Physical Geography - Exam 3 (Stephen Wooten MSU)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:58 AM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
1
New cards
nonrenewable resource
resources that are in limited supply and when consumed like a certain rate will be used up.
2
New cards
renewable resource
resources that are replenished naturally over a relatively short period of time.
3
New cards
Why is soil a renewable yet exhaustible resource
Soil forms slower than it is being used/eroded
4
New cards
what are the four components of soil
minerals, air, water, organic matter
5
New cards
saturation
all pore space is filled with water
6
New cards
what is field capacity
the amount of water soil can hold against the force of gravity
7
New cards
what is permeability?
how well water travels through pores
8
New cards
What are the five soil formation factors
parent material, time, topography, climate, organisms
9
New cards
what is residual parent material?
soil that forms from the residue left by weathering if local bedrock
10
New cards
what is transported parent material?
soil that forms from the material deposited by wind, water, or glacier ice
11
New cards
what are the four soil formation processes?
addition, transportation, depletion, and translocation
12
New cards
What is the process of soil formation that is called addition?
gains made by soil when organic matter is added
13
New cards
what is the soil formation process that is called Transportation?
the weathering of rocks and minerals and decomposition of organic material in soil
14
New cards
What is the soil formation process that is called Depletion?
the loss of dissolved components as they are carried downward by water
15
New cards
What is the soil formation process that is called translocation?
movement of dissolved and suspended particles from one depth to another within the soil
16
New cards
Loam
Using the soil texture triangle, what is 50% sand, 20% clay, and 30% silt?
17
New cards
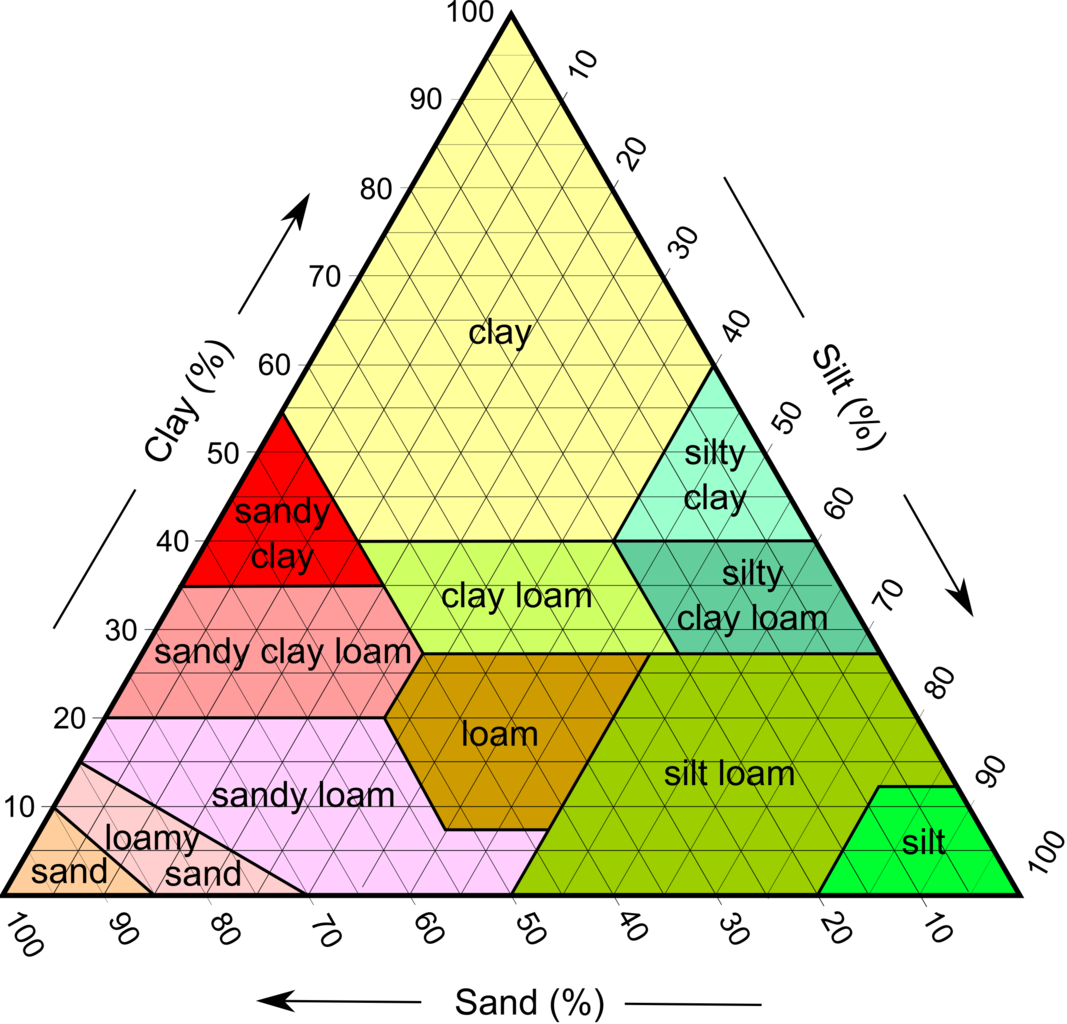
using the soil textures triangle, what is 30% sand, 60% clay, and 10% sit?
Clay
18
New cards
What is the A horizon?
the top layer of soil that is darkened by organic material
19
New cards
What is the B horizon?
the middle layer of soil that recieved dissolved particles from the above layer
20
New cards
What is the C horizon?
the bottom layer of soil where weathering has only minor effects.
21
New cards
What are the four soil structures
Platy, Blocky, Prismatic, Granular
22
New cards
what dies a platy soil structure look like?
thin plates stacked horizontally
23
New cards
What does a prismatic soil structure look like?
arranged in vertical columns
24
New cards
What does a blocky soil structure look like an what are its two sub categories?
irregular shape but fit together like Legos, angular (sharp edges) and sub angular (rounded)
25
New cards
What does a granular soil structure look like?
small and nearly rounded (think like sand)
26
New cards
What are the four carbon pools and which is the largest?
the atmosphere, biosphere, lithosphere (Earth's crust is the largest), and the oceans
27
New cards
What is happening when carbon goes from the lithosphere/biosphere to the atmosphere?
the burning of fossil fuels, volcanic eruptions, forest fires emissions by organisms
28
New cards
What is happening when carbon goes from the atmosphere to the lithosphere/biosphere?
Photosynthesis (Plants take in CO2 in order to create food for themselves)
29
New cards
What is happening when carbon goes from the atmosphere into the ocean?
the ocean is absorbing and dissolving CO2
30
New cards
What are Earths four internal layers?
the solid inner core, liquid outer core, mantle, and crust
31
New cards
What is Earth's solid core made up of?
dense iron and Nickle which exist in a solid state due to high pressure
32
New cards
What is Earth's liquid outer core made up of?
the same materials as the inner solid core, except they exist in the liquid form due to less pressure
33
New cards
What two categories does the Mantle break into?
lower and upper mantles
34
New cards
What is the lower mantle of Earth?
a layer composed of iron, magnesium, and silicon compunds
35
New cards
How many regions is the upper mantle split into and what are they called?
2, the asthenosphere (lower portion) and the lithosphere (upper portion)
36
New cards
What is the asthenosphere made of?
molten rock
37
New cards
What is found in the crust and what is the range of its thickness?
rocks, 5-40kms
38
New cards
What is the Moho discontinuity and how was it found?
the boundary between the mantle and crust, it indicates the mantle is denser than the crust. It was found because earthquake seismic wave speeds change when moving through the mantle vs the crust since the mantle is denser.
39
New cards
what is continental crust?
lower density, thicker, and made up of felsic rock
40
New cards
What is oceanic crust?
dense, made up of mafic rock
41
New cards
What are elements?
building blocks of minerals (cannot simplify any further)
42
New cards
What are minerals?
naturally occurring inorganic elements or compounds having specific formulas, definite chemical composition, physical properties, and crystalline structure
43
New cards
What are rocks?
crustal material made up of minerals
44
New cards
What are five ways to identify minerals?
chemical composition, hardness, streak, fracture, cleavage
45
New cards
What is the chemical composition of a rock?
its atomic structure
46
New cards
What is the hardness of a rock based off of?
Mohs hardness scale
47
New cards
What is the streak of a rock?
the color of a mineral when made into a fine powder
48
New cards
What is the fracture of a rock?
the way a mineral breaks
49
New cards
What is the cleavage of a rock?
the tendency of a mineral to break along a flat, planar surface based on its structure, a type of fracture
50
New cards
What are the three main rock types?
igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary
51
New cards
What are igneous rocks and hat two groups can they be broken into?
rocks that are more resistant to weathering, intrusive and extrusive
52
New cards
What is an intrusive igneous rock?
a rock resulting from cooled magma
53
New cards
What is an extrusive igneous rock?
a rock resulted from cooled lava
54
New cards
What are sedimentary rocks and what two categories can they be broken into?
rocks resulting from deposition, compaction, and cementation of rock fragments, mineral grains, and dissolved material derived from other rocks, can be broken into clastic and non clastic
55
New cards
What are clastic sedimentary rocks?
made from particles other than rocks (more common)
56
New cards
What are non clastic sedimentary rocks?
form from chemical solutions or organic deposition
57
New cards
what are metamorphic rocks forms from?
form when other rock types are subject to heat and pressure
58
New cards
What is the continental drift theory?
a hypothesis that the continents were slowly drifting around the Earth
59
New cards
What led to the continental drift theory?
Closely related fossil plants and animals that seemed likely to have evolved in the same geographic region were scattered across South Africa, South America, India, Australia, and even Antarctica
60
New cards
What is seafloor spreading?
Locations where hot rock continually rises from deep in the mantle, melting and then solidifying. Through this process, new igneous rock forms and is quickly pushed away horizontally by still-newer rock forcing its way up from below all along a mid-oceanic ridge
61
New cards
What is continental drift?
the theory about continents being connected
62
New cards
What are plate tectonics?
the theory discussing how plates move
63
New cards
what are the three plate boundaries?
divergent, convergent, and transform
64
New cards
What is a divergent plate boundary and what is an example?
two plates moving away from each other, seafloor spreading
65
New cards
What types of convergent boundaries are there?
continental-continental, oceanic-continental, oceanic- oceanic
66
New cards
What is the result of a continental-continental convergent boundary?
huge mountain ranges
67
New cards
What is the result of an oceanic-continental convergent boundary?
subduction, oceanic trench and continental mountains, continental volcano
68
New cards
What is the result of an oceanic-oceanic convergent boundary?
subduction resulting in an underseas trench, island arc
69
New cards
What is a convergent boundary?
a boundary where two or more lithospheric plates collide
70
New cards
What is a transform boundary?
two boundaries slip past each other laterally, neither creates nor destroys crust, commonly produce shallow quakes
71
New cards
What is an earthquake?
Shaking and trembling of the Earth's surface
72
New cards
What is the focus of an Earthquake?
the point in which the fault begins to rupture, which may be deep below ground
73
New cards
What is the epicenter of an earthquake?
the point at Earth’s surface vertically above the point of focus of an earthquake
74
New cards
attenuation
the ground shaking becomes weaker with increasing distance from the focus
75
New cards
amplification
soft ground can result in stringer shaking with increasing distance
76
New cards
What is the magnitude of an earthquake and what scale does it use?
the energy released as the fault ruptures, the Richter scale
77
New cards
What is the intensity of an earthquake and what scale does it use?
refers to the severity of the shaking at a particular location and it uses the Mercalli scale
78
New cards
why do tsunamis occur?
Ocean water is suddenly displaced by the movement of the crust in an earthquake or by a large landslide
79
New cards
what are the two types of lava?
Aa and Pohoehoe
80
New cards
What is Aa lava?
most abundant type of lava: rough/jagged surface, thick
81
New cards
what is pahoehoe lava?
smooth, billowy, or ropy surface; relatively
82
New cards
What are the three types of volcanoes and which one is the most destructive?
shield, cinder cone, composite/stratovolcano (most aggressive)
83
New cards
What is a shield volcano?
layer upon layer of solidified lava flows; large volcanoes but not steep. Large craters at their summits
84
New cards
What is a cinder cone volcano?
small volcanoes built from pyroclastic. They have very steep sides, and usually have a small crater
85
New cards
What is a composite volcano
these volcanoes are typically tens of miles across and ten thousand or more feet in height. They have moderately steep sides; Most destructive. Known as stratovolcanoes because of their layering of young ad older lava flows
86
New cards
What is a landform
a feature of Earth’s topography that can be distinguished and studied as a single unit.
87
New cards
what is a landscape
an aggregation of landforms
88
New cards
What is weathering
the breaking down or decomposition of rocks and other material on the Earth’s surface
89
New cards
what is mechanical weathering and what are two types
Destruction of rocks through force/stress, wedging and thermal expansion
90
New cards
What is wedging?
rocks break apart due to accumulation of sand/ice expanding in cracks
91
New cards
What is thermal expansion?
When a rock is warm, it expands, when a rock is cool, it contracts
92
New cards
What is chemical weathering
breaking down of rocks from some type of chemical reaction; changes the materials that make up the rock
93
New cards
What is biological weathering
weathering due to plants or animals such as burrowing animals or tree roots
94
New cards
What is mass movement
material that falls under the influence of gravity with little or no transporting agent
95
New cards
What are the four types of mass movement?
creep, slide, fall, flow
96
New cards
What is creep?
upper layer of soil moves faster than the layers below, which tilts vertical objects downslope
97
New cards
What is slide?
starts with a slope failure in which a block of rock or soil breaks loose and slide over a distinct surface
98
New cards
What is flow and what two types are there?
a relatively fluid downhill movement of weathered rock, loose sediments and soil, earth flow and debris flow
99
New cards
What is earth flow?
slow-moving flows often involving fine-grained and clay-rich soil
100
New cards
What is debris flow?
a fluid, fast moving slurry of sediment and water