OD: Odontogenic Neoplasms & Tumours
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Odontogenic Tissues can be categorised into Epithelium of Origin or Mesenchyme of Origin.
List Odontogenic Tissues which are Epithelial in Origin (5)
1) Oral Epithelium
2) Dental Lamina
3) Enamel Organ
4) Reduced Enamel Epithelium
5) Rests of Malassez
Odontogenic Tissues can be categorised into Epithelium of Origin or Mesenchyme of Origin.
List Odontogenic Tissues which are Mesenchyme in Origin (3)
1) Dental Papilla - forms pulp of tooth (sits below enamel organ)
2) Dental Follicle - surrounds tooth bud, forming PDL
3) Periodontal Ligament
The Dental Lamina is a source of Odontogenic Epithelium (source of most odontogenic tumours). It Gives Rise to... (5)
Ameloblastoma
Ameloblastic fibroma
CEOT (Calcified Epithelial Odontogenic Tumour)
Keratocyst- NOT an odontogenic tumour.
Gingival cysts- NOT an odontogenic tumour.
Radiographically, how do Odontogenic Tumours tend to present? (3)
1) Most present as Radiolucent Lesions
2) Some contain Calcifications
3) Most often present at the angle of the Mandible
Benign Odontogenic Tumours are classified by Histogenesis. List them (3)
1) Odontogenic Epithelium alone
2) Odontogenic Epithelium and Odontogenic Mesenchyme +/- Dental Hard Tissues
3) Odontogenic Mesenchyme Alone
What is the term given to a Malignant Odontogenic Tumour risen from Epithelium?
Carcinoma
What is the term given to a Malignant Odontogenic Tumour risen from Mesenchyme?
Sarcoma
Describe the Epidemiology of Odontogenic Tumours
- Very Rare
- 99% benign
- Ameloblastoma is the most common neoplasm
Where are the 3 different sources benign odontogenic tumours can arise from?
Odontogenic epithelium alone (group 1 WHO)
Odontogenic epithelium and odontogenic mesenchyme +/- dental hard tissues. (grp 2)
Odontogenic mesenchyme alone. (Grp 3)

Odontomes are not Neoplasms. Explain why
Odontomes are Harmatomas.
These are malformations growing during the growth phases of a patient, when growth stops, the odontomes stop growing also. They do not behave like Neoplasms
List Odontogenic Tumours which are of only Epithelial Origin?
1) Ameloblastoma
2) Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour (AOT)
3) Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumour (CEOT)
4) Squamous Odontogenic Tumour (SOT)
What is an ameloblastoma?
A Benign but locally destructive odontogenic tumour arise from Epithelial Tissue
Which age groups do Ameloblastomas affect?
30 to 50
black people
Where do Ameloblastomas commonly affect?
80% are found in the Mandible, most at the angle (but can occur anywhere in jaws)
More aggressive in maxilla
Once it exits bone and enters soft tissues - easier expansile growth - harder to treat
Why do Ameloblastomas more commonly affect the Angle of the Mandible?
Ameloblastoma arise from the Dental Lamina which is Epithelial in Origin.
Most Dental Lamina is found at the angle of the mandible
Describe 4 Features of Ameloblastoma?
1) Often Asymptomatic
2) Bucco-Lingual Expansion - degree of facial swelling
3) Root Resorption or Displacement
4) Commonly Multi-locular but can be Uni-locular on Radiographs
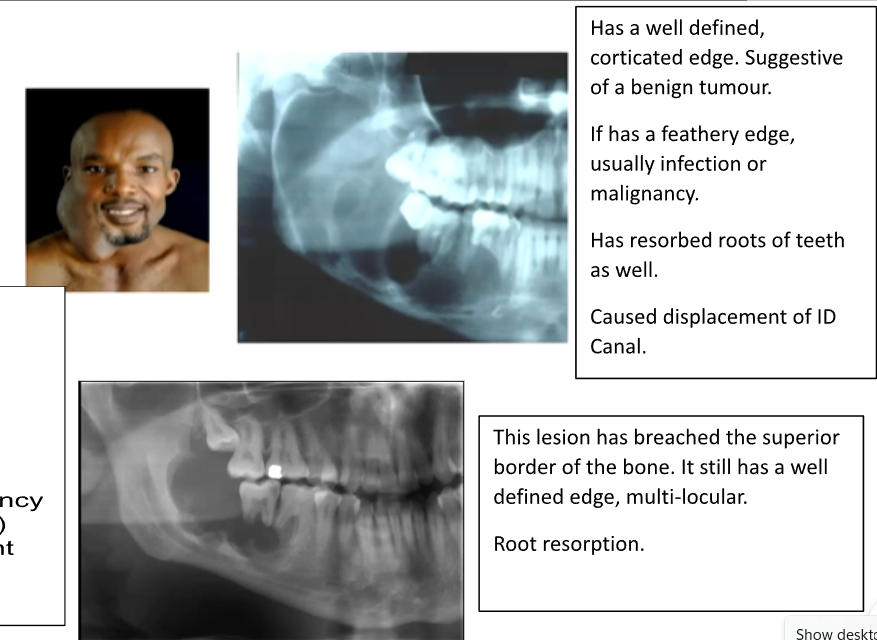
How can you differentiate an Odontogenic Keratocyst from an Ameloblastoma?
Amelobastoma have Bucco-Lingual Expansion, whereas an Odontogenic Keratocyst have antero-posterior expansion
There are 3 Subtypes of Ameloblastoma. List them
1) Conventional Type (85%): Intra-Osseous
- Follicular
- Plexiform
2) Unicystic (14%): Intra-Osseous - less common and less aggressive
3) Peripheral (1%): Extra-osseous/gingiva - may arise in soft tissues of gums
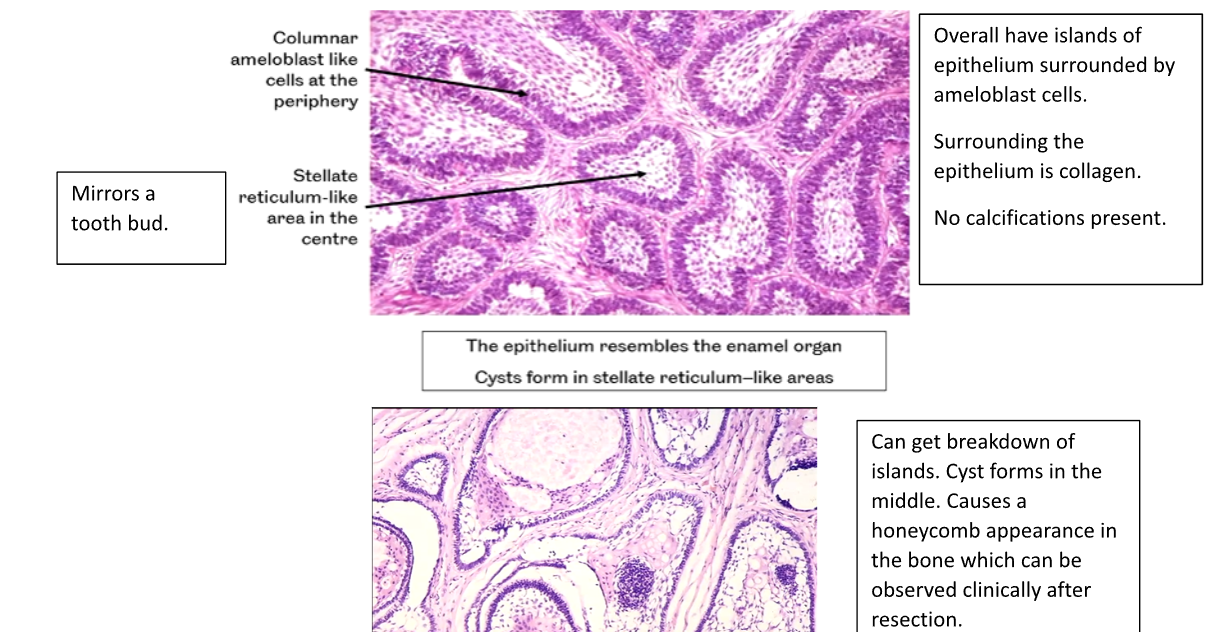
Describe the Follicular Pattern of an Ameloblastoma (3)
1) Columnar Ameloblast Like Cells at the Periphery
2) Stellate Reticulum-Like area in the Centre
3) The Epithelium resembles the enamel organ, cysts form in the Stellate Reticulum like Areas.
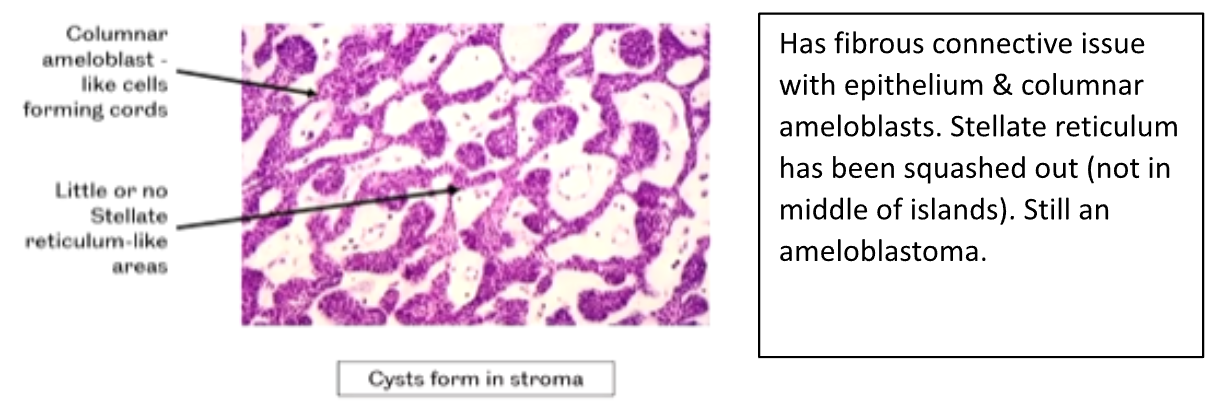
Describe the Plexiform Pattern of an Ameloblastoma (3)
1) Columnar Ameloblasts - like cells forming Cords
2) Little or No Stellate Reticulum like areas
3) Cysts form in the Stroma
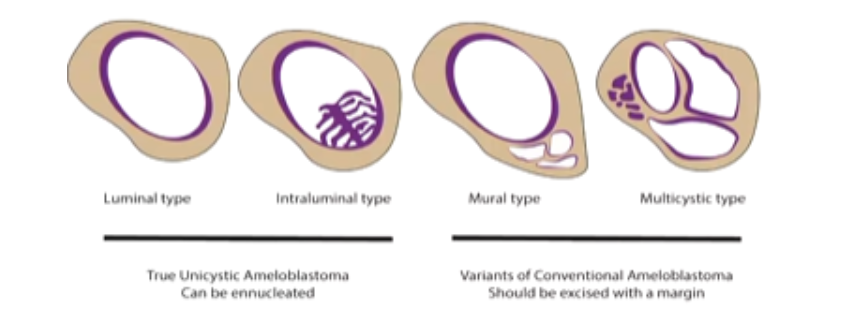
10-15% of Ameloblastomas are Unicystic.
What are the 4 Types of Unicystic Ameloblastomas
1) Luminal Type
2) Intraluminal Type
3) Mural Type
4) Multicystic Type
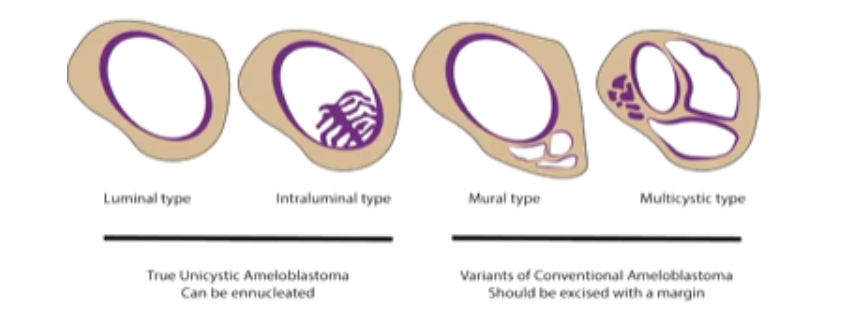
Which Unicystic Ameloblastomas are treated by Enucleation?
1) Luminal Type
2) Intraluminal Type
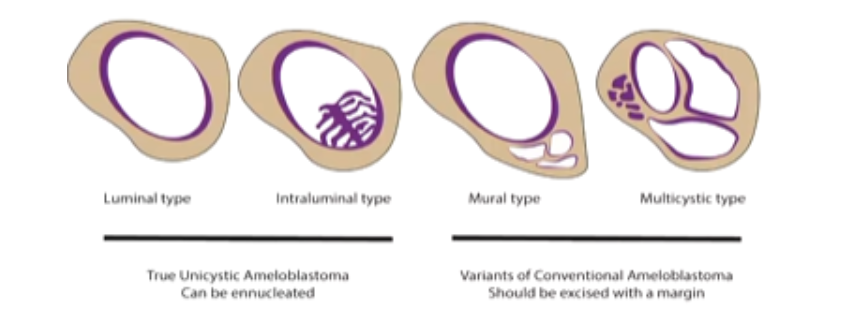
Which Unicystic Ameloblastomas are treated with Resection
1) Mural Type
2) Multicystic Type
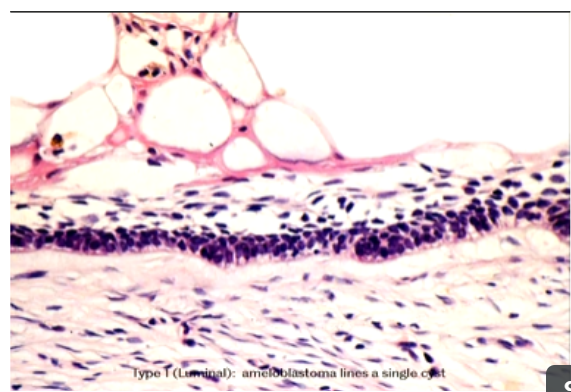
Describe the Histological Appearance of Luminal Unicystic Ameloblastomas
Ameloblastoma lines a single cyst
Cyst lining has ameloblasts. Stellate reticulum.
Rather than having a follicular appearance has a cystic lining.
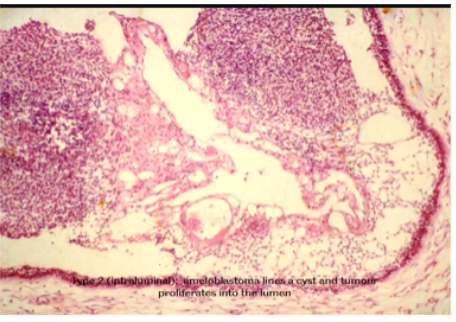
Describe the Histological Appearance of Intraluminal Unicystic Ameloblastomas
Ameloblastoma lines a cyst and tumour proliferates into the Lumen
single cyst growing into lumen
How do you manage a Conventional Ameloblastoma?
- Excision with 10mm Margins to minimise recurrence
- Reconstruction needed - maybe with section of rib
- Maxilla more challenging to treat and restore
How do you manage a True Unicystic Ameloblastoma?
Refering to Luminal and Intraluminal Types:
- Enucleation and Careful Follow-Ups
How is a diagnosis made for an ameloblastoma?
Radiograph
Clinical exam and biopsy → can only tell if its unicystic after excision
What is an Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour (AOT)?
Benign tumour
From epithelial tissue
It does not recur and is probably a Hamartoma
What age & gender do AOTs affect and where are they usually found?
Age: 10-20, F>M
Mainly maxilla
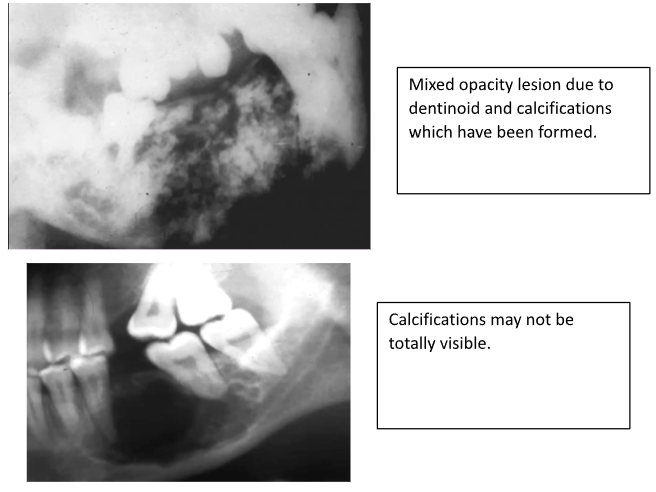
What is the radiographic appearance of an AOT?
Radiolucency often around a tooth crown - may have calcifications
Can cause displacement of teeth
Mimic dentigerous cysts (can be a differential to it)
Most commonly occur around impacted canines
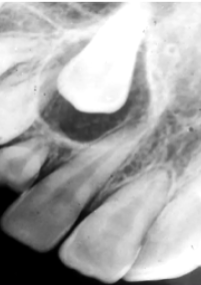
How do you differentiate a Dentigerous Cyst from an Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour?
AOT and Dentigerous Cyst affect unerupted teeth and the radiolucency attaches at the ACJ
In AOT the radiolucency will have calcifications in it therefore have small radiopacities.
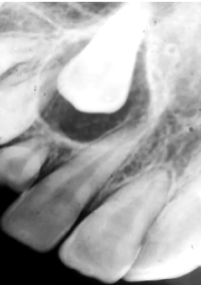
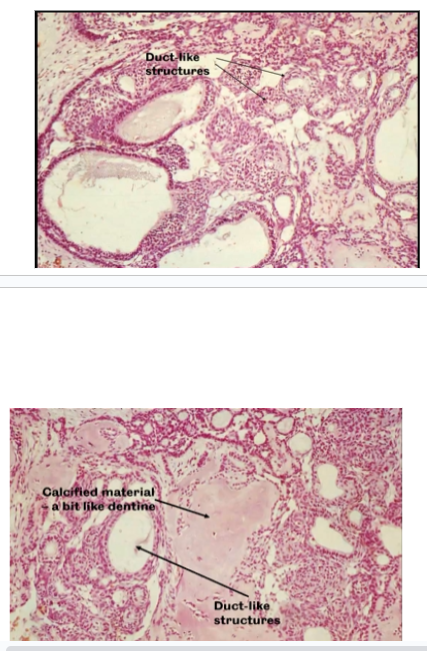
What is the Histological Appearance of an AOT?
Epithelial Cells forming sheets and Duct-Like Structures.
Calcification is common
What is the Treatment for an AOT?
Enucleation
What is a Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumour and what is its Epidemiology?
Benign locally destructive, similar to ameloblastoma, from odontogenic epithelium alone
Age: 10-60
2/3 in Mandible, molar region +/- unerupted tooth
What is the Radiological Appearance of a CEOT?
Radiolucency with Speckled Calcifications
Calcifications increase with Age
Much bigger than AOTs
Doesn’t have dentigerous relationship
What is the Histological Appearance of a CEOT?
Composed of Pleomorphic Epithelium with Calcifications
Enamel Matrix Material which may calcify
Cubodial Cells with Prickles
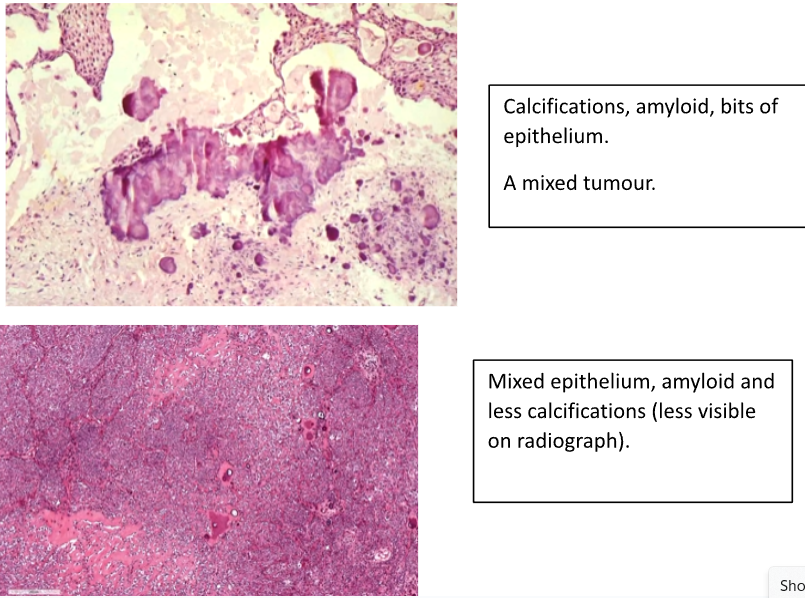
What is the Treatment for a CEOT?
As for Ameloblastoma
- Enucleation
- Resection
- Reconstruction
List 3 Odontogenic Tumours that arise from Epithelial Tissue, Mesenchyme Tissue +/- Dental Hard Tissue (group 2 WHO)
1) Ameloblastic Fibroma
2) Dentinogenic Ghost Cell Tumour
3) Odontomes
What is an Ameloblastic Fibroma and whats it epidemiology?
A benign, locally agressive mixed odontogenic tumour
Age <20
Often found in the Mandible
What is the radiological appearance of an Ameloblastic Fibroma?
Well Defined Radiolucency - No calcifications
- 80% associated with an unerupted tooth
What is the histological appearance of an Ameloblastic Fibroma?
- Branching Cords and Islands of Epithelium resembling Enamel Organ or Dental Lamina
- Characteristic Fine Cellular Stroma
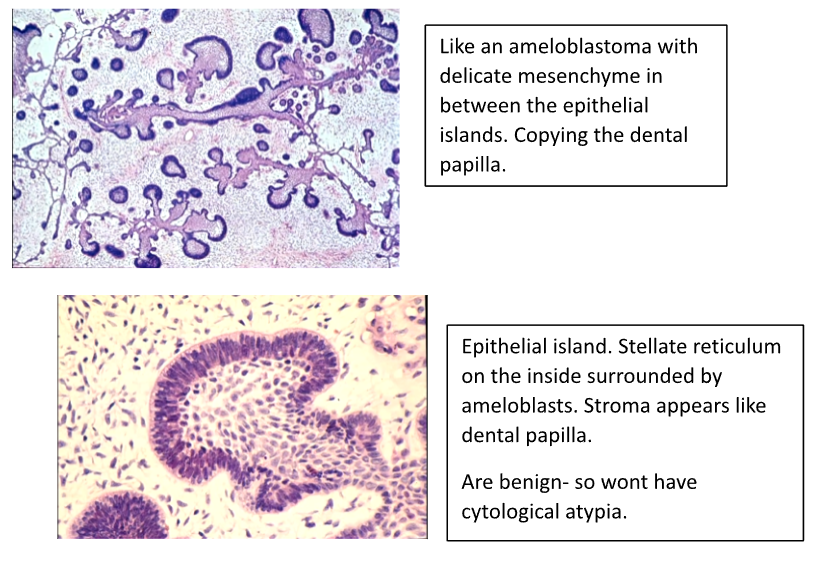
What is a Dentinogenic Ghost Cell Tumour and what’s its epidemiology?
A benign mixed odontogenic tumour,
Well define, locally aggressive
V rare, 40-60, M>F, mandible and maxilla
What is the radiological appearance of a Dentinogenic Ghost Cell Tumour?
Radiolucency with some calcifications. Tend to be well-outlined and large
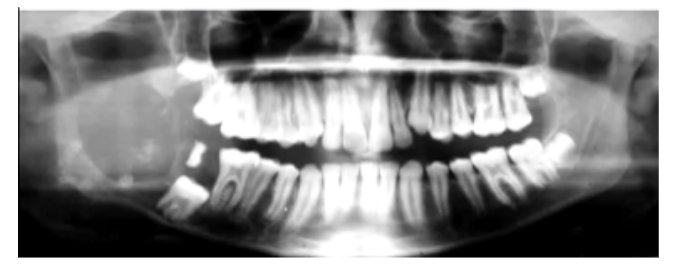
What is the Histological Appearance of a Dentinogenic Ghost Cell Tumour?
- Epithelium resembling Ameloblastoma
- Ghost Cells and Dentine
- Overlap with Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst
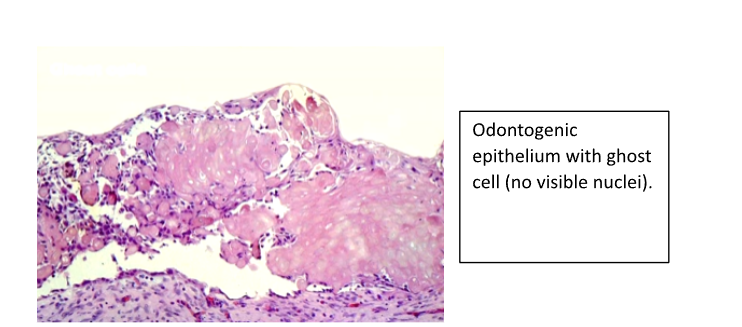
What do Ghost Cells look like?
Cells with No Nuclei within them
They can become calcified giving calcification on radiographs
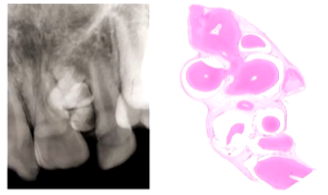
What are Odontomes AKA odontoma and what is their epidemiology?
Are harmatomas - disorganised proliferation of tissue which is normal for that location
Has limited growth potential (unlike tumour)
Up to 20 yrs (can prevent eruption of developing dentition), Both mandible and maxilla
What is the radiological appearance of an Odontome?
Radiolucency containing tooth like structures
What are the two types of Odontomes?
1) Compound Odontome
2) Complex Odontome
What are Compound Odontomes and what’s their epidemiology?
- Twice as common as a complex odontome
- Maxilla > Mandible
- Incisor/Canine Regions
- Small and Non-Aggressive
- A collection of Denticles (Little Teeth)
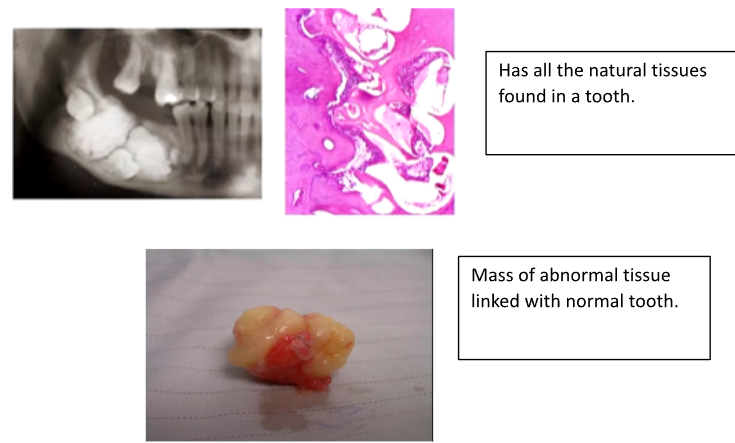
What are Complex Odontomes and what’s their epidemiology?
- Mandible > Maxilla
- Premolar/Molar Regions
- Ages 10 to 25
- Often a missing tooth in the arch - tooth fuses to odontome
- A fused mass of haphazardly arranged tooth tissues but normal morphogenetic relations are preserved
What are the 3 Odontogenic Tumours that are Mesenchyme only in Origin? (WHO group 3)
1) Myxoma/Myxo-Fibroma
2) Odontogenic Fibroma
3) Cementoblastoma
What is a Myxoma & Fibromyxoma and what’s their epidemiology?
A Benign Neoplasm
Mesenchymal in Origin
Tendency to recur
Locally destructive
10-30 yrs
Mandible> maxilla
What is the clinical appearance of a Myxoma?
Slow Growing Painless Swelling
What is the histological appearance of a Myxoma?
Triangular, Stellate Cells in Loose Myxoid Stroma
idek wtf that pic is
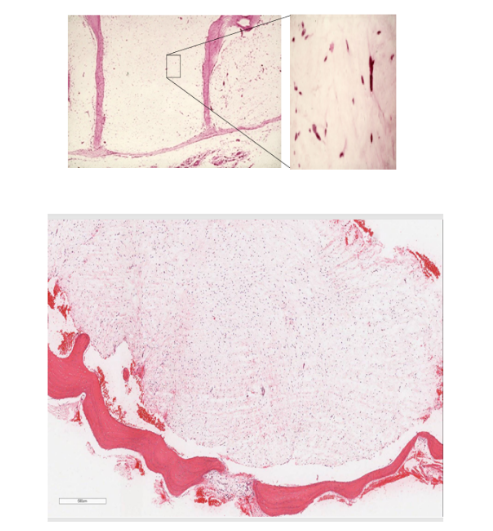
What is the treatment for a Myxoma?
Enucleation, Resection and Reconstruction (as for ameloblastoma)
What is the radiological appearance of a Myxoma?
Uni or Multi-Locular Radiolucency
- Soap Bubble Appearance
- Root Displacement or Resorption
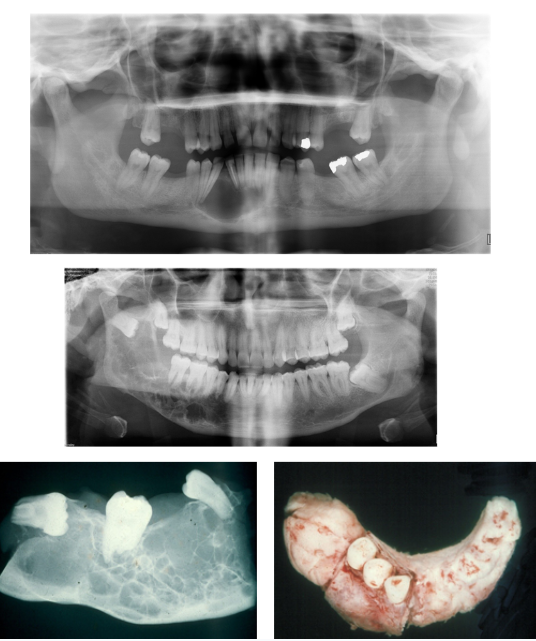
What is an Odontogenic Fibroma and what’s their epidmiology?
Benign Odontogenic Neoplasm - Mesenchymal in Origin
Wide age range, F>M
Mandible=maxilla
Not as aggressive
What are the two types of Odontogenic Fibromas?
Central and Peripheral
What is the Radiological Appearance of an Odontogenic Fibroma?
Unilocular radiolucency
What is the Histological Appearance of an Odontogenic Fibroma?
Mature Fibrous Tissue
Occasional Odontogenic Epithelial Rests but not a neoplastic part of the tumour
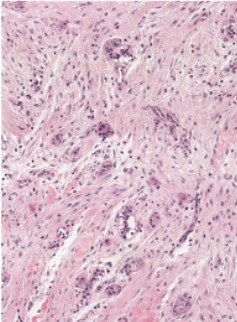
What is a Cementoblastoma and what is its epidemiology?
Benign odontogenic tumour originated from mesenchymal cells
Neoplasm of Cementoblasts
10-40, mandibular molars affected
What is the radiological appearance of a Cementoblastoma?
Radiopaque Lesion attached to Tooth Root with a Radiolucent Margin
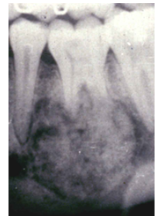
What is the Histological Appearance of a Cementoblastoma?
Sheets of Cementum and Osteoid in a Mosaic Pattern, many plump Cementoblasts
- Resemble Osteoblastoma
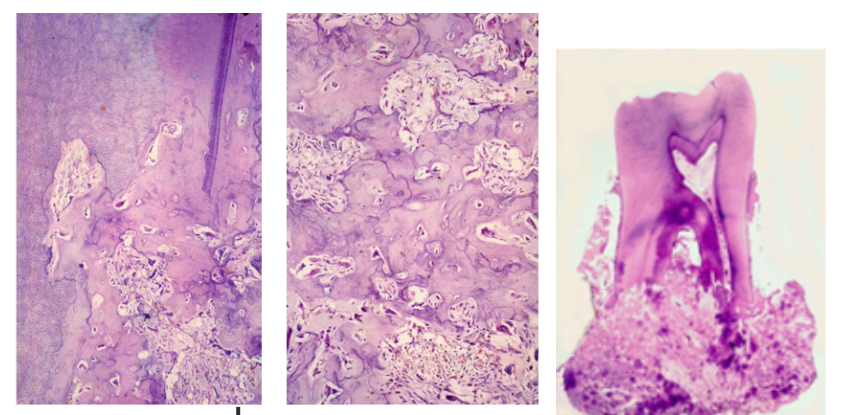
What is the Treatment for Cementoblastoma?
Surgical Excision
Malignant Odontogenic Tumours are very rare.
What are the 4 Malignant Odontogenic Tumours
1) Ameloblastic Carcinoma - appears like SCC with ameloblasts dotted around - abnormal mitoses, pleomorphsm, destructive growth, poorly defined edge
2) Primary Intra-Osseous Carcinoma
3) Clear Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma
4) Malignant Variants of Other Tumours/Cysts