AP Bio Unit 5: Cell Communication & Cell Cycle
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
DNA Function
Stores genetic info & is the blueprint for building proteins
DNA Structure
Double-stranded helix (2 sugar phosphate backbones)
Nucleic acids (polymer) are made up of nucleotide monomers
Nucleotides have three parts:
Phosphate Groups (- charged)
Deoxyribose (5-carbon sugars)
Nitrogen Bases
Adenine
Thymine
Guanine
Cytosine
RNA Structure
Single-stranded (1 sugar phosphate backbone)
Ribose Sugar
Nitrogen Bases:
Adenine
Uracil
Cytosine
Guanine
Nucleotides are connected by a ______ bond between the sugar of one and the phosphate group of the other
Phosphodiester
In DNA, the complementary nitrogen bases are connected via ______ bonds.
Hydrogen
Nucleotides are attached together through ______ ______.
Dehydration Synthesis
Pyrimidines
Nitrogen bases that are single ringed - C, T, U
Purines
Nitrogen bases that are double ringed - A, G
Pairing of Nucleotides
Pyrimidines always bond with purines
A & T = 2 Hydrogen Bonds
G & C = 3 Hydrogen Bonds
Deoxyribose has __ Carbon atoms, which are numbered clockwise.
5
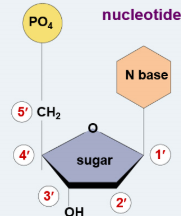
DNA Directionality
DNA is antiparallel because complementary strands run in opposite directions (5’ → 3’ & 3’ → 5’)
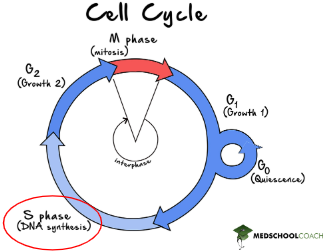
DNA Synthesis
Occurs in the S phase of the cell cycle, when the DNA is in chromatin form
Cell reproduction (mitosis)
Gamete production (meiosis)
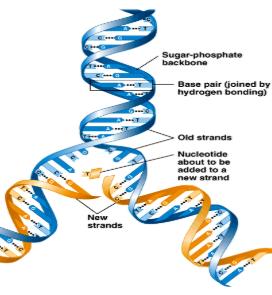
Semiconservative Process (in DNA synthesis)
The two DNA strands are complementary, which means base pairing allows each strand to serve as a template for a new strand
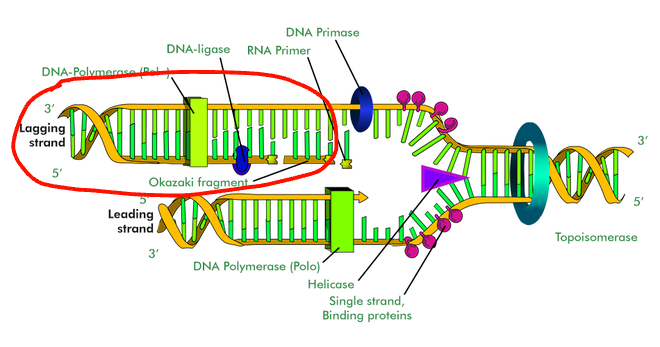
Helicase in DNA Replication
Unwinds part of the DNA double helix
Topoisomerase in DNA Replication
Helps relieve the strain of unwinding by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands
DNA Polymerases in DNA Replication
Connects nucleotides together to make a strand
RNA Polymerase (a.k.a Primase, DNA Primase, etc) in DNA Replication
Adds a few nucleotides of RNA (RNA primer) to get the process started
Ligase in DNA Replication
Connects DNA fragments together
DNA Synthesis: Step 1
DNA Helicase unwinds the DNA strands. Topoisomerase relaxes supercoiling in front of the replication fork.
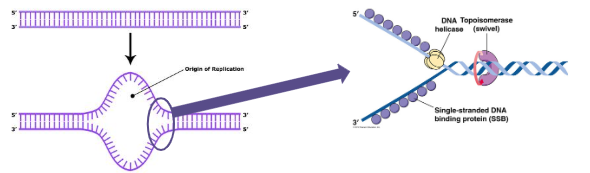
DNA Synthesis: Step 2
Complementary nucleotides are matched with the ones of the original DNA parent strand to create a new strand:
RNA polymerase (primase) adds a few nucleotides so DNA polymerase can get started; the RNA nucleotides are later replaced
DNA polymerase connects the nucleotides but can only add nucleotides to the 3’ end of a nucleotide
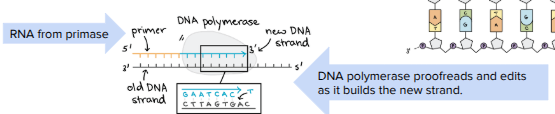
Leading Strand
Once an RNA primer is added, DNA polymerase can continuously add nucleotides in the 5’ to 3’ direction - the DNA strand is copied in a continuous way
Lagging Strand
Made in Okazaki fragments that are later joined together by ligase - the DNA strand is copied discontinuously
→ RNA primers are later removed and replaced by DNA nucleotides
Telomeres
The ends of chromosomes in eukaryotes have repeating, non-coding sequences called telomeres that serve as protective caps
→ Loss of bases at 5′ ends in every replication: Chromosomes get shorter with each replication (limits # of cell divisions to about 50) → aging process
Telomerase
Can add DNA bases at 5’ end; high activity in stem cells and cancers but not in most somatic cells
The cell cycle consists of two main stages:
Interphase (G1, S, G2) & Cell Division (Mitosis & Cytokinesis)
How do unicellular organisms use the cell cycle?
Binary Fission
How do multicellular organisms use the cell cycle?
Growth & repair
Nucleus in the Cell Cycle
Protects the DNA
Cytoskeleton in the Cell Cycle
Organizes structures in the cell
Includes the centrosomes, made up of centrioles, which are responsible for the spindle fibers that guide the chromosomes during mitosis
Spindle Fibers
Made of microtubules
Extend from the centrosome
Separates duplicated chromosomes during Anaphase by attaching to the chromesomes’ centromeres
Cells spend 90% of their time in ______.
Interphase
G1
1st gap
Everyday tasks, such as making proteins
Cell grows
G0
Resting stage
Cells could enter this stage during G1
Cell continues doing its job until it receives a signal to reenter G1 to get ready to divide
S
DNA Synthesis
Copies genetic material so each cell gets a copy
G2
2nd Gap
Prepares for cell division
Cell grows more
Produces proteins, organelles, & membranes
The four stages of mitosis are:
Prophase → Metaphase → Anaphase → Telophase
Prophase
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and chromosomes become visible
Centrioles (in an animal cell) move to opposite ends of the cell
Protein fibers form across the cell
The nucleolus disappears
The nuclear membrane breaks down

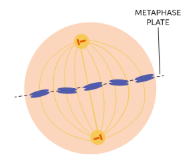
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Spindle fibers (attached to kinetochores) coordinate movement
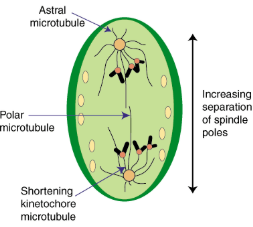
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate at kinetochores
Proteins holding the sister chromatids together are inactivated
Pulled by motor proteins “walking” along microtubules
Poles move farther apart
Telophase
Chromosomes arrive at opposite poles
Daughter nuclei form
Chromosomes disperse
Spindle fibers disperse
Cytokinesis begins
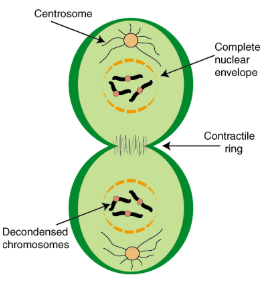
Cytokinesis
Organelles & cytoplasm are divided
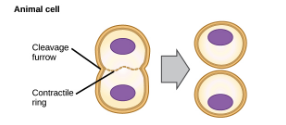
Cytokinesis in Animal Cells
Microfilaments contract, forming a cleavage furrow
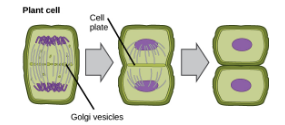
Cytokinesis in Plant Cells
Cell plate forms
Vesicles from the Golgi fuse to form two cell membranes
A new cell wall is laid down between the cell membranes
G1 Checkpoint
Do I need a new cell?
Is this cell healthy?
Are there enough nutrients to divide?
Pass - Cell enters S phase
Fail - Goes to G0
G2 Checkpoint
Did the DNA copy correctly in the S phase?
Pass - Cell enters mitosis
Fail - Apoptosis
M Checkpoint
When the DNA lines up in the middle (metaphase), will each cell get the same amount of DNA?
Pass - Cell divides
Fail - Apoptosis
Kinases
Proteins that activate or inactivate other proteins by phosphorylating them
Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (Cdks)
Kinases that are only active when attached to a cyclin
Cyclin
A protein that fluctuates in concentration in the cell
Made at certain times during the cell cycle
Also destroyed after they are no longer needed by the cell
Benign Cancer Cells
Stays in the same place
Malignant Cancer Cells
Spreads to other parts of the body
Cancer cells bypass ______.
Cell cycle controls
Proto-Oncogenes - Normal Function
When activated, they signal for cell division to start (G1 checkpoint)
Proto-Oncogenes - Mutation Function (called an oncogene)
The gene is always activated, so it continues to divide (ignores the G1 checkpoint)
Dominant - only one copy of the defective gene is needed to impact the cell
Tumor Suppressor Genes - Normal Function
Slow cell division, repairs mistakes, or triggers apoptosis
Tumor Suppressor Genes - Mutated Function
Cell does not stop division if mistakes are found
Recessive - both copies of the gene must be mutated to impact the cell
Ex: p53