Chemistry Mid Term
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
electron
the negative subatomic particle in the electron cloud of an atom
electromagnetic radiation
form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space
wavelength
unit of distance for measuring waves
frequency
number of waves that pass a given point in a certian time
emission spectrum
spectrum of light released from excited atoms of an element
heisenburg uncertainty principle
its impossible to determine the position and velocity of an electron or other particle simultaneously
octet rule
tendency of atoms to prefer to have 8 valance electrons
ions
atoms or molecules that have a change doe to having lost or gained electrons
lewis structures
a convenient and simple way to represent an element and its valance electrons
electrons are the negative subatomic particles in the atom but they behave more like…
waves
they can have different amounts of energy and thus different…
frequencies
electrons can absorb and release energy in the form of …
electromagnetic radiation
speed of light is …
constant
wavelength and frequency have an …
inverse relationship
left side of spectrum
longer wavelength, lower frequency, lower energy
right side of spectrum
shorter wave length, higher frequency, higher energy
order of electromagnetic spectrum
Radiowave, microwave, infrared, visible light (ROYGBIV), ultraviolet, x-ray, gamma ray
an electron in its ground state absorbs enough energy to …
jump energy levels
an electron in its excited state releases enough energy that it …
returns to its ground state
energy released in the form of …
electromagnetic radiation (visible light)
An atom is stable if it already has a …
full outer energy level of valance electrons (typically 8 e-)
the noble gases are already stable because …
they have full outer energy levels of valance electrons
Cations
atoms that lose e- in order to become stable which makes it positively charged and usually metals
anions
atoms that gain e- in order to become stable which makes it negatively charged and usually nonmetals
bohr model
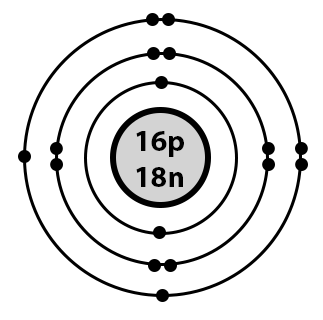
lewis structure

observation
objective; based on senses
inference
subjective; based on perceptions
qualitive data
data based on qualities
quantitative data
data based on quantities (numbers and measurements)
conversion factors
ratios of equivalent values (meaning they equal 1)
Significant figures
the number of digits in a measurement that reflect how accurate the measurement is
dimensional analysis
a technique for converting numbers into different units, without changing their values
matter
anything that has mass and volume
mass
a measure of the amount of matter
volume
a measure of how much space something takes up
atom
the smallest unit of an element that maintains the identity of the element
element
a pure substance that can’t be broken down into anything simpler or more stable
compound
a pure substance that can be chemically broken down into simple and more stable substances; when atoms of two or more elements are chemically combined
substance
pure matter with a fixed composition throughout
mixture
combination of matter with a variable composition throughout
homogeneous mixture
a mixture with an even distribution of components
solution
when one substance (solute) is dissolved into another (solvent)
solubility
the measure of how well a solute dissolves in a solvent
aqueous solution
when the solute is dissolved in water
alloy
a solution of metals
heterogeneous mixture
a mixture with an uneven distribution of components
law of conservation of matter
matter is never created or destroyed, it only changes forms
proton
the positive subatomic particle in the nucleus of an atom
neutron
the neutral subatomic particle in the nucleus of an atom
electron
the negative subatomic particle in the electron cloud of an atom
valance electrons
electrons in the outermost energy level of the electron cloud
Quarks
Make up protons and neutrons and their attraction holds the nucleus together
atomic number
number of protons in an atom of the element; used to identify an element
mass number
number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
groups
aka families; the vertical columns on the periodic table
Periods
the horizontal rows on the periodic table
isotopes
atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
average atomic mass
weighted average of all of the different versions of an element; measure in amu
ion
a charged atom