AST101 Midterm 1
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
the universe
the further we look away, the further back in time we look, the universe is cooling and expanding, the universe is transparent now, but back then it wasn’t
Primordial plasma
13.7 billion years ago, red stuff at the edge of the universe
Orbit
planet all ___ in the same plane (ecliptic plane)
the planets all ___ in the same direction
the sun rotates in the same direction that the planets ___
the planes all have elliptical orbits
the closer the planet is to the sun, the faster it ___
Mercury
closest to the sun
no atmosphere
highly cratered surface
rocky exterior with huge iron core
temprature between -170 to 427
no moons
Venus
roughly same size as earth
lots of volcanos
thick CO2 atmosphere
runaway greenhouse effect which makes it hotter than mercury
its always 460c everywhere
rains acid
no moons
rotates very slowly backwards
Earth
around same size as Venus
lots of volcanoes
O2 + N2 atmosphere
large oceans regulate CO2
one large moon
23.4 degree orbital tilt produces significant seasons
Mars
lots of volcanoes
thin CO2 atmosphere
oceans have evaporated
no evidence of life
2 small moons
polar ice/ dry ice caps
dust storms
25.2 degree orbital tilt produces significant seasons
terrestrial planets
small
rocky
relatively thin or no atmosphere
few moons
made from heavy elements
(Earth, Venus, mercury, Mars)
Jupiter
largest planet in the solar system
thick gaseous atmosphere surrounds a giant ball of liquid hydrogen
has very faint rings
many moons: more than 60
Saturn
second largest in solar system
has rings
many moons: more than 60
structure like Jupiter
Uranus
coldest planet
small rocky core
thick H2/ He atmosphere
rotation axis tilted 98 degrees
thin rings and lots of moons
Neptune
furthest planet from the sun
structure similar to Uranus
rotation axis tilted 28 degree
more surface features than Uranus
strongest words in the solar system: up to 21,000 Km/h
Jovian Planets
Gas + Liquid
large
many moons
mostly light elements
(Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune)
Asteroid Belt
Around a million asteroids larger than 1km diameter
total mass is around 3% of the moon’s
Kuiper Belt
Vast collection of small icy bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune
includes several of the dwarf planets, including Pluto
total mass around that of the earth’s moon
Comets
smaller icy bodies from the outer solar system
highly elliptical orbits
emit tails when they get close to the sun
Summer
daylight is longer and darkness is shorter
sun gets higher in the sky, so sunlight is more direct
Winter
daylight is shorter and darkness is longer
sun does not get as “high” in the sky, so sunlight is at an angle
Moon phases and eclipses
the sun illuminates one side of the moon. the other side is in shadow
the phase we see depends on where the moon is compared to the sun
phases repeat each time the moon orbits the earth once
a solar eclipse happens when the moon blocks the sun
a lunar eclipse happens when the moon enters the Earth’s shadow. This is not the cause of phases
New Moon
when the moon is in the direction of the sun
the only time a solar eclipse can happen
unlit side faces the earth
rises with the sun and sets with the sun
not generally visible
waxing crescent
3-4 days after the new moon
rises around 3 hours after the sun
sets around 3 hours after the sun
easiest to see right after sunset
waxing quarter/first quarter
1 week after the new moon
moon is lit from the side
rises around 6 hours after the sun
sets around 6 hours after the sun
easiest to see at night before midnight
waxing gibbous
10-11 days after the new moon
rises around 9 hours after the sun
sets around 9 hours the sun
easiest to see at night - but may set before sunrise
full moon
2 weeks after the new moon
the only time a lunar eclipse can happen
rises around 12 hours after the sun rises
sets around 12 hours after the sun sets
visible most of the night
waning gibbous
10-11 days before the next new moon
rises around 3 hours after the sun rises
rises before midnight, and is up the rest of the night
waning quarter/third quarter
around a week before the next new moon
rises around 6 hours before the sun rises
sets around 6 hours before the sun sets
rises around midnight, and is up the rest of the night and morning
waning crescent
2-4 days before the next new moon
rises around 3 hours before the sun rises
sets around 3 hours before the sun sets
easier to see before sunrise
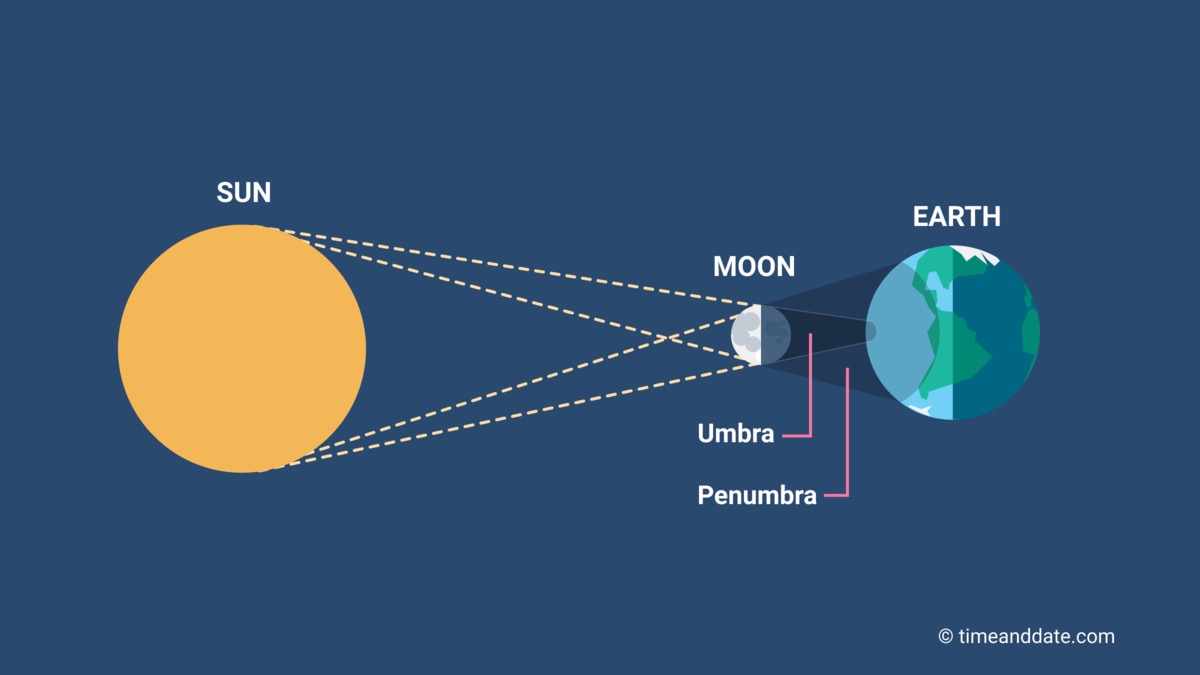
solar eclipse
when the moon blocks light from the sun
happens when the new moon crosses the ecliptic plane
because the moon’s orbit is tipped relative to the ecliptic plane, this happen rarely (every few years, somewhere on earth)
it only casts a shadow on small part of earth
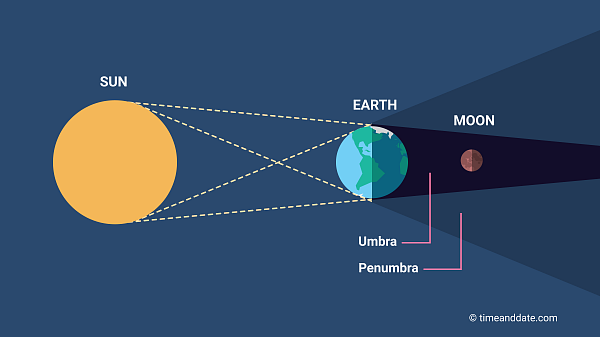
Lunar Eclipse
when the moon enters the earth’s shadow
happens when a full moon crosses the ecliptic plane
can be seen from anywhere on earth
more common than solar eclipse (the earth is larger than the moon, so has a larger shadow)
the geocentric universe
the earth is the centre of the universe
all celestial objects revolve around the earth

retrograde motion
planets move from night to night relative to the stars
the planets don’t follow a uniform pattern relative to the stars
they appear to turn around relative to the stars
this turn around is called ____ ____
cycles and epicycles
the retrograde motion of the planets is inconsistent with planets moving in circles around the earth
BUT, it is consistent with a “circles within circles” pattern, like a spirograph
Nicolaus Copernicus
catholic canon/ scholar
diplomat
economist
translator
famous for:
the sun is the centre of the universe
planets orbit the sun in circles
the moon orbits the earth
apparent retrorade motion
earth orbits faster than mars
as earth passes mars, the position of mars on the sky, compared to background stars, changes
this can explain the motion of the planets on the sky
Kepler’s first law
the orbit of each planet about the sun is an ellipse with the sun at one focus
Kepler’s second law
a planet moves faster in the part of its orbit nearer the sun and slower when farther from the sun, sweeping out equal areas in equal times
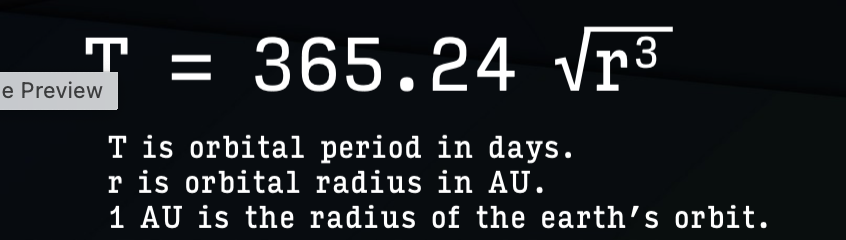
Kepler’s third law
more distant planets orbit the sun at slower average speeds, obeying a precise mathematical relationship
speed
the rate of change of position.
velocity
speed and direction
car goes due north at 60 km/hour
acceleration
the rate of change of velocity
speed change from 0km/h ro 100 km/h in 9s
newton’s first law
an object in motion remains in motion unless acted upon by an outside force
newton’s second law
acceleration is proportional to force and inversely proportional to mass
A=F/m
more force means more acceleration
more mass means less acceleration
Newton’s third law
for every force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force
shuttle is propelled upwards by a force equal and opposite to the force with which gas is propelled downwards
momentum
mass times velocity
p=mV
if you add up the momentum of everything in a closed system, you will find that no matter what happens, this momentum is conserved
Angular momentum
mass times velocity times distance
w=mVr
if you add up the angular momentum of everything in a closed system you will find that no matter what happens, angular momentum is conserved
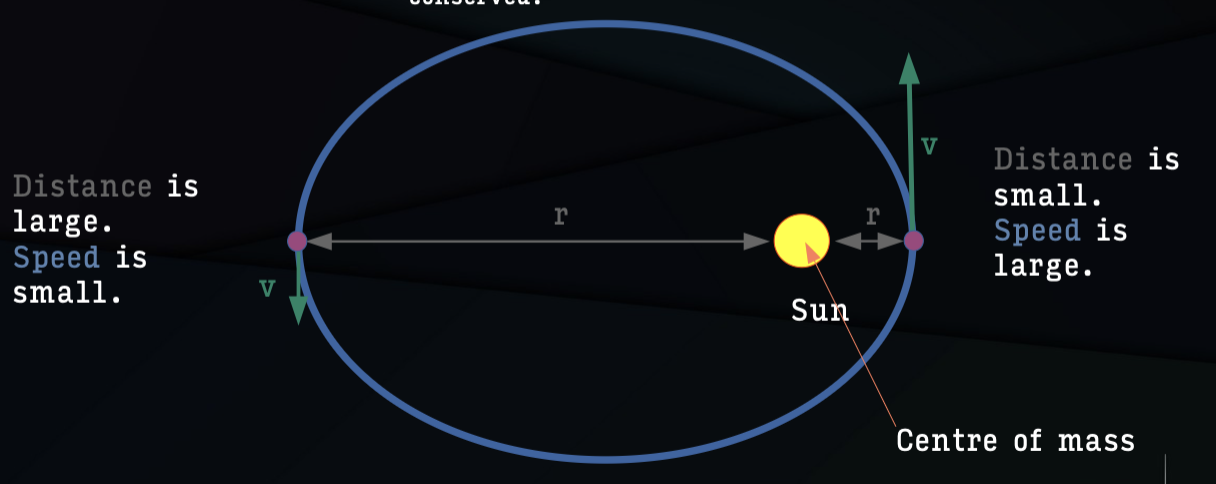
newton’s universal law of gravitation
there is a force between any 2 objects in the universe
the force is proportional to the product of the masses of each object
the force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance
the force depends on M1 times M2
if you double the mass of either object, you double the force
if you half the mass of either object, you half the force
the force depends on the distance between the centres of the 2 objects
if you double the distance, you reduce the force by a factor 2×2=4
if you half the distance, you increase the force by a factor of 2×2=4
freefall
why is the astronaut floating another not falling to earth?
because he is in orbit, like his space craft
when the only force acting on an object is gravity, we say you are in ______
Tidal Locking
friction with the rotating earth causes the tidal bulge to lag behind.
this lag applies a force on the earth, causing its rotation to slow down
the rotation period was 14 hours when the earth formed, now it is 24 hours
the tidal force on the moon by the earth is much larger than the tidal force of the moon on the earth
so the moon has already stopped relative to earth
tides
the predictable, periodic rise and fall of sea levels caused by the gravitational forces of the Moon and Sun, which create bulges of water on Earth's surface
spring tide
in a full moon or a new moon, the tidal forces from the moon and the earth add
happens when the sun, moon and earth are lined up. the moon can be on either side
thee are the largest tides and
happen 2 times a month›

Neap Tide
in a quarter moon, the tidal forces from the sun partially cancel the tidal forces from the moon
smallest tides of the month
happens when the sun, moon, and earth are minimally lined up

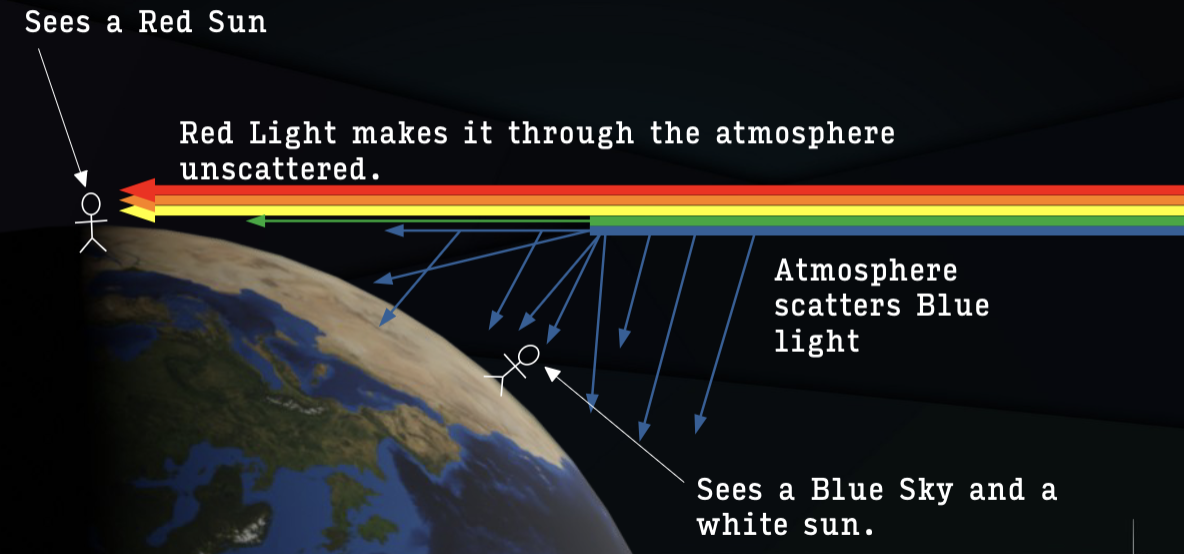
why is the sunset red
because the sunlight must travel through more of the Earth's atmosphere, scattering away the shorter, blue wavelengths of light and leaving the longer, red and yellow wavelengths to reach our eyes
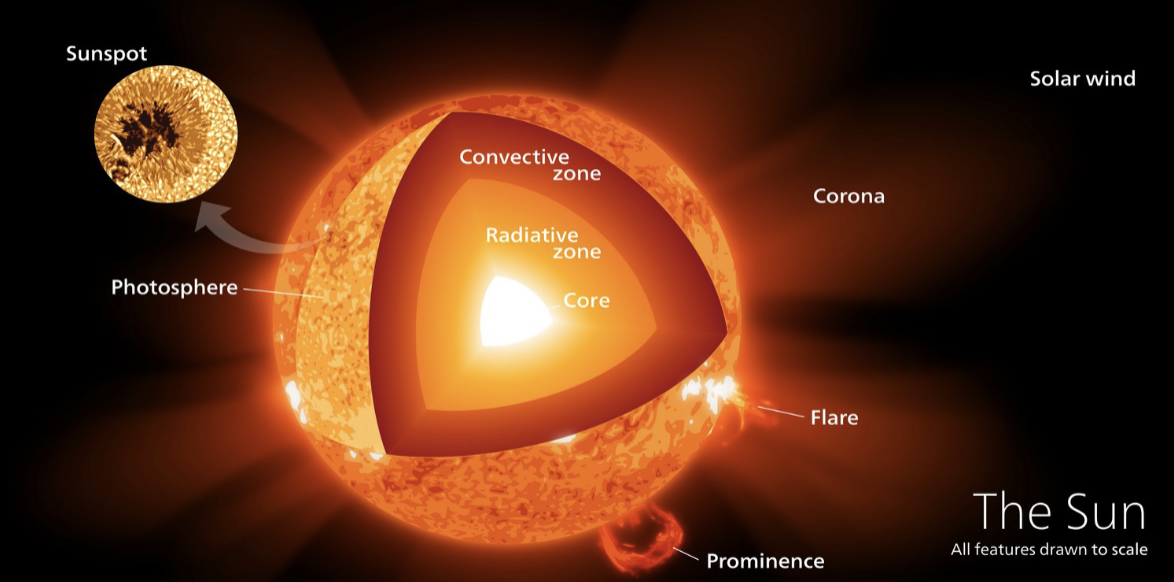
the sun
core → radiative zone → convective zone → photosphere
where does energy come from
matter is made of atoms
atoms stick to each other to form molecules
a chemical reaction is a change in what molecules you have, the atoms stay the same
some reactions, like burning natural gas give off energy
helium atom
2 protons
2 neutrons
2 electrons
the proton and neutron are in the nucleus
the electrons from a ‘cloud’ around the nucleus
at high temperatures, the electrons are stripped away from the nucleus. This is called Plasma
Fusion in the Sun
if you can somehow combine 4 protons you get:
2 positrons (+ charged electrons)
2 neutrinos
2 gamma rays
1 helium nucleus
this has a lower mass than you started with
the remaining mass becomes energy, according to Einstein’s famous equation: E=mc2
hard to do
the + charge on the protons makes them repel each other
they have to collide at very high speed to stick, or they will just bounce
pressure, temperature, and density
gas and plasma are made of particles
the particles are moving
when they bounce off something, they apply pressure
higher temperature: moving faster, higher pressure
higher density: more particles, higher pressure
Hydrostatic Equilibrium in the sun - increased density
_____ ______ ‘equilibrium → rate of fusion increases → temperature increases → pressure increases → core expands → density drops → equilibrium restored
Hydrostatic Equilibrium in the sun - decreased density
_____ ____ ‘equilibrium’ → rate of fusion decreases → temperature decreases → pressure decreases → core contracts → density increases → equilibrium restored
Nuclear Fission
235U has 92 protons and 143 neutrons (235 total)
if a slow neutron hits it, it forms 236U, which is unstable. the strong force can no longer hold it together
it breaks up into smaller pieces
the total mass of these smaller pieces is less than we started with
the remaining mass converted to energy according to E=mc2
celestial equator
is an imaginary line that extends out from the Earth's Equator into the celestial sphere.
asteroid
a rocky or metallic object that orbits the Sun, smaller than a planet but larger than a meteoroid