Lecture 12 Caries Diagnosis and Caries Risk Assessment (copy)
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
202 Terms
CAMBRA
caries management by risk assessment
what is caries
Dental caries is a multitactorial, transmissible, infectious oral disease caused primarily by the complex interaction of cariogenic oral flora (biofilm) with fermentable dietary carbohydrates on the tooth surface over time
caused y transmitted infectious bact. through
vertical and horizontal transmission
teeth have biofilm with certain bact. types that if fed w/ fermentable carbs
overtime bact. will degrade surface by demineralizing
enamel, dentin, causing lesion, break down with cavitation
caries balance: protective factors
remineralization
Saliva & sealants
Antibacterials
Fluoride/Ca2+/PO43-
Effective lifestyle habits
Risk-based reassessment
caries balance: risk factors
demineralization
Bad bacteria
Absence of saliva
Destructive lifestyle habits
caries balance: disease indicators
White spots
Restorations < 3years
Enamel lesions
Cavities in dentin
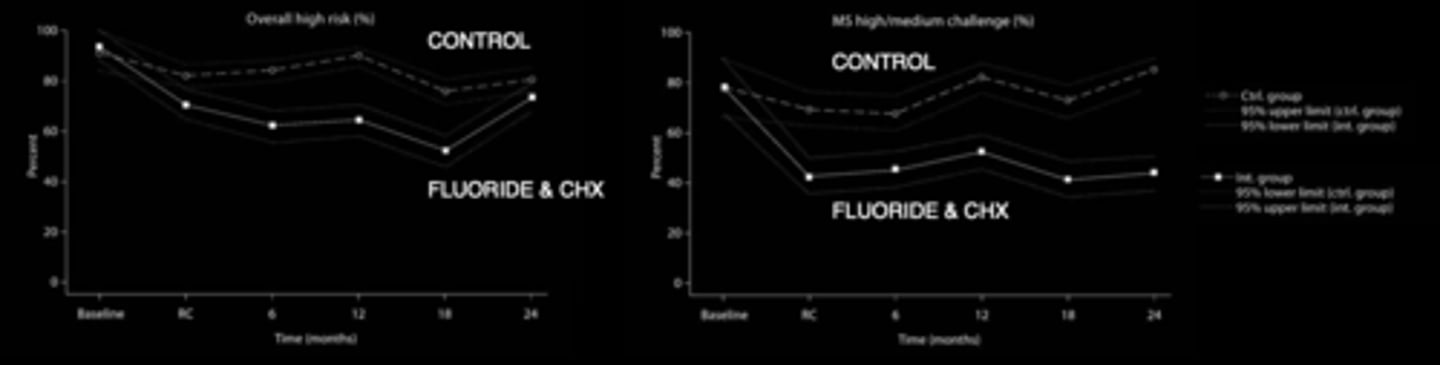
what happened when patients with high oral bacteria were given CHX and fluoride?
lower oral bacteria
disease indicators and salivary status - high risk: disease indicators
Visible cavities
Radiographic enamel and/or dentin lesions (clinical signs of disease)
Demineralizations (smooth surfaces, pits & fissures)
Restored caries in last 3 years (new patients)/
1 year (patients on file) [caries history]
Reduced salivary function
high risk CDT code
D0603
environmental/risk factors: moderate risk
Visible heavy plaque on teeth
Deep pits and fissures
Exposed roots
Appliances present
Frequent snacking (>3x daily between meals)
Recreational drug use
Saliva reducing factor
moderate risk factors: deep pits and fissures
determined at birth; can place sealants; deep pits/fissures on occlusal, buccal, palatal, can have increase plaque accumulation in these fissures; increase likelihood of caries
moderate risk factors: exposed roots
cervical areas with gum recession, plaque on dentin is more dangerous with demineralization
elderly patients with recession are at higher risk of developing root caries
moderate risk factors: frequent snacking (>3x daily between meals)
feeds bacteria
moderate risk factors: salivary reducing factor
medications can decrease salivary flow; radiation therapy; autoimmune diseases (Sjögren's syndrome)
is visible heavy plaque an indicative factor of caries disease?
not always, is a risk factor placing the patient at moderate risk
moderate risk CDT code
D0602
low risk CDT code
D0601
protective factors: low risk
Fluoridated community
Fluoride toothpaste x1/x2 daily
Fluoride rinse/gel daily CHX in last 6 months
Xylitol 4x daily in last 6 months
Adequate salivary flow
low risk protective factors
Fluoridated community
Fluoride toothpaste
toothpaste with higher fluoride concentration can be prescribed
what are some other sources of fluoride?
CA water, milk, salt
chlorhexidine (CHX)
anti-bacterial agent in a rinse (common after extractions; can stain teeth if used for long time)
low risk protective factor
Xylitol
sugar alcohol; bacteria can take it in but not ferment it
low risk protective factor if taken 4x daily in last 6 months
plaque stagnation areas
pits and fissures (need sealants)
root (exposed root)
cervical
interproximal
restorations
ortho appliances
(where caries are more likely to occur; first place to look, then look at other areas for abnormalities; without proper care, plaque can accumulate in these areas)
visual tactile
thin instruments to touch surface for irregularities, lesion
impedance
electric current to measure presence and depth of lesion
radiography
see between teeth shadows, sign of disease
transillumination
light, visible light, infrared, blue light to detect shadows
fluorescence
cause biofilm to fluoresce
can measure the activity
dyes
ink to put on teeth, dentin colored areas to remove colored dentin --> diseased dentin
sensitivity
True positive rate. Measures the proportion of actual positives that are correctly identified as such.
E.g., teeth/surfaces that have caries lesions
specificity
True negative rate. Measures the proportion of actual negatives that are correctly identified as such
identify healthy conditions
e.g. teeth/surface that are healthy/sound
what does it mean if there is a specificity of 99% out of 100 patients without caries?
means 99 patients are caries-free
visual-tactile
Visual inspection only:
Sensitivity: 0.12
Specificity: 0.93
Visual inspection + probing: Sensitivity: 0.14-0.80
Specificity: 0.93
explain what it means that Visual inspection only has a Sensitivity of 0.12 and Specificity of 0.93?
out of 100 lesions, might pick up 12 but miss 88 --> sensitivity
out of 100 lesions, 93 are healthy and do not have caries --> specificity
what can increase visual inspection's sensitivity?
when used with probing
explain what it means that Visual inspection with probing has a Sensitivity of 0.14-0.80 and Specificity of 0.93?
out of 100 lesions, should be detecting 14 to be carious (higher if professional is more experienced)
out of 100 lesions, 93 are correctly identified as healthy, only 7 of healthy sires are erroneously identified as diseased
why does visual-tactile caries detection have a low sensitivity
miss a lot just visually, especially in interproximals
what instruments should be used for visual-tactile caries detection?
perio-probe with round end, not sharp explorer (use blunt end; can use round explorer)
caries detection: visual-tactile
use instrument to feel cavitation, roughness, demineralization
alone is insufficient
enamel lesion
damage with sharp explorer
demineralization around fissure area, sharp explorer can further weaken the enamel
demineralized enamel is softer, loses 90% of original hardness, and can be more easily scratched by sharp tools
what effect does visual magnification have on sensitivity and specificity?
sensitivity increased
specificity decreased (improves)
transillumination
Visible Light (LED light shine through enamel, tooth)
Sensitivity: 50-85%
Specificity: 95%
Best: dentin, fractures, white spots, fillings
tip attachment

transillumination indications
detecting cracks, existing fillings
transillumination
Near Infrared Digital Imaging Transillumination (NIDIT)
Near infrared light - 780 nm
Sensitivity: 68%
Specificity: 93% (high)
do caries appear dark or light in transillumination?
dark --> don't let light through
fillings also don't let light through
caries detection: fluorescence
Laser Light 655 nm (red)
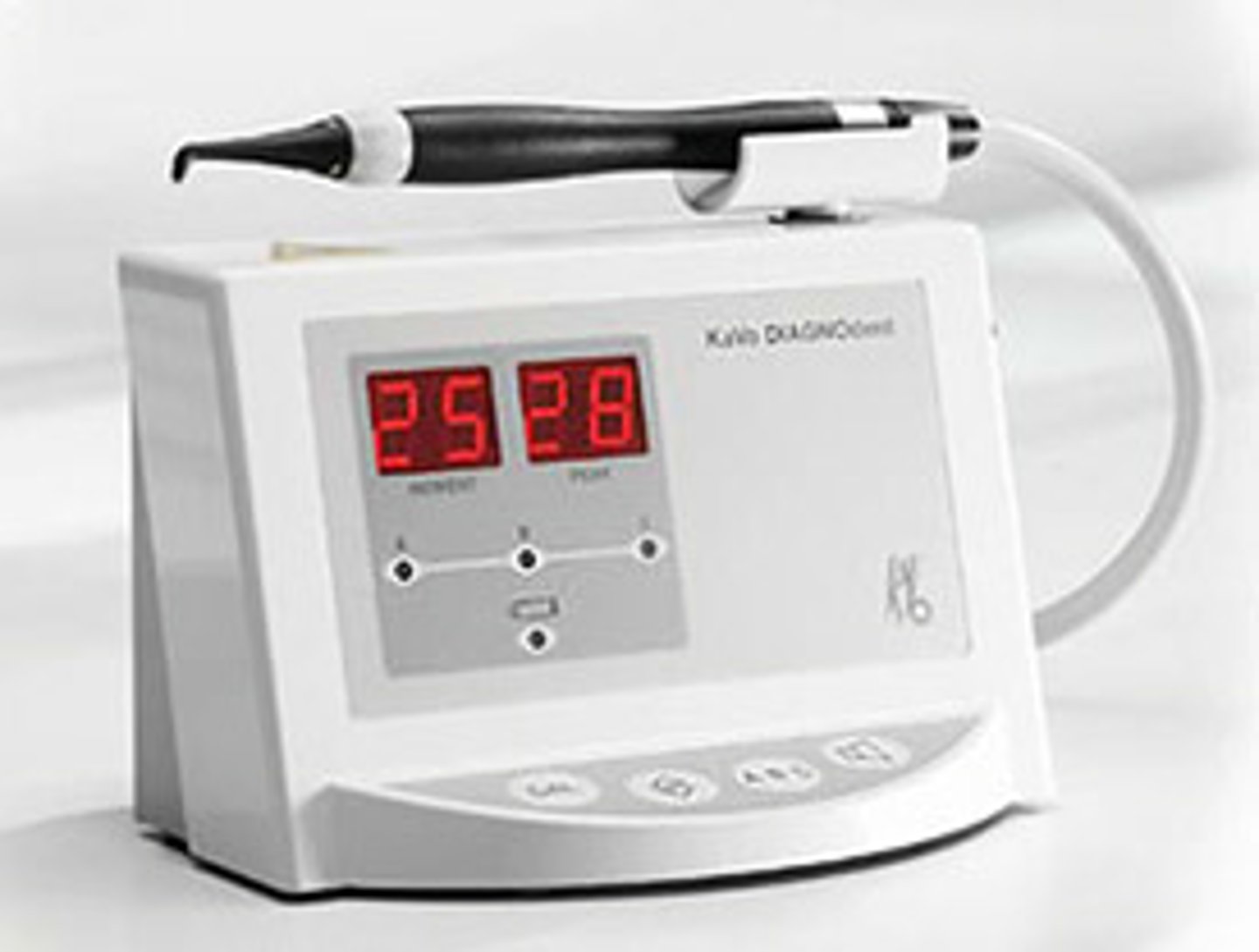
DiagnoDent
fluorescence by caries-induced changes in teeth
0-10 Healthy tooth structure
11-20 Outer half of enamel
21-30 Inner half of enamel
>31 Dentin caries
describe how caries detection with fluorescence works
laser light hits tooth if caries causing bact/calculus present will fluoresce
red porforins- metabolic products with bacteria which will fluoresce and be detected
what mode of caries detection is Diagnodent used for?
fluorescence
Diagnodent (laser induced fluorescence)
fluorescence
glass tip contacts tooth laser fluoresces when activity is detected
angle it to see whole lesion
peak reading if high number, high activity, high frequency of tone

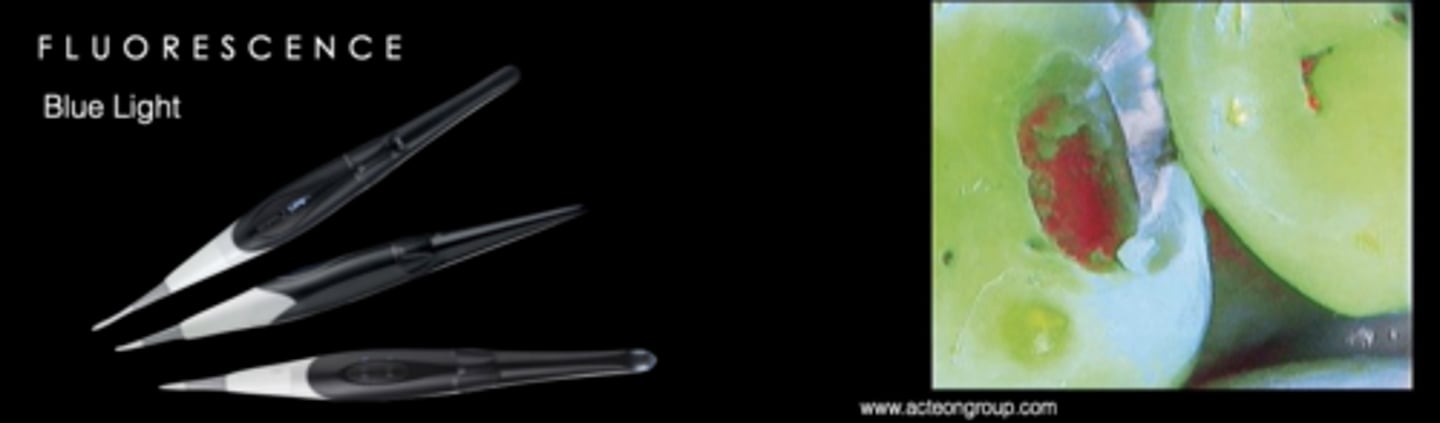
Qantitative Light Fluorescence (QLF)
Blue Light
makes tooth fluoresce green
reduced to no fluorescence in carious areas
can show plaque/biofilm
reading demineralization
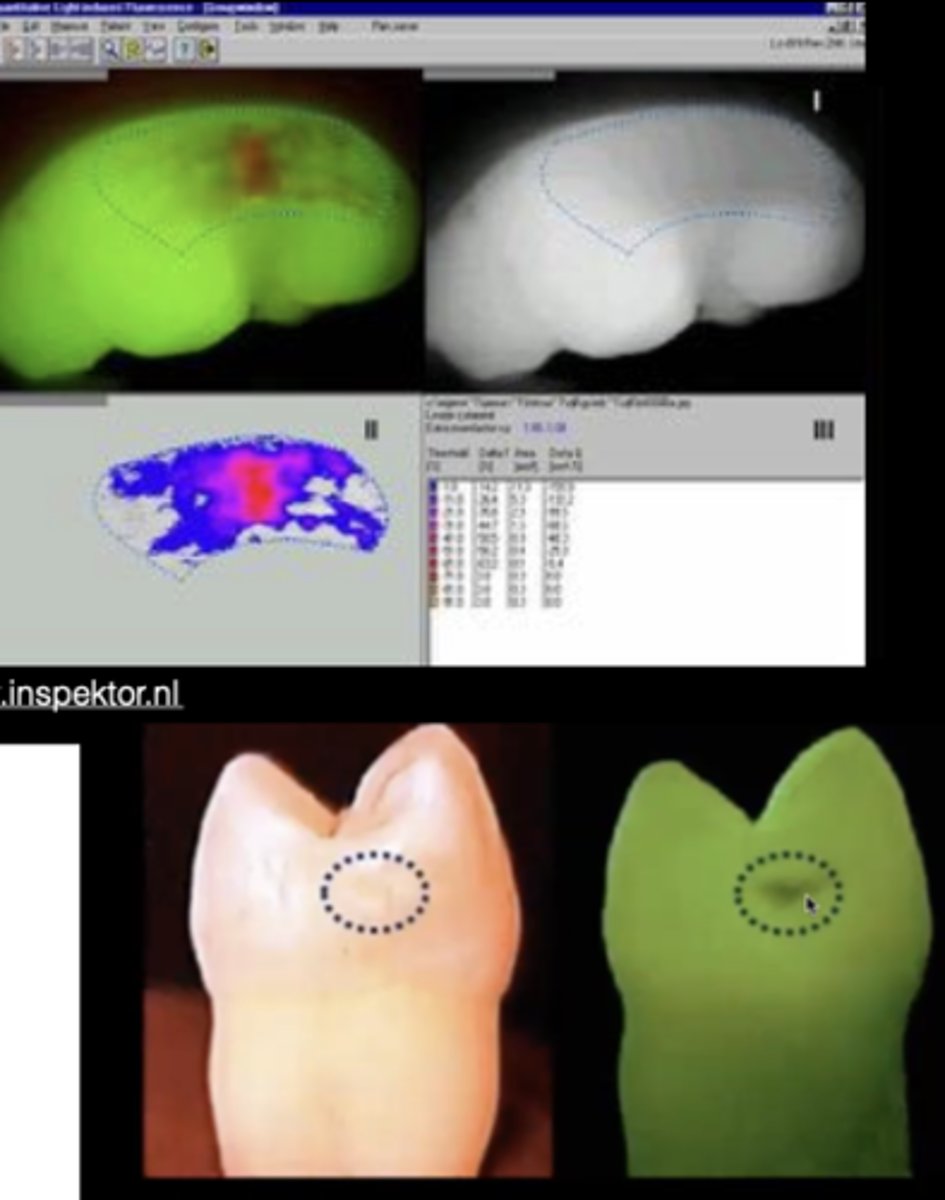
SIROInspect
caries detection by fluorescence
Laser Light 405 nm with 530 nm filter
FACE
blue laser light causes cavitated dentin to fluoresce
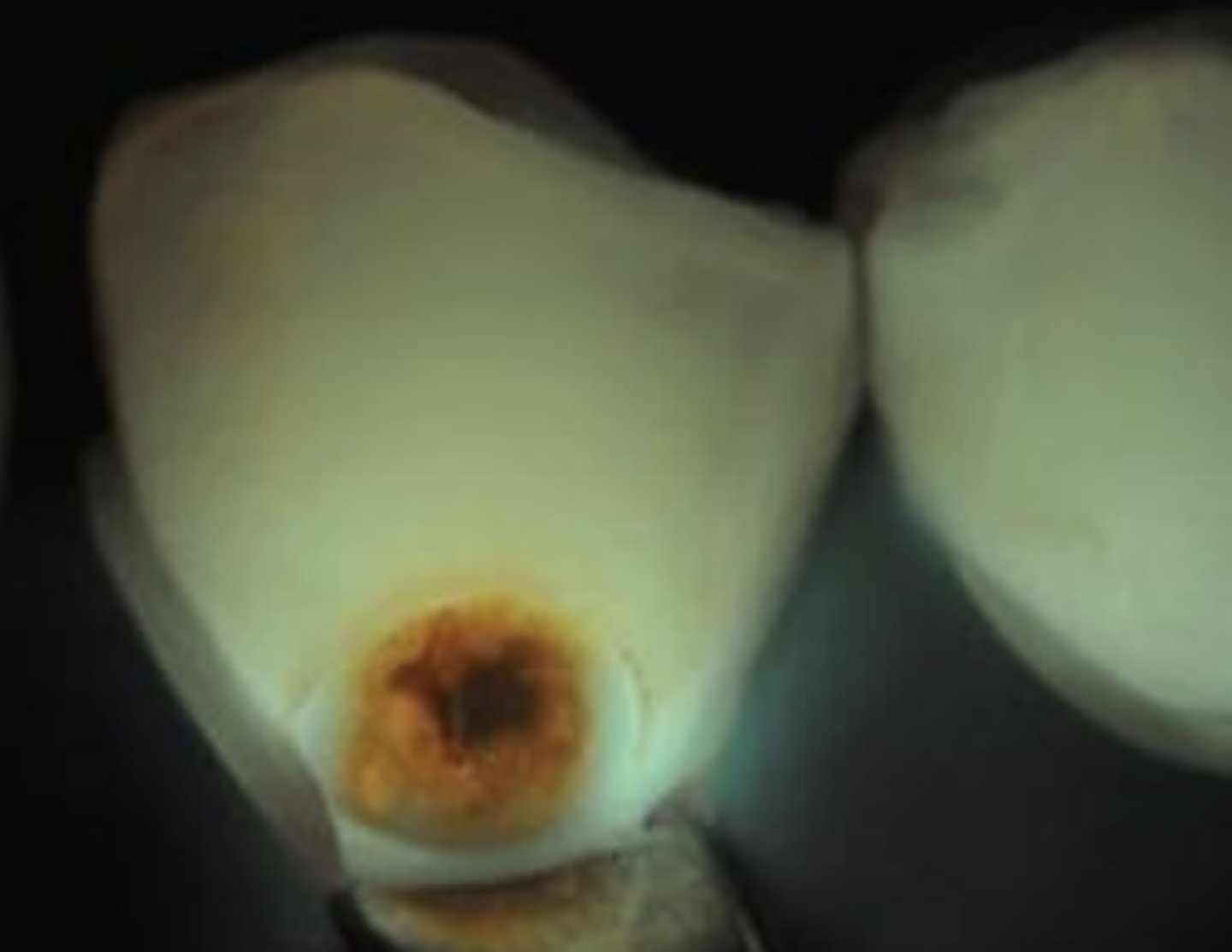
fluorescence: blue light
see on computer for documentation
can see demineralized dentin

caries detection: impedance
AC Impedance spectroscopy technique (ACIST)
tip contacts tooth
Sensitivity: 0.67-0.96 Specificity: 0.71-0.98
impedance sensitivity and specifity
Sensitivity: 0.67-0.96 Specificity: 0.71-0.98
radiography sensitivity and specificty
Sensitivity: 0.45-0.70 Specificity: 0.70-0.97
caries detection: radiography
ionizing radiation (x-rays) through teeth to film behind teeth to cpature
x-rays go through more easily when there's demineralization => shadows
Sensitivity: 0.45-0.70 Specificity: 0.70-0.97
how do restorations appear in an x-ray?
radio-opaque
how do caries appear in an x-ray
radio-opaque
burn-out effect
thinner tooth structure, more x-rays go through
caries detection: dyes
Stains matrix of less mineralized dentin, but not bacteria
E.g., methylene blue or fuchsin red in propylene glycol
Sensitivity: 0.71-0.74
Specificity: 1.00
red dye enters demineralized dentin and stains
only stains demineralized areas, not healthy areas
dyes sensitivity and specificity
Sensitivity: 0.71-0.74
Specificity: 1.00
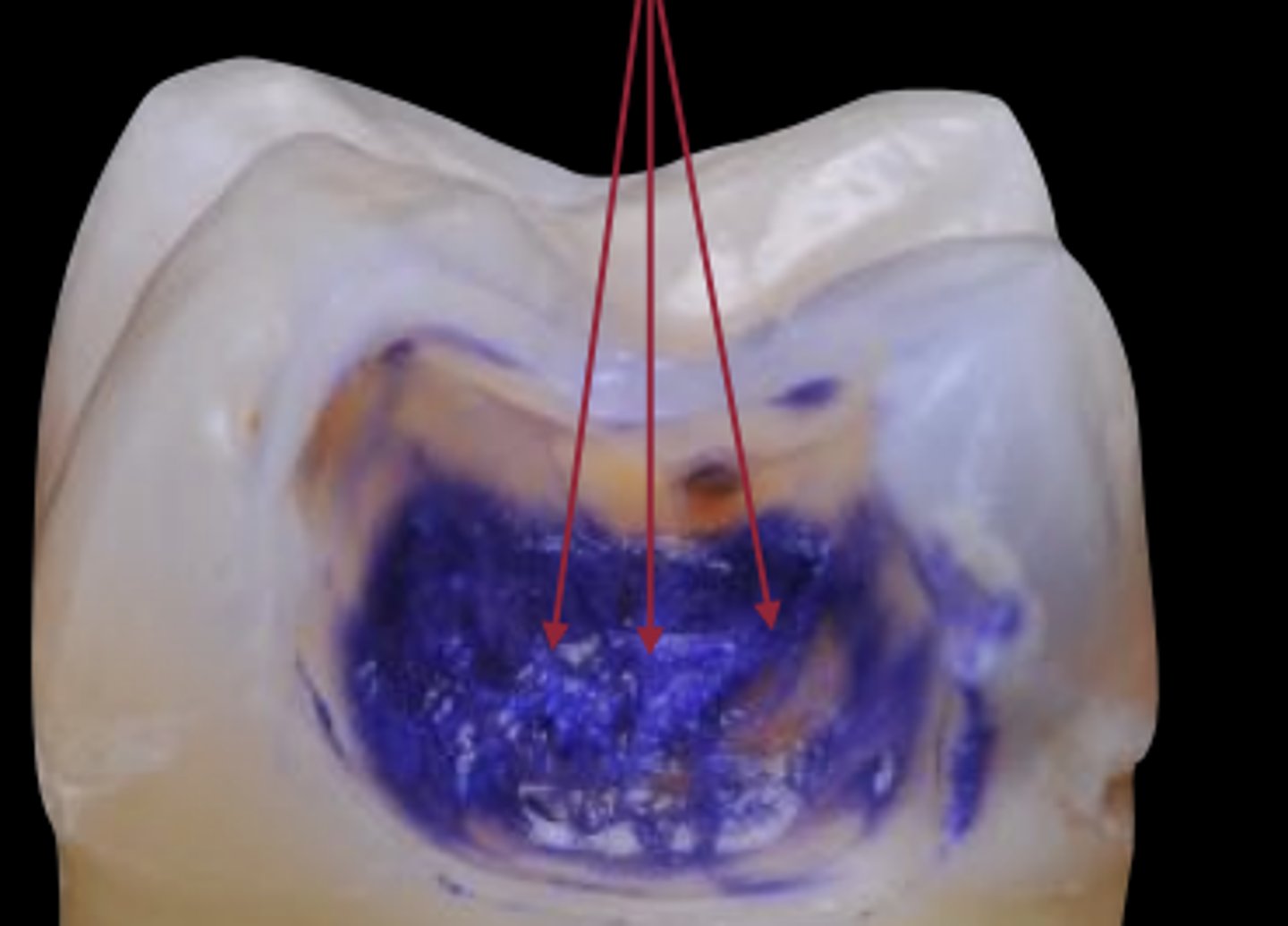
caries dye: caries infected
place dye for 5s, rinse, intense colors need cleaning
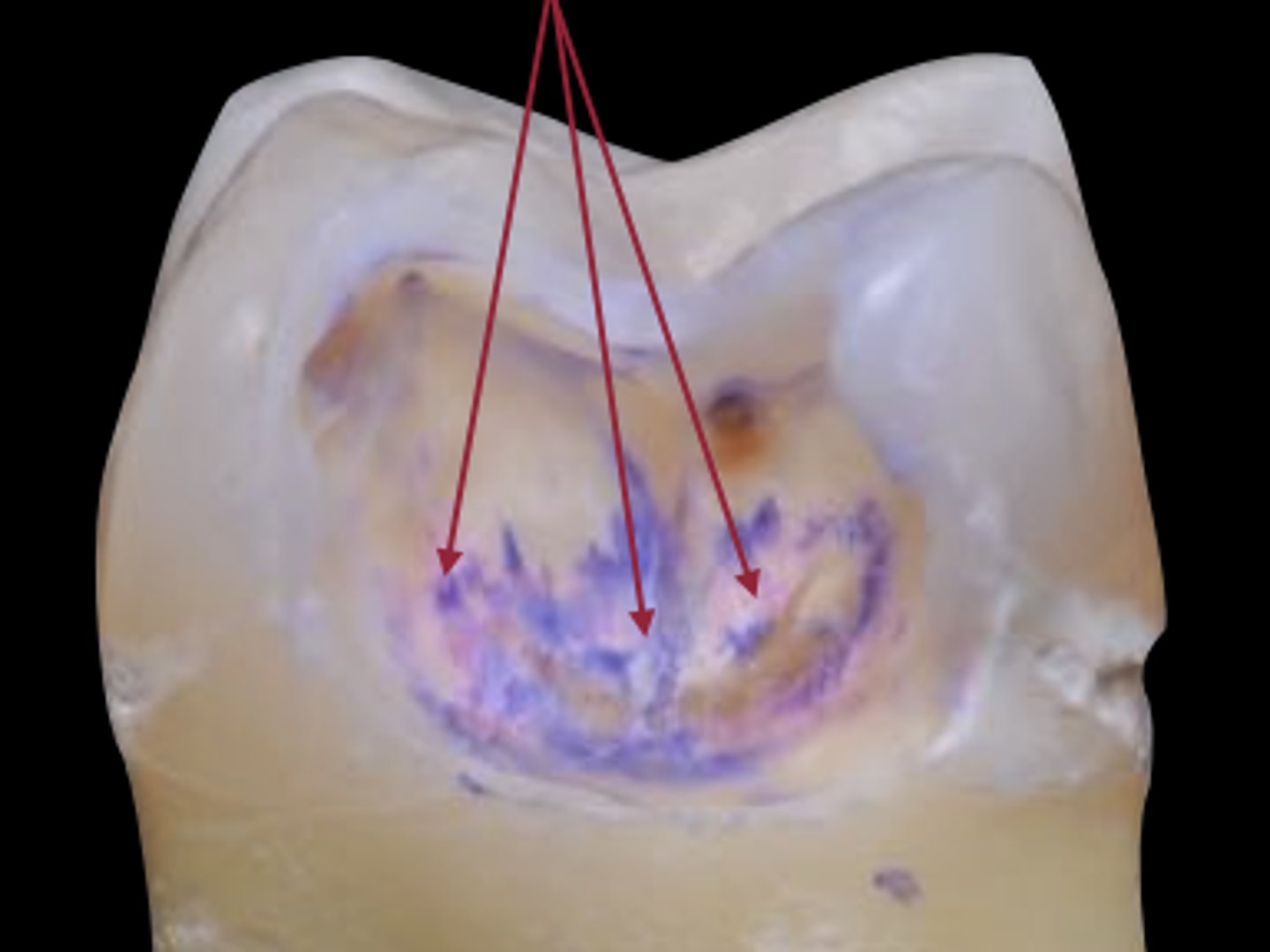
caries dye: caries affected
less intense colors --> can remove
caries dye: clean
dye can enter cracks in teeth, might over-reduce the tooth
3º dentin, where pulp chamber used to be, as caries was progressing, dentin reacted against it, causing sclerosis of tubule, turning 1º dentin into 2º dentin and build protective 3º dentin in pulp chamber to avoid opening the nerve chamber
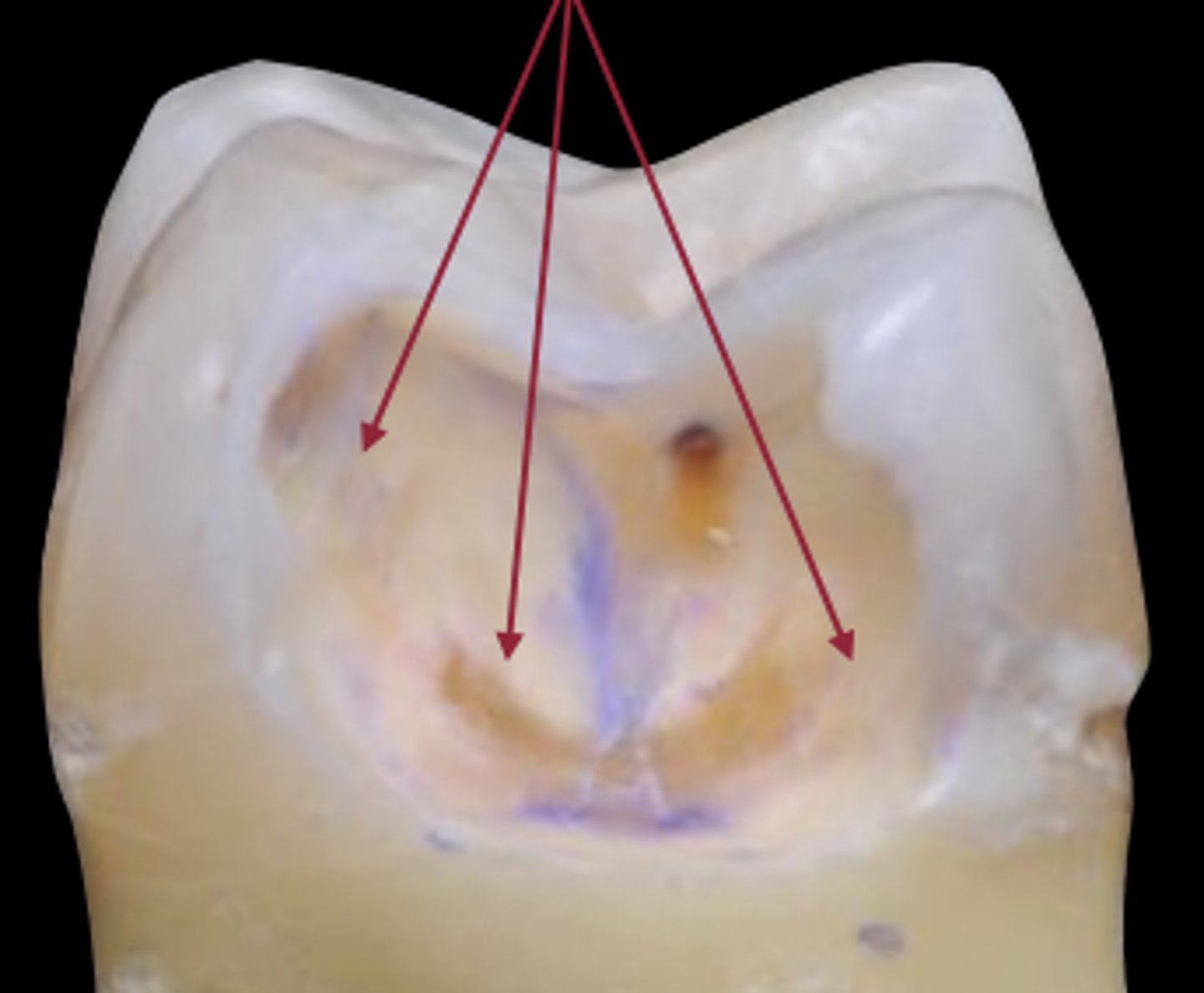
lesion activity: inactive/arrested
location of lesion: Lesion not in plaque stagnation area
Plaque over lesion: Not thick or sticky
Surface appearance: Shiny; color: brown-black
Tactile feeling: Smooth, hard enamel/hard dentin
Gingival status: No inflammation, no bleeding on probing
active lesions appearance
look dull/yellowish, darken with time
dull surface, no luster, white lesion
lesion activity: active
location of lesion: Lesion in plaque stagnation area (pit, fissure, interproximal, gingival)
Plaque over lesion: Thick and/or sticky
Surface appearance: Matte/opaque/loss of luster; color: white, yellow
Tactile feeling: Rough enamel/soft dentin
Gingival status: Inflammation, bleeding on probing
fluorosis
during tooth development, increase F- consumed; too much F- causes streaks
developmental ws
during tooth development, 1º tooth might have had trauma, bumped into underlying developing tooth
how can underlying lesions be seen?
enamel is transluscent so underlying lesions will show through
disease progression
initial lesion
micro-cavitation
decay
ICDAS stage 0
E0
healthy
what is the relationship between deepness of interproximal lesion and radioluscency on a radiograph?
increased deepness of interproximal lesion, increased radiolucency on radiograph
ICDAS stage 1
E1
demineralization
white spot, not visible when tooth is wet
ICDAS stage 2
E2
white spot scar, permanent, deeper into DEJ
demineralization
ICDAS stage 3
D1
demineralization
pores of white spot lesion widen
discoloring particle accumulation in pores to make white spot brown
lesion reached dentin
ICDAS stage 4
D2
localized enamel breakdown
shadow under enamel
ICDAS stage 5
D2
enamel broke out down, dentin exposed
caries into mid-1/3 of dentin towards pulp
breakdown is less than 50% of tooth surface
what is the difference between stage 5 and 6?
stage 5- breakdown is less than 50% of tooth surface
stage 6- breakdown is more than 50% of tooth surface
pulpitis
inflammation of pulp; painful
ICDAS stage 6
D3
lesion progress up to the nerve --> painful
breakdown is more than 50% of tooth surface
ICDAS 0/E0

ICDAS 1/E1
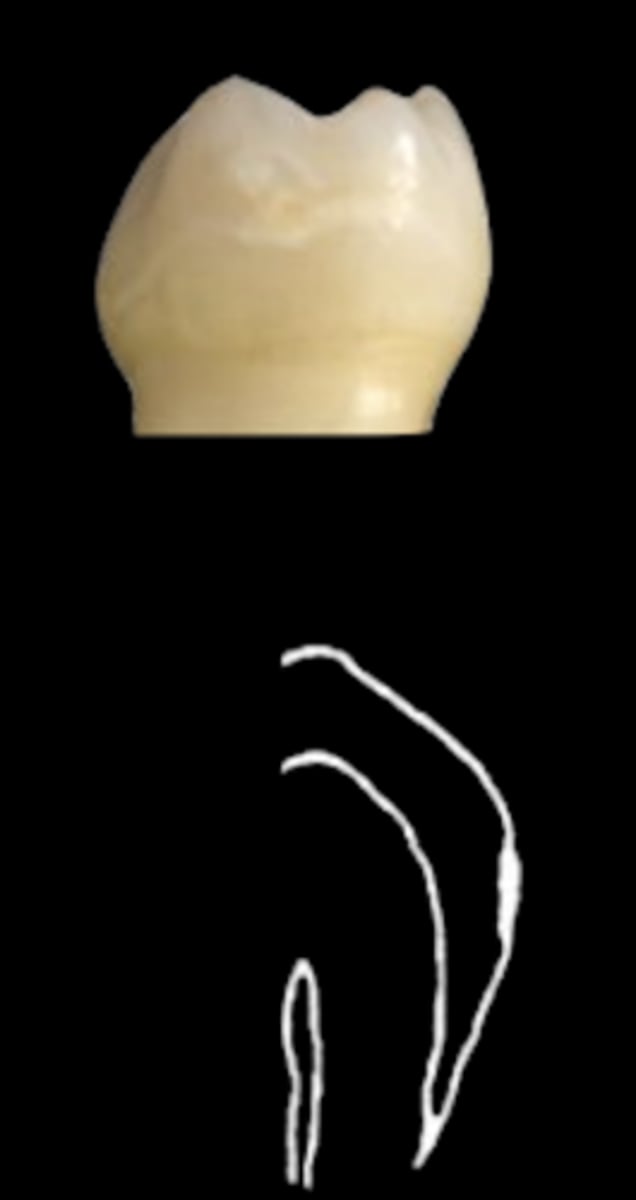
ICDAS 2/E2
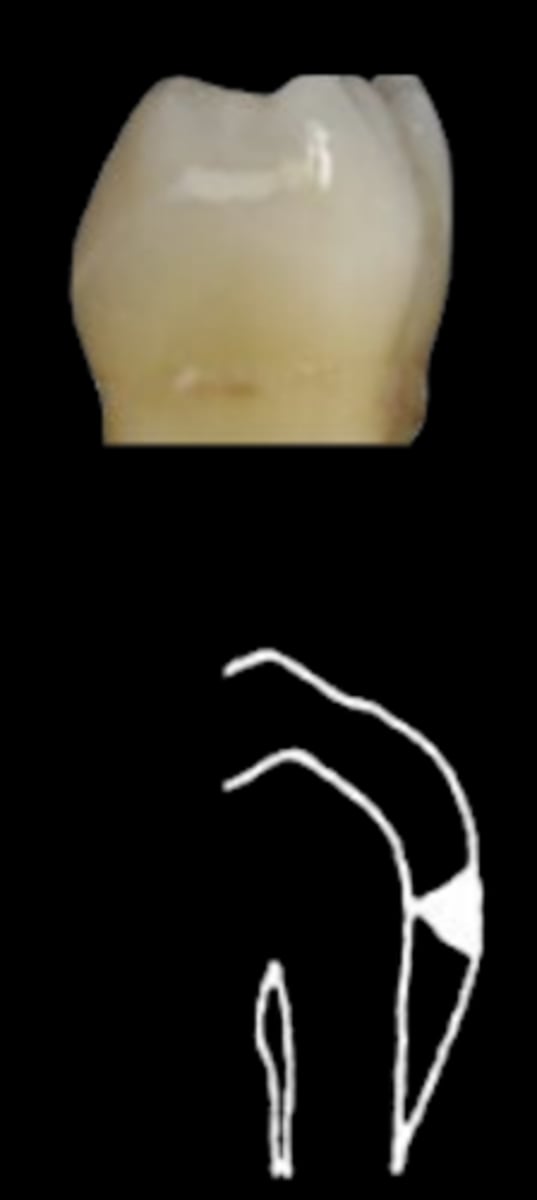
ICDAS 3/D1

ICDAS 4/D2
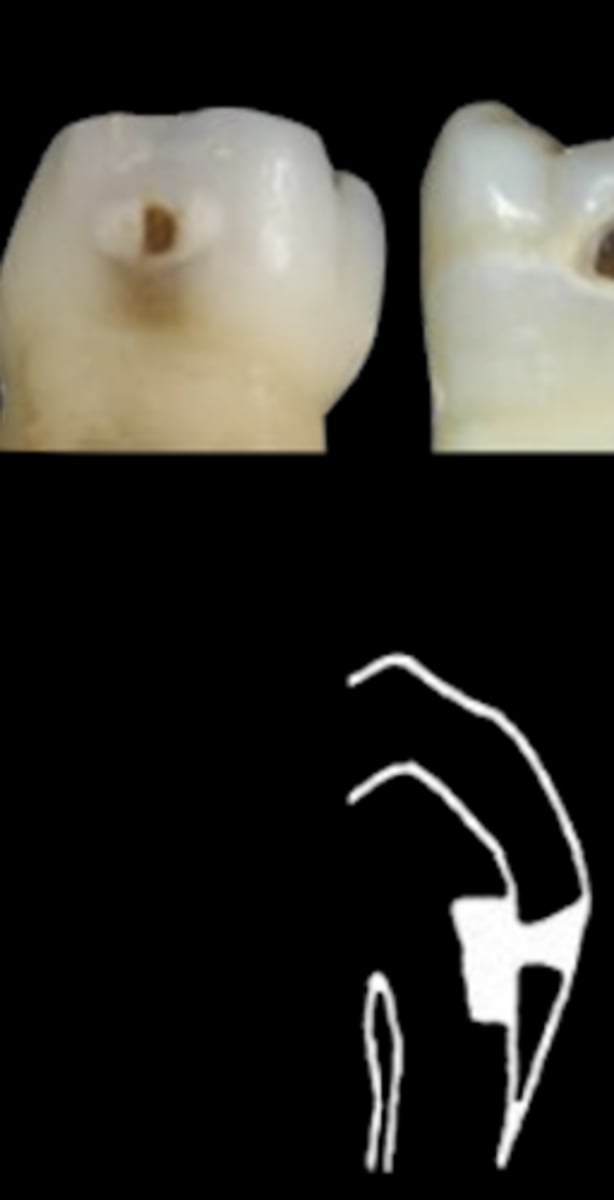
ICDAS 5/D2
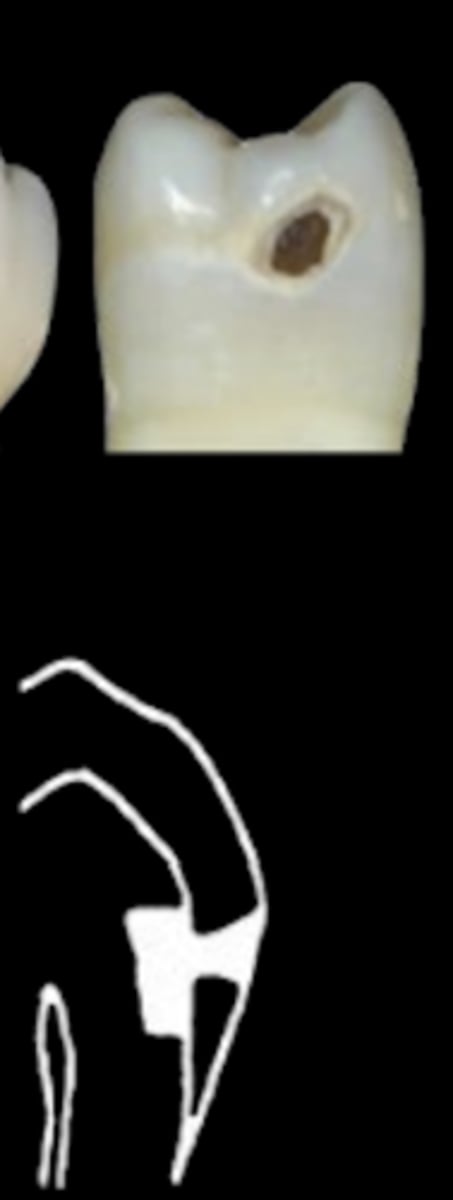

ICDAS 6/D3
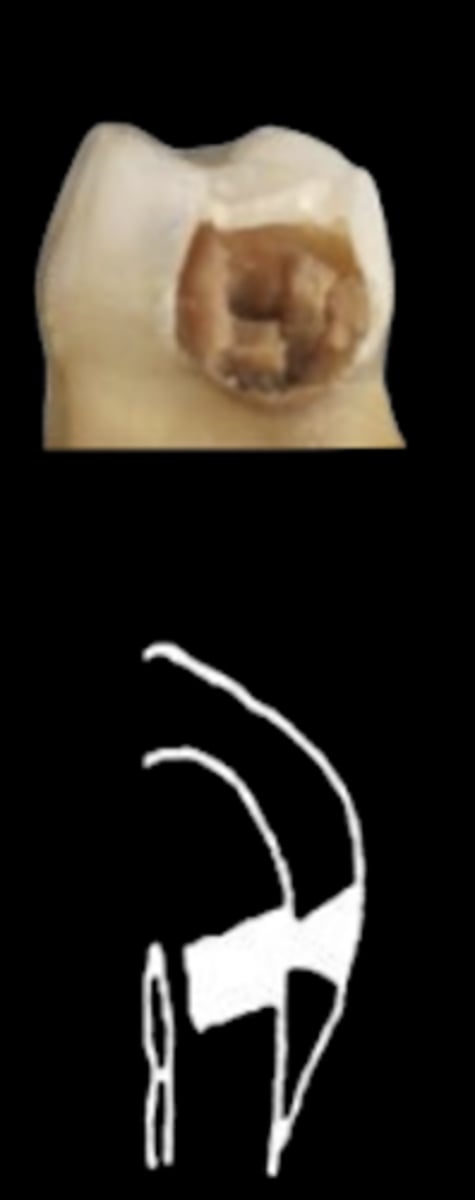
ICDAS 0
Sound surface: no change after air drying
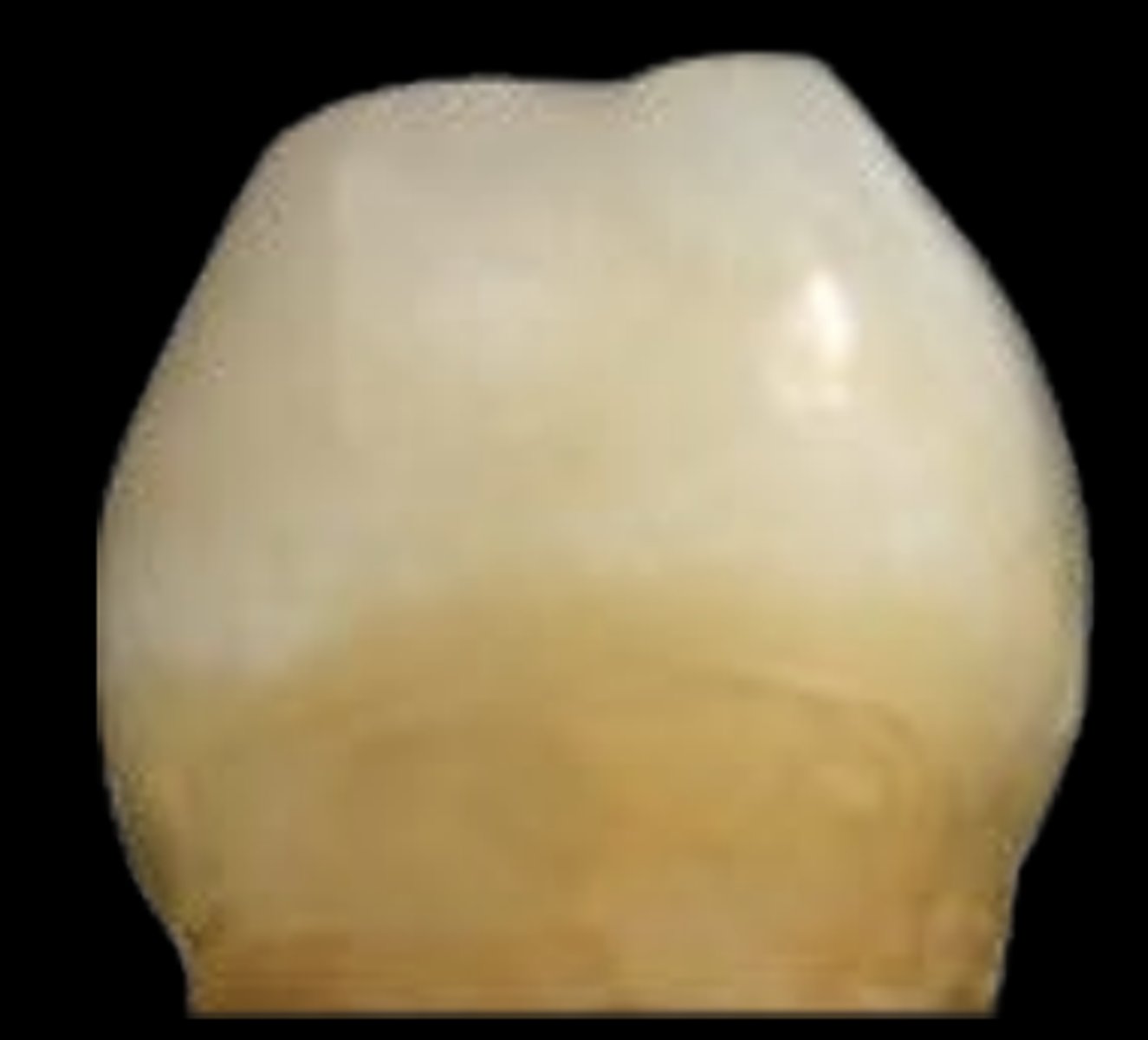
ICDAS 1
First visual change in enamel: seen only after air drying
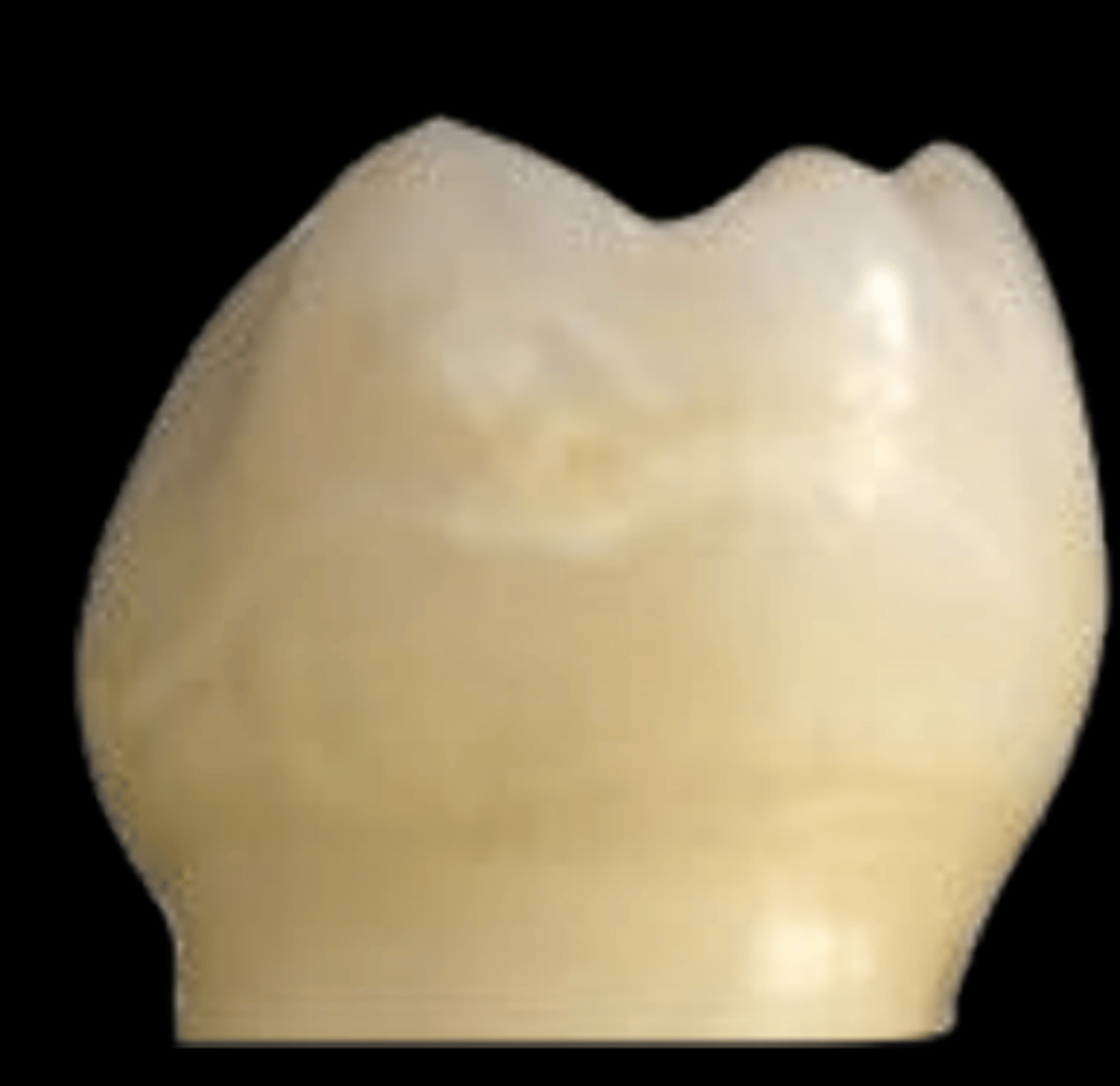
ICDAS 2
Distinct visual change in enamel when viewed wet: opacity or discoloration
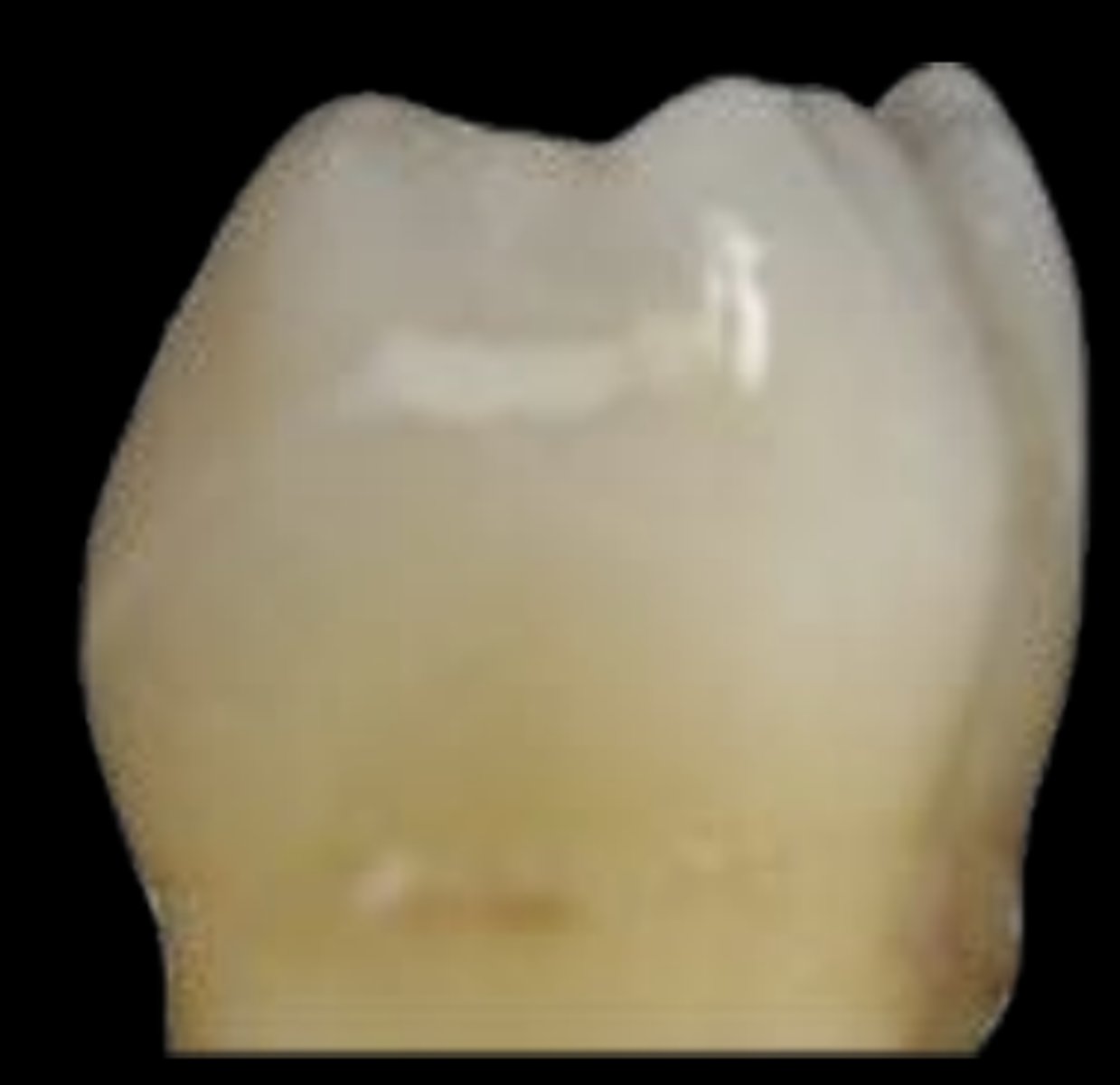
ICDAS 3
Initial enamel breakdown with no visible dentin or underlying shadow; discontinuity of surface enamel
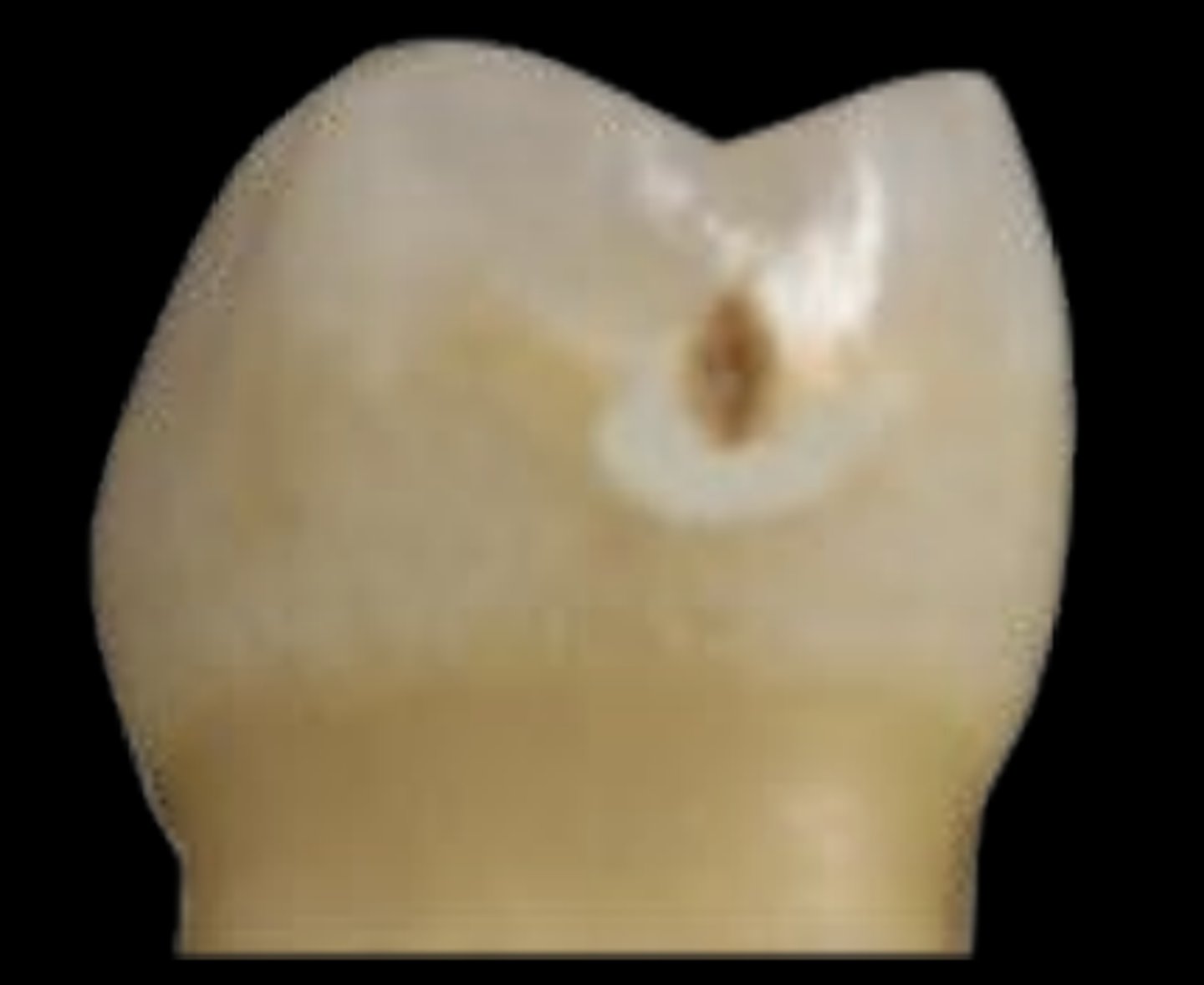
ICDAS 4
Underlying dark shadow from dentin, with or without localized enamel breakdown
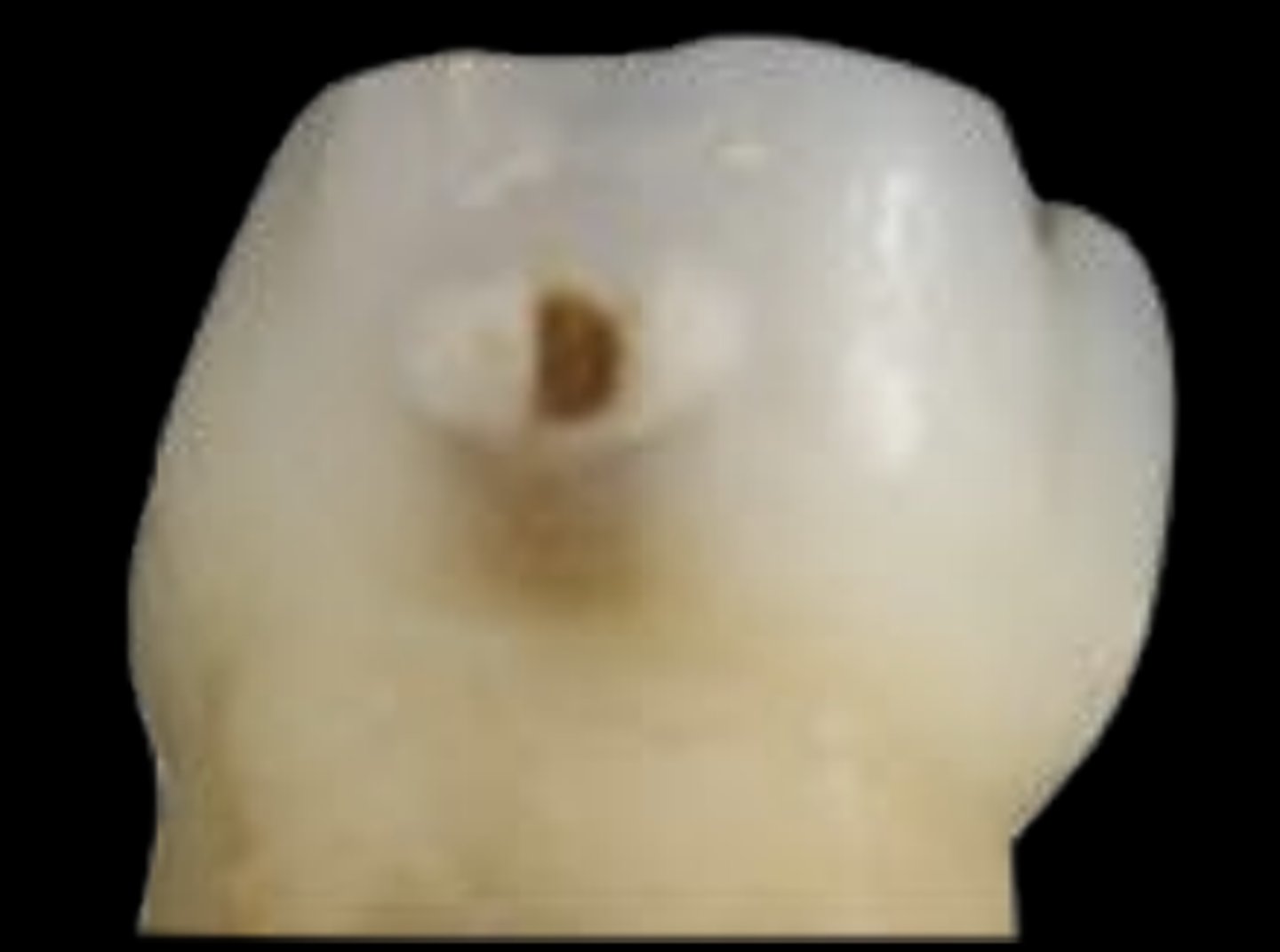
ICDAS 5
Distinct cavity with visible dentin; involving less than half of tooth surface
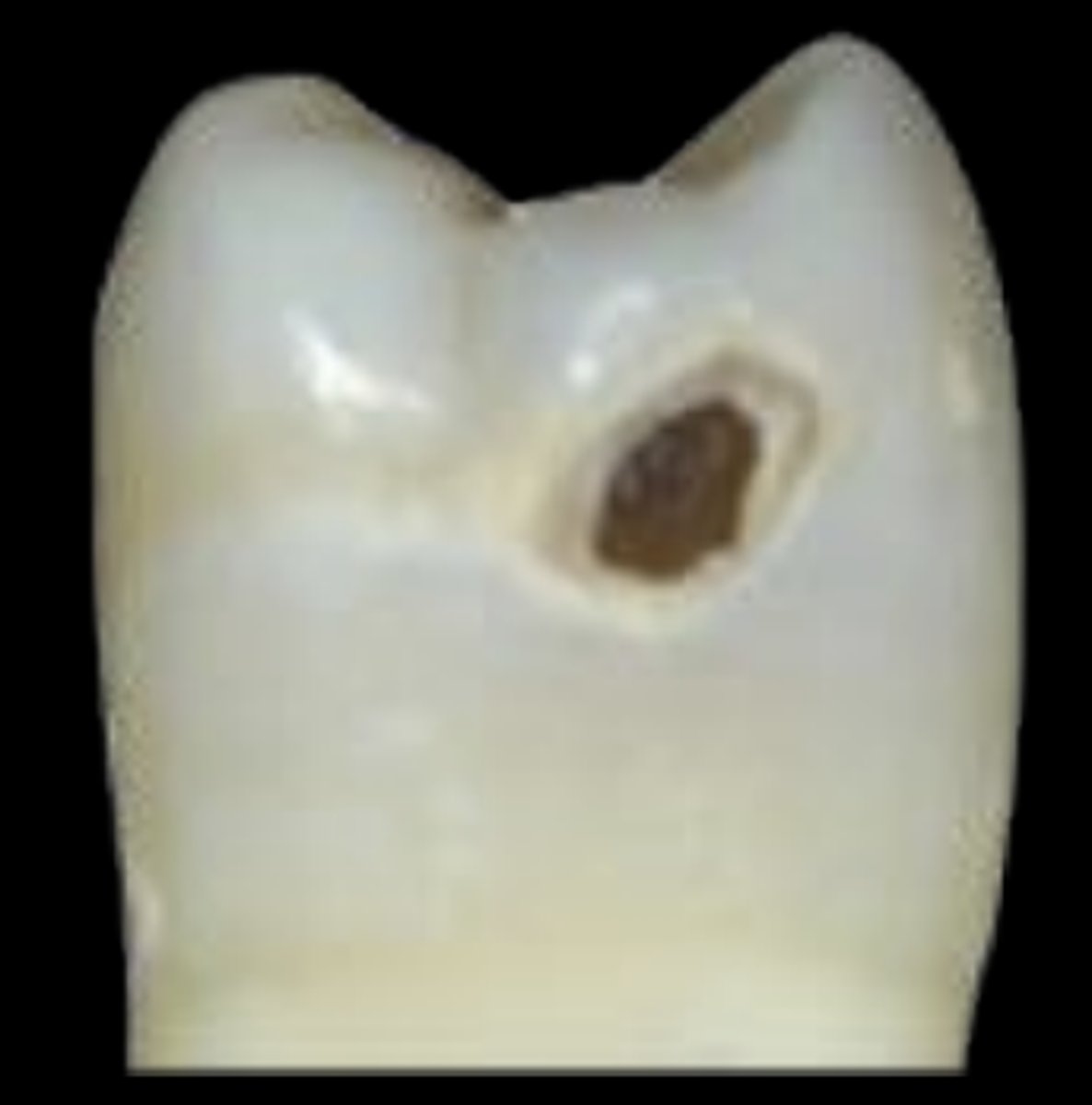
ICDAS 6
Extensive cavity with visible dentin; deep and involving more than half of the tooth surface
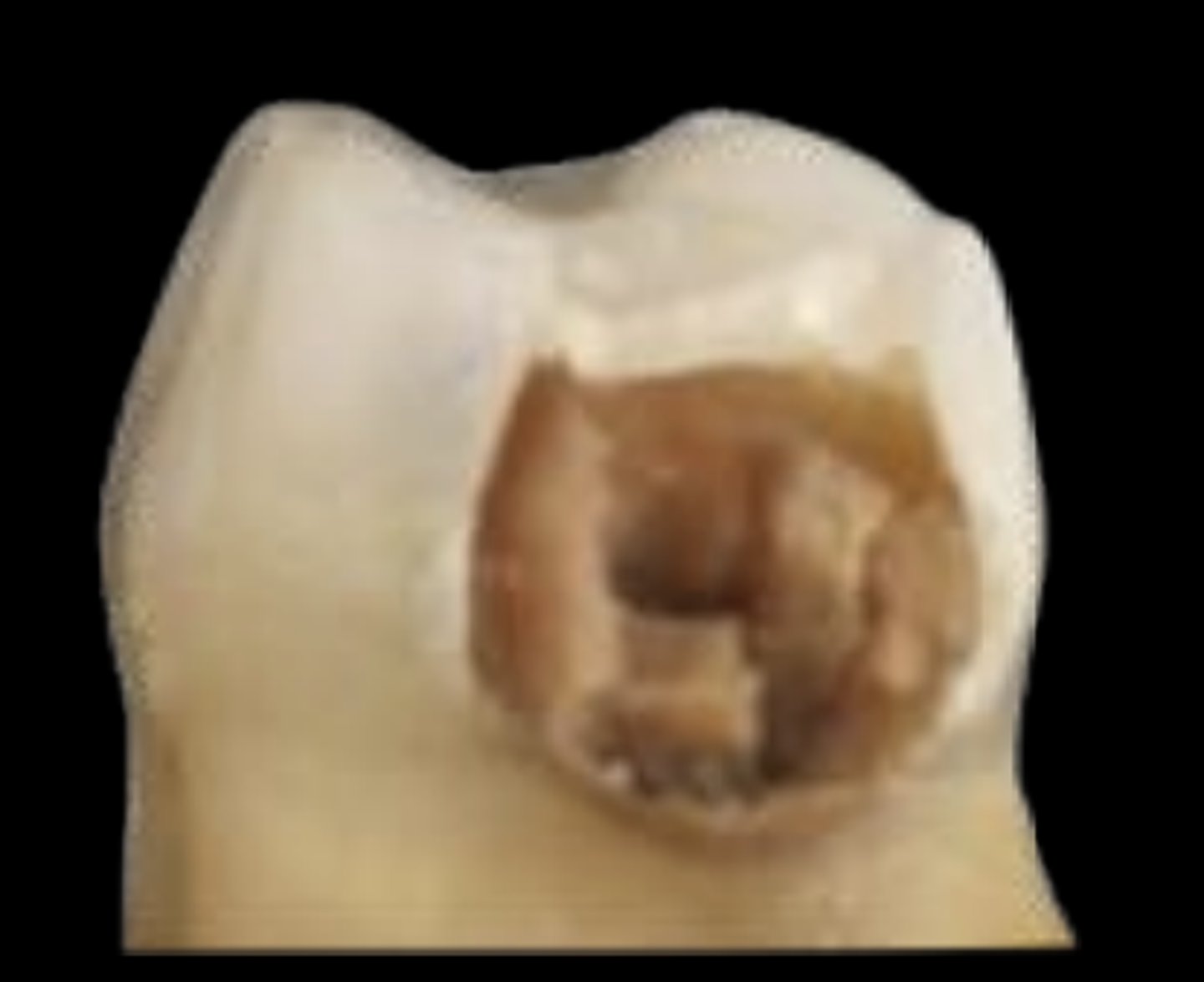
what ICDAS stages typically require treatment?
stage 5 and 6
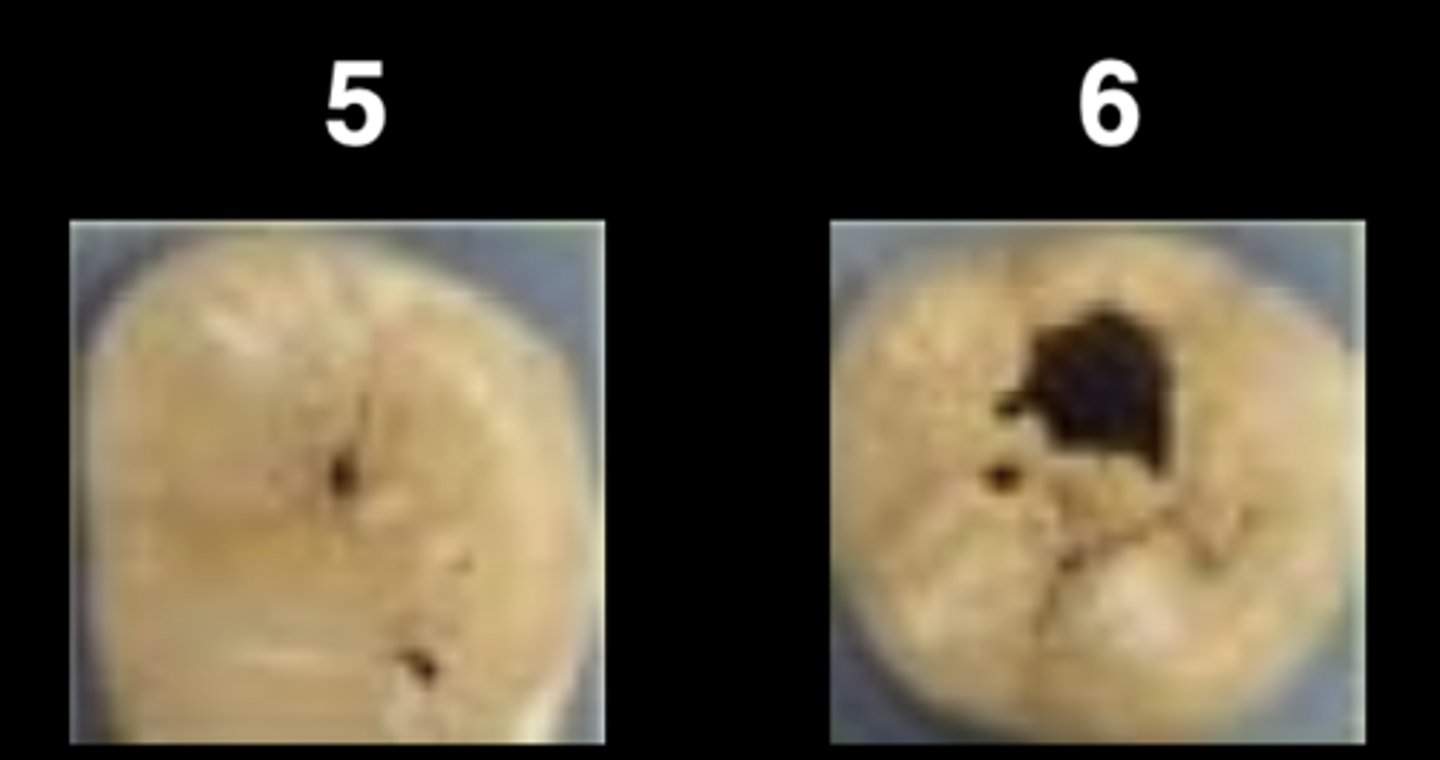

ICDAS stage 0 (occlusal)
Sound surface: no change after air drying
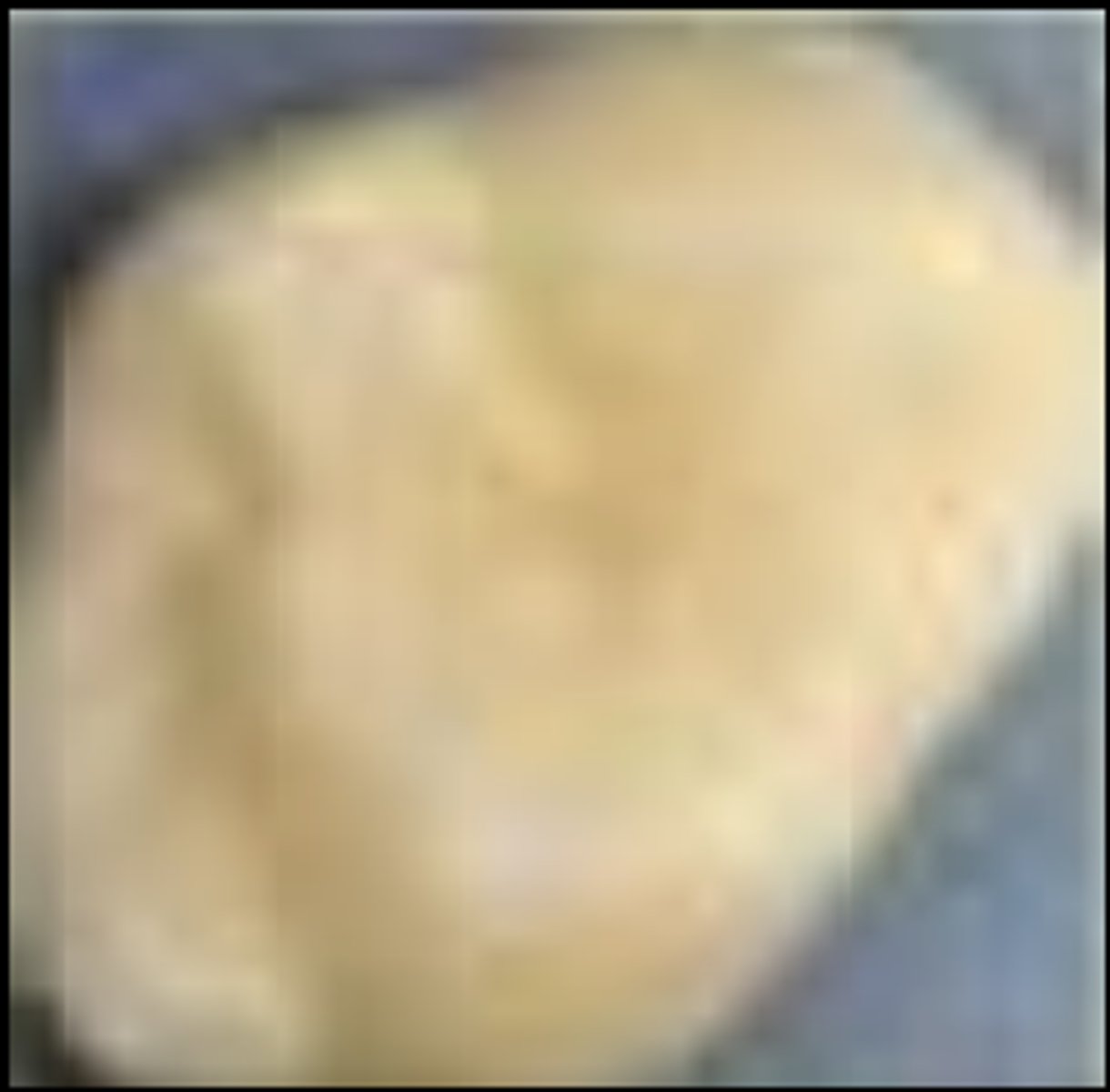

ICDAS stage 1 (occlusal)
First visual change: seen only after air drying,color change limited to pit & fissure
• monitor, seal, noninvasive
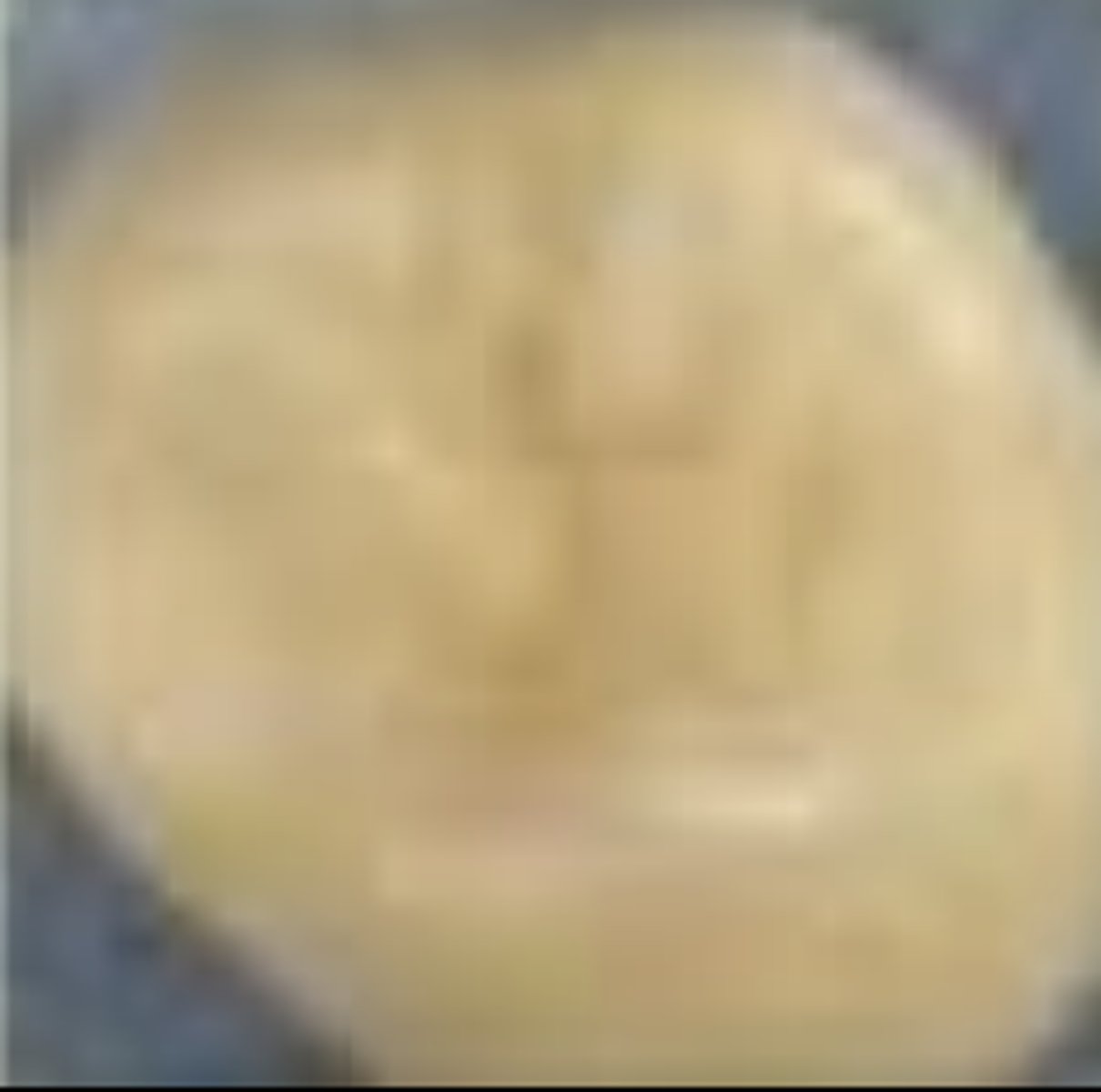

ICDAS stage 2 (occlusal)
Distinct visual change: seen when wet, wider than fissure
• monitor, seal, noninvasive
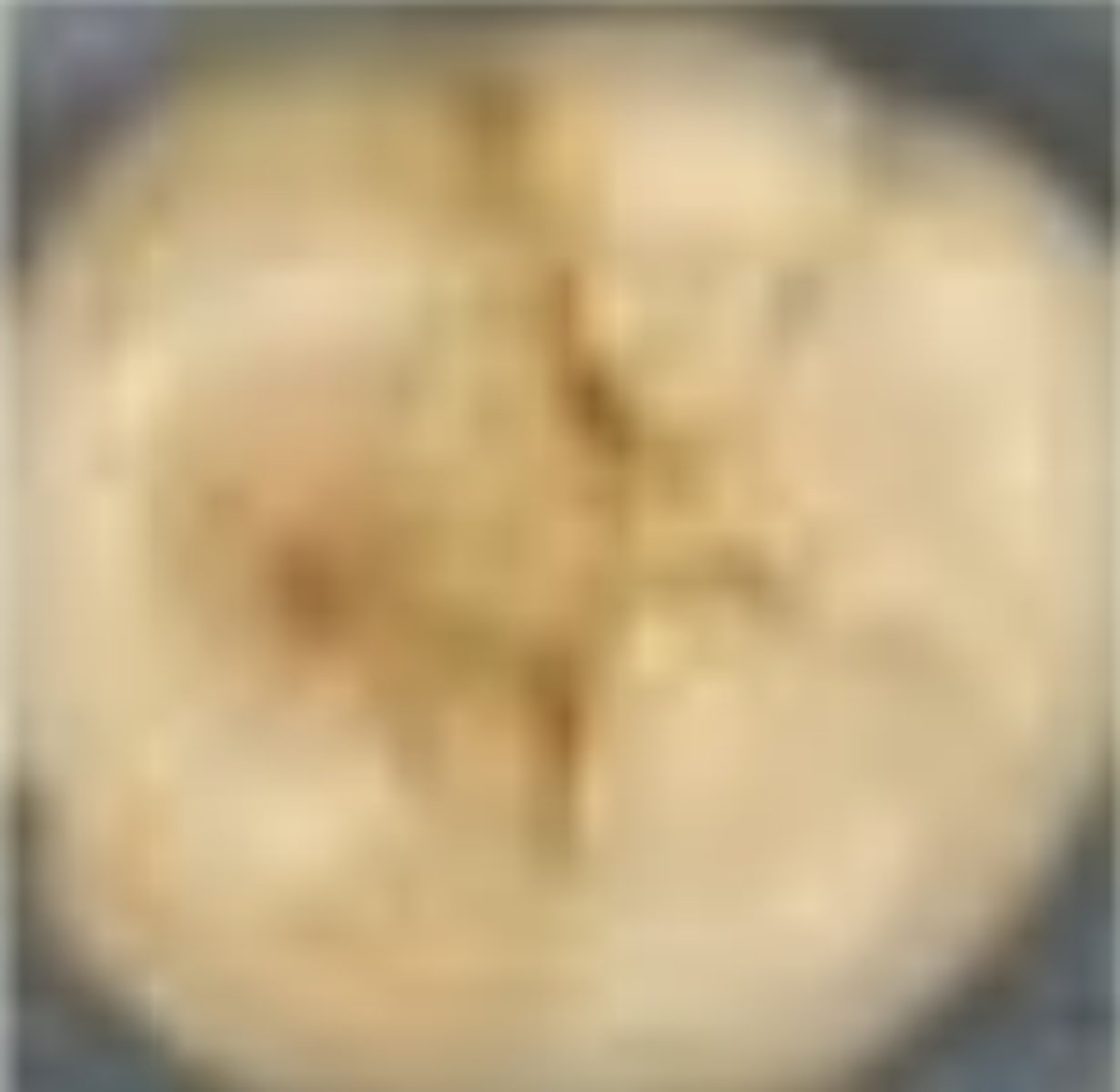

ICDAS stage 3 (occlusal)
Localized enamel breakdown with no visible dentin or underlying shadow; discontinuity of surface enamel, widening of fissure
• monitor, seal, noninvasive
