MGMT 340 - Exam 3
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
What are the 7 theories of leadership?
1. Trait theories
2. Behavioral theories
3. Contingency Theories (Fiedler's & SLT)
4. LMX
5. Charismatic leadership
6. Transactional leadership
7. Transformational leadership
What is Leadership?
Leadership is the ability to influence a group toward the achievement of a vision or set of goals.
Trait theories
- Trait theories of leadership focus on personal qualities and characteristics
- People are born with it
- Help us predict leadership
Two conclusions of trait theories of leadership
1. Traits can predict leadership emergence.
2. This does not necessarily mean the leader is successful at getting the group to achieve its goals.
Behavioral Theories
Behavioral theories of leadership imply we can train people to be leaders.
Found two behaviors that accounted for most leadership behavior:
1. Initiating Structure
2. Consideration
Initiating structure is
the extent to which a leader is likely to define and structure his or her role and those of employees in the search for goal attainment. It includes behavior that attempts to organize work, work relationships, and goals.
Explain leader in high initiating structure
someone who "assigns group members to particular tasks," "expects workers to maintain definite standards of performance," and "emphasizes the meeting of deadlines."
Consideration is
the extent to which a person's job relationships are characterized by mutual trust, respect for employees' ideas, and regard for their feelings.
Explain leader in high consideration structure
A leader high in consideration helps employees with personal problems, is friendly and approachable, treats all employees as equals, and expresses appreciation and support.
_______ & ________ positively affect employee motivation and unit performance
1. Initiating structure
2. Consideration
Fiedler contingency model
Effective group performance depends upon the proper match between the leader's style and the degree to which the situation gives control to the leader.
least preferred coworker (LPC) questionnaire
to measure whether a person is task- or relationship-oriented
3 situational factors of Fiedler's Contingency Theory
1. Leader-member relations
2. Task structure
3. Position power
Leader-member relations
the degree of confidence, trust, and respect members have in their leader.
Task structure
the degree to which the job assignments are procedural
Position power
the degree of influence a leader has over power variables such as hiring, firing, discipline, promotions, and salary increases
Situational leadership theory (SLT):
a contingency theory that focuses on the followers' readiness
How is successful leader achieved?
by selecting the right leadership style, which is contingent on the level of the followers' readiness ("the extent to which people have the ability and willingness to accomplish a specific task.").
Situational Leadership Curve
S1: Directing
S2: Coaching
S3: Supporting
S4: Delegating
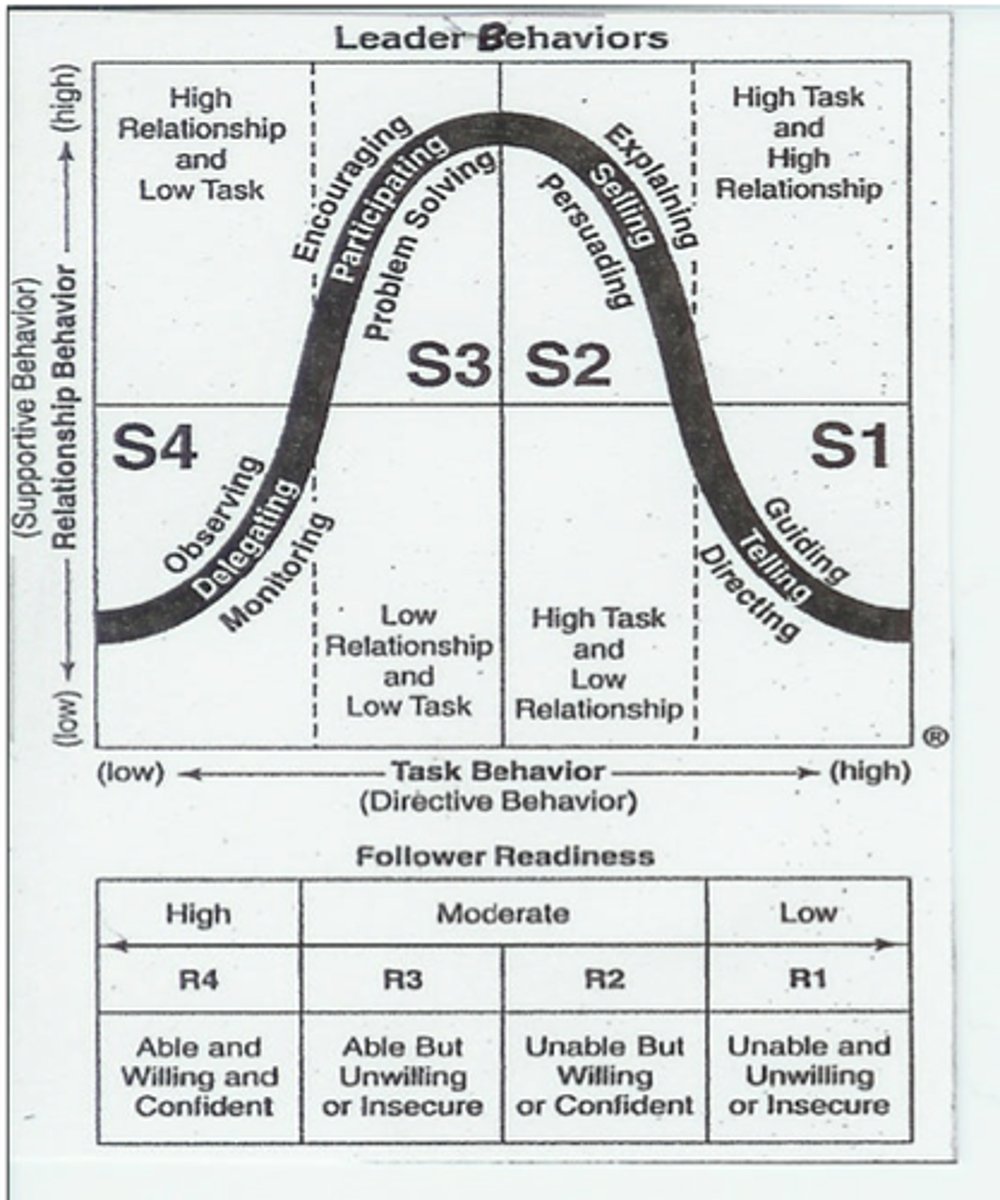
S1: Directing
high directive, low supportive
Guiding & direct; provide instructions
S2: Coaching
High Direct/High support
Explaining
S3: Supporting
High support/ low directing
Encouraging; it's for people who have skills but lack confidence
S4: Delegating
Low supportive/
Low directing
For people who have skills and are confident
Readiness of Followers
R1: unable and insecure
R2: unable but confident
R3: able but insecure
R4: able & confident
Jamie who just joined CSUF know how to teach MGMT340 course because she already taught the course in other universities and she's pretty excited and ready to start the semester. What would be the best way to lead her if you are the dept chair of the management?
S4: delegating
R1 & R2 represents ________ directed
Leadership
R3 & R4 represents _________ directed
Individual
LMX (Leader-member exchange)
argues that because of time pressures, leaders establish an unique relationship with each follower
Key characteristics of charismatic leadership
1. Vision & articulation
2. Personal risk
3. Sensitivity to follower needs
4. UNconventional behavior
Explain vision & articulation
has a vision and proposed a better future
EX. Martin Luther King
Personal risk
willing to take on high personal risk
EX. Elon Musk
Sensitivity to follower needs
Perceptive to others' abilities & responsive to their needs
Unconventional behavior
Engages in behaviors that are perceived as novel & counter to norms
Are Charismatic Leaders Born or Made?
- Some individuals are born with charismatic traits, others are trained to exhibit charismatic behaviors
-- Develop the aura of charisma.
-- Create a bond that inspires others to follow
-- Bring out the potential in followers by tapping into their emotions
Does Effective Charismatic Leadership Depend on the Situation?
•People are especially receptive when they sense a crisis, when they are under stress, or when they fear for their lives.
The Dark Side of Charismatic Leadership
•Many leaders don't necessarily act in the best interest of their companies.
•Many have allowed their personal goals to override the goals of the organization.
•Individuals who are narcissistic are also higher in some behaviors associated with charismatic leadership.
•Transactional leadership composed of:
1. Contingent reward
2. Active - management by exception
3. Passive - management by exception
Laissez-Faire
Hands off leadership
Transactional leadership: Passive - management by exception
Leader waits for mistakes, then corrects them
Transactional leadership: Active - management by exception
Leader monitors for mistakes, then corrects them
Transactional leadership: Contingent reward
Leader attains follower agreement on what needs to be done, and gives promised or actual rewards in return for adequate performance
Transformational leadership
Inspire followers to transcend their own self-interests for the good of the organization
Four dimensions of Transformational leadership
1. Idealized influence "Charisma"
2. Inspirational motivation
3. Intellectual stimulation
4. Individualized consideration (coaching)
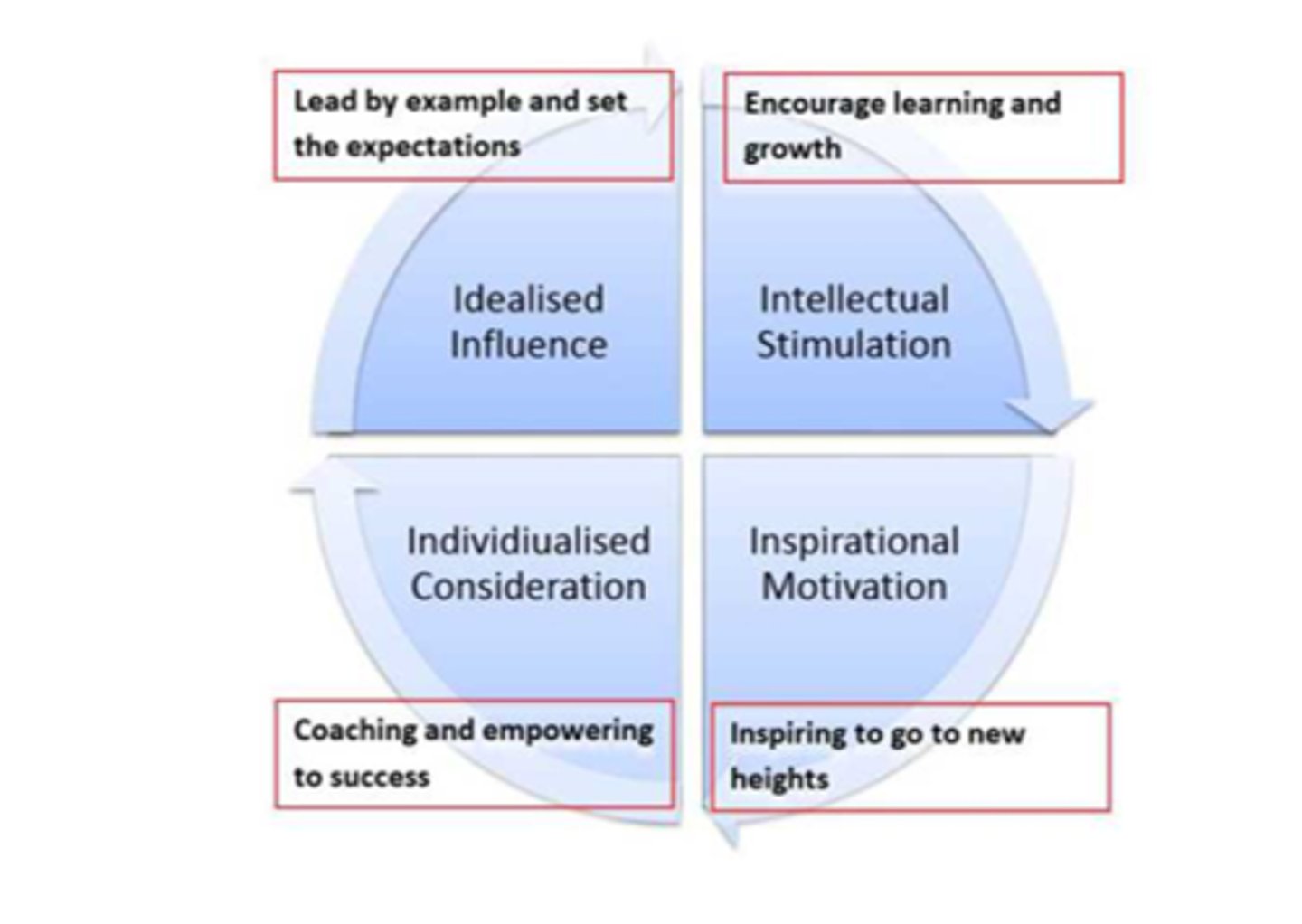
Idealized influence "Charisma"
Provide vision and sense of mission, instills pride, gains respect and trust.
Inspirational motivation
Communicate high expectations, uses symbols to focus efforts, expresses important purposes in simple ways
Intellectual stimulation
Promotes intelligence, rationality, and careful problem solving
Individualized consideration (coaching)
Gives personal attention, treats each employee individually, coaches, advises.
Why is transformational leadership is important?
more strongly correlated with lower turnover rates, higher productivity, lower employee stress and burnout, and higher employee satisfaction.
Compare and contrast transformational & charismatic leadership
- Charismatic leadership places more emphasis on the way leaders communicate - are they passionate and dynamic?
- Transformational leadership focuses more on what they are communicating - is it a compelling vision?
- Both focus on the leader's ability to inspire followers.
Trust Propensity (disposition-based trust)
A general expectation that the words, promises, and statements of individuals and groups can be relied upon
Trustworthiness
- Cognition-based trust
- Involving ability, benevolence, integrity
-
Affect based trust
feelings toward trustee
Ability
skills, competencies, and areas of expertise that the individual possesses.
Benevolence
the degree to which an authority wants to do good for the trustor, the desire to do nice things.
Integrity
the degree to which an authority adheres to a set of values and principles that the trustor finds acceptable. Honesty and truthfulness
Affect-based trust
Emotional - it is based on the feelings we have for people, not rational evaluations of their trustworthiness
Trust affects what?
1. Risk taking
2. Info sharing
3. Group affectiveness
4. Productivity
Power
- Influence the behavior of others and resist unwanted influence
- Most important aspect of power is that it is a function of dependence.
- A person can have power over you only if he or she controls something you desire.
- Does not require goal compatibility, merely dependence.
How does leadership different from power?
•Leaders use power as a means of attaining group goals [Leader's goal = subordinates' goal (Goal compatibility]
Example
Leader [Goal = increasing the sales records of the branch]
Subordinates ( Goal = increasing the sales)
What are the two groups of power?
Organization (formal) power & personal power
Formal power
- based on an individual's position in an organization
three types of formal power
1. Coercive
2. Reward
3. Legitimate
Coercive power
The ability of a manager to punish others
Reward power
the ability of a manager to give or withhold tangible and intangible rewards others want
Legitimate power
- Position Power
Personal power
Comes from the person themselves
Personal power consists of
expert power & referent power
Expert power
Derived from the person's expertise, skill, or knowledge
referent power
Exists when others have a desire to identify and be associated with a person
Influence is
The use of an actual behavior that causes behavioral or attitudinal changes in others
Directions of Influence
•Downward (managers influencing employees)
•Lateral (peers influencing peers)
•Upward (employees influencing managers)
Most effective influence (or Power) Tactics
•Rational persuasion: presenting logical arguments and factual evidence to demonstrate a request is reasonable.
•inspirational appeals: developing emotional commitment by appealing to a target's values, needs, hopes, and aspirations.
•consultation: increasing the target's support by involving him or her in deciding how you will accomplish your plan.
•collaboration: Making it easier for the target to complete the request
Moderately effective influence (or power) tactics
•exchange: rewarding the target with benefits or favors in exchange for following a request.
•personal appeals: asking for compliance based on friendship or loyalty.
•ingratiation: using flattery, praise, or friendly behavior prior to making a request.
•apprising: When the requestor clearly explains why performing the request will benefit the target personally
Least effective influence (or power) tactics
•pressure: using warnings, repeated demands, and threats.
•coalitions: enlisting the aid or support of others to persuade the target to agree.
Which influence tactic is this?
we really don't know how to prepare the exam 3 effectively, could you please let us know.. How to...?
Consultation
Which influence tactic is this?
Research found that students tend to increase 10% their exam score when they have a study partner! Would you help me?
Rational Persuasion
Which influence tactic is this?
We could complete the exam 3 summary sheet easily and quickly if you join our study group
Collaboration
Which influence tactic is this?
Helping me to complete this study guide summary will SAVE MY LIFE!!
Inspirational Appeal
Which influence tactic is this?
Can you show me your exam 3 summary? You know what? It is actually beneficial for you because I can double check if you made any mistakes when I study
Apprising
Which influence tactic is this?
You are the smartest person among our team members. I need your help! Could you show me your exam 3 summary?
Ingratiation
Which influence tactic is this?
Can you show me your exam 3 summary? Dude! You are my friend!
Personal Appeals
Which influence tactic is this?
If you are not helping me out, I'm going to give you zero point when we do a peer-review
Pressure
Which influence tactic is this?
Jason, Arielle and Josh all agreed to work on-line only, you should agree with this method
Coalitions
What would be the effective tactics?
1. Upward influence - rational persuasion
2. Downward influence - inspirational appeals
3. Lateral influece - personal appeals & coalitions
Political behavior
activities that are not required as part of one's formal role in the organization, but that influence the distribution of advantages within the organization.
What are some political behaviors?
•withholding information,
•whistle-blowing,
•spreading rumors,
•leaking confidential information.
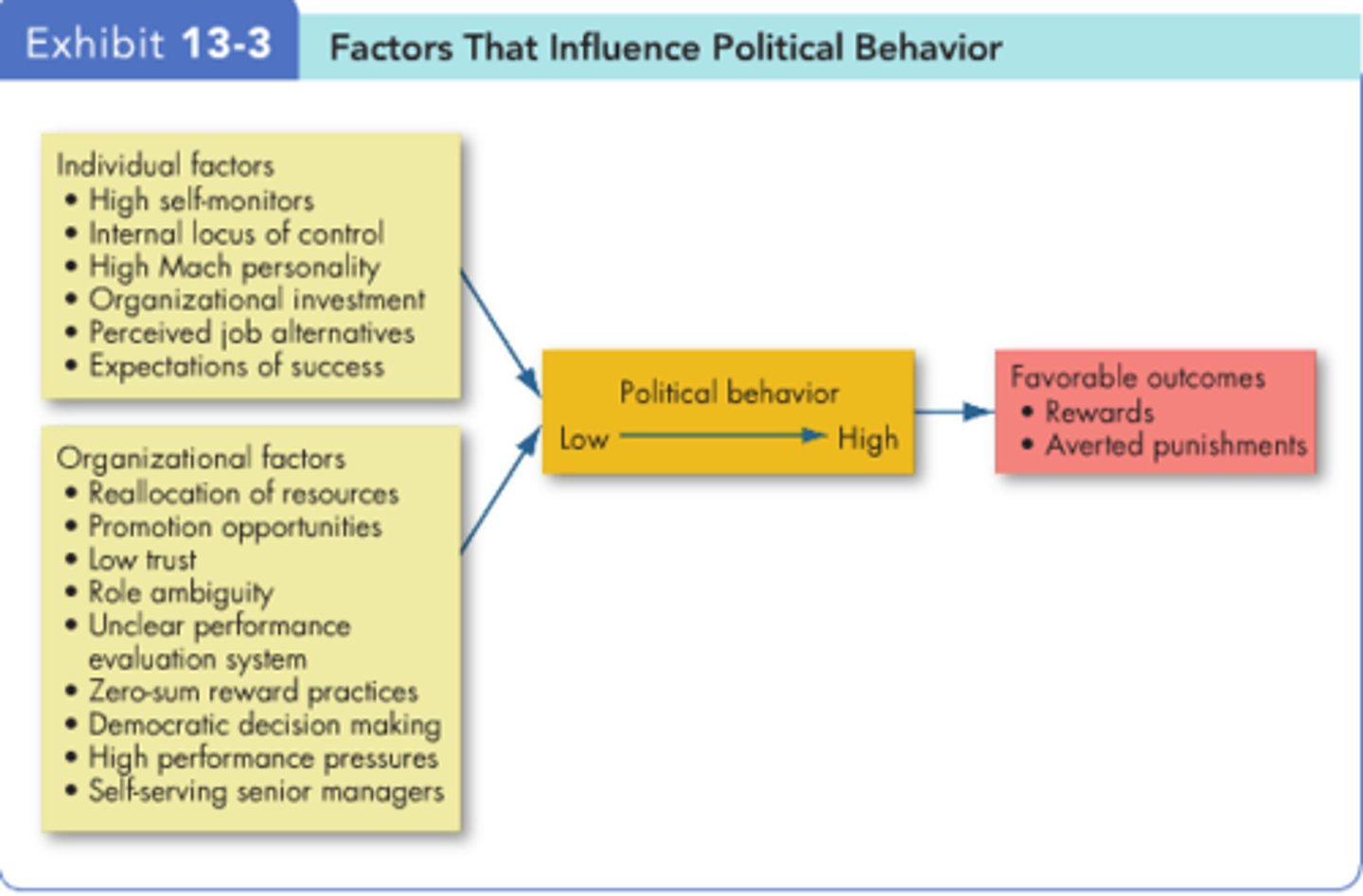
Factors that influence political behavior
individual and organizational
Employee responses to organizational politics
decreased job satisfaction, increased anxiety and stress, increased turnover, reduced performance
Impression management (IM):
-The process by which individuals attempt to control the impression others form of them.
Think about reality vs. expectations
What is Conflict?
•a process that begins when one party perceives that another party has negatively affected, or is about to negatively affect, something that the first party cares about.
•
•Functional conflict
•That supports the goals of the group and improves its performance.
•Dysfunctional conflict
•that hinder group performance
Three Types of Conflict
task
relationship
Process
•Task Conflict
•relates to the content and goals of the work.
•Relationship conflict
•focuses on interpersonal relationships.
•Always dysfunctional
•Most psychologically exhausting to individuals
•Process Conflict
•is about how the work gets done.
What type of conflict is this?
I feel so bad when Sharron (team member) always be a straight shooter. It just hurt my feeling and I don't understand her personality. I really don't want to work with her
Relationship conflict
What type of conflict is this?
While I think our team needs to complete the project in person to practice the presentation, Tom (team member) wants to complete the work just online using a google document. I think this is very inefficient!
Process conflict
What type of conflict is this?
I want to work on google's motivation as the topic of the final project, but my team member wants to work on Disney culture as the topic! Hum.... I don't think we can make the best outcome with that topic though..
Task conflict