CMPP: Dialysis and Renal Transplantation
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Hemodialysis
form of renal replacement therapy that may be required for CKD
DM, CV diseases, infections
over 50% of pts requiring dialysis are due to __, and deaths on dialysis are primarily due to __________ and ________.
A -- Acidosis (metabolic acidosis)
E -- Electrolytes (hyperkalemia)
I -- Ingestion (drug overdose)
O -- Overload (pulmonary edema)
U - Uremia (GFR<10, pericarditis, intractable GI symptoms, encephalopathy)
indications for dialysis
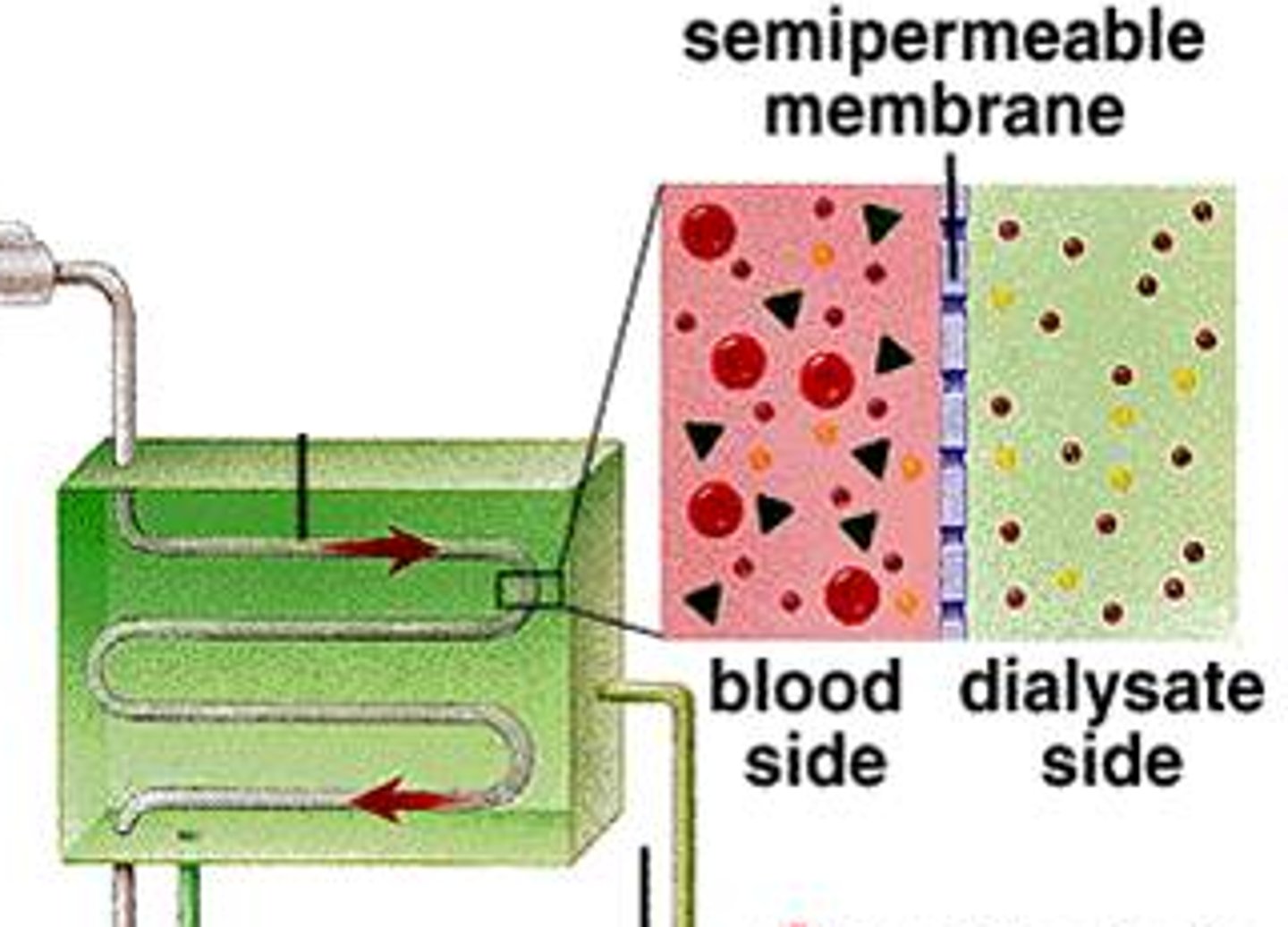
dialysate (fluid introduced into dialyzer)
dialyzer (machine where pts blood and dialysate mix)
the pump (delivers the blood to the dialyzer)
three essential components of hemodialysis
arterial blood passes through semi-permeable membrane
anticoagulant (IV heparin) runs through to prevent thrombosis
what tends to flow through the dialyzer?
dialyzer filters waste products, electrolytes, and drugs
filtered blood returns to venous system "reabsorbed"
excess fluid and various blood components are excreted (urine)
what is actually occurring during the process of dialysis?
allows perfusion of blood and dialysate compartments simultaneously at high flow rates
--> composed of bundles of capillary fibers (glomeruli) through which blood circulates while dialysate travels around the fibers
what is the function of the plastic chamber in dialysis?
GFR gets lower
how does a longer time between dialysis sessions alter the GFR?
AV fistula, prosthetic graft, tunneled dialysis catheter
what are the options for dialysis access?
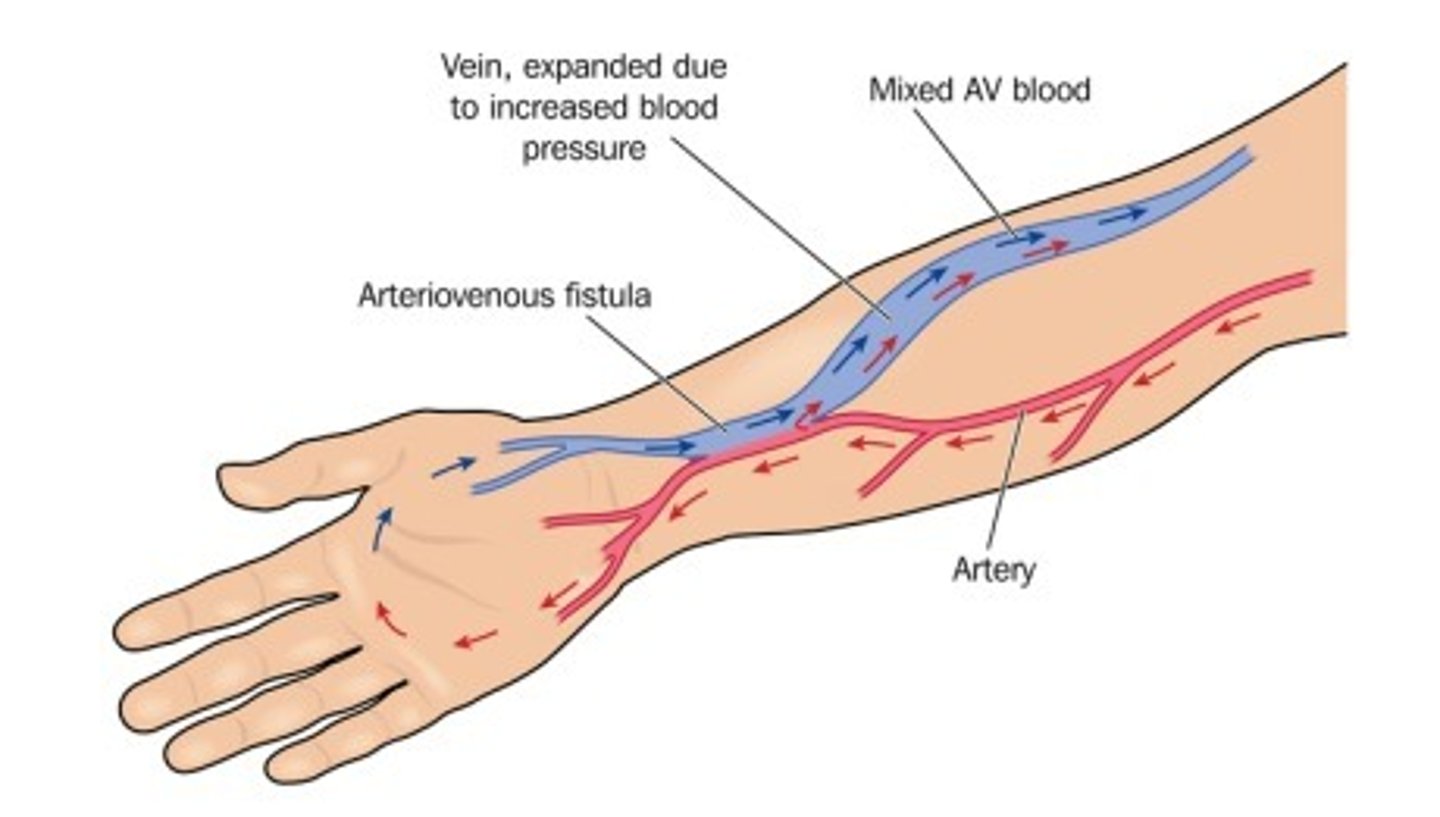
AV fistula
joining of an artery and vein together, so blood mixes; used in some dialysis patients; generally placed in NON-dominant forearm; "matures" over 2-3 months; ideally placed at lest 6 months prior to the anticipated need; mean long term latency rates up to 7 years; lowest risk of complications out of all of the dialysis access options
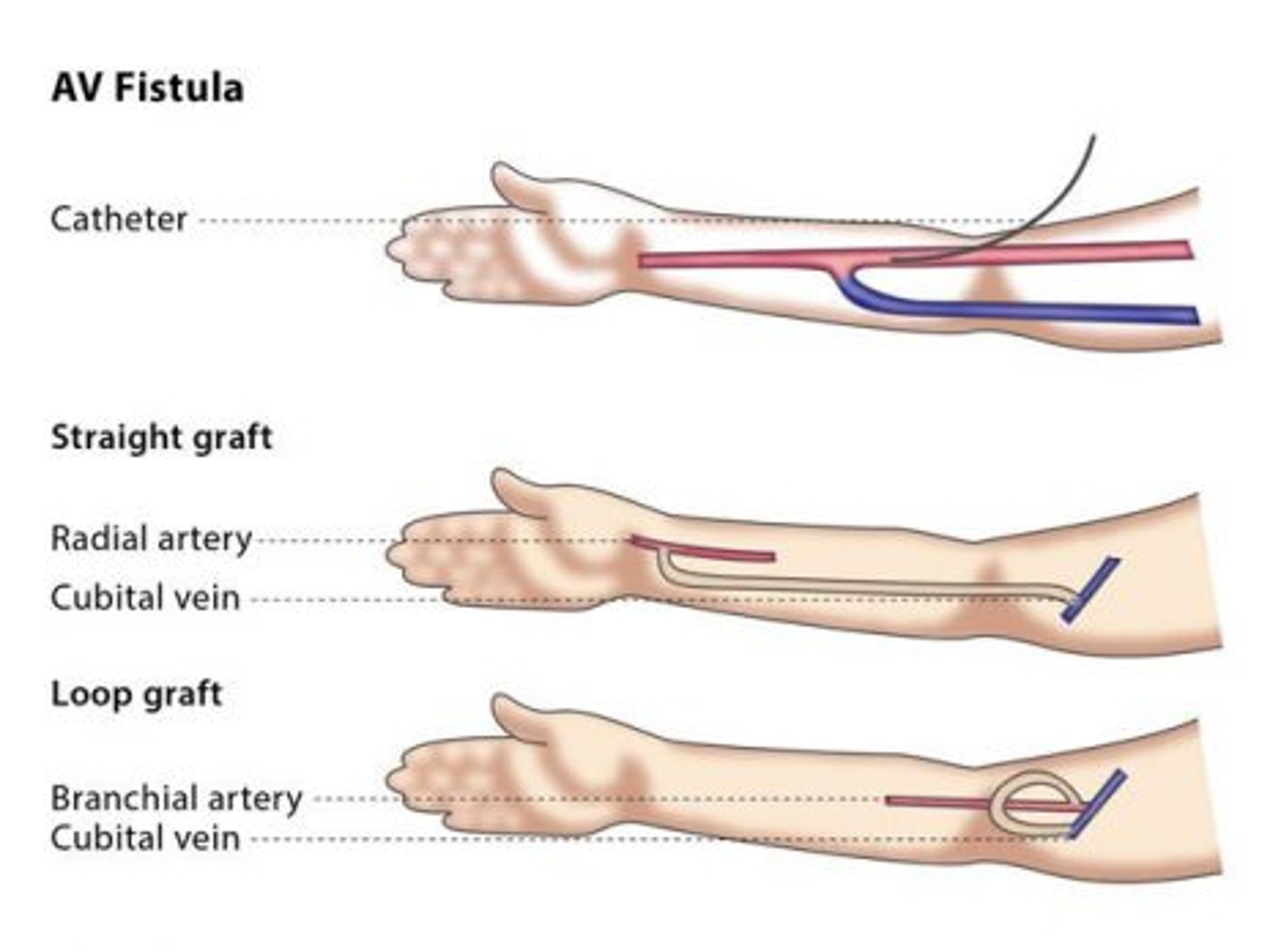
Prosthetic AV graft
interposition of prosthetic material between an artery and a vein; indicated if native AV fistula fails or anatomy does not support its placement; can be used in 2-3 weeks, but has increased risk of complications; mean long-term potency rates up to 2 years
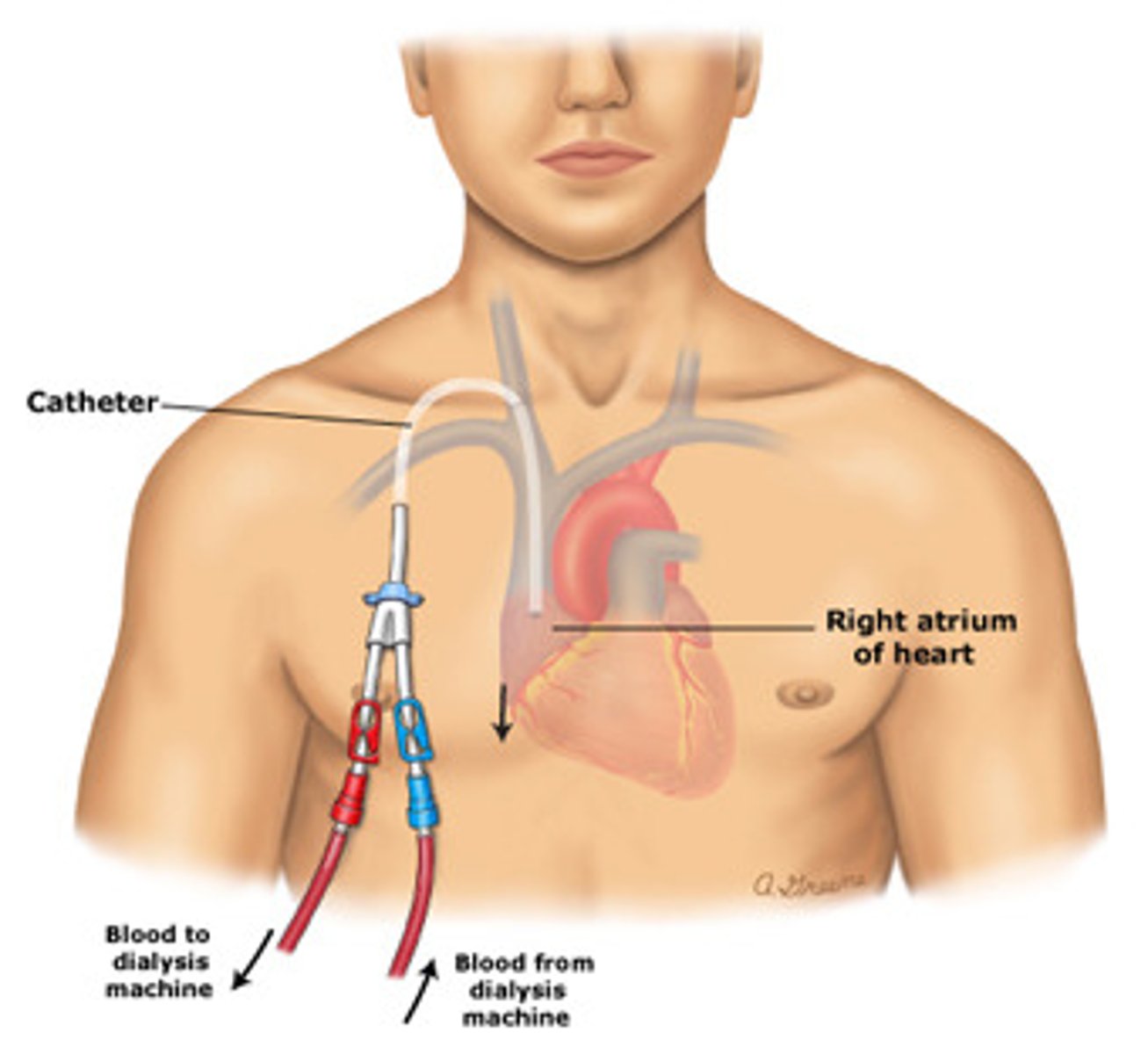
if AV fistulas/AV grafts have failed or emergency dialysis is required (no time for access to mature)
when is a Tunneled dialysis catheter indicated?
stenosis, thrombosis, infection
access sites for dialysis can be complicated by...
BP measurements and blood draws
what should be avoided being done in a patient's "AV fistula arm"
internal jugular vein, IMMEDIATELY!
tunneled catheters are usually placed in the ____________, and they may be used after how much time?
three times weekly, 3-5 hours
dialysis is typically performed _________ weekly, and each session lasts ______.
intradialytic hypotension
what is the #1 complication of dialysis?
due to excess and/or too rapid fluid removal
why does intradialytic hypotension occur?
discontinuing dialysis and providing a IV 0.9 NS fluid bolus
how is intradialytic hypotension managed?
Dry weight
weight following an "ideal" dialysis session (normal BP, no lightheadedness or muscle cramps; no SOB/edema)
to restore the patient to their dry weight over 4 hours
what is the goal of each dialysis session?
high Na concentration in the dialysate
--> indicates fluid overload
what are some contributing factors to intradialytic hypertension?
underlying CAD patients at increased risk
most commonly occurs in elderly diabetics
what are some risk factors for intradialtic dysrhythmias?
lower extremities
muscle cramps associated with dialysis are most severe in the...
bifrontal with associated N/V
decreasing flow rates and acetaminophen
how do headaches associated with dialysis manifest, and what is the treatment?
histamine release and underlying uremia
skin moisturizers and antihistamines
why does pruritus occur with dialysis and how do we manage it?
"Sunday night syndrome"
Hyperkalemia
Florid pulmonary edema
risks of missing dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis
solute and water exchange occurs between the peritoneal cavity and the peritoneal capillaries
continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD)
up to 3 L of dialysate is infused into the peritoneal cavity though a peritoneal catheter; fluid is allowed to "dwell" for 2-4 hours and is infused 3-5 times daily; can also do a nighttime dwell
Continuous cyclic peritoneal dialysis (CCPD)
a machine performs 3-5 exchanges per night while the patient sleep
peritonitis: fever, abdominal pain, cloudy peritoneal fluid
peritoneal dialysis can be complicated by...
renal transplantation
what is the most commonly transplanted organ/tx of choice for CKD?
AIDS
active hepatitis
absolute contraindications to receive a kidney transplant
malignancies, HIV, or hepatitis
--> living or deceased
what are some contraindications for being a kidney donor?
renal arteriogram
what imaging study is done before a kidney transplantation to assess for the likelihood of surgical complications?
right iliac fossa
transplanted kidneys are usually placed in the...
b/c with a transplanted kidney,, there are concerns for rejection, and the only way to test for rejection is a biopsy
--> a biopsy would prove to be quite difficult with a retroperitoneal organ
why are transplanted kidneys placed superficially (not put in retroperitoneum)?
external iliac artery and vein
vascular supply and venous drainage for a transplanted kidney comes from the...
donor ureter is connected to recipient urinary bladder
what other urinary component is transplanted/connected with the kidney?
cellular/humoral Abs
--> recipient's lymphocytes respond to HLA of the donor's kidney
--> Recipient's killer T cells destroy kidney
what is the pathophysiology of organ rejection?
mild increase in the serum creatinine
what is the earliest objective finding with rejection?
Nonspecific "flu-like" symptoms
what is the most common presentation of transplant rejection?
contact transplant center
biopsy for definitive diagnosis
--> be careful when administering meds, so that nothing interacts with anti-rejection meds!
what is requires for the management of a transplant rejection
Patient is immunosuppressed -- cannot mount an immune response
--> fever without obvious cause
why are clinical manifestations of post-transplantation infection blunted?
Hyperplastic parathyroid -- parathyroid is overactive b/c the pt's Ca2+ was binding phosphorus so parathyroid thought the body needed more, but it keeps going even though the primary issue has been resolved.
why is hypercalcemia a common complication of a kidney transplant?
HTN, nephrotoxicity, neurotoxiticy, DM, anemia, thrombocytopenia
what are some common complications secondary to anti-rejection medication