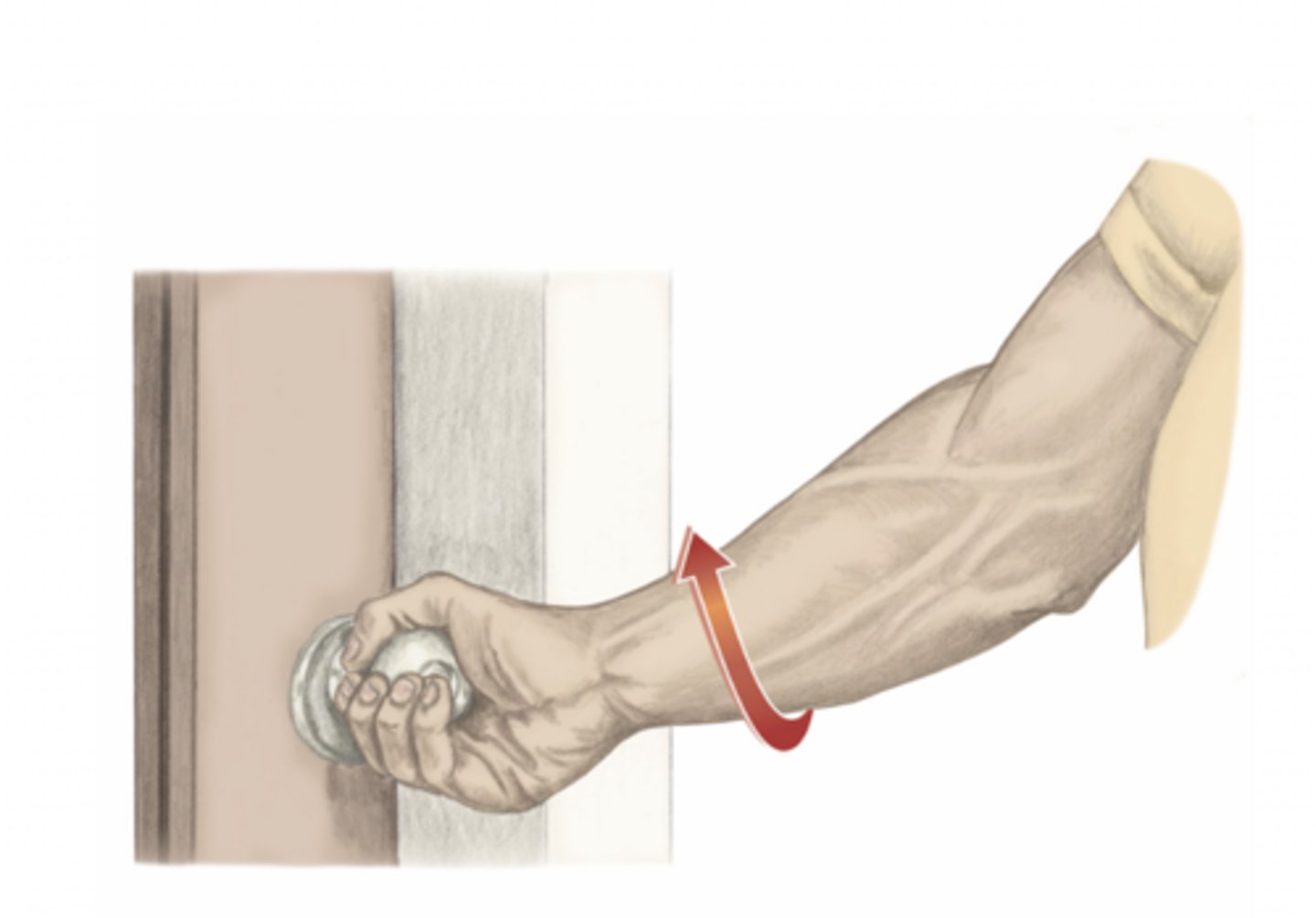
supination of the forearm
please identify the movement and its location
inversion of the foot
please identify the movement and its location
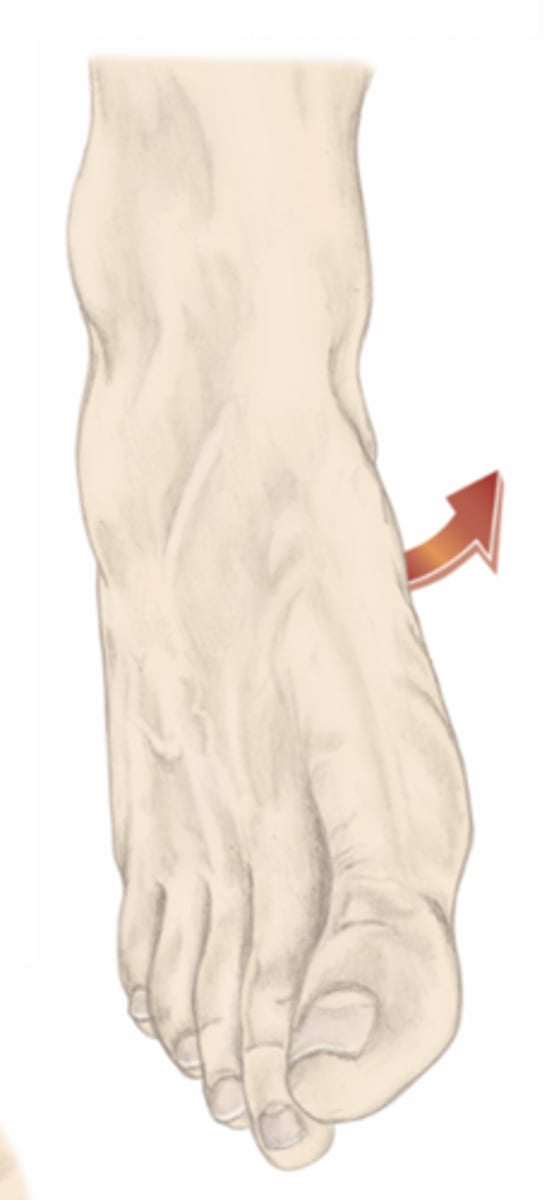
eversion of the foot
please identify the movement and its location
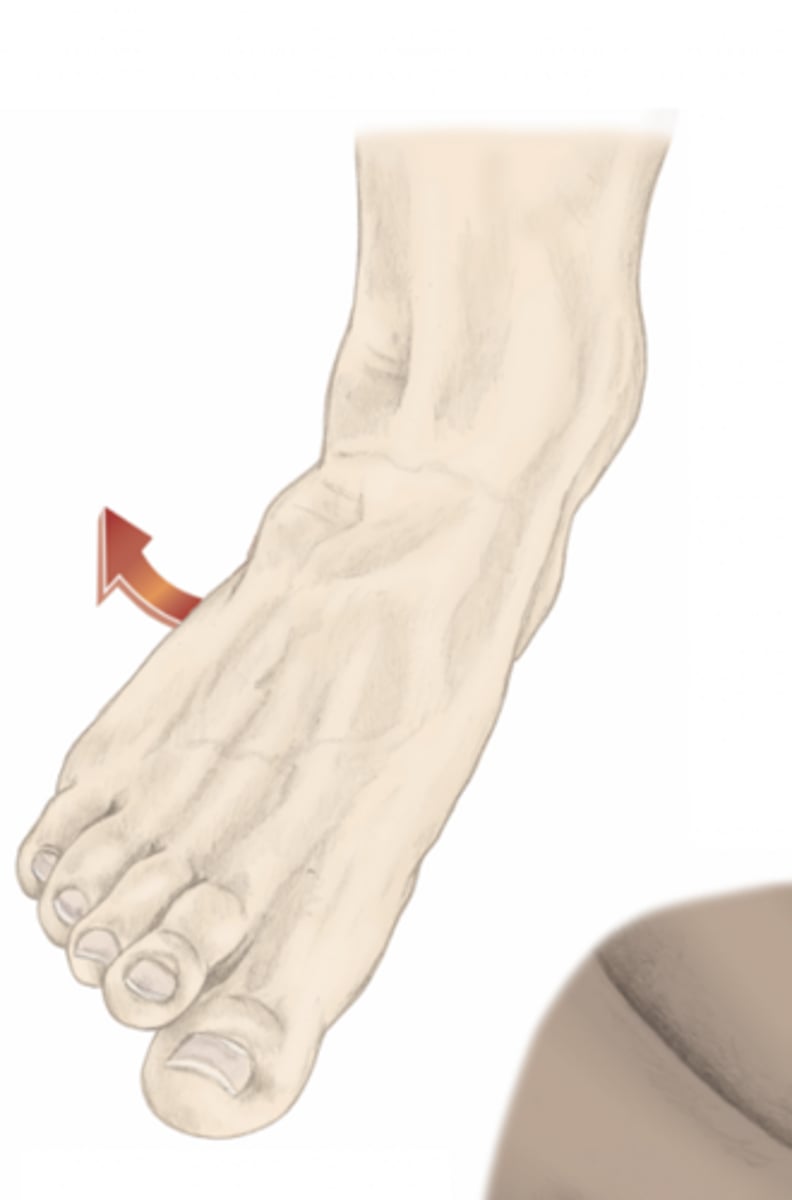
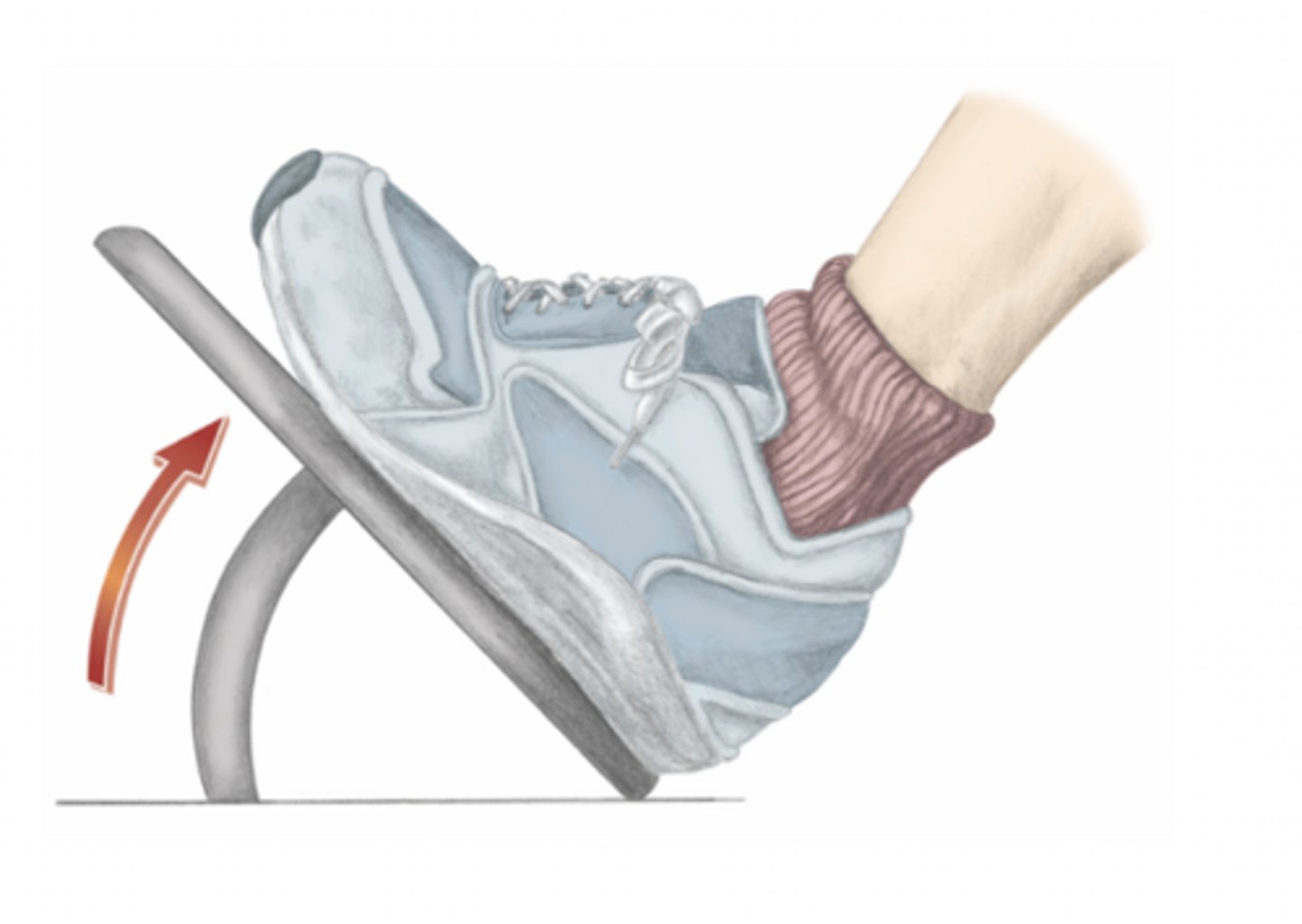
dorsiflexion of the foot
please identify the movement and its location
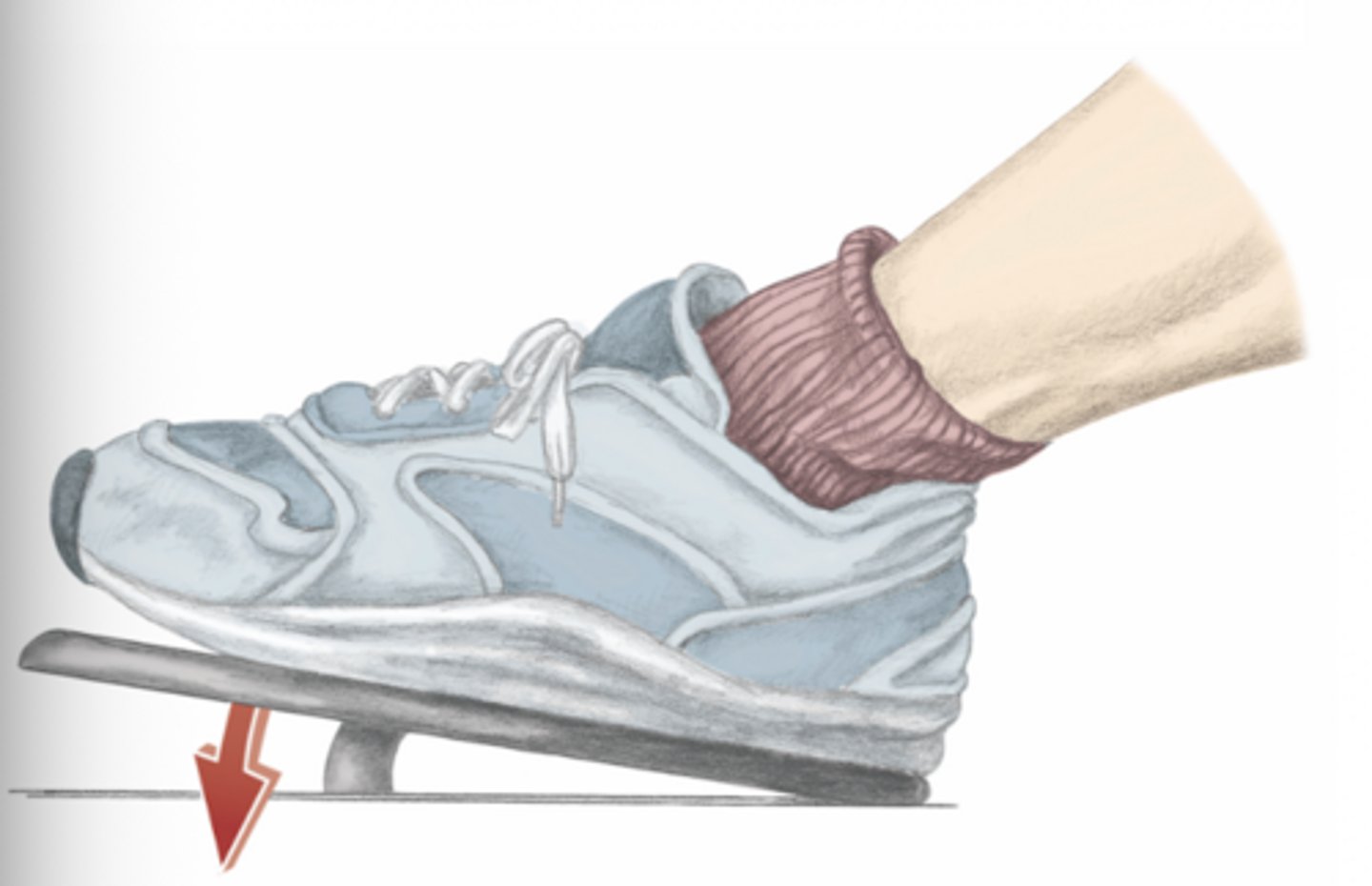
plantarflexion of the foot
please identify the movement and its location
lateral deviation of the jaw
please identify the movement and its location
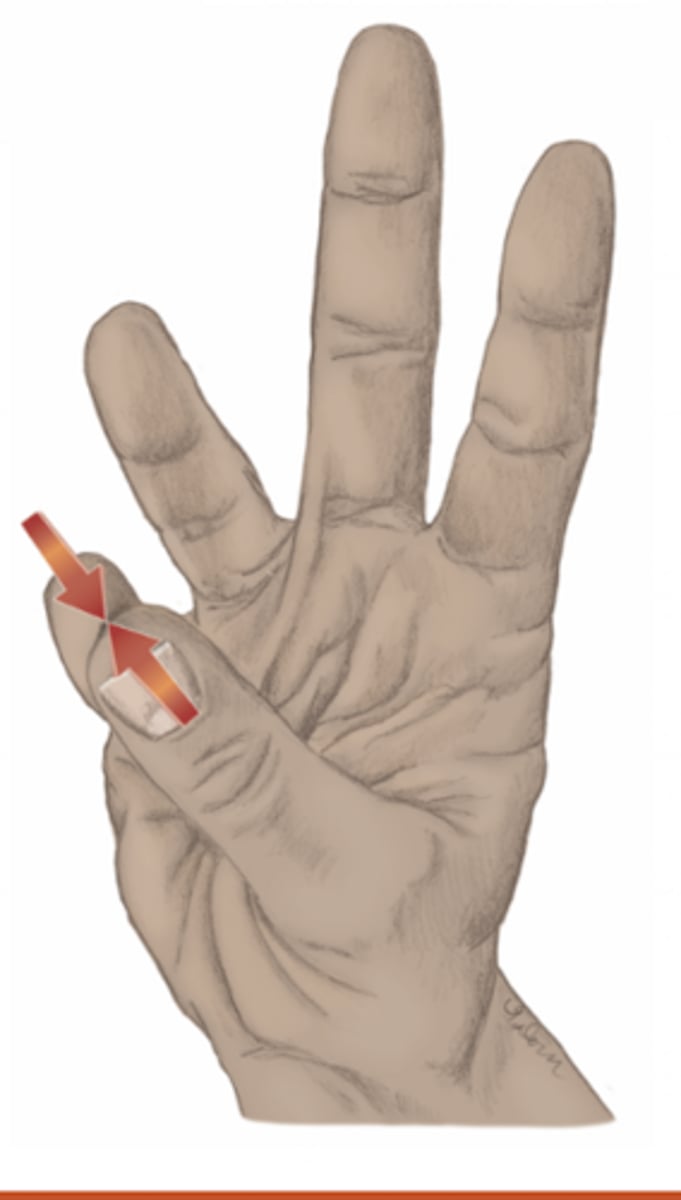
opposition of the thumb
please identify the movement and its location
sagittal, frontal, and transverse
What are the three planes of movement?
sagittal, frontal
flexion and extension happen in the ______ plane and ______ axis
transverse, vertical
rotation happens in the ______ plane and ______ axis
frontal, sagittal
adduction and abduction happen in the ______ plane and ______ axis
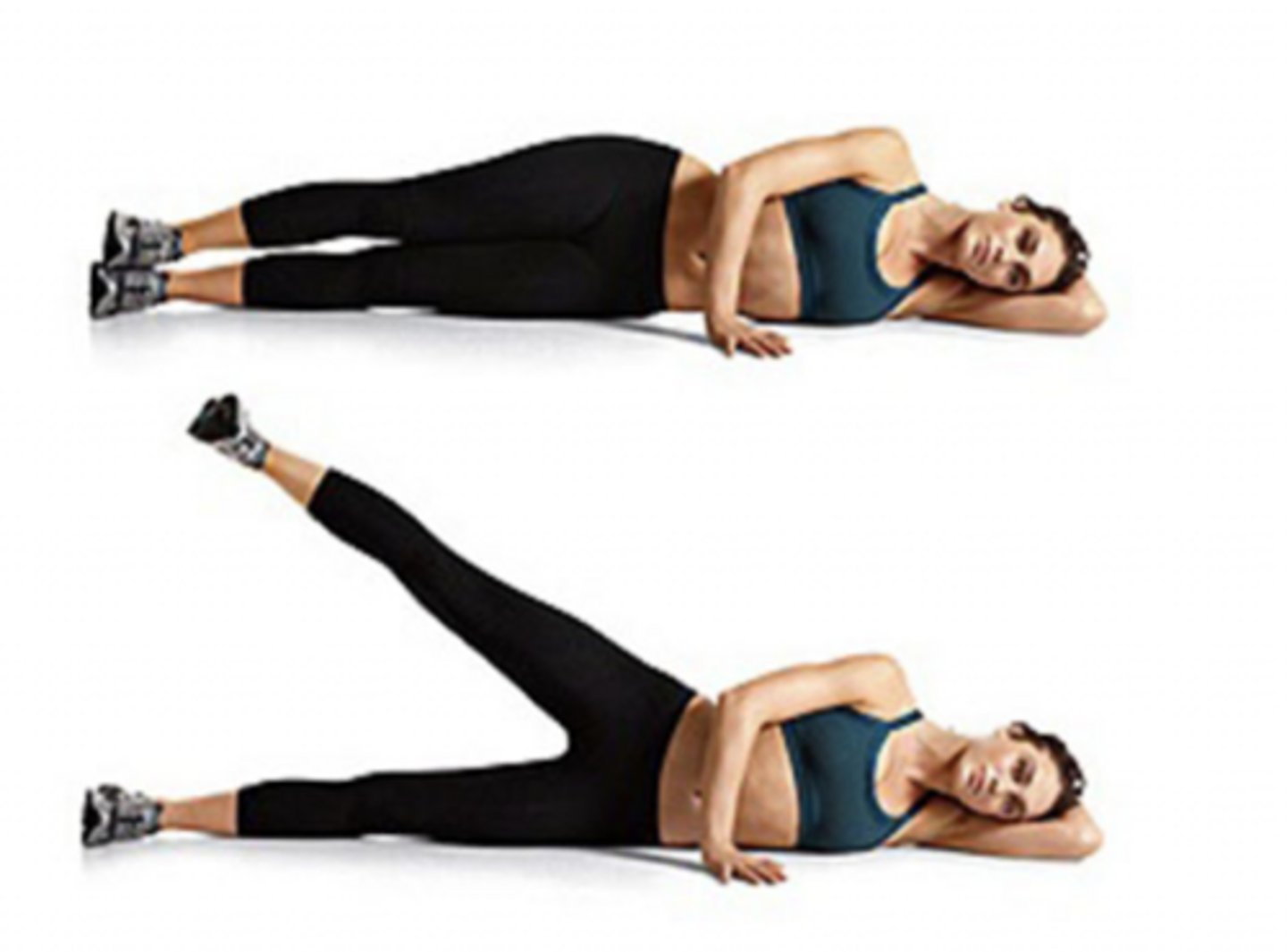
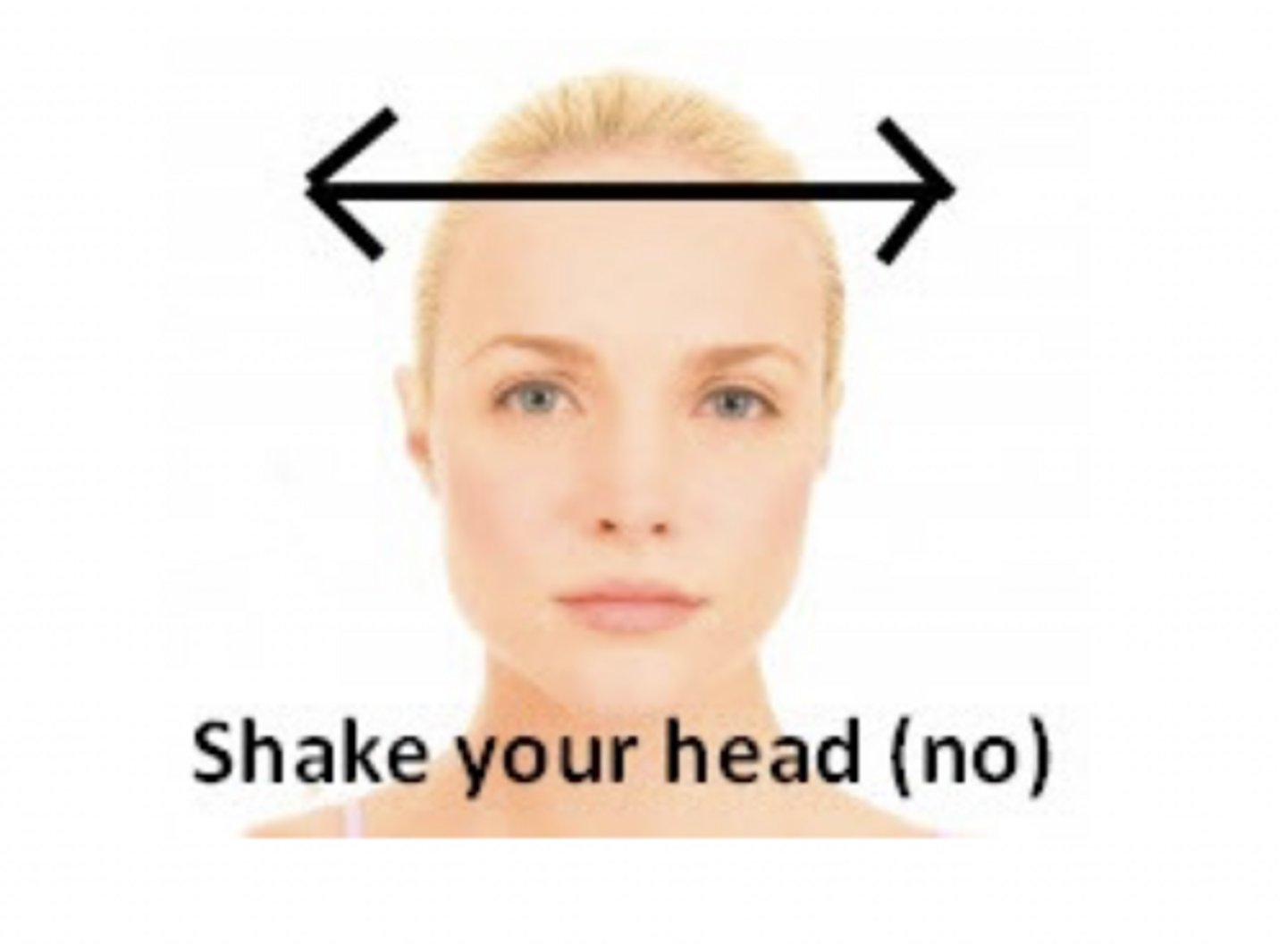
Frontal plane and sagittal axis
Which plane of movement and axis of rotation is this patient going through?

transverse plane and vertical axis
Which plane of movement and axis of rotation is this patient going through?
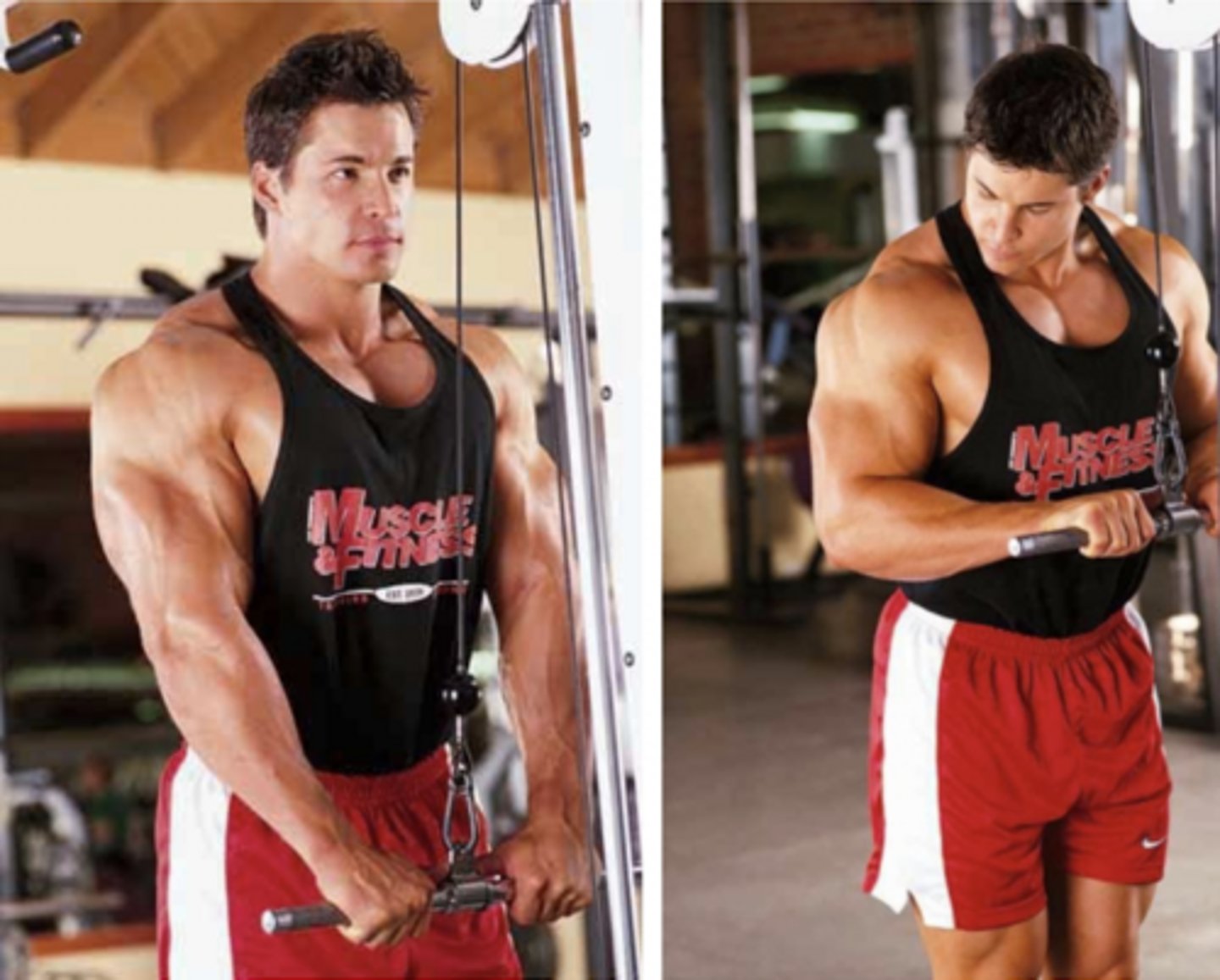
sagittal plane and frontal axis
Which plane of movement and axis of rotation is this patient going through?

a continuous network of connective tissues that forms beneath the skin to attach, stabilize, enclose, and separate muscles and other internal organs
What is fascia and what is it's purpose?
a sheetlike tendinous expansion, mainly serving to connect a muscle with the parts it moves
What is an aponeurosis and what is it's purpose?
any region on the body in which tendon groups from different muscles pass under one connective tissue band
What is an retinaculum and what is it's purpose
increased pressure inside a compartment, which compresses capillaries, nerves, and muscles. This causes decreased blood flow and nerve disruption, which can kill the tissue and nerves.
What is compartment syndrome?
surgical emergency or fasciotomy
What is the treatment for compartment syndrome?
protection, support, storage, movement, and hematopoiesis
What are the functions of the skeletal system
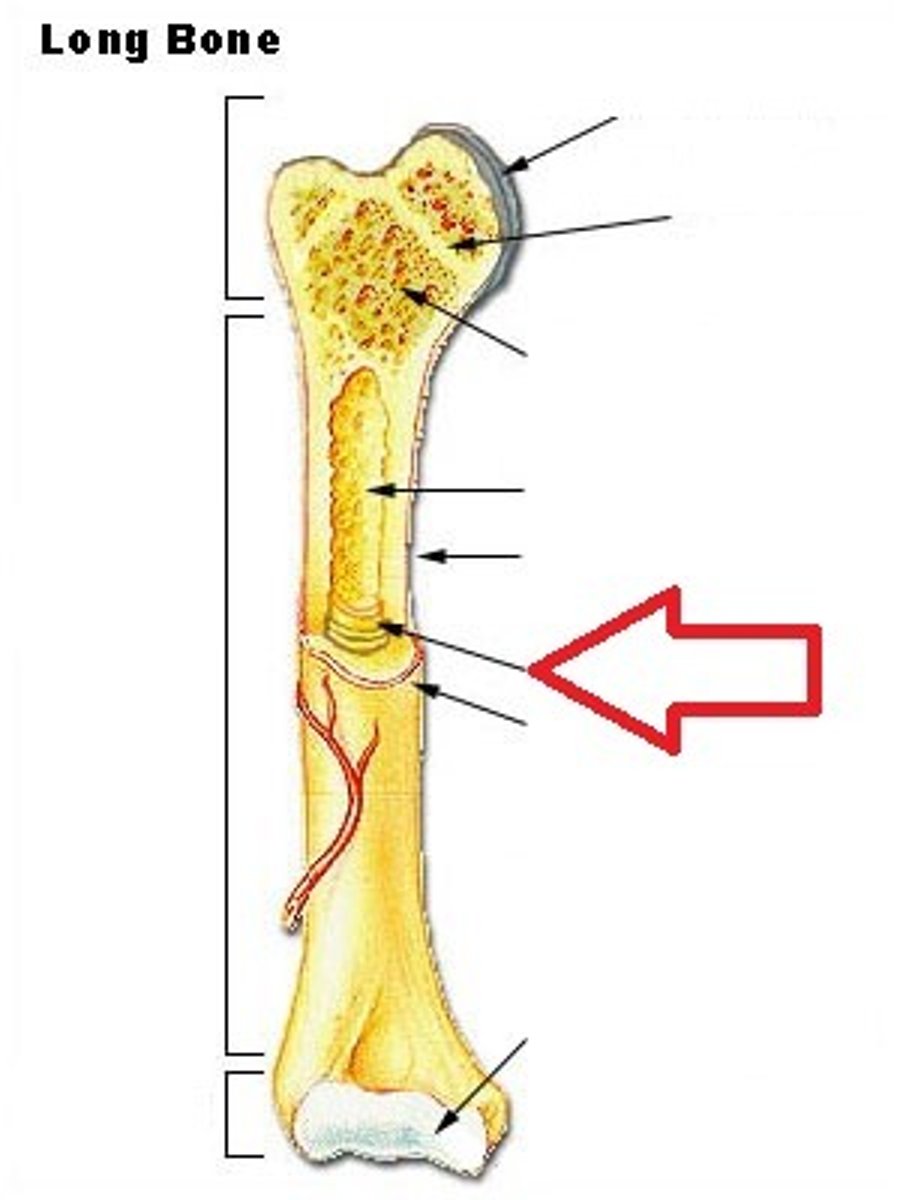
long bone
What kind of bone is this?

short bone
What kind of bone is this?
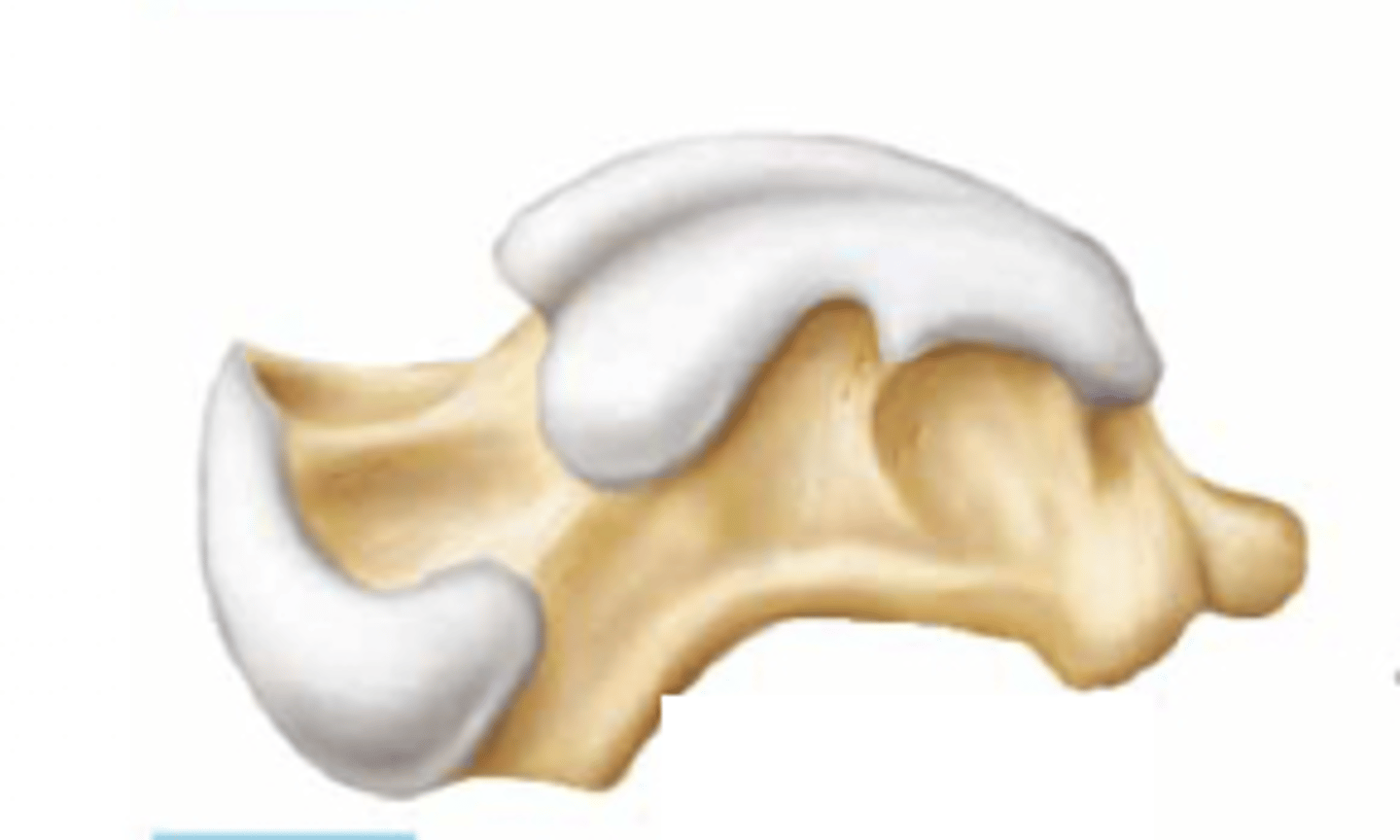
flat bone
What kind of bone is this?
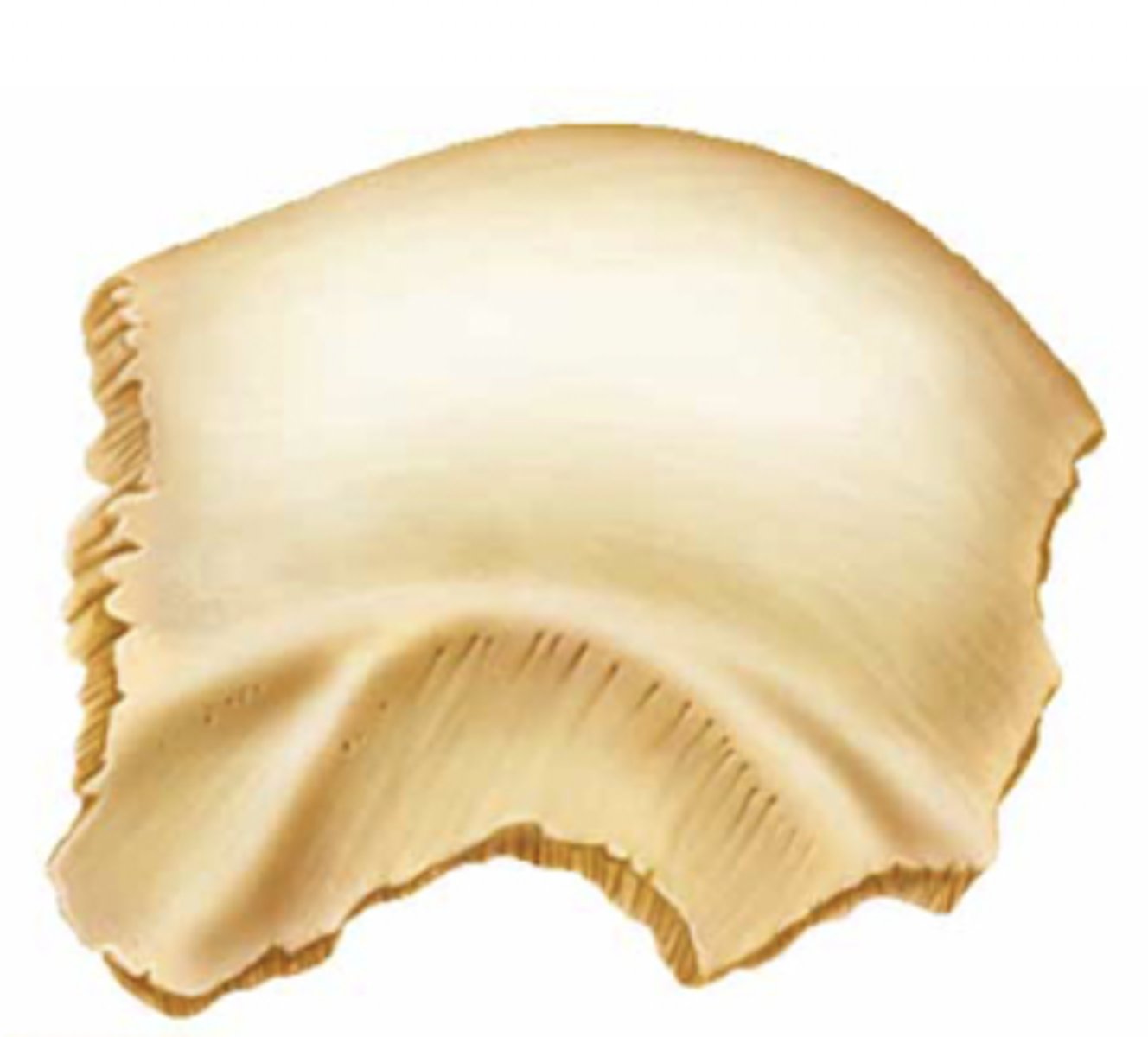

irregular bone
What kind of bone is this?
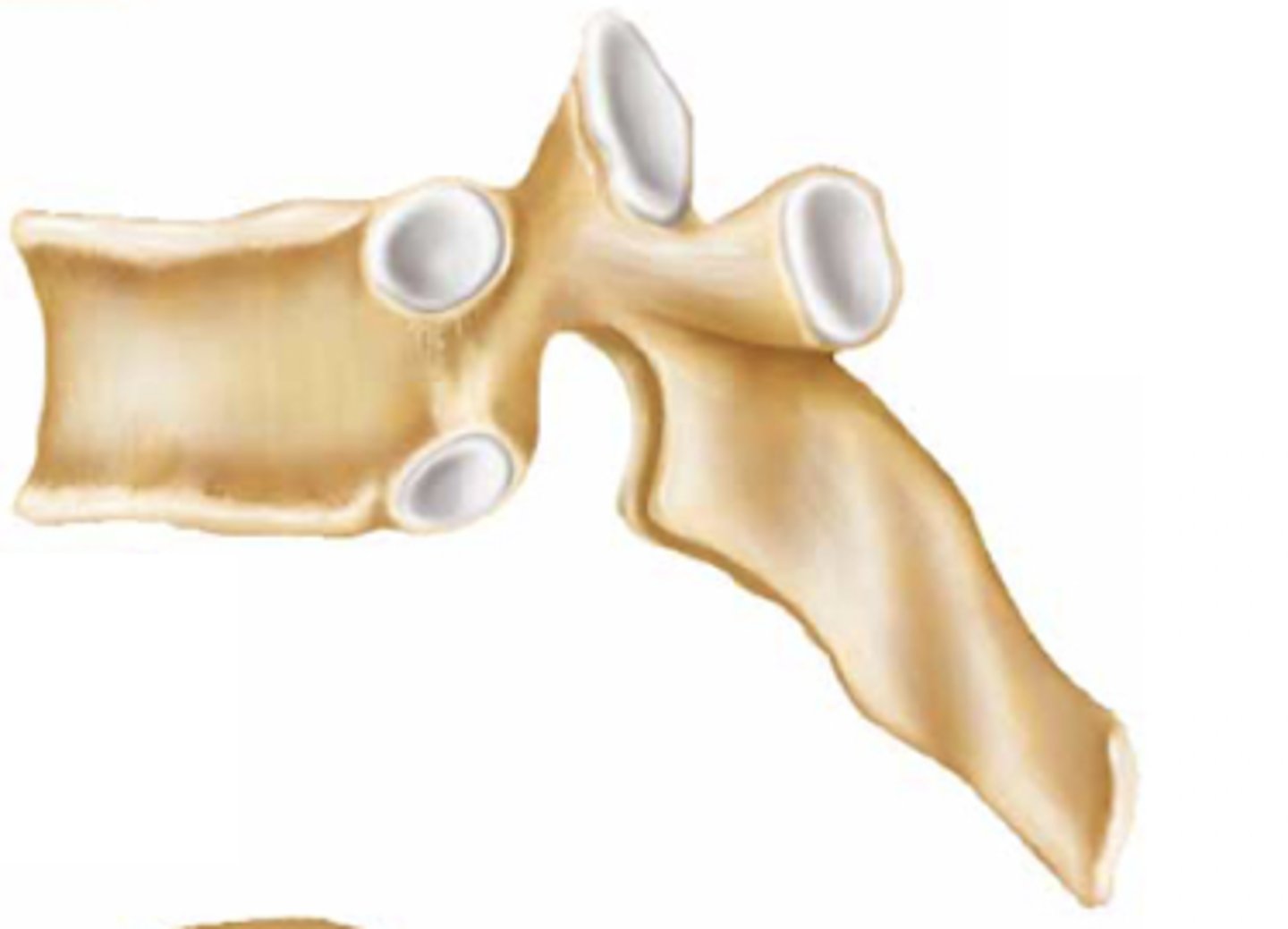
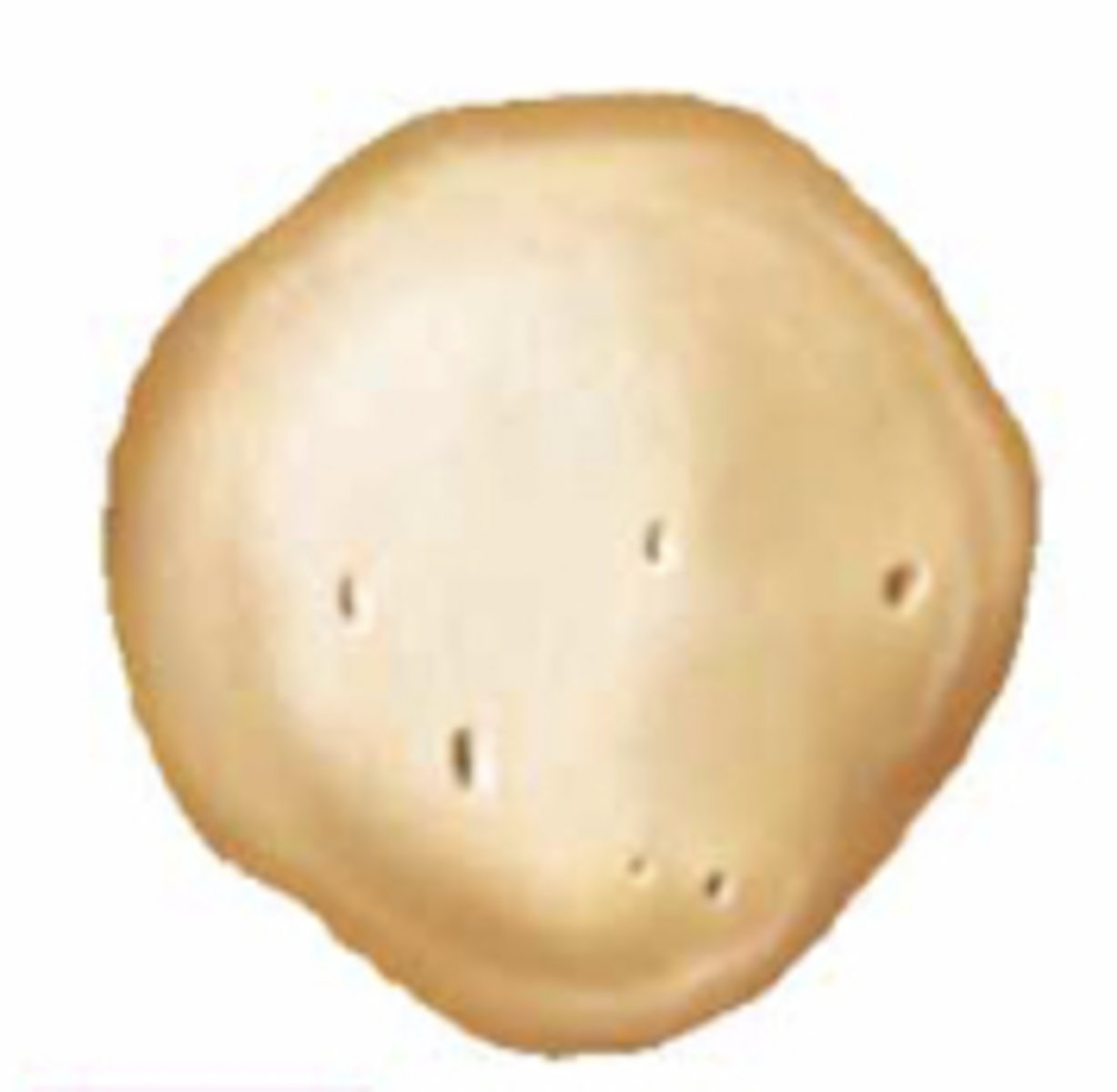
sesamoid bone
What kind of bone is this?

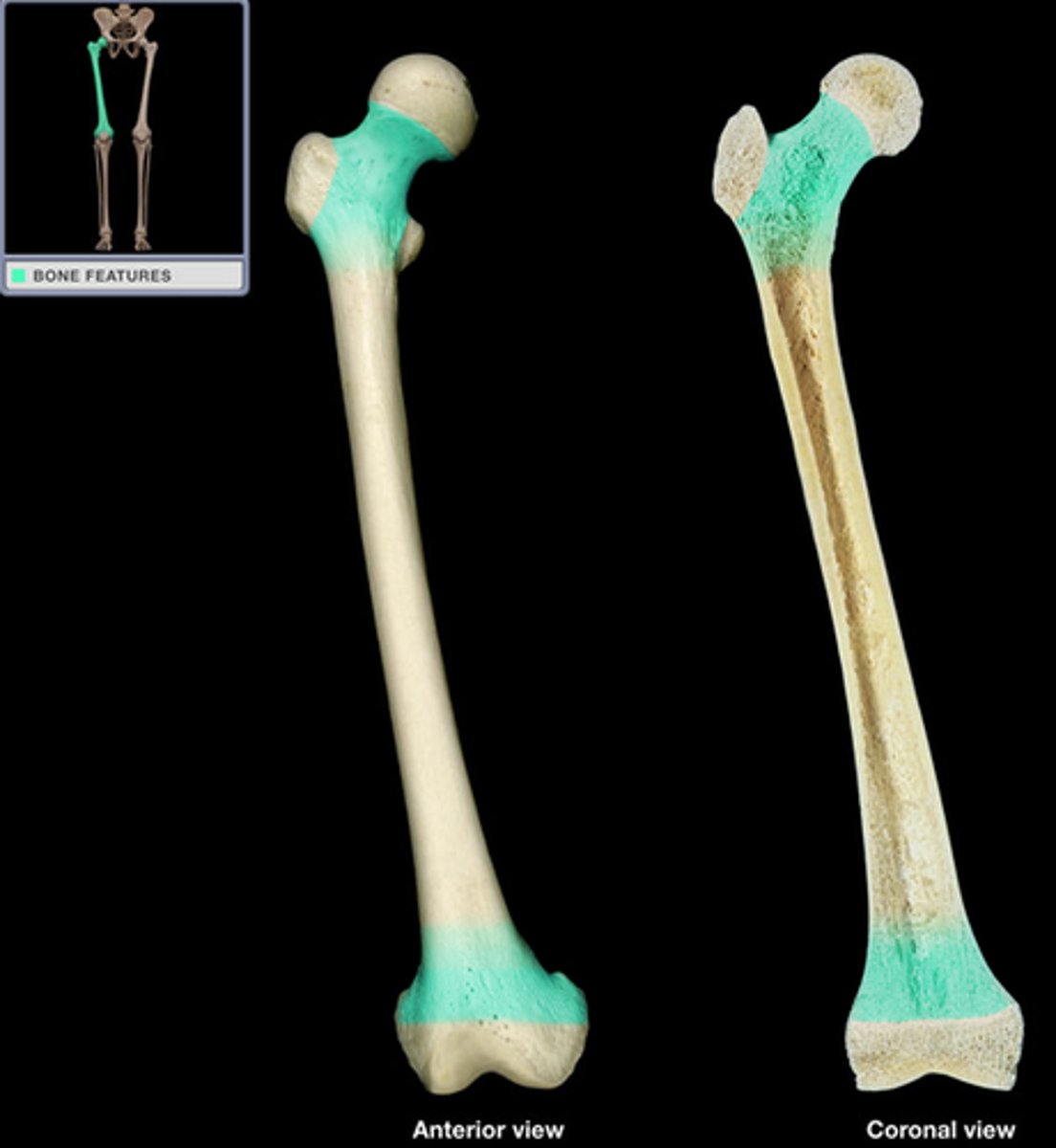
epiphysis
What part of the long bone is this?
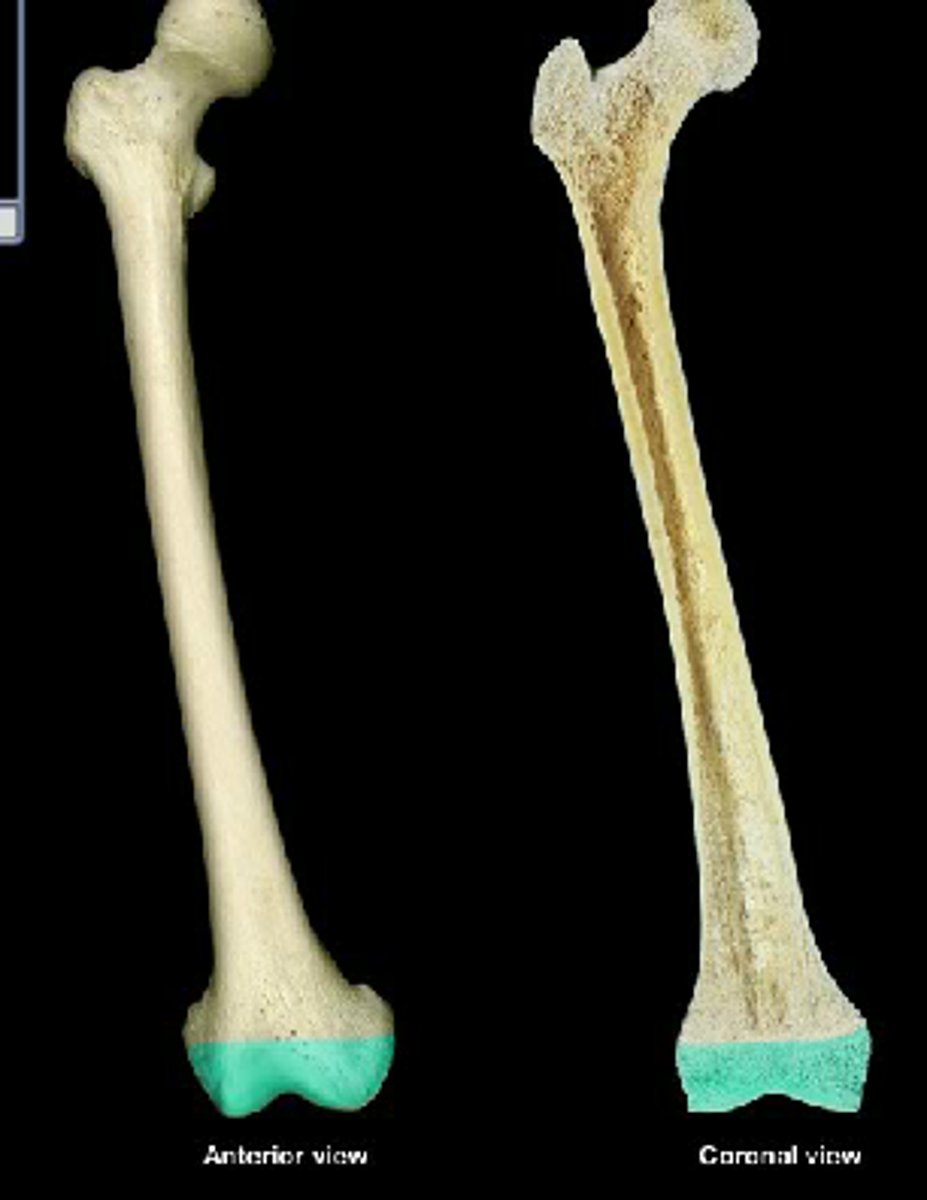
diaphysis
What part of the long bone is this?
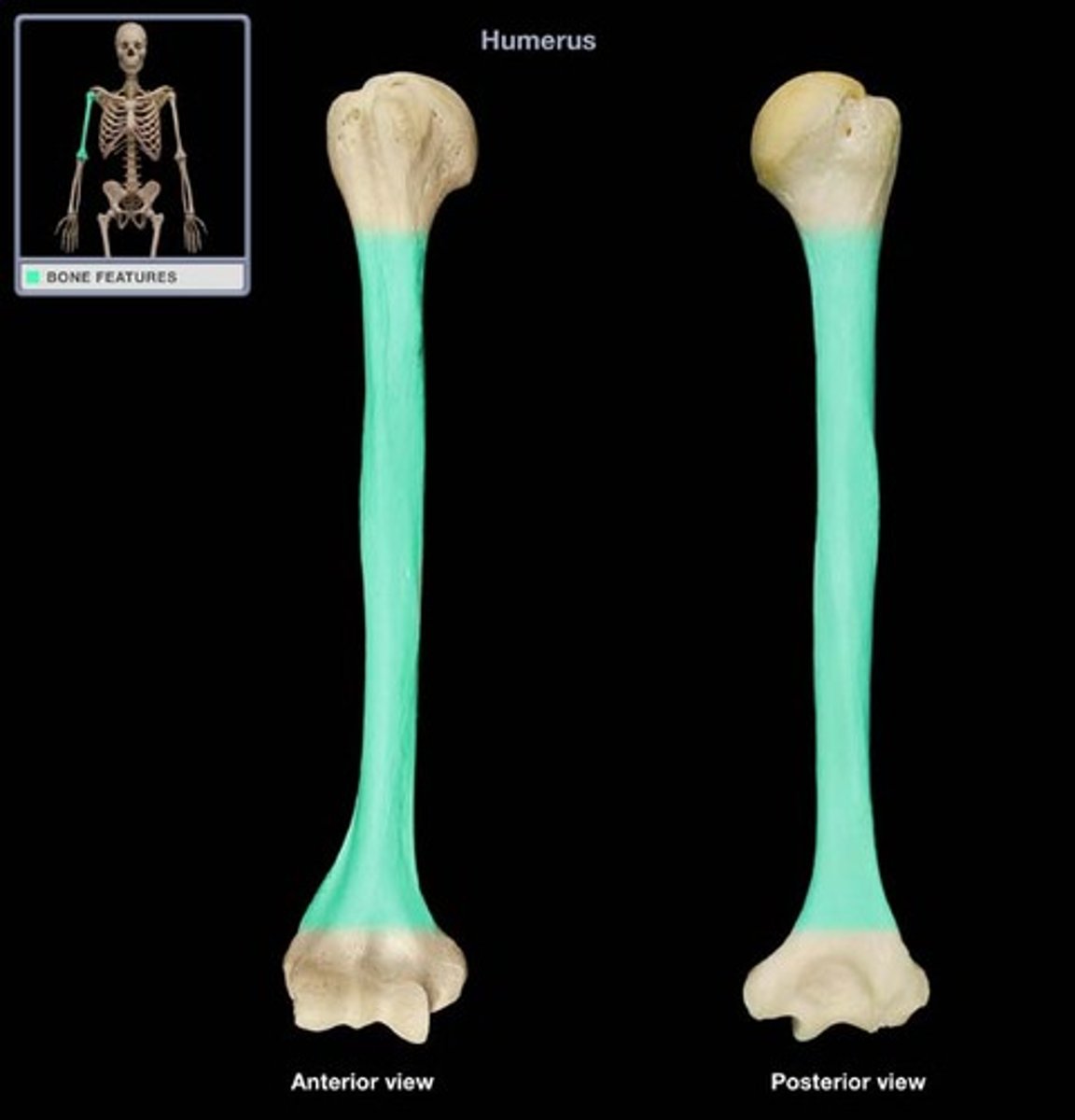
metaphysis
What part of the long bone is this?
articular cartilage
What part of the long bone is this?
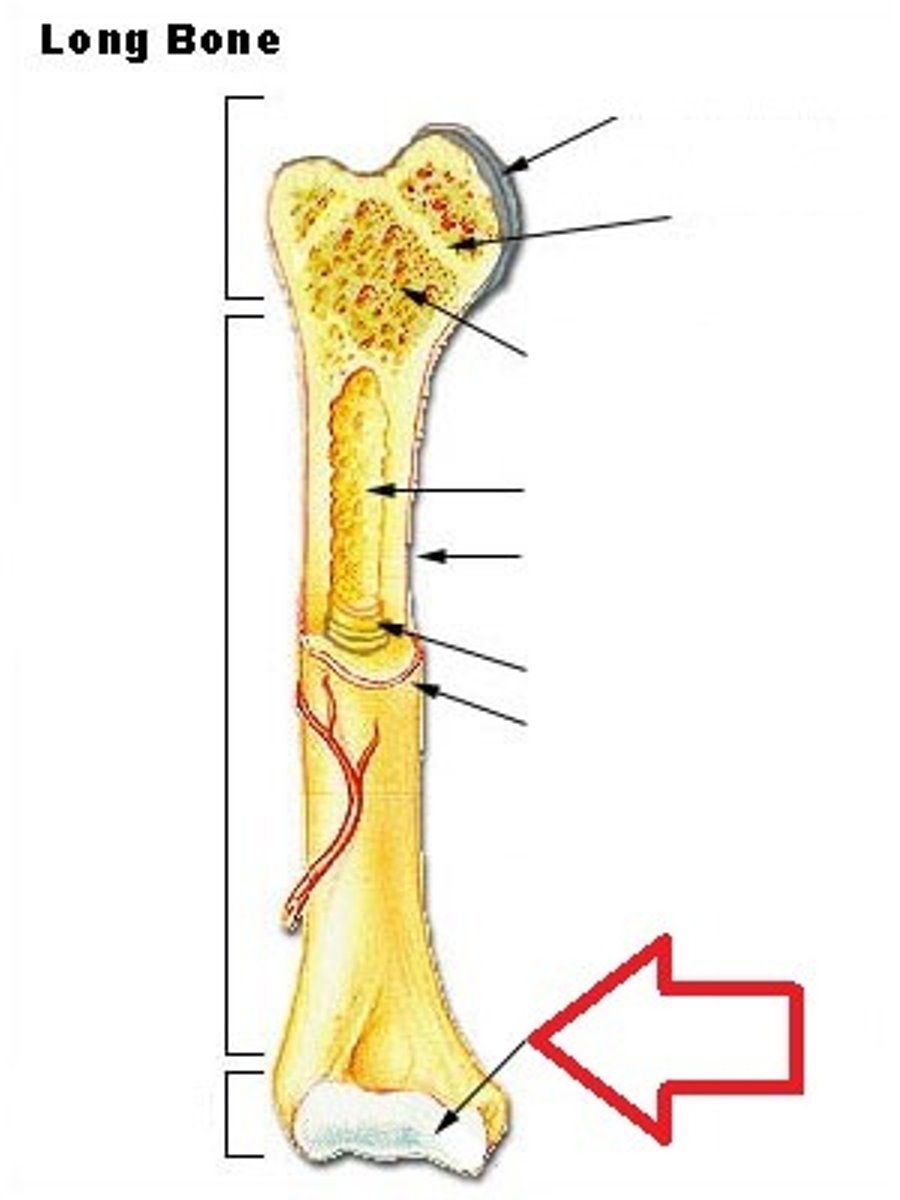
periosteum
What part of the long bone is this?
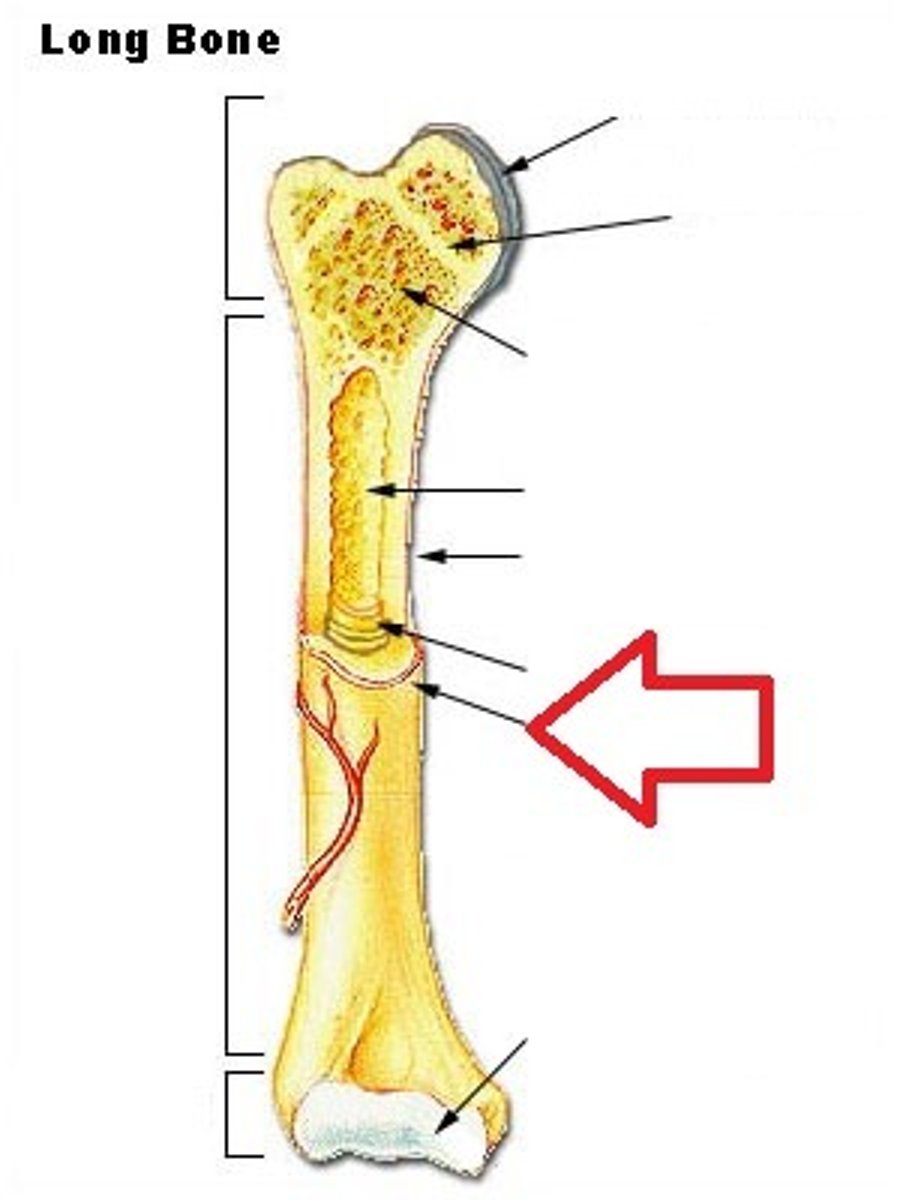
endosteum
What part of the long bone is this?
bones form between sheets of primitive connective tissue. Examples include flat skull bones, clavicles, and sternum
What is intramembranous ossification and what are some examples?
bones that form from hyaline cartilage models. Examples include long bones and most of the skeleton.
What is endochondral ossification and what are some examples?
osteoclasts, releasing, resorption
______ break down bone, ______ calcium. This is called ______
osteoblasts, storing, deposition
______ build bone, ______ calcium. This is called ______
calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate, collagen, water
What are some properties of bone?
type of tissue
What are the structural classifications of joints defined by?
fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
What are the three structural classifications of joints?
held together by dense connective tissue
What is a fibrous joint?
held together by cartilage
What is a cartilaginous joint?
have a complex structure, and are always diarthrotic
What is a synovial joint?
degree of movement
What are the functional classifications of joints defined by?
synarthrotic, amphiarthrotic, diarthrotic
What are the three functional classifications of joints?
an immovable joint
What is a synarthrotic joint?
a slightly movable joint
What is a amphiarthrotic joint?
a freely movable joint
What is a diarthrotic joint?
syndesmosis, suture, and gomphosis
What are the three types of fibrous joints?
suture and gomphosis
What fibrous joints are synarthrotic
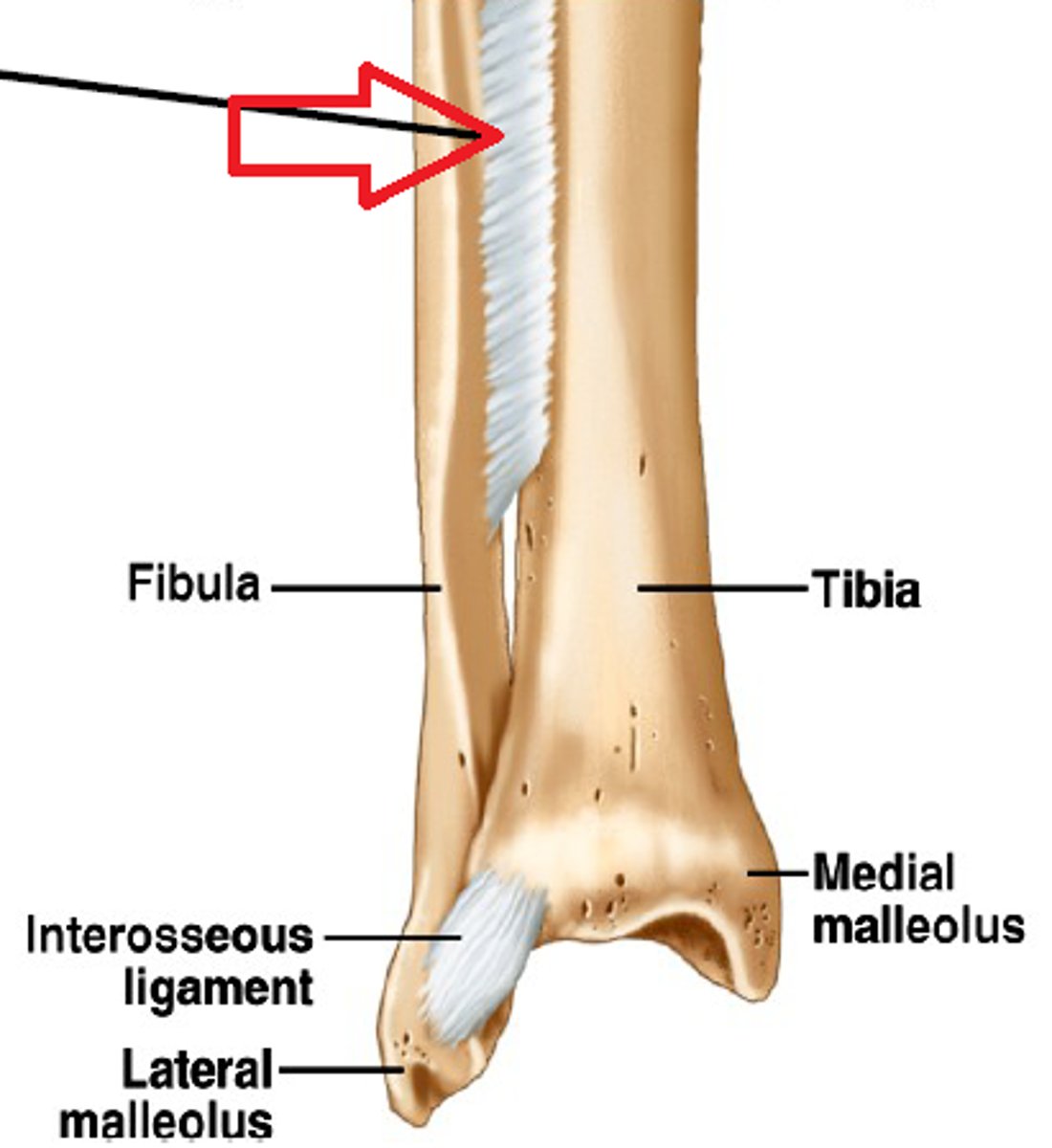
syndesmosis
What fibrous joints is amphiarthrotic?
a fibrous joint that is bound by either a sheet of dense connective tissue or a bundle of dense connective tissue
What is a syndesmosis joint?
between the tibia and the fibula (distal end and diaphysis)
What is an example of a syndesmosis joint?
amphiarthrotic, fibrous
A syndesmosis joint is functionally a ______ joint and structurally a ______ joint.
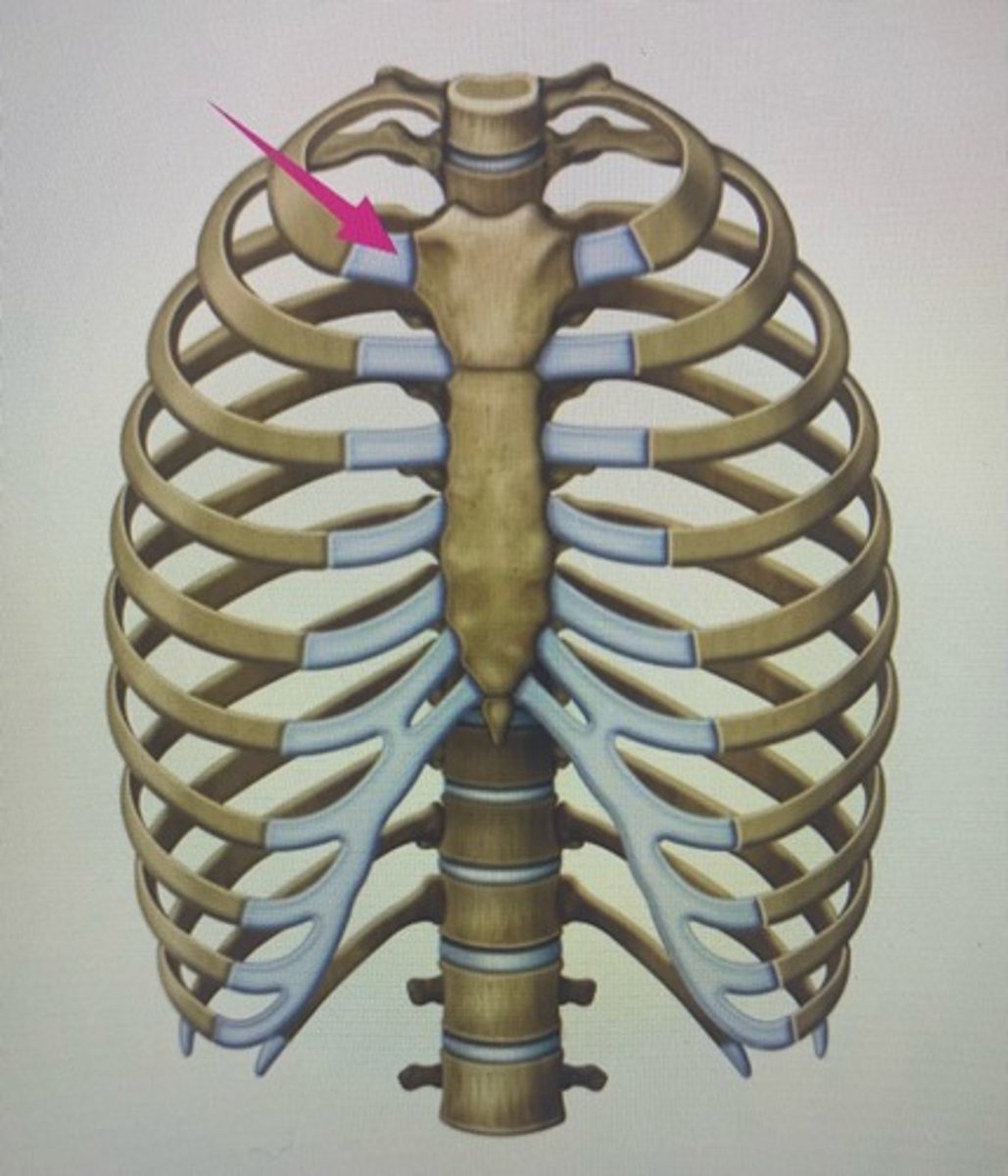
syndesmosis joint
What joint is this?
synchondrosis and symphysis
What are the two types of cartilaginous joints?
bones united by hyaline cartilage
What is a synchondrosis joint?
amphiarthrotic, cartilaginous
A synchondrosis joint is functionally a ______ joint and structurally a ______ joint
bone separated by fibrocartilage
What is a symphysis joint?
amphiarthrotic, cartilaginous
A symphysis joint is functionally a ______ joint and structurally a ______ joint
epiphyseal plate and costochondral (the ribs)
What is are examples of a synchondrosis joint?
pubic symphysis and IVD
What are examples of a symphysis joint?
synchondrosis joint
What joint is this?
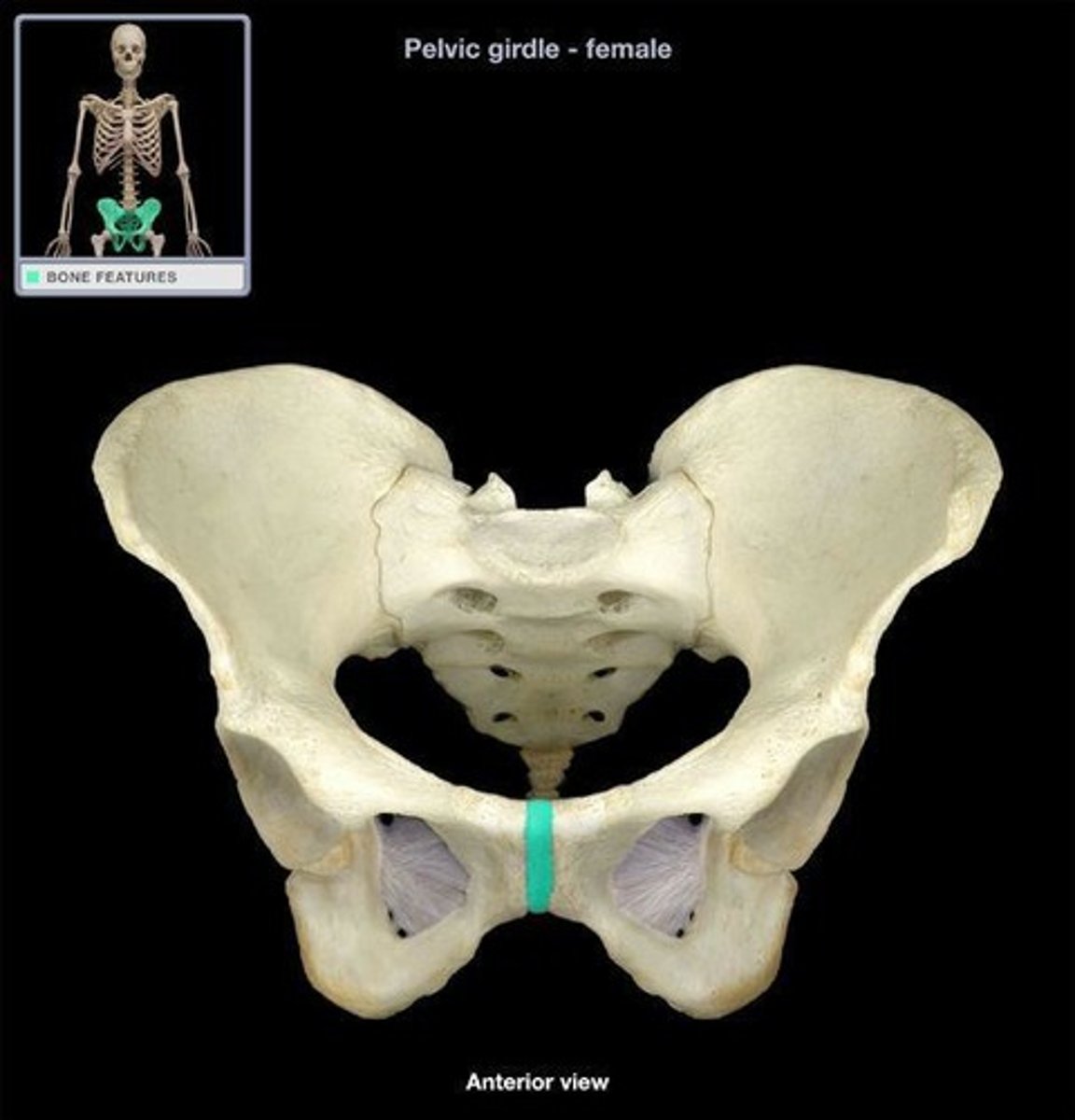
symphysis joint
What joint is this?
synovial
Most joints in the skeleton are ______.
diarthrotic
All synovial joints are functionally ______.
enarthrodial, condyloidal, arthrodial, ginglymus, trochoid, and sellar
What are the six synovial joints?
enarthrodial
the ball and socket joint is also known as the ______ joint.
condylar
the condyloidal joint is also known as the ______ joint.
arthrodial
the plane joint is also known as the ______ joint.
ginglymus
the hinge joint is also known as the ______ joint.
trochoid
the piviot joint is also known as the ______ joint.
sellar
the saddle joint is also known as the ______ joint.
ball and socket joint
What joint has the widest range of motion and is multiaxial?
hip and shoulder
What are some examples of a ball and socket joint?
condylar joint
What joint can go in a back and forth or side to side movement and is biaxial?
2nd-5th metacarpophalangeal joints (knuckles)
What is a example of a condylar joint?