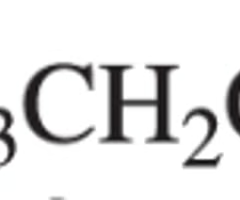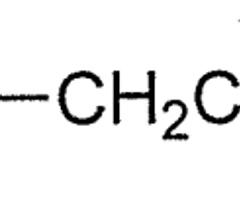Chemistry exam 3
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
As atoms get closer…
energy decreases and the stability of the system increases due to attractive forces between them.
The minimum point of a curve on a internuclear distance graph…
Bond length (equilibrium bond distance re) represents the optimal distance where the bond is most stable, and the potential energy is minimized.
If atoms get too close
the energy shoots up because nucleus- nucleus repulsion becomes large, electron clouds overlap, and atoms push each other away
If you stretch a bond a lot
energy goes toward zero, the part of the curve reaches zero energy again is called bond dissociation
Deeper well
Stronger bond, means you have to add more energy to break the bond
Narrow well
stiffer well, the bond resists stretching, vibrates rapidly, requires high- frequency IR light
Wide well
More flexible bond, vibrates lower IR frequency
Leftward minimum
smaller Re
Rightward minimum
larger Re
Higher change in EN
More polar the bond
EN: 0- 0.4
nonpolar covalent EN
EN: 0.5- 1.7
polar covalent
EN: >1.7
ionic (very polar)
Trigonal Planar dipoles
can cancel out
Tetrahedral dipoles
can cancel out
Trigonal Pyramidal dipoles
DO NOT CANCEL
Bent dipoles
DO NOT CANCEL OUT
Linear dipoles
may cancel IF THEY ARE EQUAL
Trigonal Bipyramidal dipoles
nonpolar
seesaw dipole
always polar
T-shaped dipoles
always polar
Octahedral dipole
when symmetrical, nonpolar
square pyramidal dipoles
always polar
Square planar dipoles
nonpolar when symmetrical