electrolytic cells
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
key features of an electrolytic cell?
power supply; push electrons to the negative electrode
features a single container with electrolyte solution, generally with a porous divider
oxidation occurs at the anode - positive electrode
reduction occurs at the cathode - negative electrode
How does metal plating and the purification of copper involve an application of electrolysis?
Purification of copper: The impure copper is made the anode, so it is oxidised to form Cu2+ and the impurities fall to the bottom.
The cathode is made of pure copper.
The copper ions gain electrons (i.e. are reduced) at the cathode, thus purifying the copper.
Electroplating: applies electrolysis by using a direct electric current to deposit a thin layer of one metal onto a substrate, which acts as the cathode
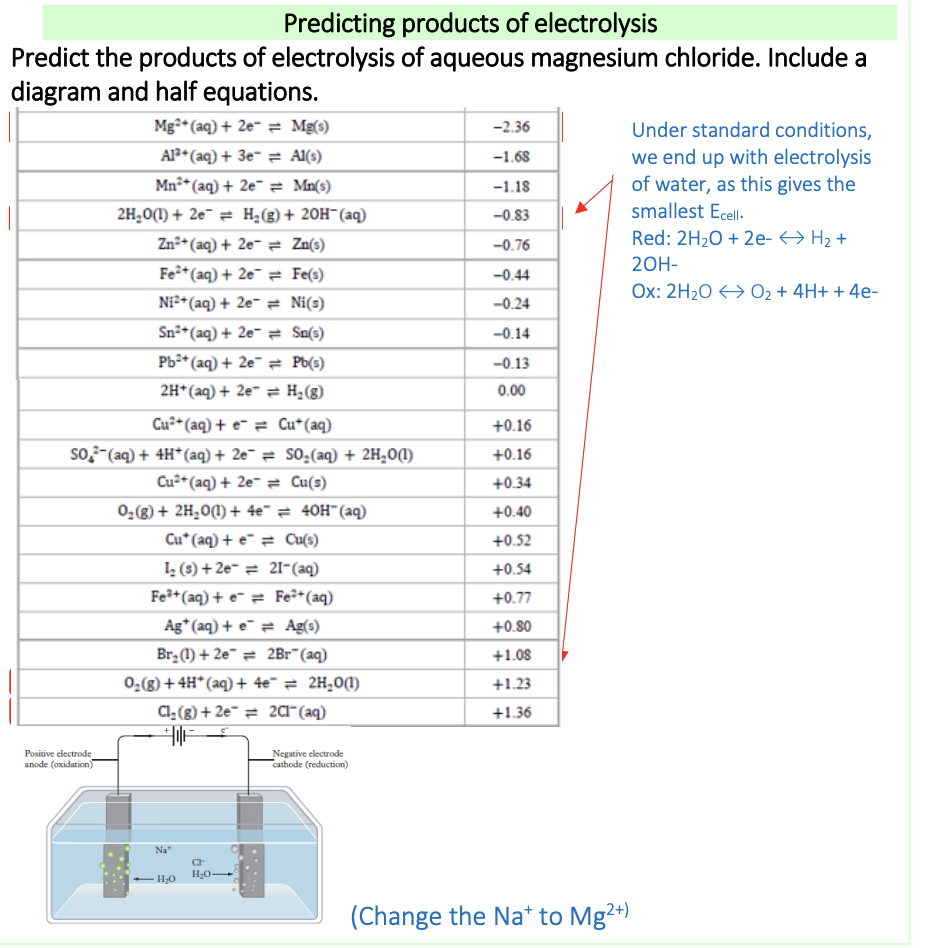
Why does the oxidation and reduction of water need to be taken into consideration in aqueous electrolysis, and not in molten electrolysis?
molten electrolysis: the only ions present are those of the molten substance, e.g Na+ and Cl- for molten sodium chloride
Aqueous electrolysis: when it’s being conducted, water needs to be considered as the water half-equations compete with the reactants
Reaction products can be determined using the electrochemical series
What are the factors affecting electrolysis of aqueous solutions?
nature of electrolyte: e.g aqueous or molten
E°cell value: When competing reactions may occur (e.g. do to presence of water), the half-reactions that will give the smallest E°cell value will occur, as less energy needs to be provided
Concentration of electrolyte: The table of standard electrode potentials refers to 1M solutions. Nonstandard concentrations change the electrode potentials, and this can change the products of electrolysis as happens with dilute vs concentrated sodium chloride solutions
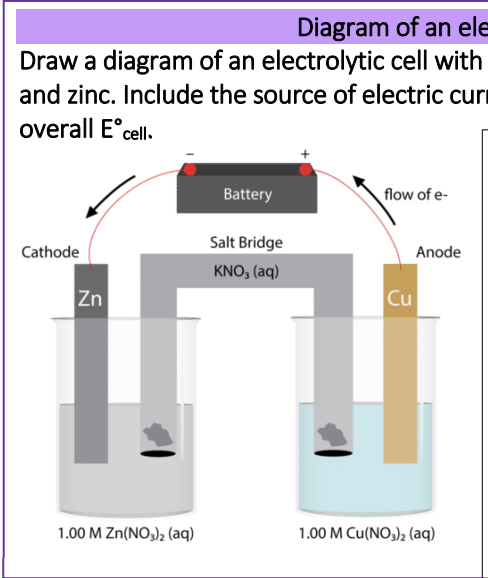
This is not a spontaneous reaction. Cu was the cathode for a galvanic cell, but is now the anode, so copper is now being oxidised. (Electrolytic cells are usually shown with a single container, not separate half cells with a salt bridge.)