DNA Mutations and Repair
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
When do mutations occur?
dna replication error
UV/ chemical damage
hydrolytic reactions
When does a mispairing become solidified into the DNA
in the FIRST ROUND OF REPLICATION= MISPAIRED
in the second round of replication the mispaired base gets a matching base
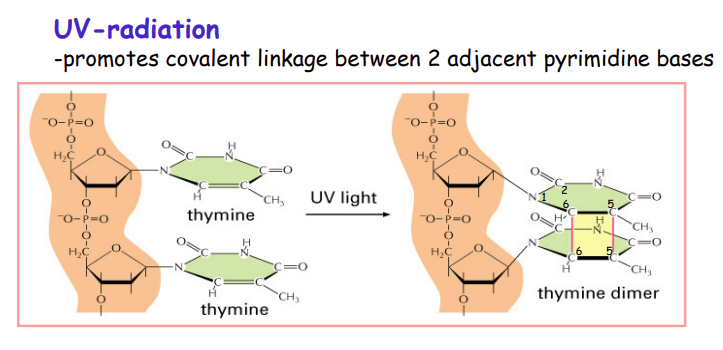
What does UV radiation do?
FORMS A PYRIMIDINE DIMER
carbon 6 linked to carbon 6 AND carbon 5 to carbon 5 of thymine
pyrimidine stacked pyramid
What does nitrous acid do?
deaminates the bases
cytosine—> uracil which turns GC—> AT
N=NH2 become NH-NO
adenosine—> hypoxanthine which turns AT —> GC
mutate HXT —> replicate HXC—> replicate GC
What’s an incalating agent?
A PLANAR molecule that hops in BETWEEN 2 BASES ON THE SAME STRAND causing a new base on the bottom strand
CCC ethidium bromide TTT
GGG a nucleotide AAA

What’s a mutation caused by ethidium bromide called?
frameshift mutation
How does depurination occur?
no base
PDE bond intact
makes a sugar and phosphate inside the genetic code
Which base is easily deaminated
Cytosine (hence Uracil not inside DNA as uracil is caused by a mutation so the fire alarm can go off when uracil shows up in dna )
What is a substitution mutation?
“Point mutation” / “single base pair” causing either
missense mutation→ amino acid coded changed
e.g. Val-→ Ser
nonsense mutation→ MAKES A STOP CODON “non more translation”
silent mutation→ coding region changed but amino acid is the same
Name two types of frameshift mutations
deletion
insertion
How bad is a change in one of the strands
Enzymes and proteins can REMOVED MUTATED STRAND AND USE THE UNMUTATED ONE AS A TEMPLATE= all is good in the world
How are mismatches repaired when the mismatch happens downstream of GATC where Mut H binds?
after replication,ONLY THE OLD STRAND IS METHYLATED
old-CH3 vs new- :(
MutL and MutS complex binds to the mismatch
MutH binds to A on the new unmethylated GATC seq
MutLSH complexes making a loop
MutH is activated and cleaves the UNMETHYLATED STRAND on the 5’ side of GATC
UvrD (DNA Helicase II), unwinds unmethylated strand from the cleavage- GATC to the mismatch
exoI or exoX removes SEGMENT of unmethylated strand (3’→5’ exonuclease activity)
single strand binding protein stabilises the ssDNA segment while DNA Pol III adds in the bases
DNA ligase closes the nick
How are mismatches repaired when the mismatch happens upstream (3’ side) of GATC where Mut H binds?
after replication,ONLY THE OLD STRAND IS METHYLATED
old-CH3 vs new- :(
MutL and MutS complex binds to the mismatch
MutH binds to A on the new unmethylated GATC seq
MutLSH complexes making a loop
UvrD (DNA helicase II) unwinds DNA
Exo VII or RecJ is a 5’→ 3’ exonuclease
SSB and DNA Pol III
DNA ligase
Is MutH @ eukaryotes
nope
How does base excision repair work?
by DNA Glycosylases specific to damaged base
Uracil-DnaGlycosylase removes U by CLEAVING N-GLYCOSIDIC BOND causing an APYRIMIDINIC SITE
AP endonuclease recognises the baseless site and an INCISION IS MADE @ EITHER DIRECTION OF AP SITE
DNA segment removed
DNA POL I FILLS IN GAP
DNA LIGASE
How does NUCLEOTIDE excision repair work?
fixes LESIONS THAT DISTORT HELIX aka thymine dimer
ABC exci-nuclease will HYDROLYSE THE TWO PDE BONDS THAT DISTORTS THE HELIX
ABC exci-nuclease will REMOVE 12NTDS
UvrA + UvrB= A2B complex
complex binds @ lesion
UvrA bends DNA @ lesion
UvrC binds + UvrB
Uvr cuts damaged DNA 8ntds upstream of dimer and 4/5 nts downstream BY USING DIFFERENT DOMAINS FOR UP/DOWNSTREAM
UvrD releases UvrC and the dimer + ntds removed
DNA Pol I fills gap
DNA Ligase
Difference between human vs E.Coli excinucleases
Human = removal of 22-29nts instead of the 5+8nts
What’s Xeroderma Pigmenntosum?
autosomal recessive
skin cancer risk higher
CANT REPAIR DNA AFTER UV DAMAGE (sensitive to sun)
due to no excision repair ( 7 genes, jusy one needs to be mutated!)
Heriditary Non-Polypoaia Colon Cancer cause
hereditary cancer
autosomal DOMINANT
can’t repair mismatches
most commonly implicated -hMSH2 (Human Mut S homolog 2) -hMLH1 (Human Mut L homolog 1)