Abnormal Hematology: RBC Morphology, Indices, and Inclusions
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Cold agglutinins
Your own antibody attacking your RBC.
Normocytic
Normal size of RBC 80-100 femtoliters.
Microcytic
RBC smaller than 80 femtoliters.
Macrocytic
RBC that are bigger than 100 femtoliters.
Dimorphic population
2 different groups of RBC, small and big RBC together.
Hypochromic
Central pallor is bigger than 3um.
Polychromasia
Cells appear grey-blue in color due to residual RNA making it a premature RBC.
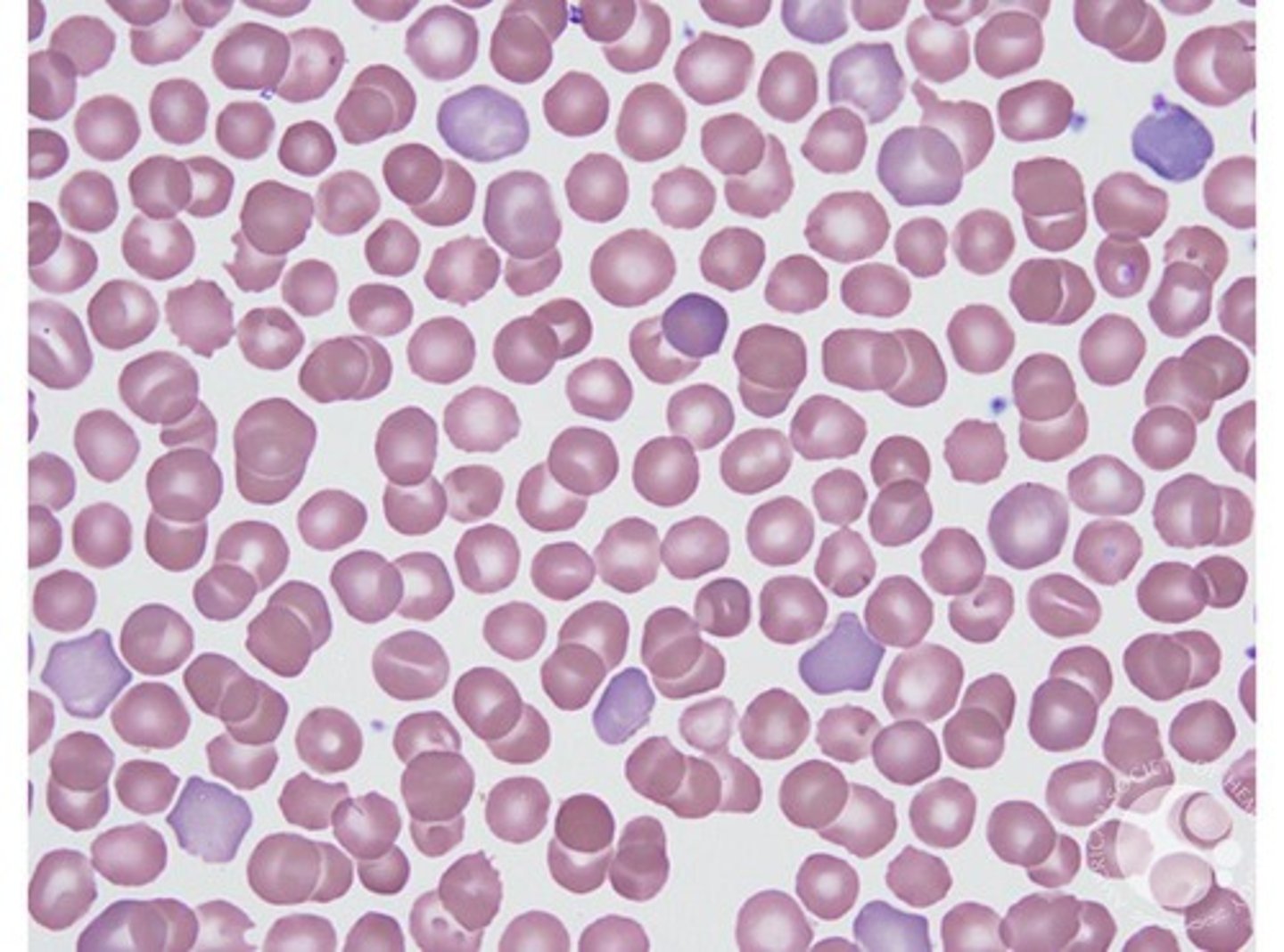
Agglutination
Irregular grape like cluster of red blood cells caused by cold agglutinins.
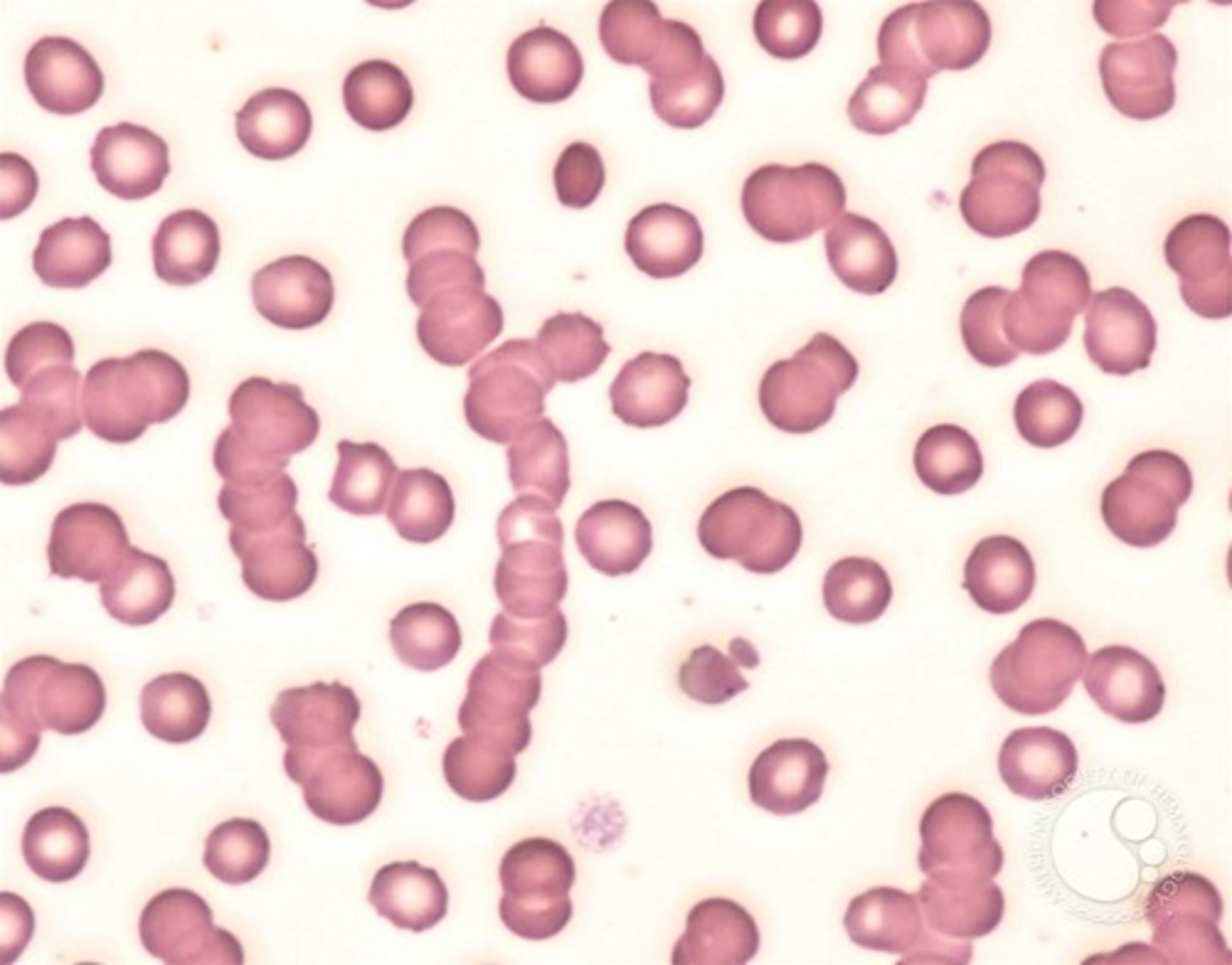
Rouleaux
RBC are aligned on top of each other resembling a stack of coins.
Anisocytosis
The variation of RBC shape.
Acanthocytes
Also called a spur cell; RBC with 3-12 spicules of varying lengths irregularly disturbed across the surface.
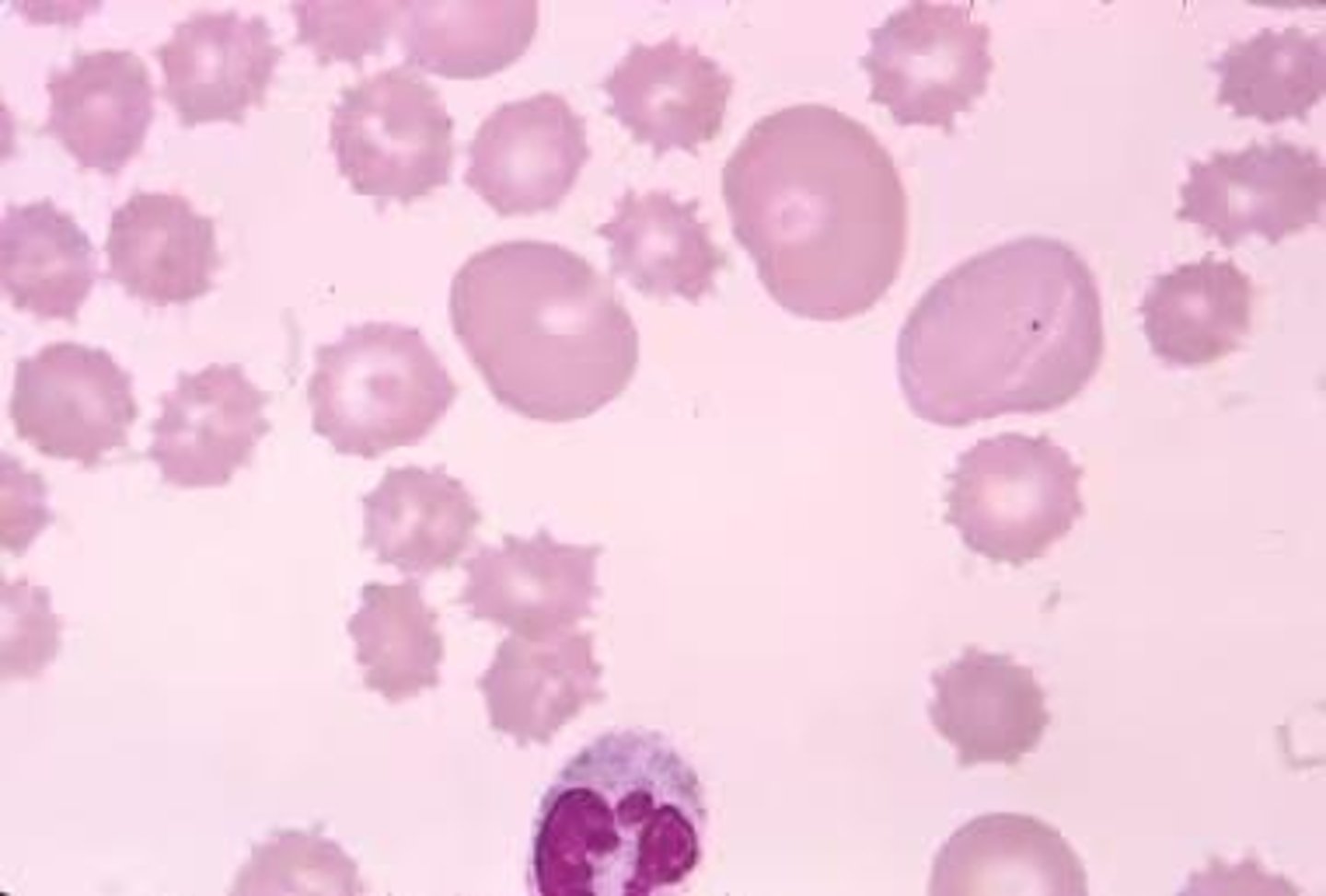
Burr cells
Also called an echinocyte; RBC with approx 10-30 rounded spicules evenly placed over the surface.
Elliptocytes
Cigar shaped with hemoglobin on both ends of the cell.
Helmet cells
Also called schistocytes; RBC fragment that looks like a half moon with two distinct projections.
Teardrop cells
Also called dacrocytes; looks like a teardrop and found after spleen pits out inclusions.
Ovalocytes
More egg shaped with greater tendency to vary in hemoglobin content.
Schistocytes
RBC fragment resulting from trauma to the RBC membrane.
Sickle cells
Also called drepanocytes; RBC that are crescent or sickle shaped with pointed projections.
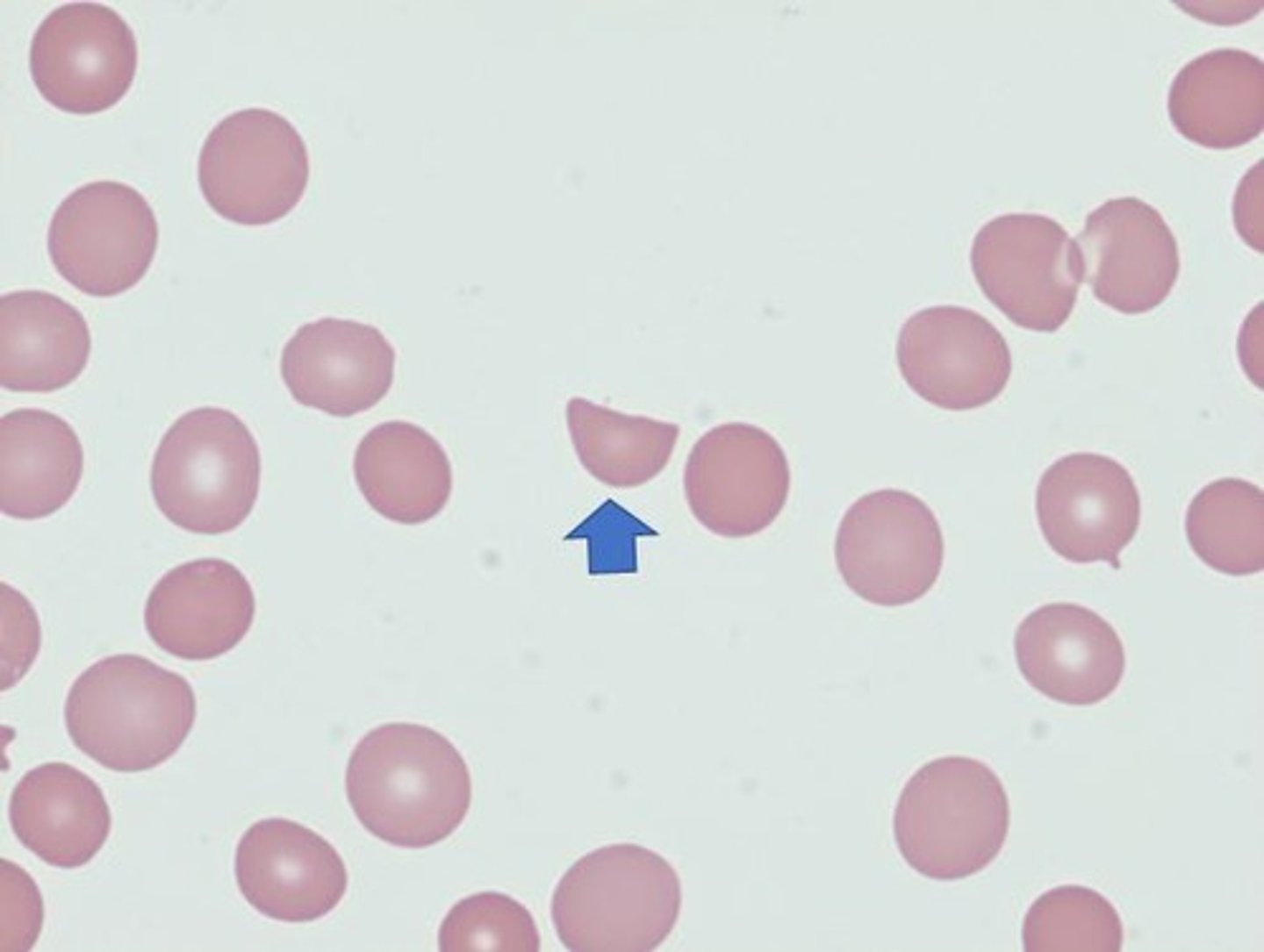
Spherocytes
RBC lack central pallor due to abnormal cell membrane, more fragile and cannot take in water.
Stomatocytes
Has a cut silt like through the RBC due to membrane defect, increased permeability to sodium.
Target cells
Also called codocytes; thin bell shaped cells with increased surface to volume ratio.
CBC results in agglutination
Causes falsely elevated MCV, MCH, and MCHC; falsely decreased RBC count.
Characteristic parameter for spherocytes
MCHC greater than 36 g/dL.
Spherocyte ability to take in water
More fragile and cannot take in water otherwise it will burst.
Stomatocyte ability to take in water
Increased permeability to sodium letting water enter the cell.
Target cell
Called a codocyte cell
Target cell morphology
Thin bell shaped cells with increased surface to volume ratio
Appearance of target cells
Resemble a target with a bullseye in the center
Fragility of target cells
Less fragile than normal RBC and is able to take in water
Conditions associated with target cells
Seen most commonly in liver diseases, renal disease, and hemoglobinopathies
Associated conditions of target cells
Associated with hereditary stomatocytosis, alcoholic cirrhosis, and lead intoxication
Howell-Jolly bodies
Small, round DNA remnants at cell periphery
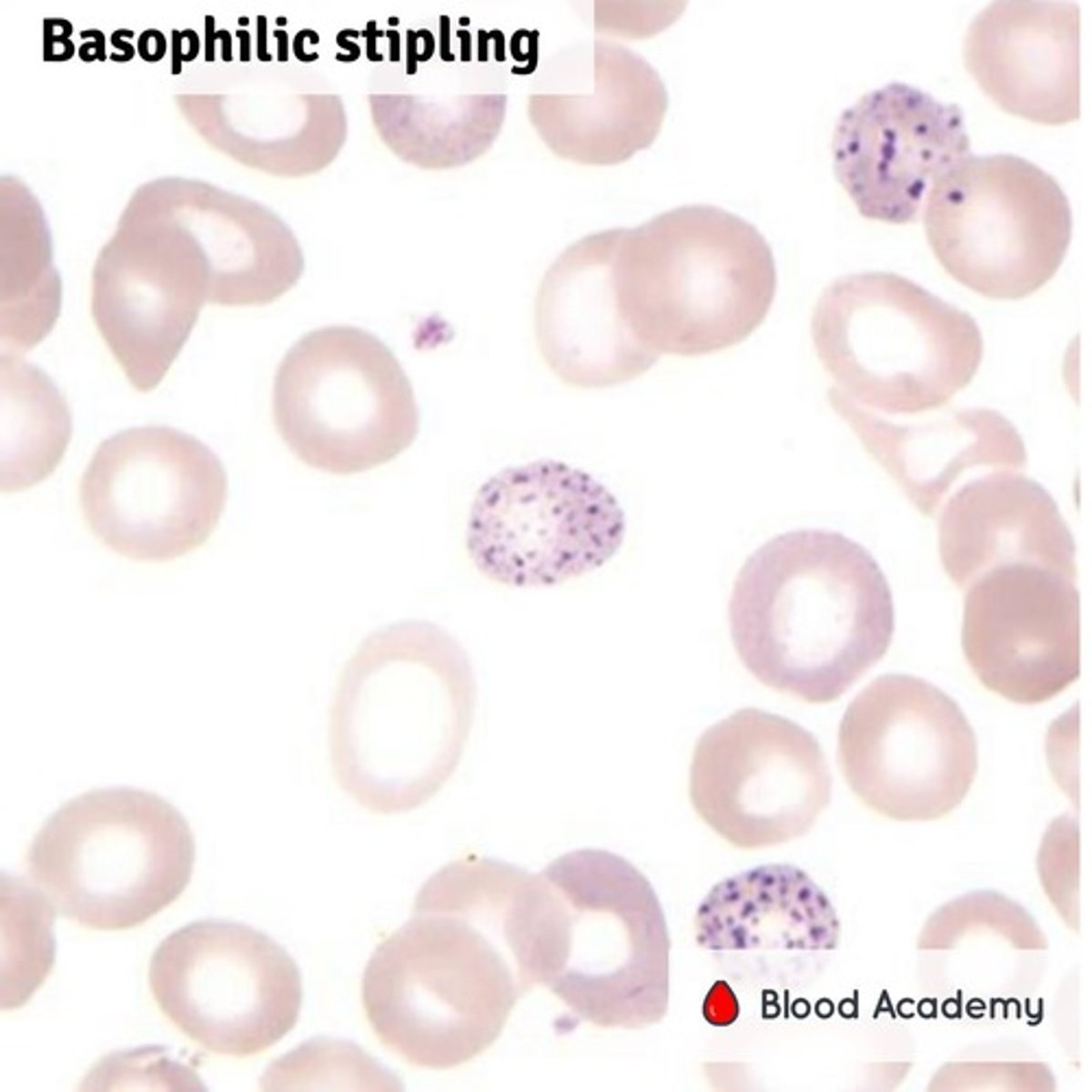
Basophilic stippling
Multiple fine or coarse blue granules composed of aggregated RNA
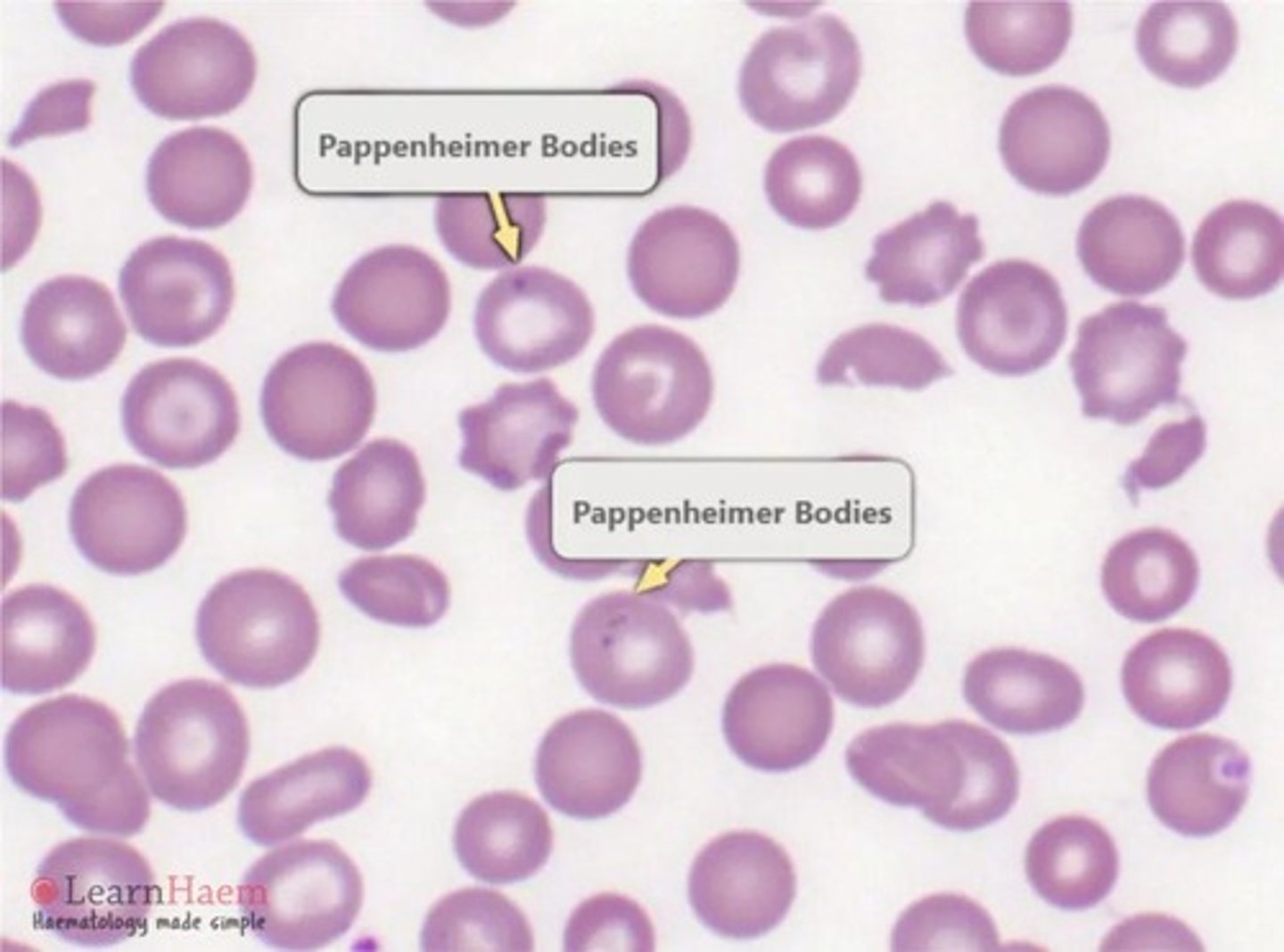
Pappenheimer bodies
Iron granules (non-heme) in clusters at cell edge
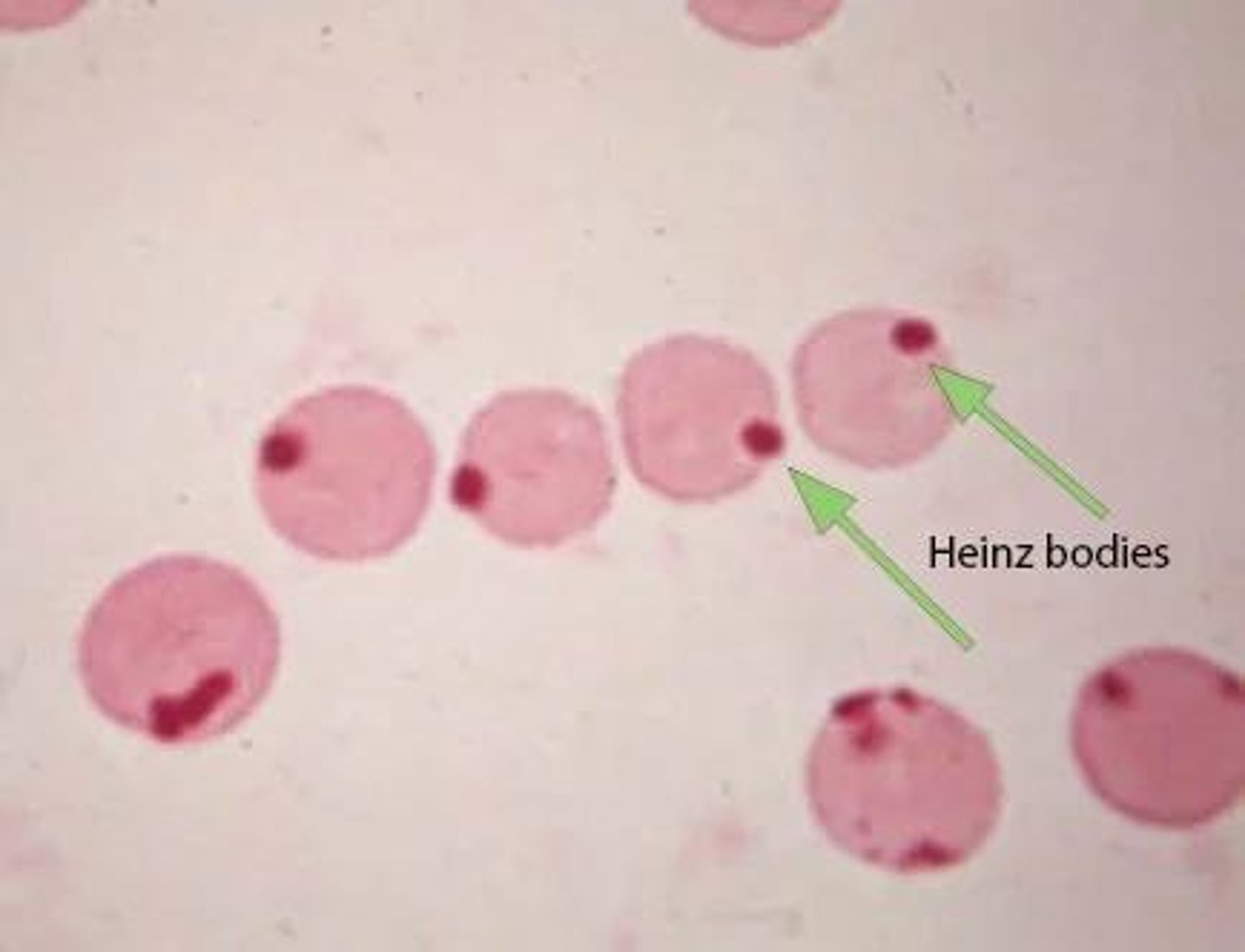
Heinz bodies
Denatured/oxidized hemoglobin
Cabot rings
Mitotic spindle remnants (microtubules)
Reticulocytes
Early RBC with residual RNA
HbC crystals
Dense, rectangular crystals with a bar of gold appearance
HbSC crystals
Finger-like, blunt-ended projections
Plasmodium (Malaria)
Signet ring appearance seen in malaria
Babesia
Has maltese cross appearance in blood circulation
MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume)
80-100 fL = normocytic, >100 fL = macrocytic, <80 fL = microcytic
MCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin)
Formula: MCH = HGB × 10 ÷ RBC
MCHC (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration)
Formula: MCHC = HGB × 100 ÷ HCT
Color (Chromasia)
Normochromic — normal hemoglobin content, Hypochromic — enlarged central pallor
RBC Clumping
Agglutination — RBC clumping; can resolve with warming
Ovalocytes / Elliptocytes
Ovalocytes: oval RBCs, Elliptocytes: cigar-shaped RBCs
Sickle Cells (Drepanocytes)
Crescent-shaped with pointed ends
Keratocytes (Helmet/Bite Cells)
Half-moon shape with two projections
Echinocytes (Burr Cells)
10-30 evenly spaced, rounded spicules
Acanthocytes (Spur Cells)
3-12 irregular, unevenly spaced spicules
Dacrocytes (Teardrop Cells)
Teardrop-shaped; tips should point in the same direction
Codocytes (Target Cells)
Thin, bell-shaped cells with increased surface-to-volume ratio
Still learning (7)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!