HBS Unit 1
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
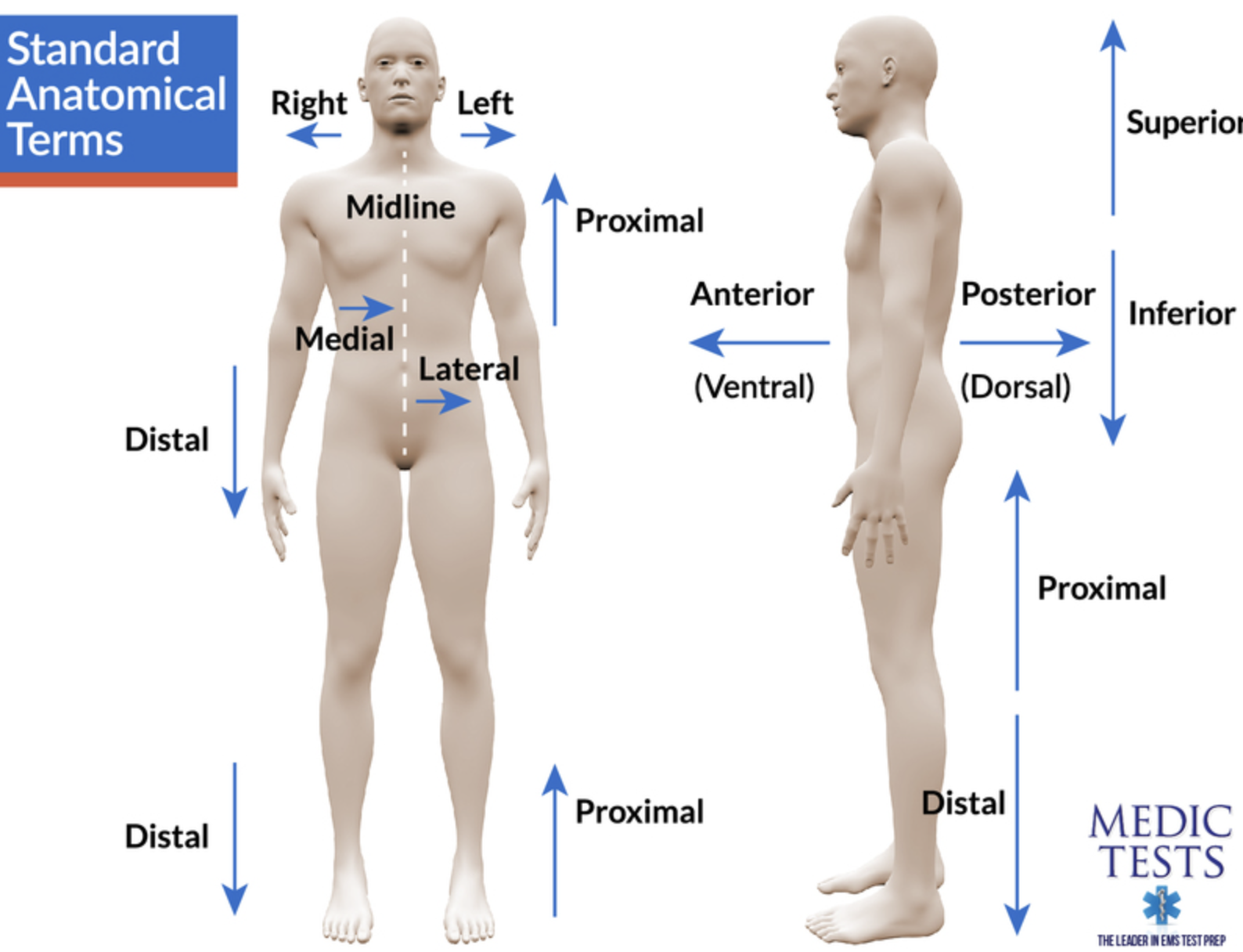
anterior
front of the body
posterior
back of the body
venteral
front of the body of a animal on 4 limbs
dorsal
back of the body of a animal on 4 libs
inferior
away from the head, lower
superior
toward the head, upeer
medial
towards of the midline of the body
lateral
away from the middle of the body
distal
lower to something on the arms or legs, ex: hand is distal to shoulder
proximal
higher to something on the arms or legs, ex shoulder is proximal to the hand
superficial
closer to the surface of the body
deep
further away from body surface
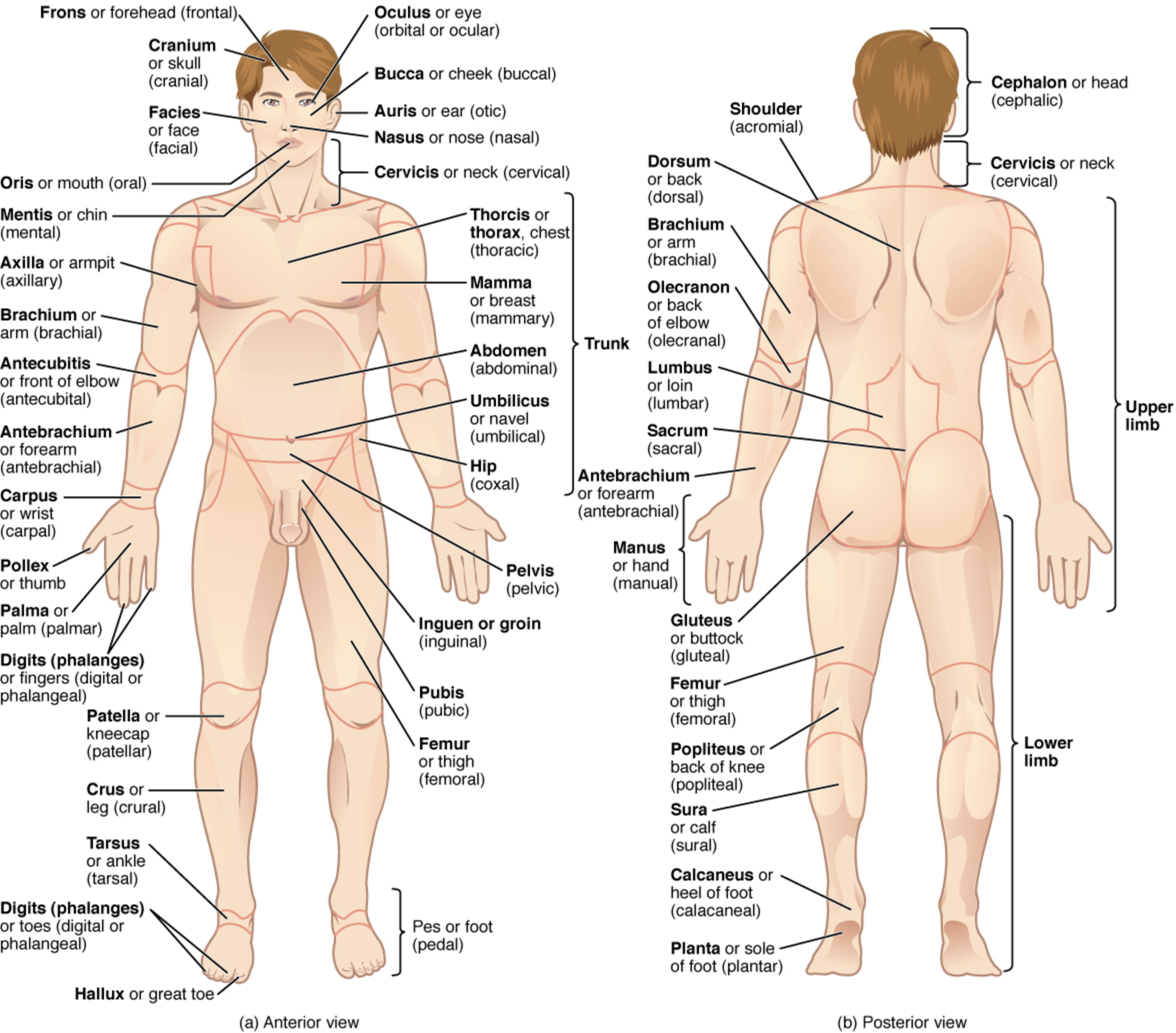
Abdominal
Relating to the region of the body between the diaphragm and the pelvis, containing the stomach, intestines, and other digestive organs.
Antecubital
The area located in front of the elbow, also known as the "cubital fossa."
Axillary
Pertaining to the armpit or the region beneath the shoulder joint.
Brachial
Relating to the upper arm, between the shoulder and the elbow.
Buccal
Referring to the cheek or the mouth cavity, particularly the inner surface of the cheek.
Calcaneal
Relating to the heel bone (calcaneus) of the foot.
Carpal
ertaining to the wrist, specifically the eight bones that make up the wrist joint.
Cephalic
Referring to the head or the superior portion of the body.
Cervical
Referring to the neck or the cervical spine, which consists of the first seven vertebrae of the spine.
Coxal
Pertaining to the hip or hip bone (coxal bone).
Digital
Relating to the fingers or toes.
Femoral
Referring to the thigh, specifically the region between the hip and the knee.
Gluteal
Relating to the buttocks or the gluteus muscles.
Inguinal
Referring to the groin area, where the thigh meets the abdomen.
Lumbar
Pertaining to the lower back, specifically the region of the spine between the rib cage and the pelvis.
Nasal
Relating to the nose or the nasal cavity.
Occipital
Pertaining to the back of the head or the occipital bone.
Olecranal
Referring to the elbow, specifically the bony prominence at the back of the elbow.
Oral
Relating to the mouth.
Orbital
Referring to the eye socket or the region around the eyes.
Patellar
Pertaining to the knee, specifically the kneecap.
Pelvic
Relating to the pelvis, the lower part of the trunk, including the hips and reproductive organs.
Popliteal
Referring to the area behind the knee.
Sacral
Pertaining to the sacrum, the triangular bone at the base of the spine, between the hip bones.
Scapular
Referring to the shoulder blade or the region around it.
Sternal
The long flat bone that forms the center front of the chest wall. The sternum is attached to the collarbone and the first seven ribs. Also called breastbone.
Tarsal
Pertaining to the ankle or the group of bones in the foot that form the ankle joint.
Thoracic
The area of the body between the neck and the abdomen
Umbilical
Relating to the navel or belly button, the central part of the abdomen.
Vertebral
the bones of the spine or backbone
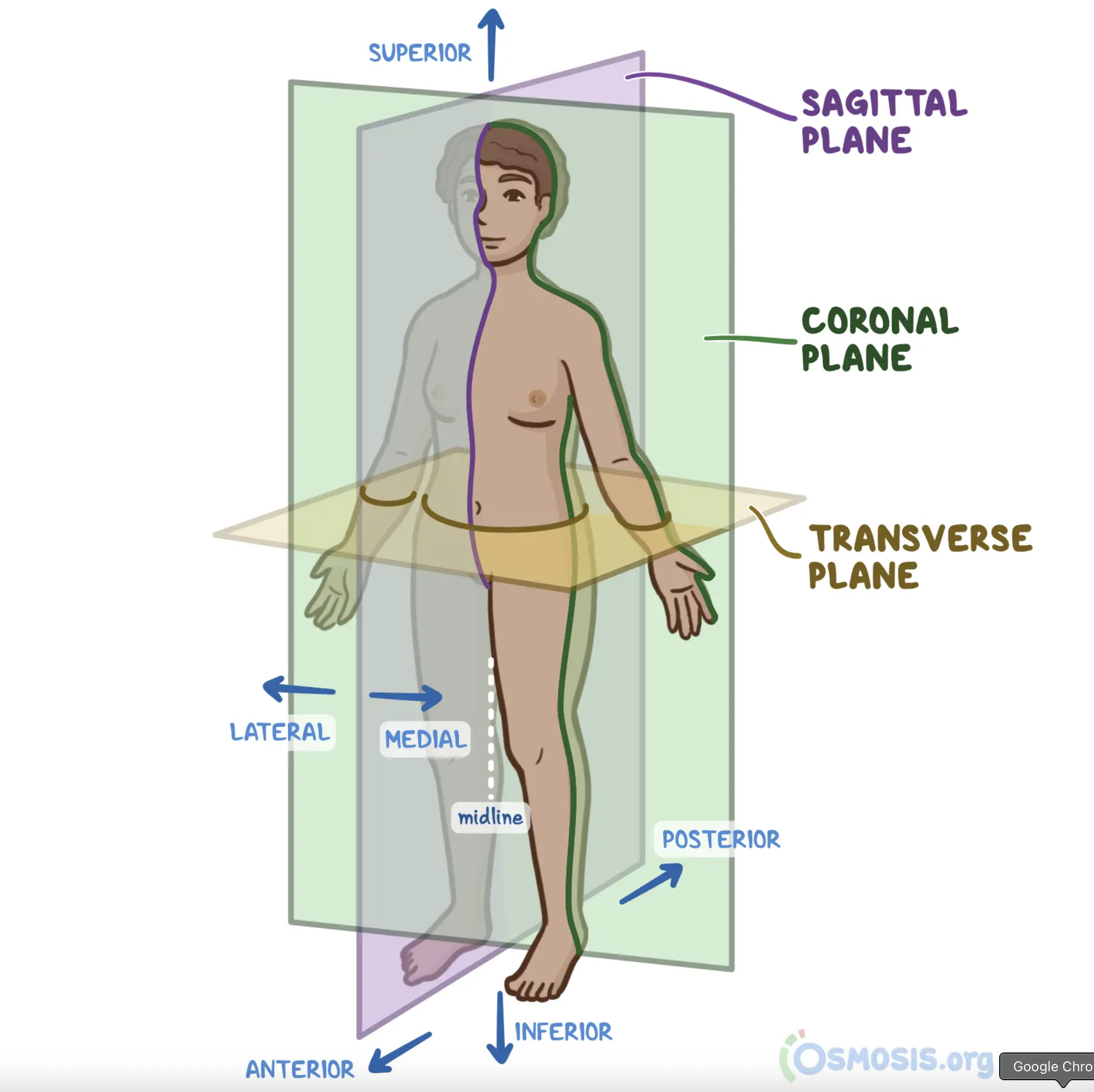
Transverse (Axial) Plane
Divides the body horizontally into superior and inferior portions.
Median Plane
Divides the body vertically into equal left and right portions.
Sagittal Plane
Divides the body vertically into unequal right and left portions.
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
Divides the body vertically into anterior and posterior portions.
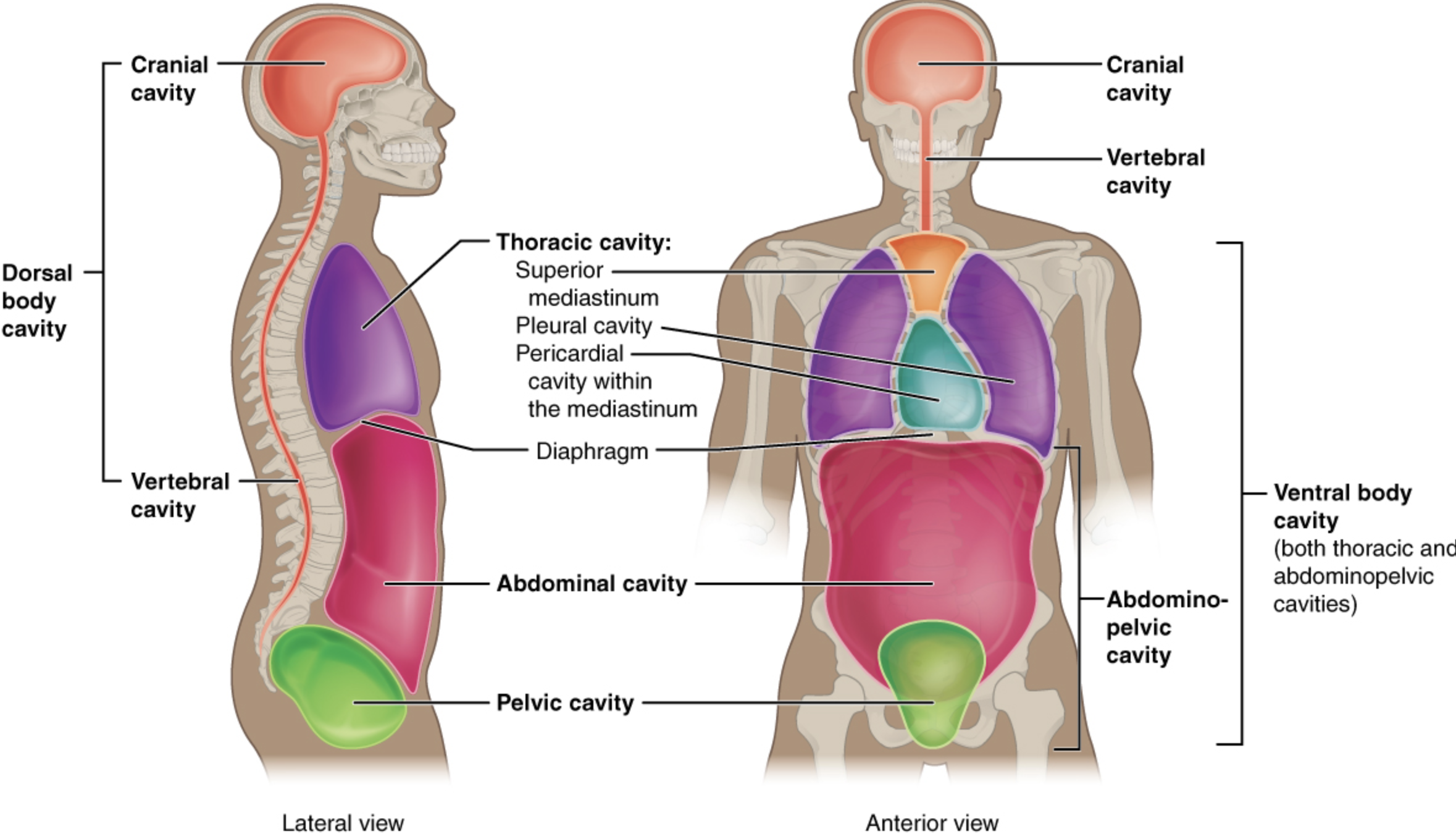
Cranial Cavity
The space within the skull that houses and protects the brain
Dorsal Body Cavity
The body cavity that consists of the cranial and vertebral cavities, housing the brain and spinal cord.
Pelvic Cavity
The space enclosed by the pelvic bones, containing the urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum.
Ventral Body Cavity
The front part of the body cavity, divided into the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic cavities, containing organs like the lungs, heart, digestive organs, and reproductive structures.
Thoracic Cavity
The chest cavity, which houses the lungs, heart, and other structures within the ribcage.
Vertebral Cavity
The cavity formed by the vertebrae that surrounds and protects the spinal cord.
Abdominal Cavity
The space within the abdomen that contains digestive organs like the stomach, intestines, liver, and spleen.
Abdomino-pelvic Cavity
The combined cavity consisting of both the abdominal and pelvic cavities, which contains most of the digestive, urinary, and reproductive organs.
Carpals
small irregular bones that make up the wrist joint
Clavicle
s-shaped bone that connects sternum(breastbone) to scapula(shoulder blade)
Femur
upper leg bone, thigh bone
Fibula
long slender bone lateral to the lower leg
Frontal Bone
large, single, u-shaped bone that forms the forehead, anterior part of skulls vault
Humerus
long bone in the upper arm that extends from shoulder to elbow
Mandible
lower jawbone
Maxilla
upper jawbone
Metacarpals
five long bones that form palm of the hand
Metatarsals
five long bones in the middle of the foot, located between the tarsal bones and phalanges
Occipital Bone
flat, trapezoid shaped bone located at the back and base of the skull
Parietal Bone
large,flat,quadrilateral bones that form the top and sides of the skull, protects brain
Patella
triangular shaped bone located at the front of the knee joint
Pelvic Girdle
ring shaped boney structure formed by two hip bones, sacrum, coccyx, connecting the spine to lower limbs, serves as strong foundation for the body
Phalanges
bones that make up the fingers and toes
Radius
lateral of the two long bones in the forearm running from elbow to the thumb
Rib Cage
bone, cage-like structure that has 12 pairs of ribs, thoracic vertebrae, and sterum, encloses and protects vital organs like heart and lungs
Scapula
shoulder blades, triangular-shaped bone located in upper back
Sphenoid
detailed structure of the sphenoid bone, complex, butterfly-shaped bone located at te base of the skull
Sternum
anterior part of the rib cage, breastbone
Tarsals
irregular bones that make up the ankle
Temporal
at the side and base of the skull
Tibia
medial bone in the lower leg, shinbone
Ulna
medial bone in the forearm
Vertebral Column
segmented bony structure made of individual bones called vertebrae and discs that protect the spinal cord, provides structural support, and allows for movement
Zygomatic
paried bone that forms the prominent structure of the cheek
Connective Tissue
This tissue supports, binds, and protects other tissues and organs, including bone, blood, adipose tissue, and cartilage.
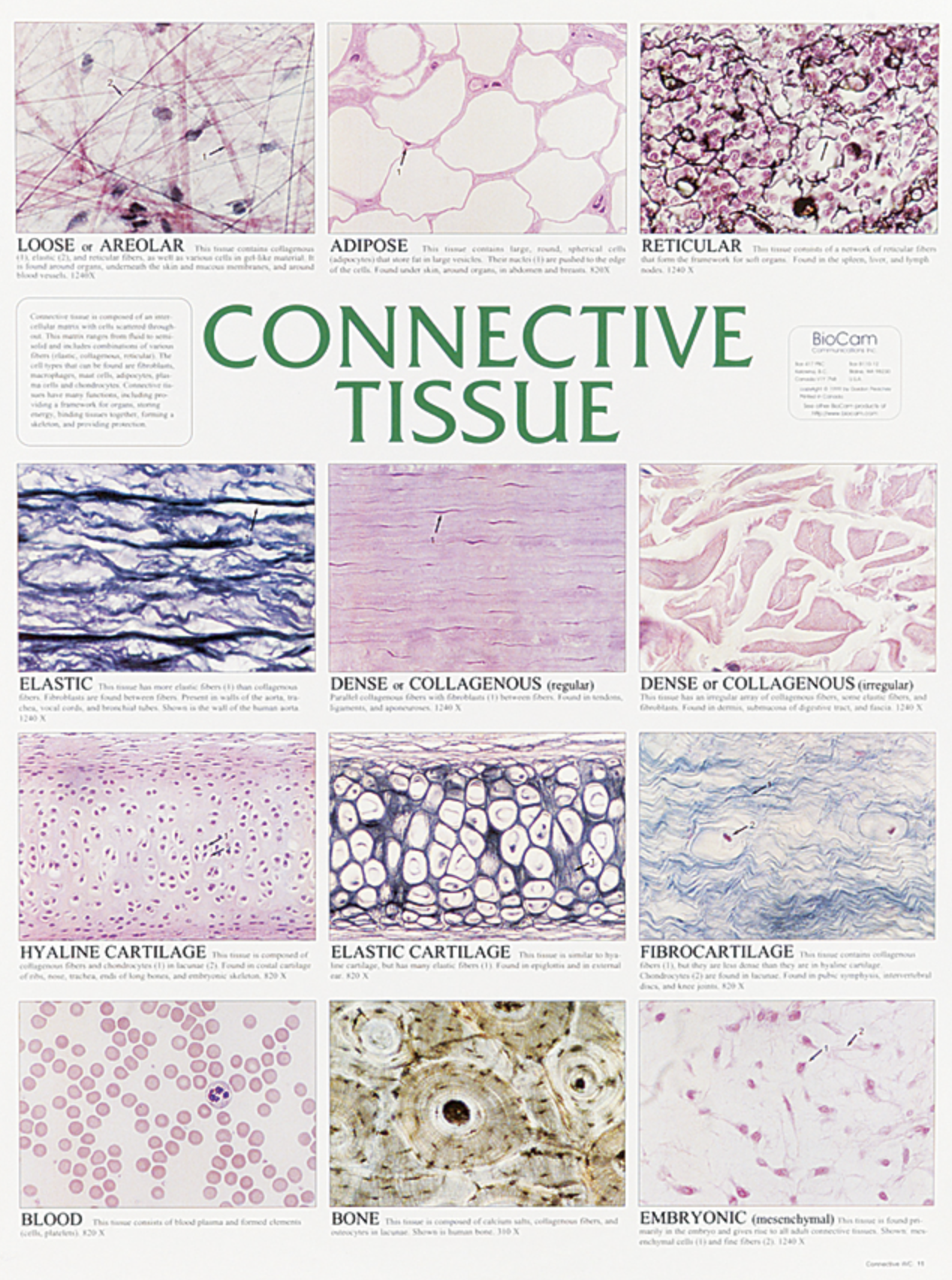
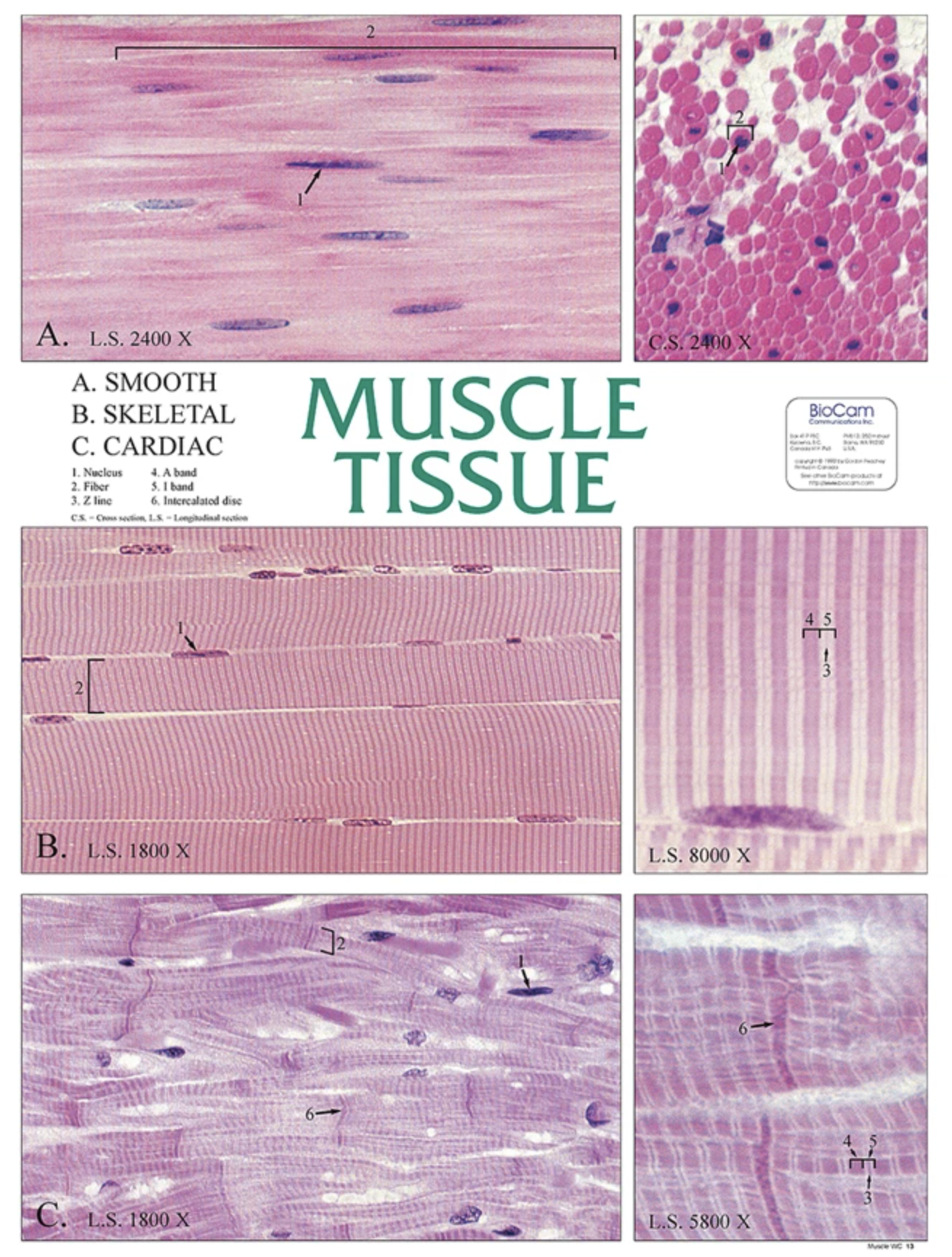
Muscle Tissue
Specialized for contraction, muscle tissue enables movement and includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle types.
Nervous Tissue
Composed of neurons and glial cells, nervous tissue is responsible for transmitting electrical signals throughout the body, enabling communication between different parts.
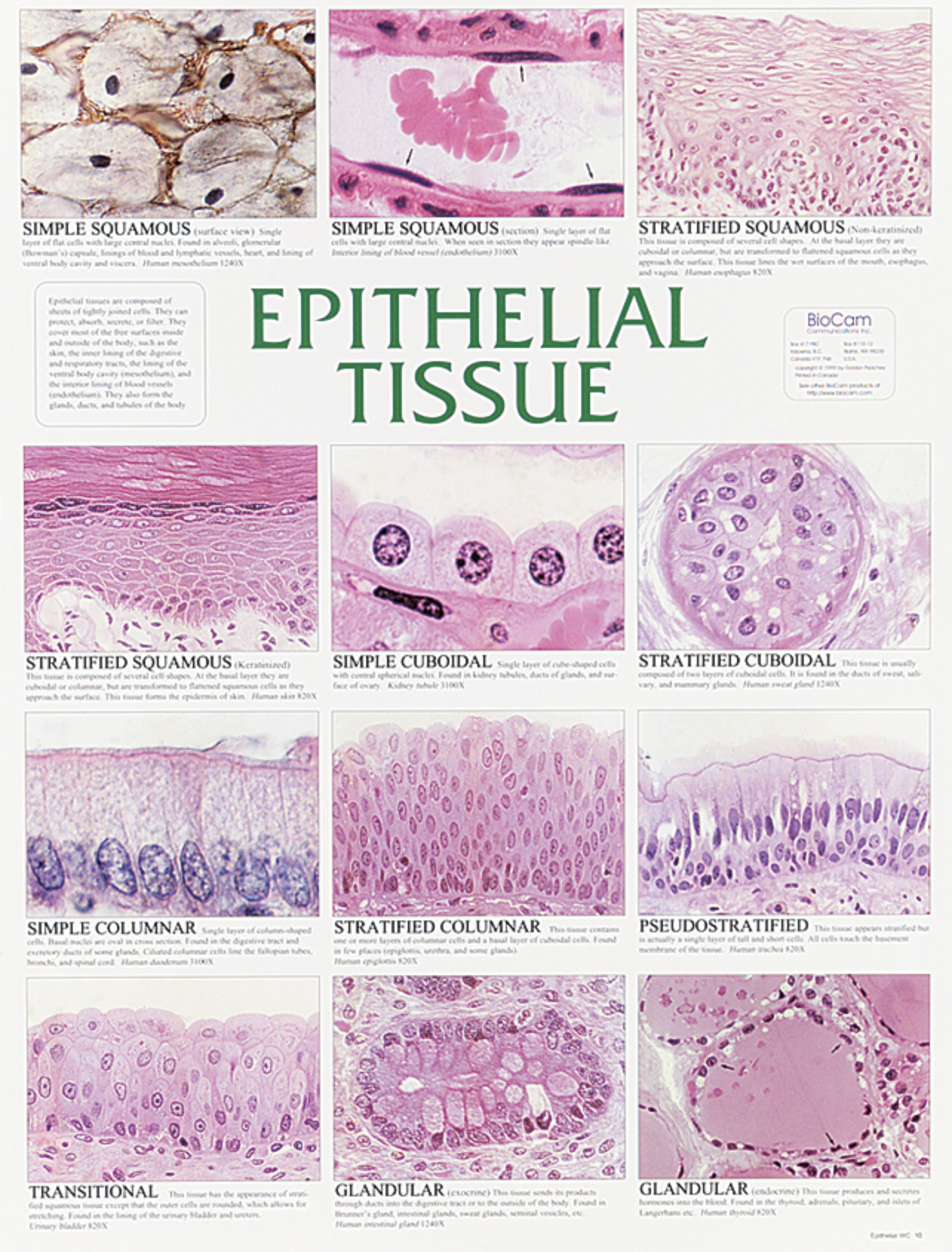
Epithelial Tissue
This tissue forms protective layers covering body surfaces and lining internal cavities, playing roles in absorption, secretion, and filtration.
Flat Bones
Flat bones consist of a layer of spongy bone between two thin layers of compact bone. They have marrow but no marrow cavity. EX: Left parietal bone
Long Bones
Long bones consist of a shaft and two ends of a thick outside layer with a marrow-filled cavity. The ends of the bone contain spongy bone. EX: Right humerus
Short Bones
Short bones are roughly a cube shape with vertical and horizontal dimensions being approximately equal. They consist of mostly spongy bone. The outside surface is a thin layer of compact bone. EX: Right carpals
Irregular Bones
Irregular bones consist of thin layers of spongy bone surrounded by compact bone and do not fit any of the previous bone descriptions. EX: Thoracic vertebrae
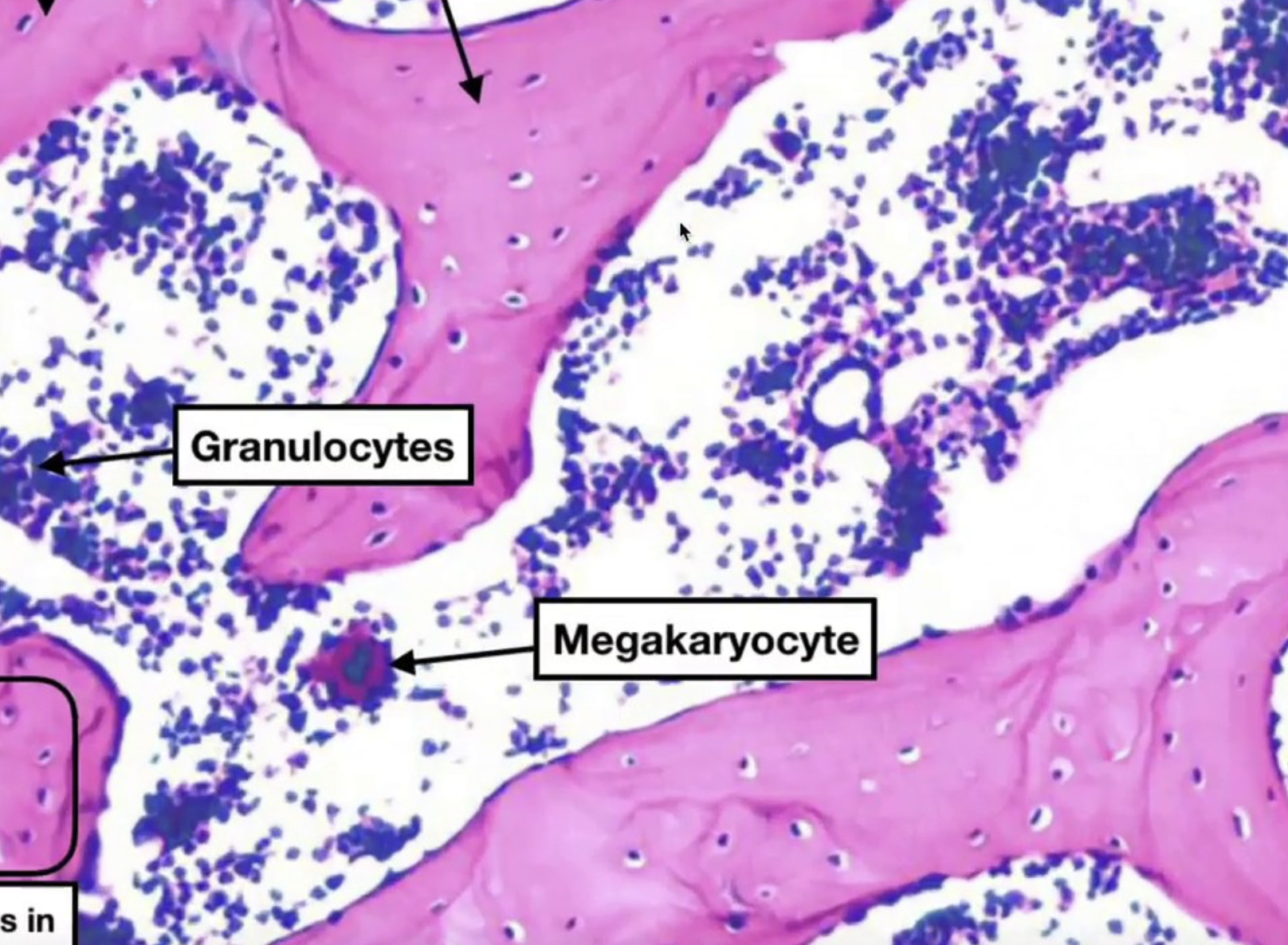
Spongy Bone
lightweight and porous, aiding in shock absorption and housing bone marrow for blood cell production.
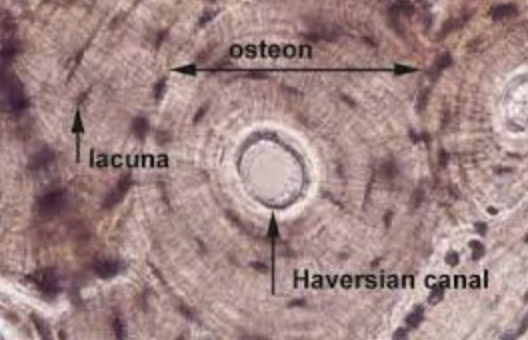
Compact Bone
dense and solid, providing structural support and strength to the skeleton.
Ephiphysis
ends of the bones
Medular Cavity
The central cavity within long bones, which contains yellow bone marrow and is involved in the storage of fat.
Yellow Marrow
A type of bone marrow primarily made of fat cells, found in the medullary cavity of long bones, and serving as an energy reserve.
Periosternum
A dense layer of connective tissue that covers the outer surface of bones, playing a role in bone growth, repair, and nutrition.
Diaphysis Shaft
The long, tubular central portion of a long bone, made mostly of compact bone and housing the medullary cavity.
Metaphysis
where the bone grows