Biology - Unit 4: the life of the cell
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/15
Last updated 10:04 PM on 10/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
1
New cards
cell
simplest collection of matter that is aliv
2
New cards
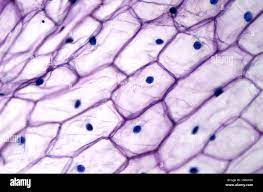
Light Microscope
Light passes through a specimen and then through magnifying lenses
3
New cards
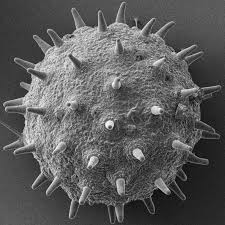
Scanning Electron Microscope
focus a beam of electrons onto the surface of a specimen, providing images that look 3D
4
New cards
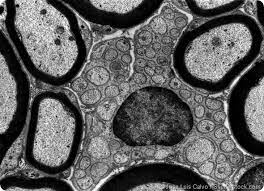
Transmission Electron Microscopes
focus a beam of electrons through a specimen, providing a cross-section of the specimen
5
New cards
prokaryote
No membrane-enclosed nucleus
Circular DNA located in the nucleoid
No membrane-bound organelles
Includes bacteria and archaea
Size: 1 - 5 µm,
Age: 3.5 billion years old
Circular DNA located in the nucleoid
No membrane-bound organelles
Includes bacteria and archaea
Size: 1 - 5 µm,
Age: 3.5 billion years old
6
New cards
Eukaryote
Have a membrane-enclosed nucleus
DNA stored in the nucleus
Has membrane bound-organelles
Includes protista, fungi, animals, and plants
Size: 10 - 100 µm,
age: 1.5 billion years old
DNA stored in the nucleus
Has membrane bound-organelles
Includes protista, fungi, animals, and plants
Size: 10 - 100 µm,
age: 1.5 billion years old
7
New cards
Plant Cells
Has chloroplasts, cell walls, and huge vacuoles
8
New cards
Animal Cells
Have centrioles and lysosomes (some plants may have lysosomes)
9
New cards
Every Cell
has plasma membrane, cytosol, DNA, ribosomes, macromolecules, follow criteria for being alive.
10
New cards
Cell Size is limited by its surface area
exchange occurs at the surface and more surface area=more efficiency therefore more small cells means more efficiency
11
New cards
organelle
a specialized part of a cell; analogous to an organ in the human bod
12
New cards
nucleus
spherical storage of the DNA, manages cell functions, and contains mRNA which makes ribosomes.
13
New cards
Cytosol
gelatin-like fluid that lies inside the cell membrane that contains salts, minerals, and organic molecules and surrounds the organelles
14
New cards
ribosomes
two subunits of mRNA and a protein involved in making proteins.
15
New cards
Endoplasmic Reticulum
system of tubes that move things around the cell
16
New cards
Rough ER
ER but covered in Ribosomes that make and transport proteins.