chemistry - fuels & earth science: fuels (8.1 - 8.17)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
8.1 what are hydrocarbons?
compounds that contain carbon & hydrogen ONLY
8.2 crude oil
complex mixture of hydrocarbons
contains molecules in which carbon atoms are in chains/rings
important source of useful substances (fuels & feedstock for petrochemical industry)
finite resource
8.3 crude oil separated by fractional distillation - why?
crude oil not runny enough/ignited easily enough to be used as fuel
separated into simpler, more useful mixtures
8.3 crude oil separated by fractional distillation - how?
diff. hydrocarbons have diff. boiling points
crude oil heated strongly to evaporate it
hot vapours piped into bottom of column
in fractionating column: (hottest at bottom, coldest at top)
vapours rise through column & cool
vapours condense when reach part of column below their boiling point
liquid falls into tray & piped away
vapours with lowest boiling points don’t condense - leave top as mixture of gases
bitumen has highest boiling point - leaves at bottom as hot liquid
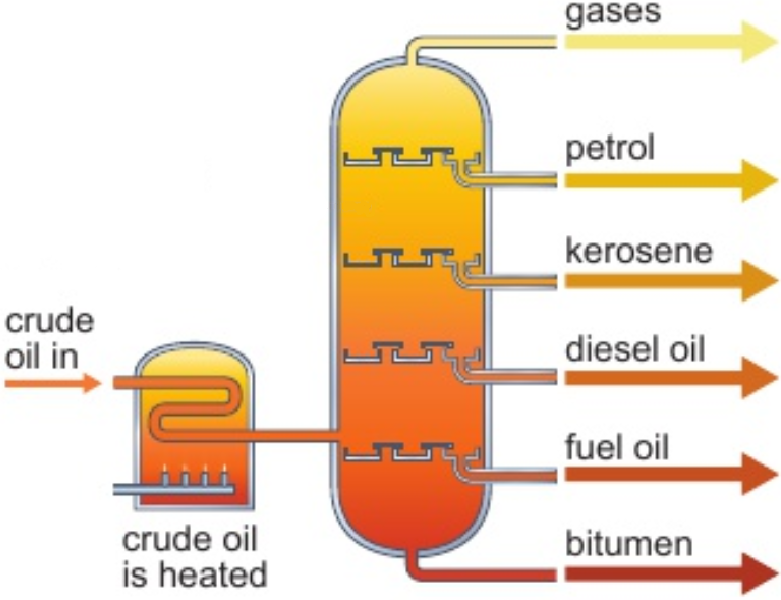
8.4 order of fractions
gases
petrol
kerosene
diesel oil
fuel oil
bitumen
8.4 uses of fractions - gases
domestic heating
domestic cooking
8.4 uses of fractions - petrol
fuel for cars
8.4 uses of fractions - kerosene
fuel for aircraft
8.4 uses of fractions - diesel oil
fuel for some cars
fuel for trains
8.4 uses of fractions - fuel oil
fuel for large ships
in some power stations
8.4 uses of fractions - bitumen
surfacing roads & roofs
8.5 how hydrocarbons in diff. fractions differ in number of carbon & hydrogen atoms molecules contain, boiling points, ease of ignition, viscosity
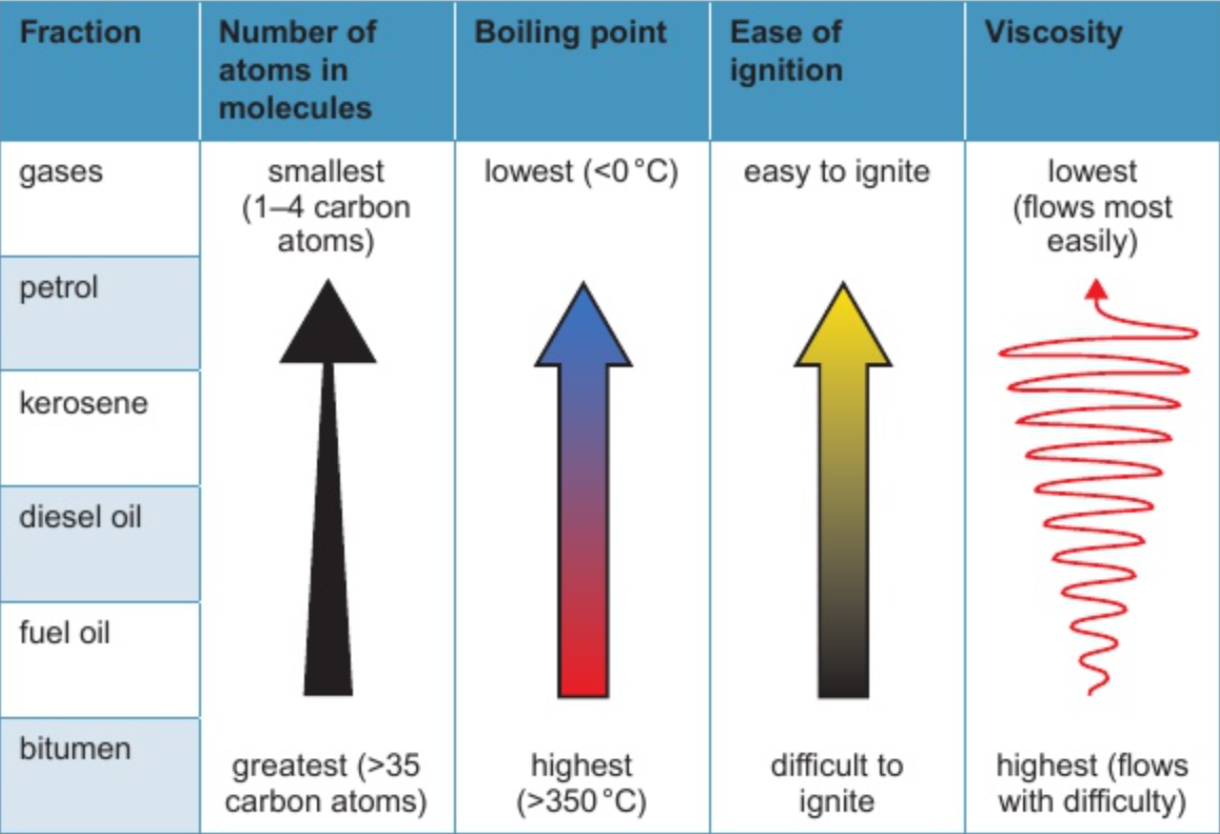
8.5 what homologous series are hydrocarbons in diff. fractions from?
(mostly) from alkane homologous series
8.6 homologous series
series of compounds which:
have same general formula (e.g. alkanes = CnH2n+2)
differ by CH2 in molecular formulae from neighbouring compounds
show gradual variation in physical properties (shown by boiling points)
have similar chemical properties
8.7 complete combustion of hydrocarbon fuels
carbon dioxide + water produced
energy given out
8.8 why can incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons produce carbon & carbon monoxide?
some carbon atoms:
fully oxidised to carbon dioxide
only partially oxidised to carbon monoxide
released as smoke & soot (carbon)
incomplete combustion of hydrocarbon fuels
limited supply of air/oxygen
carbon + carbon monoxide + water produced
energy given out (less than complete combustion)
8.9 how does carbon monoxide behave as toxic gas?
combines with haemoglobin in RBCs - prevents oxygen combining
reduces amount of oxygen in blood stream - makes people sleepy/unconscious/can cause death
8.10 problems caused by incomplete combustion in appliances that use carbon compounds as fuel - producing carbon monoxide
reduces amount of oxygen in bloodstream - makes people sleepy/ unconscious/can cause death
(causes problems if appliances unventilated)
8.10 problems caused by incomplete combustion in appliances that use carbon compounds as fuel - producing soot
blocks pipes carrying waste gases away from appliance
blackens buildings
causes breathing problems if collects in lungs
(causes problems if appliances poorly maintained/ unventilated)
8.11 impurities in some hydrocarbon fuels - production of sulfur dioxide
hydrocarbon fuels may contain sulfur compounds (impurities)
hydrocarbon fuel burnt - sulfur reacts with oxygen, forms sulfur dioxide
8.12 acid rain - formed
sulfur dioxide dissolves in rain water - forms sulfuric acid
8.12 acid rain - problems
makes soil acidic - crops don’t grow well
causes excess acidity in rivers & lakes - prevents fish eggs hatching, kills fish & insects
reacts with calcium carbonate - increases rate of weathering of limestone/marble buildings & breaks down their structures
increases rate of corrosion of metals
8.13 fuels burned in engines - produce pollutants
car engines - fuel mixed with air & ignited inside engine
oxygen & nitrogen in air react together at high temps.
produces oxides of nitrogen = pollutants
8.14 hydrogen as fuel in cars instead of petrol - advantages
renewable resource: by-product of cracking, produced by reacting methane (from natural gas) with steam
petrol from crude oil = finite resource
environmental benefits: produces water vapour but no carbon dioxide
petrol produces carbon dioxide = greenhouse gas → global warming, climate change
easily ignited
combustion releases large amounts of energy
8.14 hydrogen as fuel in cars instead of petrol - disadvantages
difficult to store in large amounts: gas at room temp.
petrol = liquid at room temp.
8.15 petrol, kerosene, diesel oil - renewable/non-renewable
non-renewable fossil fuels
8.15 petrol, kerosene, diesel oil - obtained from
crude oil
8.15 methane - renewable/non-renewable
non-renewable fossil fuel
8.15 methane - found in
natural gas
8.16 cracking
breaks down larger, saturated hydrocarbon molecules (alkanes)
forms smaller, more useful hydrocarbon molecules - some unsaturated (alkenes)
saturated - type of hydrocarbon, bond
alkanes
carbon atoms joined by single covalent bonds (C-C)
unsaturated - type of hydrocarbon, bond
alkenes
contain carbon-carbon double bond (C=C)
8.17 why is cracking necessary?
crude oil separated by fractional distillation - volume of each fraction usually doesn’t match demand
demand for smaller hydrocarbon molecules > demand for larger hydrocarbon molecules - smaller hydrocarbon molecules more useful
cracking produces shorter chained alkanes from longer chained alkanes