BIOL 204 Exam 1 lecture 3
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Does the enterogastric reflex stimulate or inhibit gastric acid secretion
Inhibit
Does CCK stimulate or inhibit gastric acid secretion
inhibit
Does secretin stimulate or inhibit gastric acid secretion
inhibit
Does lower pH stimulate or inhibit gastric acid secretion
inhibit
Does acetylcholine stimulate or inhibit gastric acid secretion
stimulate
Does increased pH stimulate or inhibit gastric acid secretion
stimulate
Does food stretching stomach walls stimulate or inhibit gastric acid secretion
stimulate
Does histamine stimulate or inhibit gastric acid secretion
stimulate
Does sight taste, or smell of food stimulate or inhibit gastric acid secretion
stimulate
Does gastrin stimulate or inhibit gastric acid secretion
stimulate
What happens when food arrives in the duodenum from the stomach
Chemoreceptors detect lower change in PH and chemical composition of food
Stimulate the release of CCK and secretin
CCL and secretin act on the stomach liver, gallbladder and pancreas
CCK and secretin effect on stomach
slow acid production and movement
after food arrives in duodenum
Secretin effect on liver
secretion of bicarbonate and water by cholangiocytes
CCK affect on gallbladder
increases the secretion of bile through contraction
CCK effect on pancreas
more enzyme secretion by acinar cells
CCK and secretin at the level of liver and gallbladder
CCK acts on the gallbladder to release bile
secretin in cholangiocyte stimulates secretion of bicarbonate
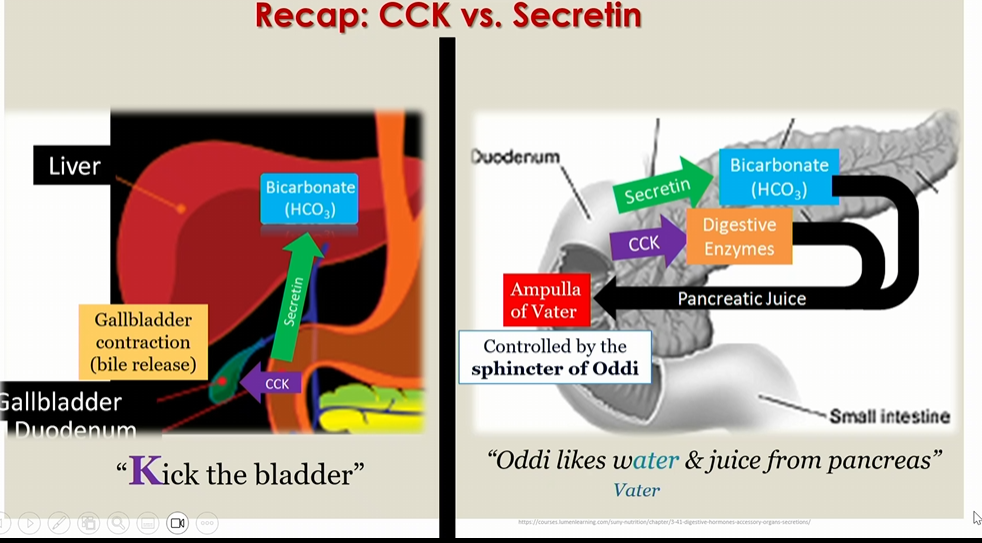
CCK and secretin at the level of the gallbladder
Secretin stimulates bicarbonate
CCK stimulates the release of digestive enzymes
All go into the ampulla of vater
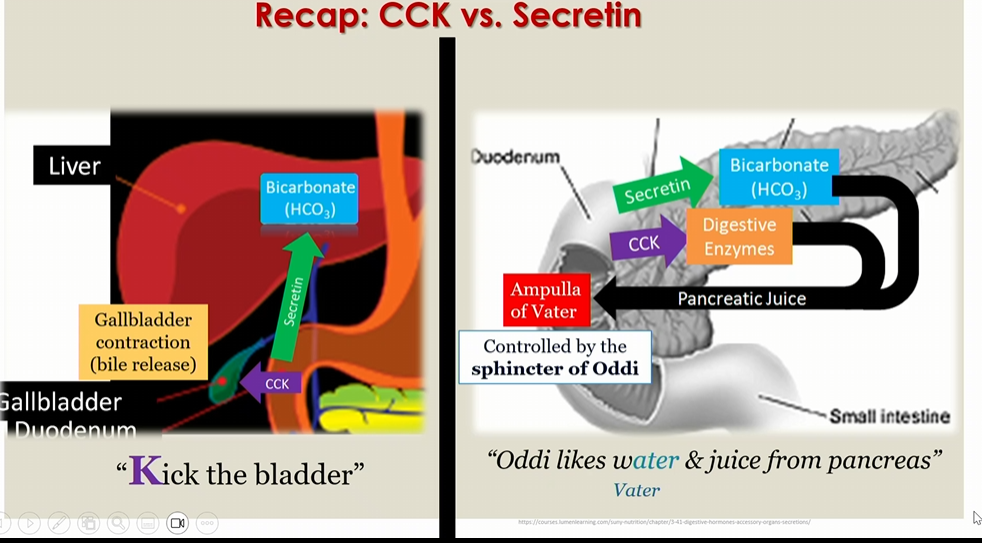
Ampulla of vater
storage area of pancreatic juice, controlled by sphincter of oddi
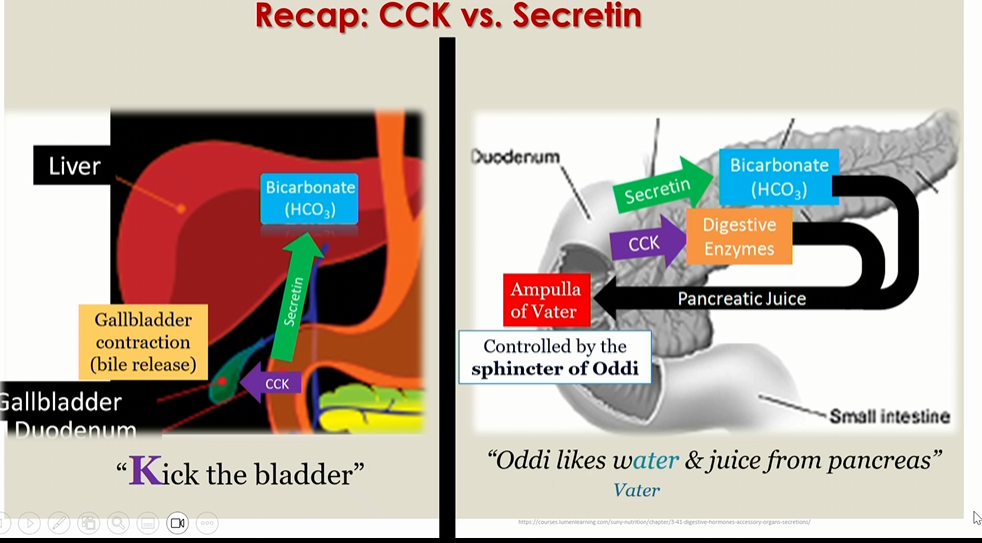
Sphincter of oddi
Controls secretion of Ampulla of vater
Pyloric sphincter
separates the stomach from the duodenum
regulates the passage of chyme
What controls the flow from the ileum into the large intestine
Ileocecal valve
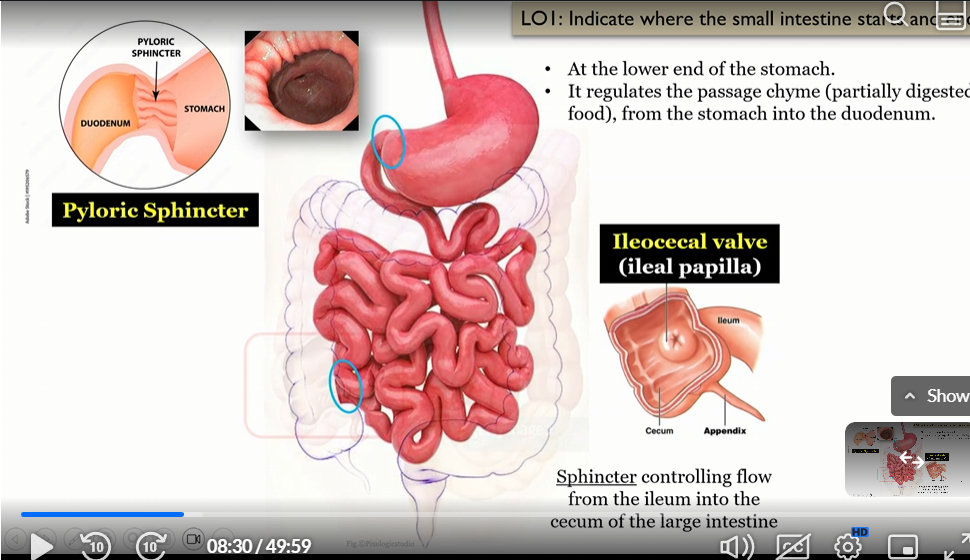
Ileocecal valve
ileal papila
sphincter controlling flow from the ileum into the cecum of the large intestine
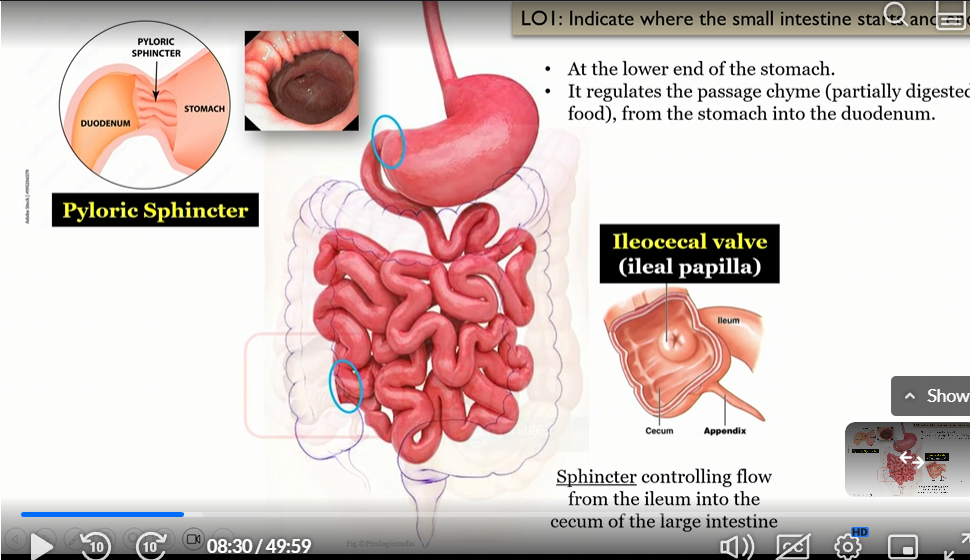
is the Ileocecal valve a true sphincter
false
Duodenum location
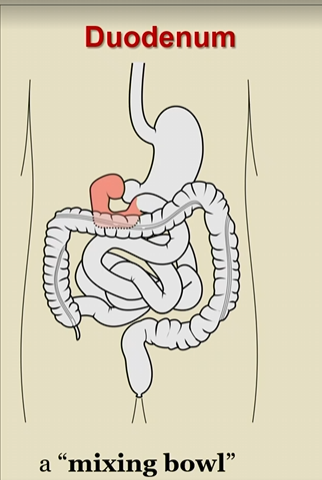
Duodenum function
Neutralizes chyme from stomach
uses duodenal glands
which secretes bicarbonate and intestinal juice

Duodenal glands
in duodenum
secrete bicarbonate and intestinal juice

Pancreatic juice in duodenum makeup
bicarbonate and digestive enzymes

bile in duodenum makeup
bicarbonate and bile salts

Pancreatic juice in duodenum makeup
bicarbonate and digestive enzymes

where Duodenal glands
in the duodenum, neutralize chyme Duodenal glands

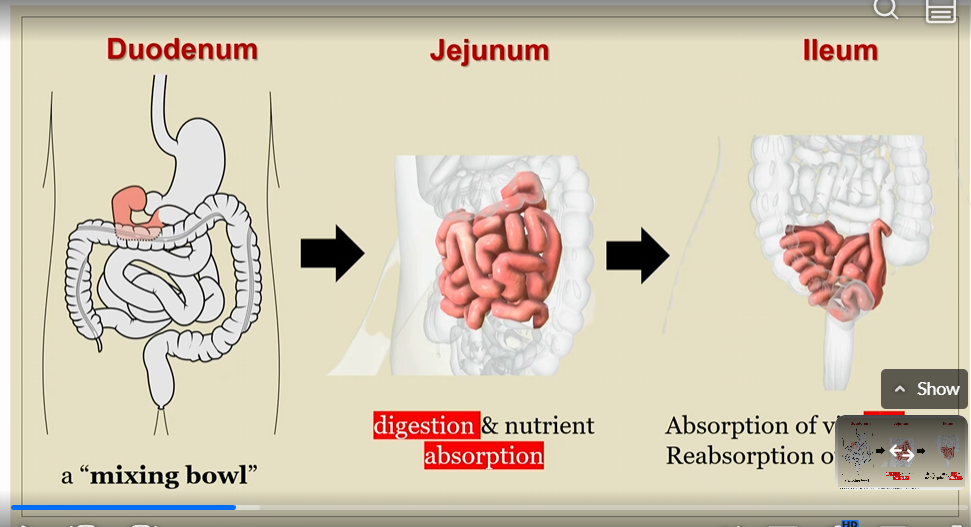
Jejunum
in small intestine
digestion and nutrient absorption
ileum
absorption of vit B12 and reabsorption of bile salts
Order of small intestine
Duodenum, jejunum, ileum
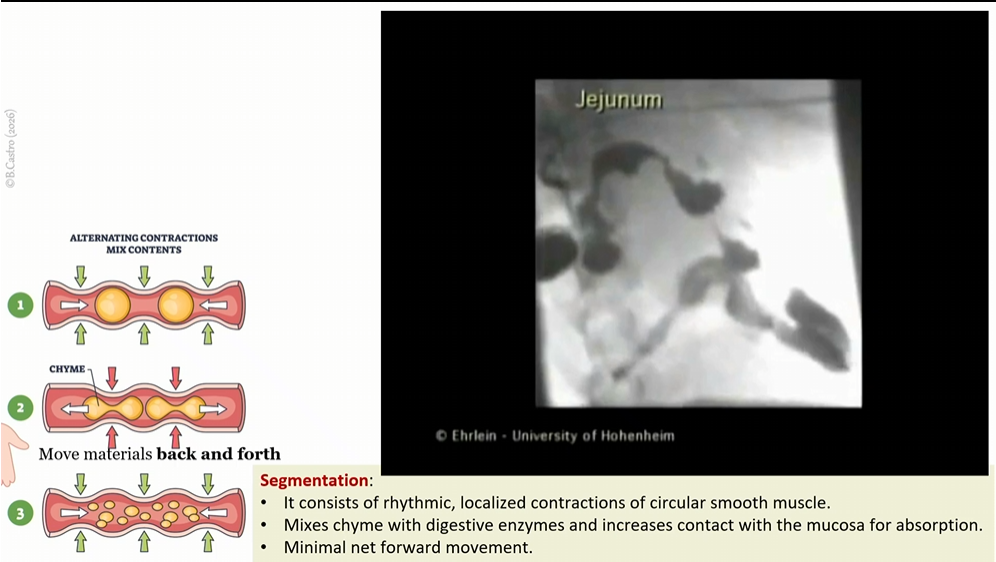
Segmentation
in small intestine, rhythmic contractions of circular smooth muscle
mixes chyme with digestive enzymes and increases contact with mucosa for absorption.
minimal net forward movement
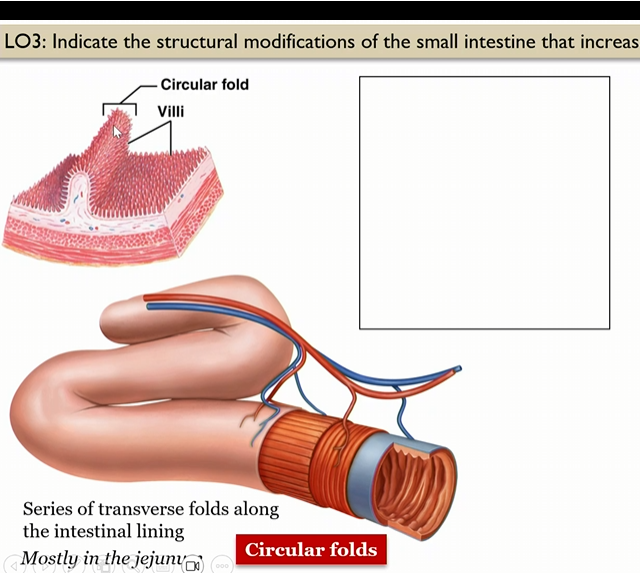
Where are circular folds mainly at
in the jejunum
Brush border
collection of villi on the surface of each enterocyte
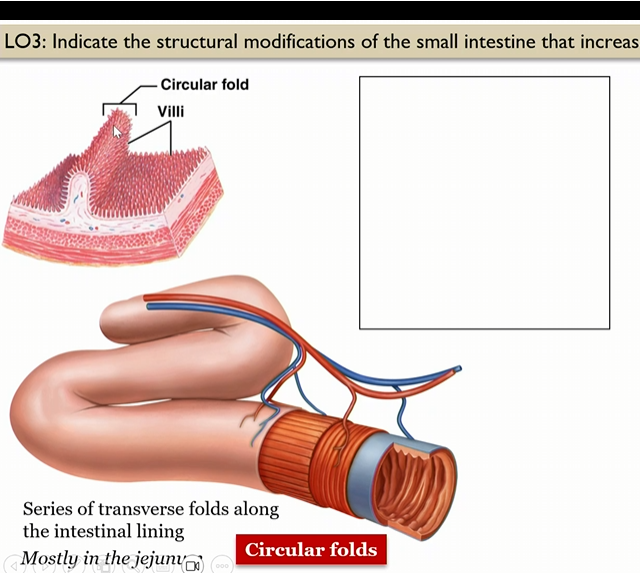
Circular folds
series of transverse folds along the intestinal lining, mosty in jejunum
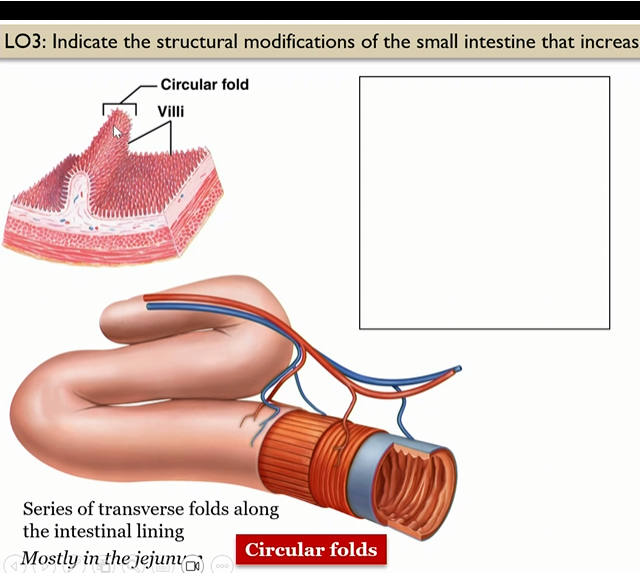
Villi
in small intestine, in the circular folds, mostly in jejunum
form a brush border on surface of each enterocyte
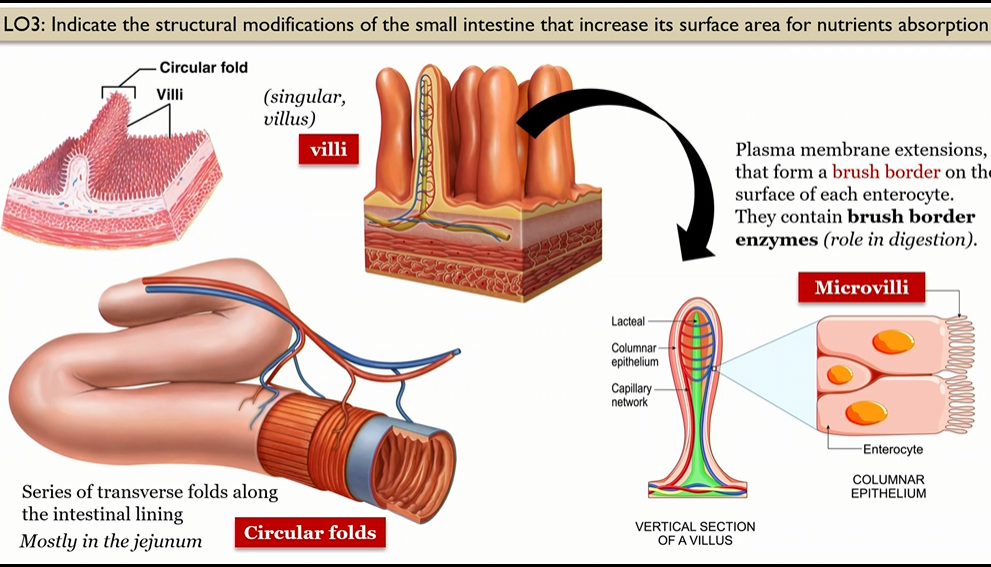
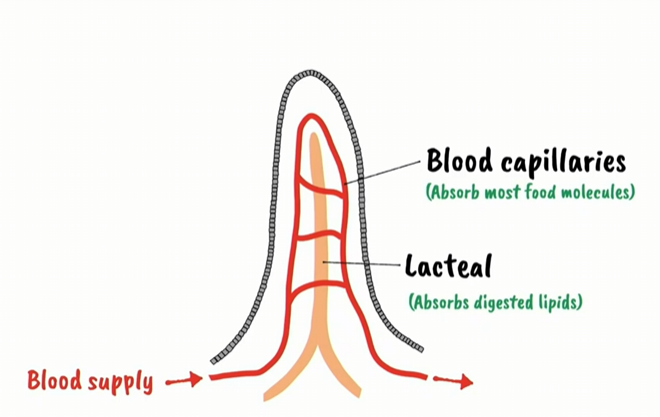
villi cross section
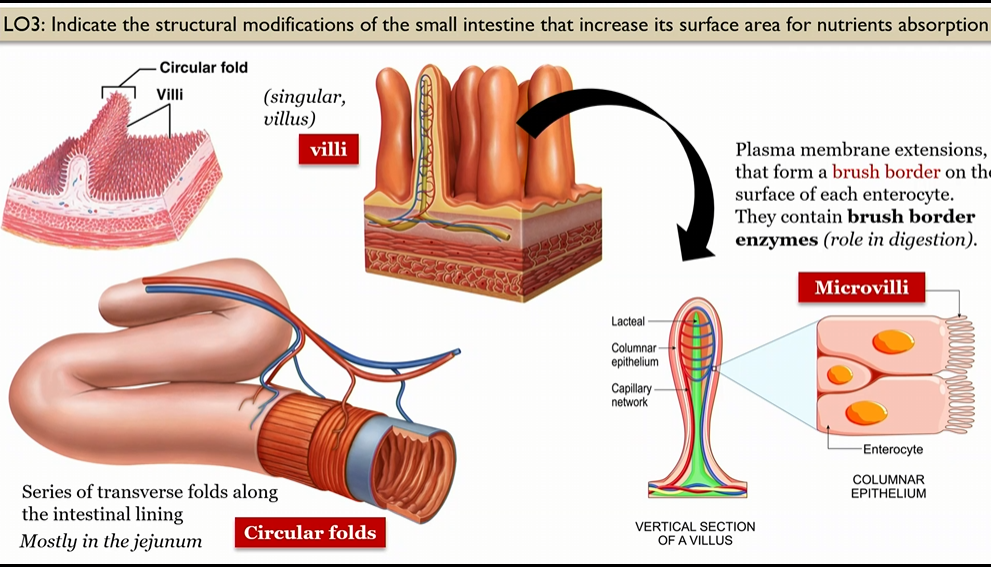
blood capillaries in villi
absorb most food molecules
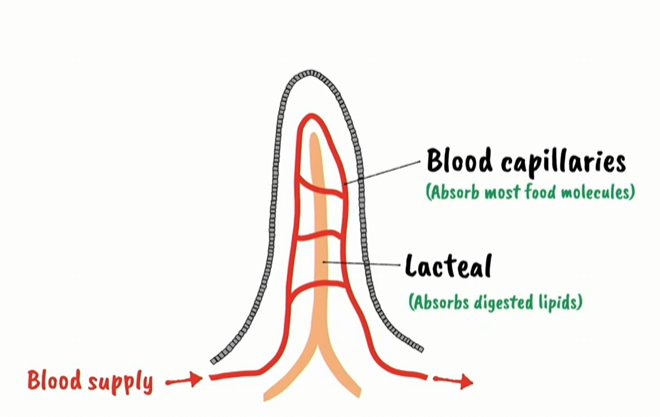
lacteal in villi
absorb digested villi
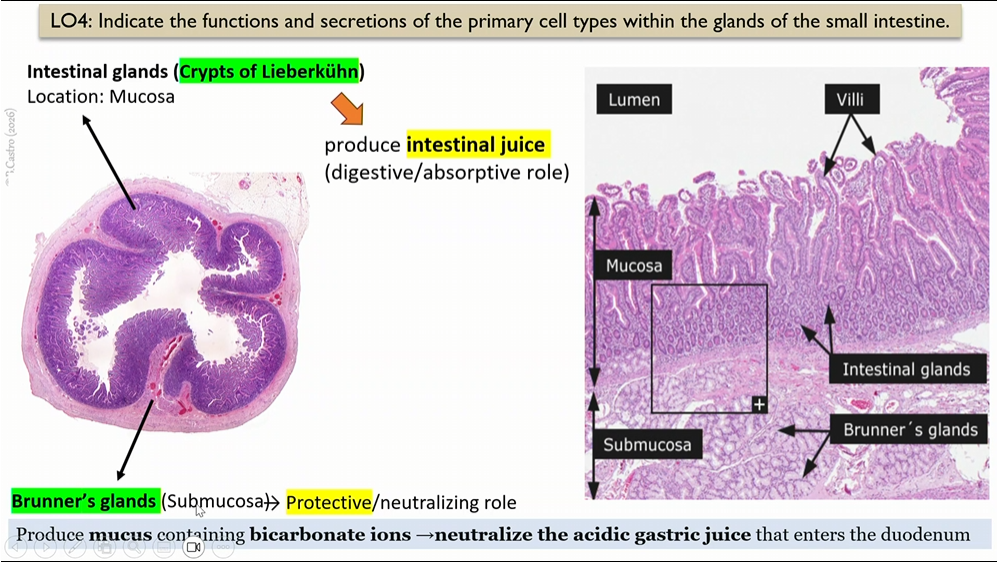
Brunners glands
intestinal glands
submocosa that serve as a protective role
produce mucus that have bicarbonate ions, neutralize the acidic gastric juice that enters the duodenum
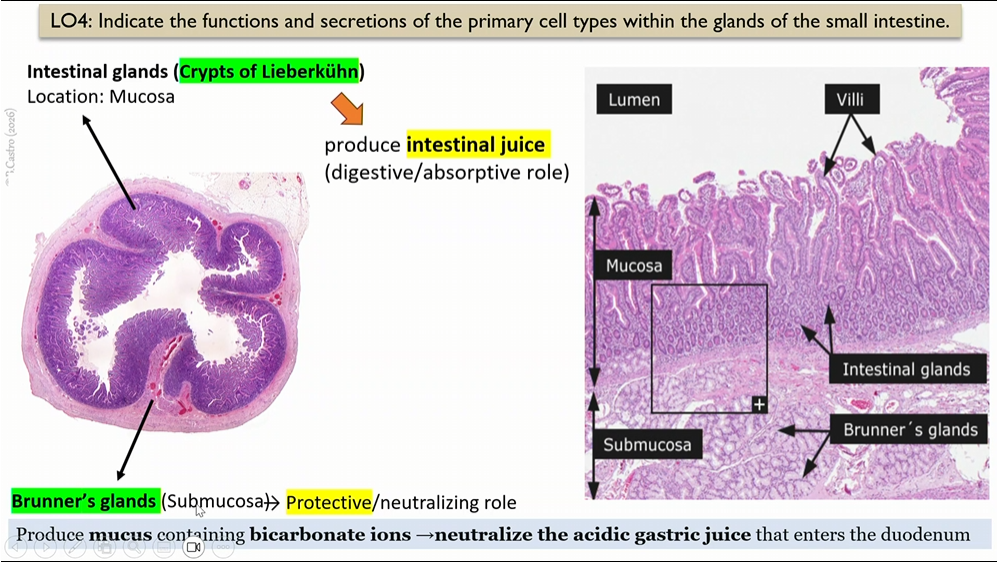
Crypts of lieberkuhn
produce intestinal juice (DIGESTIVE/ASORPTIVE ROLE)
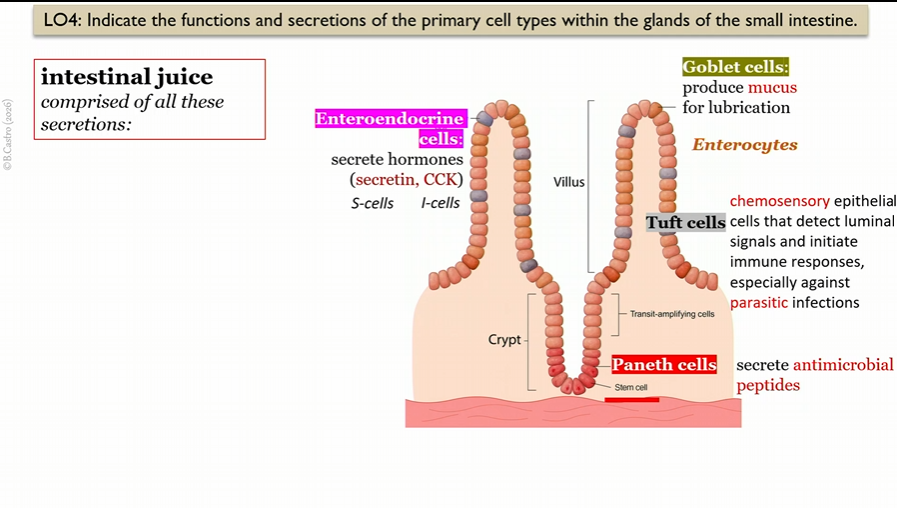
intestinal juice secretions
secretin, CCK, mucus, antimicrobial peptides
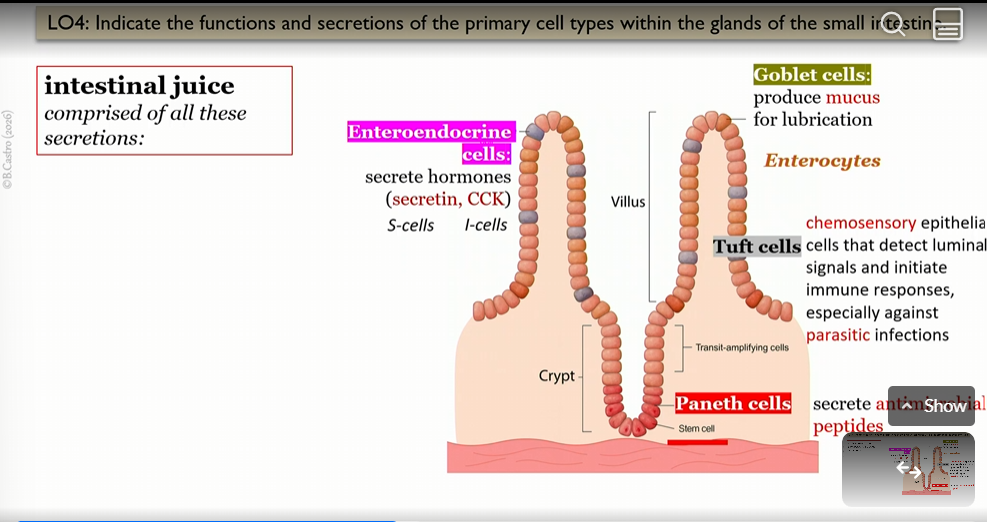
Enteroendocrine cells
in villi in small intestine, create intestinal juice
secrete hormones
(secretin, CCK)
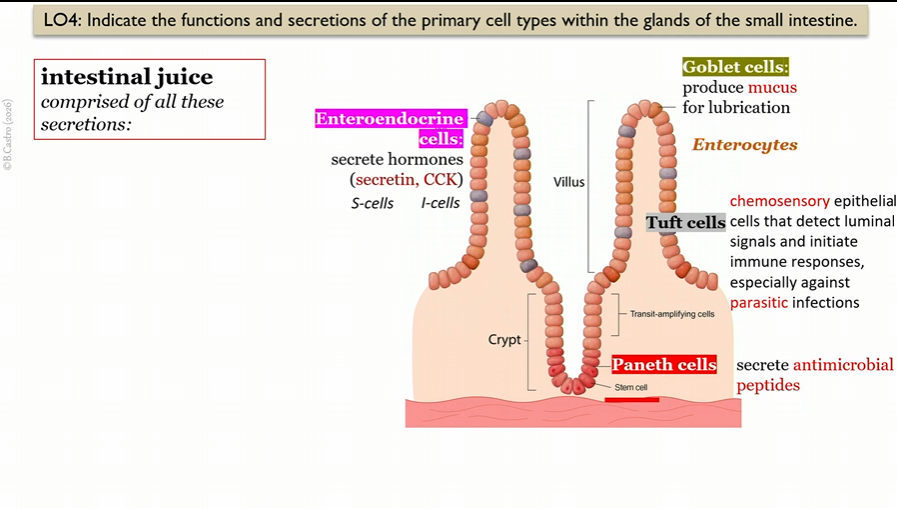
S cells
Type of Enteroendocrine cell that create Secretin
in villi in small intestine
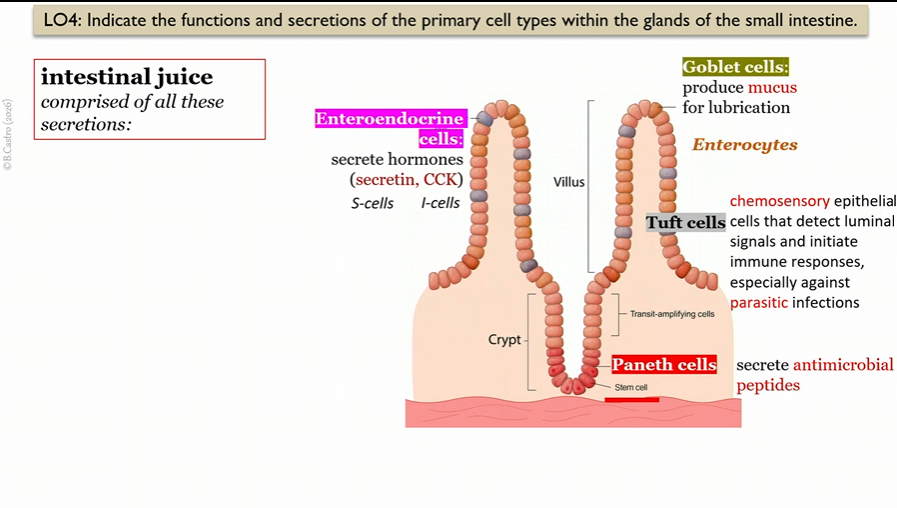
I cells
Type of Enteroendocrine cell that create Secretin
in villi in small intestine
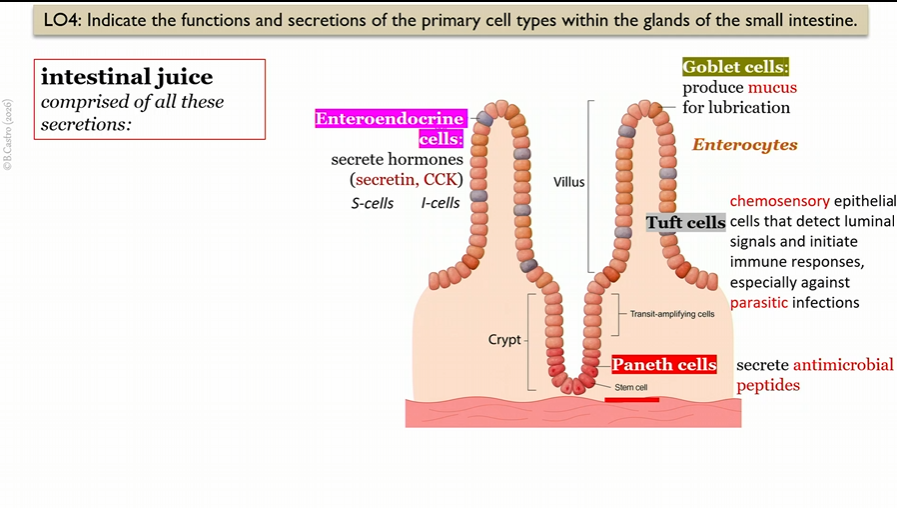
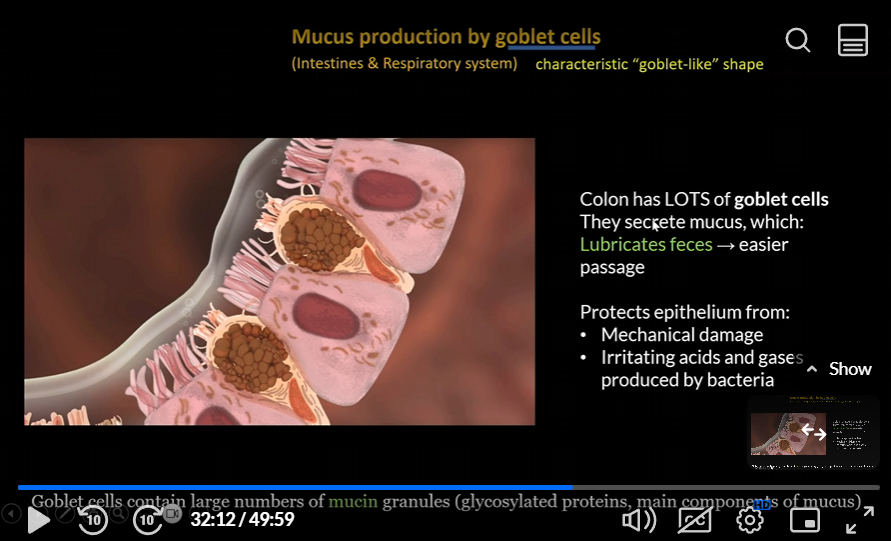
Goblet cells
in villi in small intestine, create intestinal juice
secrete mucus for lubrication
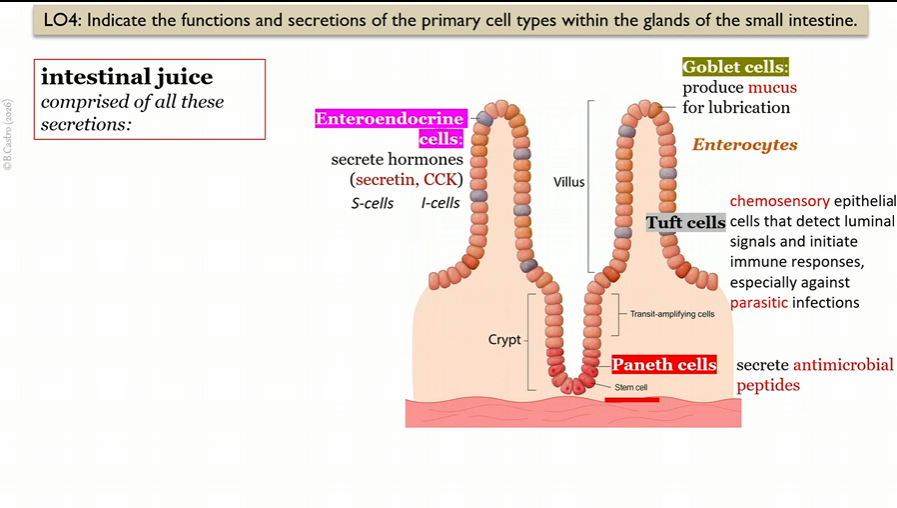
Tuft cells
in villi in small intestine
chemosensory epithelial cells that detect luminal signals and initiate immune responses, especially parasitic infections
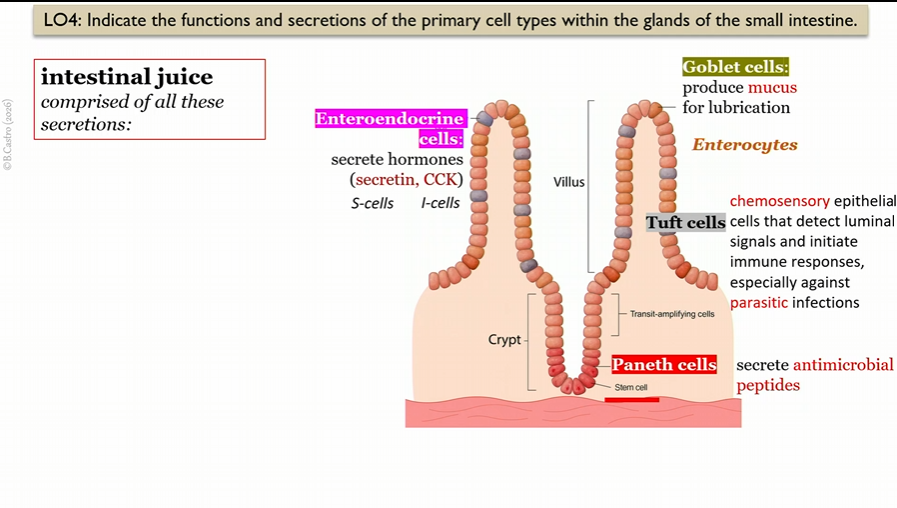
Paneth cells
in villi in small intestine, create intestinal juice
secrete antimicrobial peptides
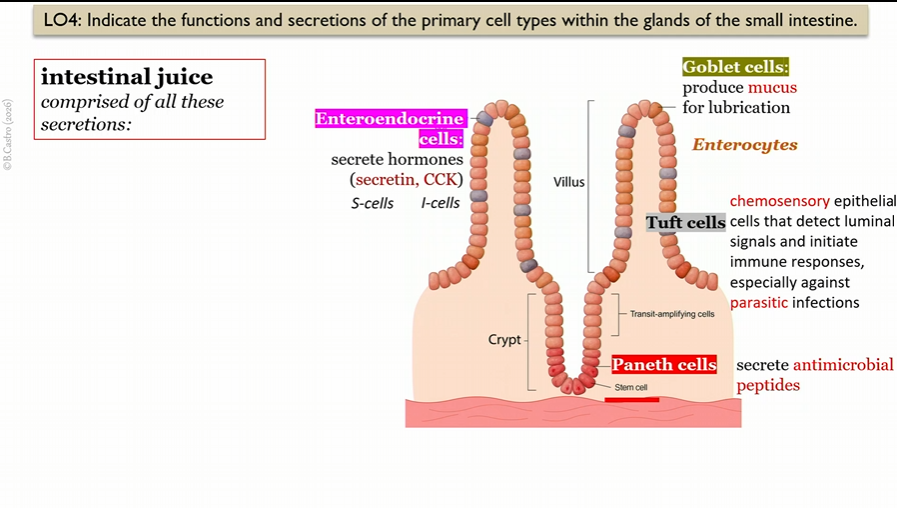
Villi anatomy
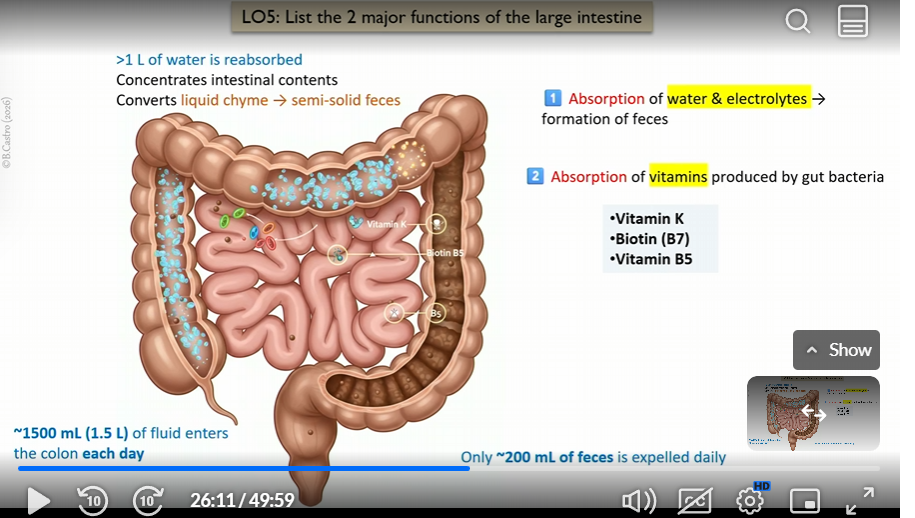
2 Major functions of large intestines
absorption of water and electrolytes ( formation of feces)
absorption of vitamins produced by gut bacteria
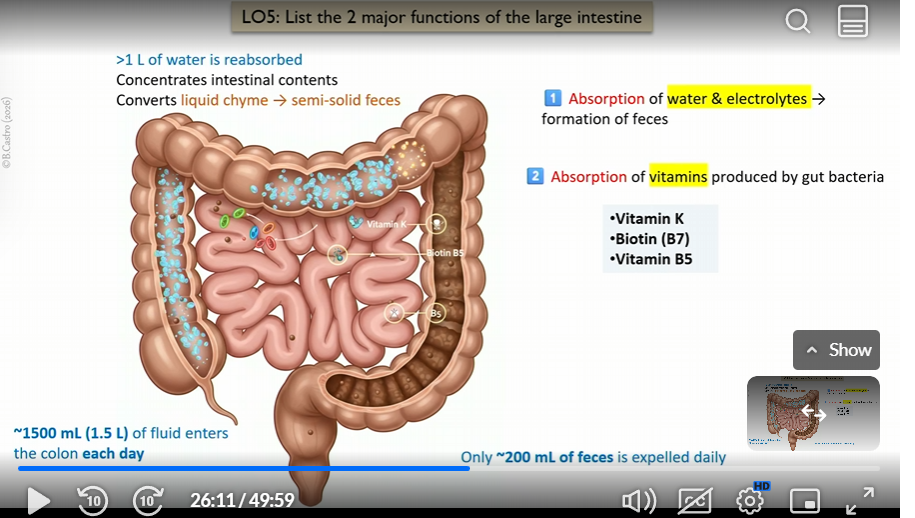
Vitamins that the large intestines absorbs
K B7(biotin) B5
What is movement in the large intestine done by?
smooth muscle
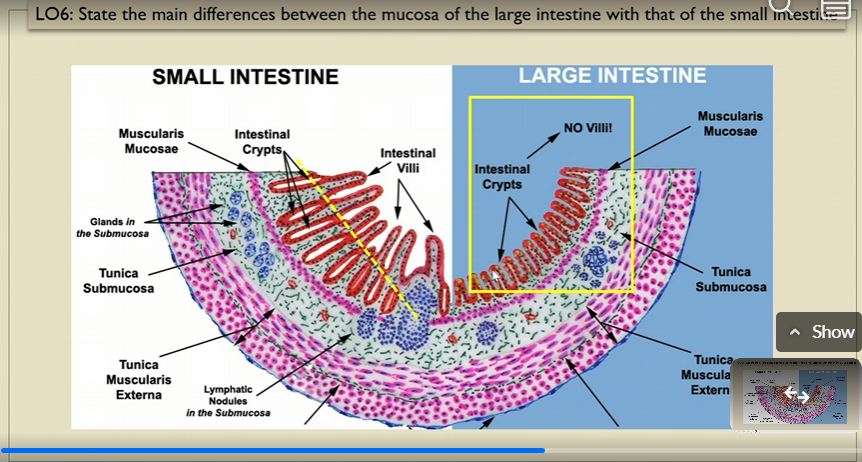
Does the muscosa of the large intestine have villi?
no
colon mucus
lots of goblet cells in the colon, which lubricates feces, leading to easier passage
protects epithelium from mechanical damage
irritating acids and gases produced by bacteria
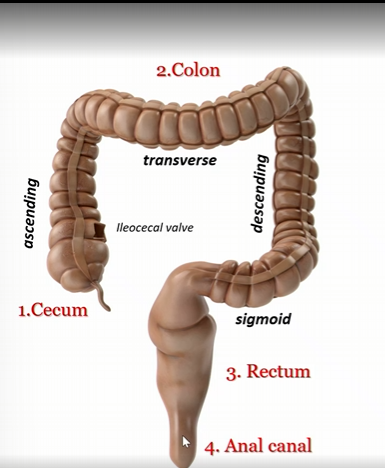
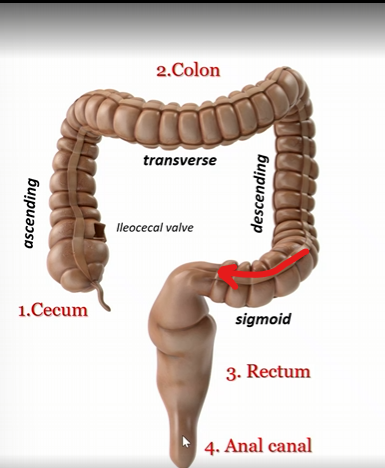
Cecum
first part of large intestines
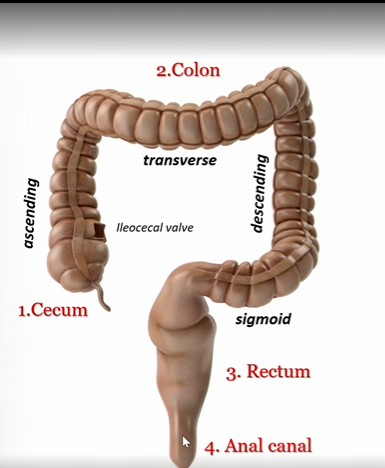
colon
second part of large intestine
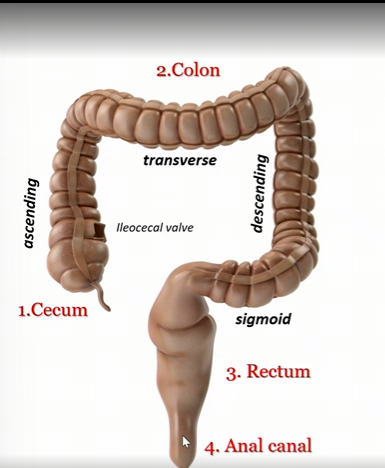
rectum
third part of large intestine
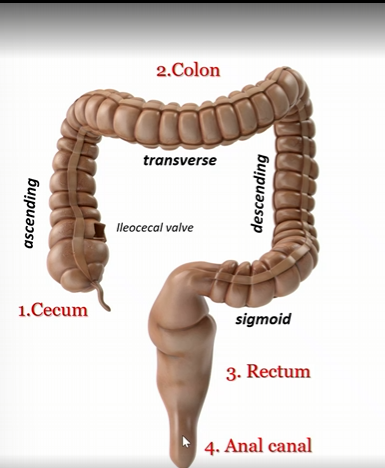
anal canal
fourth part of large intestine
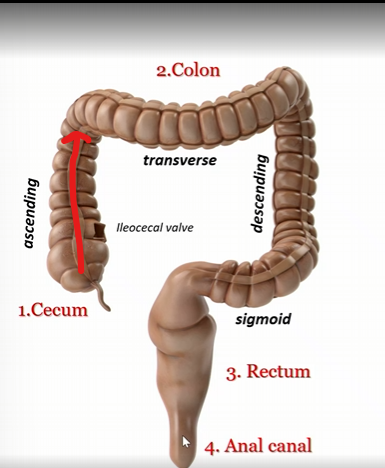
Ascending colon
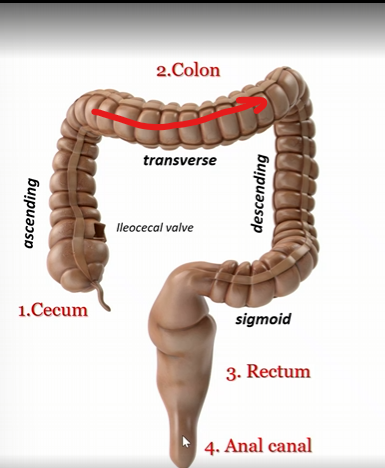
Transverse colon
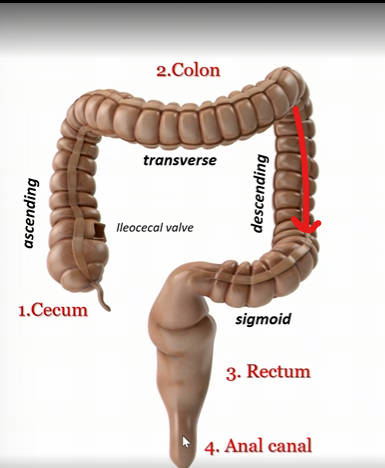
Descending colon
sigmoid colon
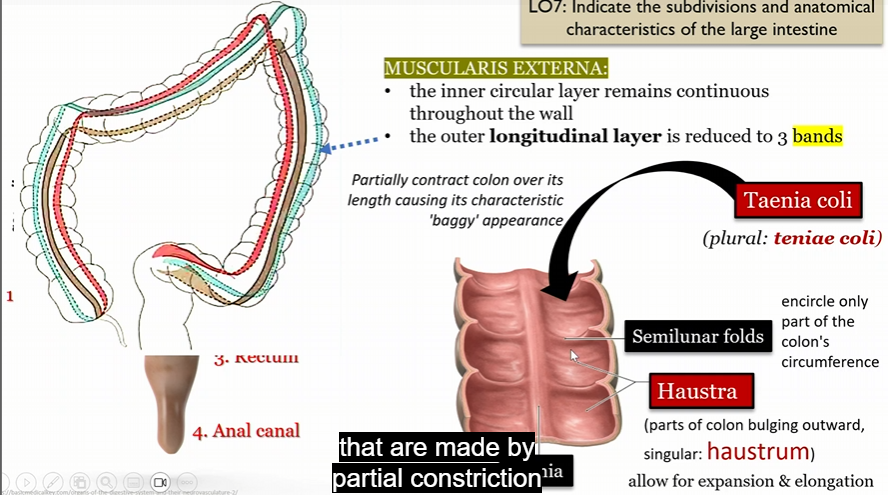
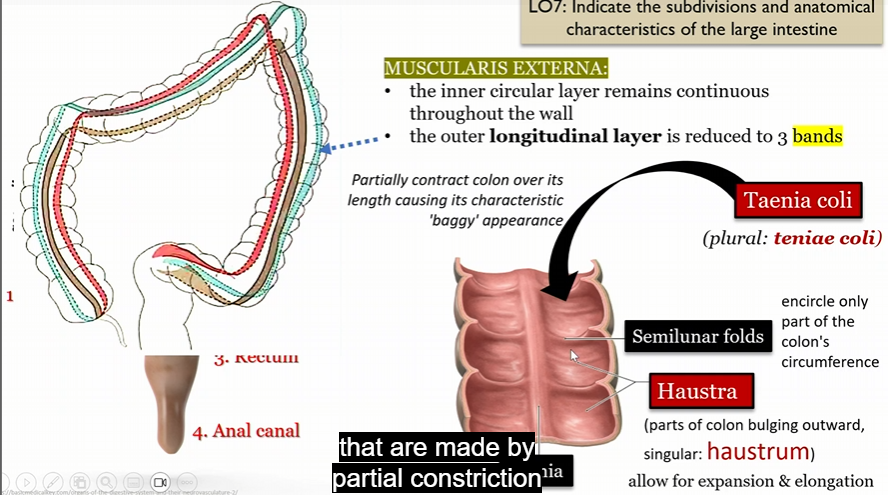
Muscularis externa
In large intestine
inter circular layer remains continuous throughout the wall
outer longitude layer reduced to 3 bands
paritally contract colon leading to the “baggy” appearance
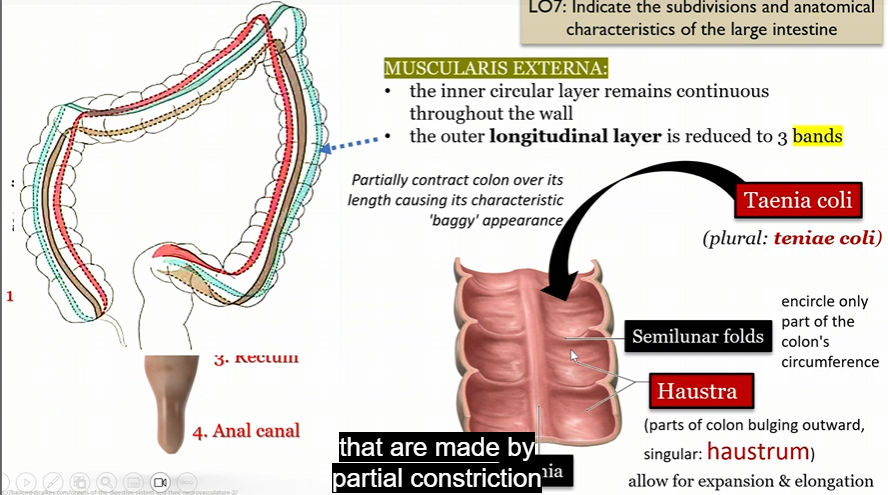
Tenia Coli
In large intestine
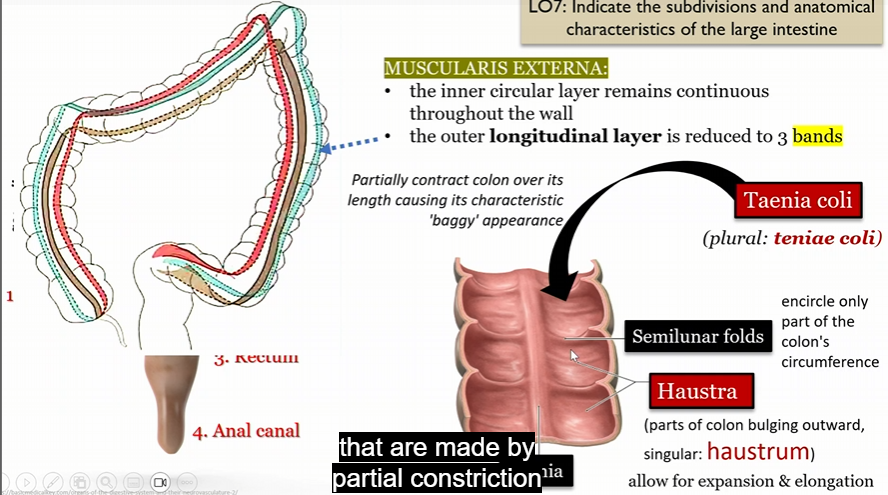
Semilunar folds
In large intestine
encircle part of the colon’s circumfrence
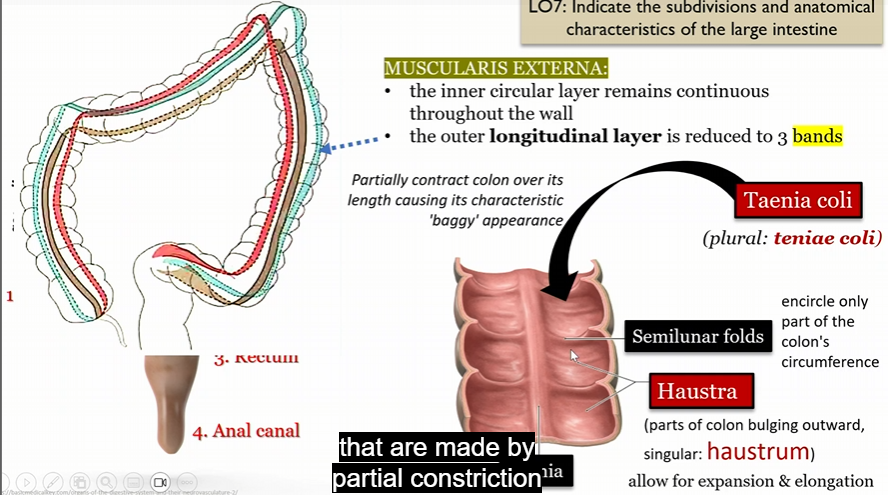
Haustra
In large intestine
parts of colon bulging outward (haustrum)
allow for expansion and elongation
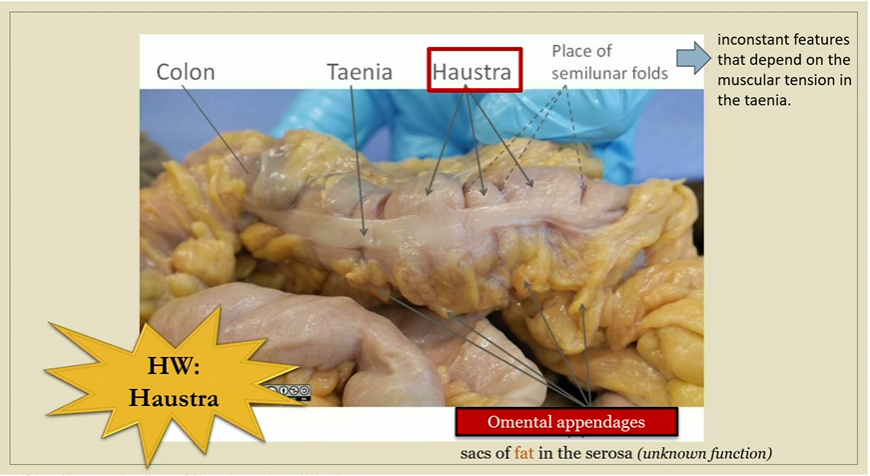
Taenia
In large intestine
Omental apendages
In large intestine, unknown function
Sacs of fat in the serosa
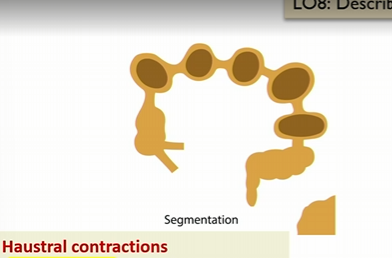
Haustral contractions
Segmentation like,
local back and forth contraction of the colon in haustra
mixes the intestinal content
maximizes contact with mucosa, allowing water and electrolyte absorbtion
Key point: segmentation does not move feces forward much
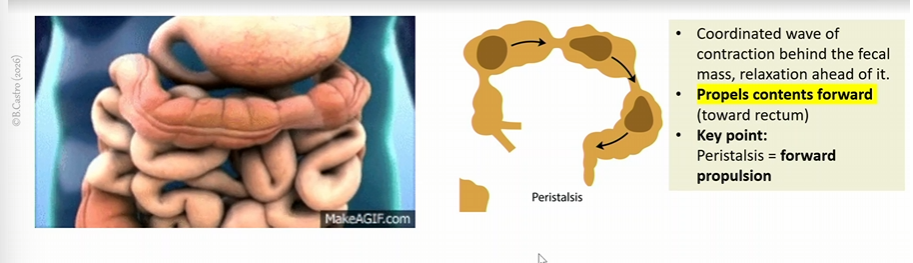
Peristalsis in large intestines
coordinated wave of contraction behind the fecal mass
relaxation ahead of it
propels contents fowards (towards rectum)
Mass peristalsis
pooping enticing reflex
strong peristaltic waves
move feces across large segments of the colon at once
1-3 times a day
done by gastrocolic reflex

Gastrocolic reflex
stomach fills with food ENS in the stomach wall initiates a reflex that stimulates the colon to contract (promoting mass movements) this reflex helps move food residue towards the rectum, making space for new food intake

Defecation reflex
normally internal anal sphincter and external anal sphincter is contracted,
but upon rectal distension of the stool, the internal anal sphincter will voluntarily relax
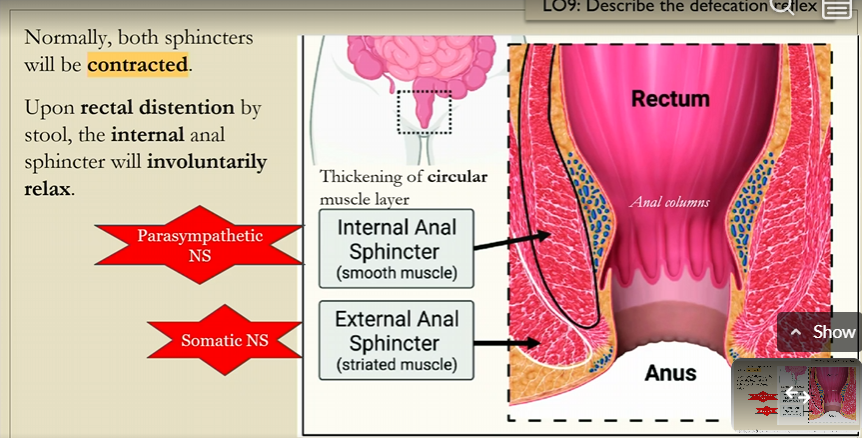
Internal Anal sphincter
smooth muscle
parasympathetic NS
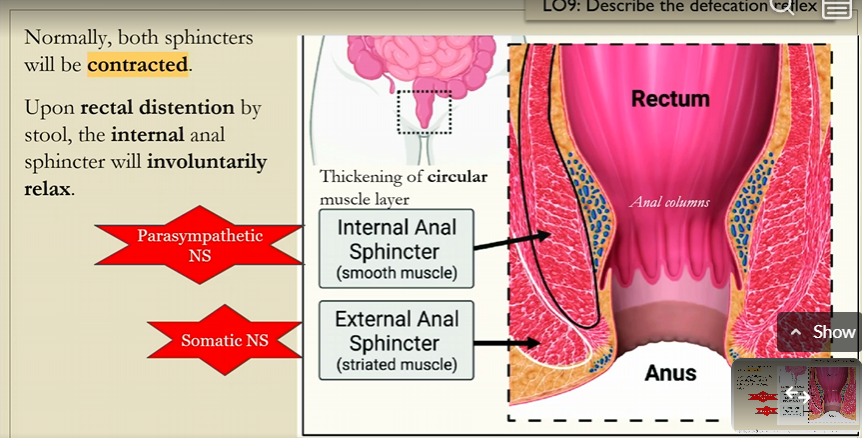
external anal sphincter
striated muscle
excretion of stool controlled by voluntary relaxation of the external anal sphincter
somatic NS
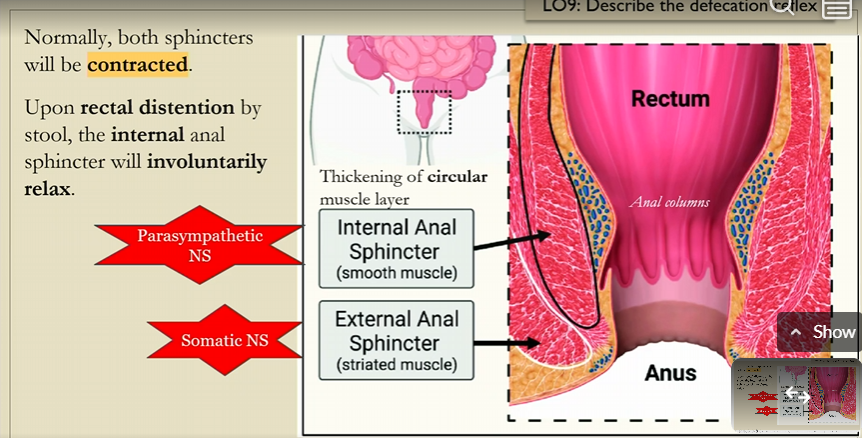
Initiation of poop reflex in smooth internal anal sphincter
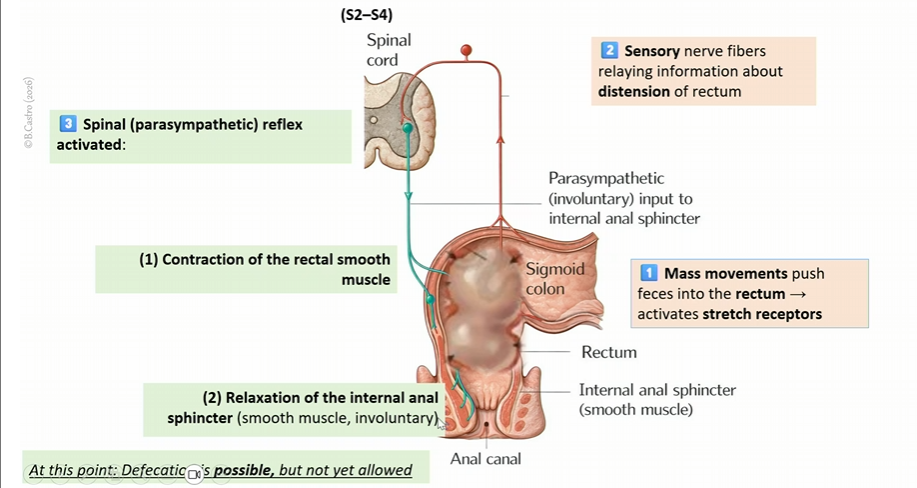
Mass movements push feces into the rectum, which activates stretch receptors
sensory nerve fibers relay information about distention of the rectum
spinal parasympahtetic reflex activated
contraction of the rectal smooth muscle
relaxation of internal anal sphincter (smooth muscle, involuntary)
DEFACTACATION IS NOW POSIBLE, BUT NOT YET ALLOWED
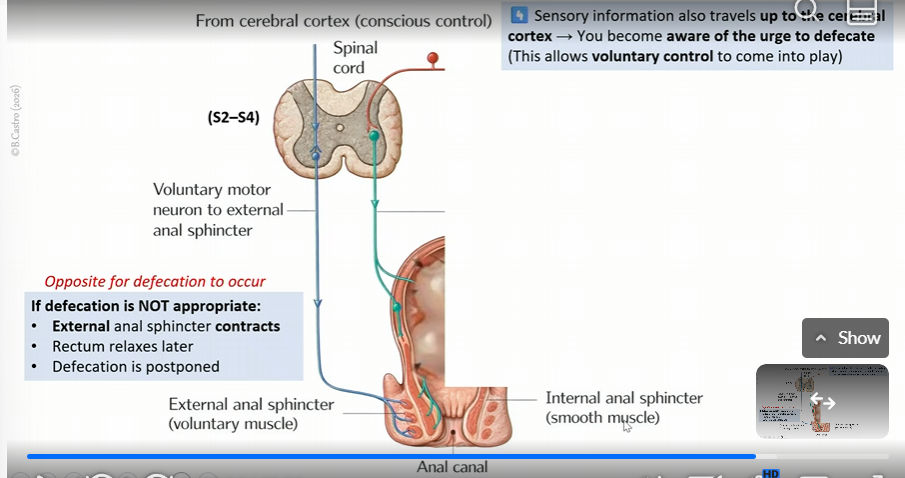
Initiation of poop reflex in external internal anal sphincter
After internal external sphincter becomes relaxed
sensory info goes to cerebral cortex and you are made aware of the urge to defecate
(allows voluntary control to come into play)
voluntary motor neuron then goes to external anal sphincter via the cerebral cortex
if defecation is not appropriate, external anal sphincter contracts a
rectum relaxes later
defecation is postponed
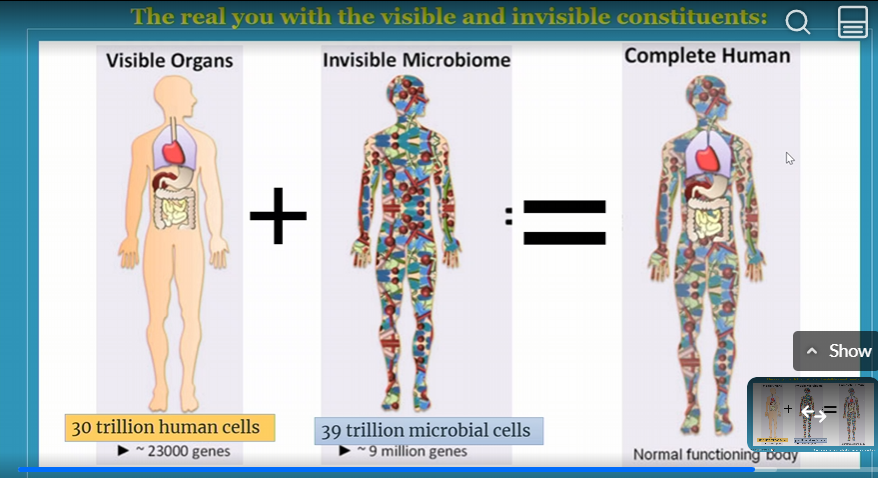
how much human cells do we have
30 trillion
how much microbial cells do we have
39 trillion
Where is the highest concentration of enteric bacteria
large intestines (800 species)
Gut microbiome
alll microorganisms living in your digestive system
unique to every person microscopic ecosystem
Function of gut microbiome
humans lack enzyme to digest many fibers, beneficial gut bacteria use fiber as a food source.
production of important vitamins
trains and regulates the immune system via helping it distinguish helpful and harmful pathogens
prevents colonization by pathogens via direct competition
Function of gut microbiome - fiber digestion
bacteria ferment SCFAs like butyrate, the promary source of energy for colon epithelial cells, which helps maintain a strong intestinal barrier
SCFAs
Done by gut microbiome
short chain fatty acids like butyrate which are the primary source of energy for colon epithelial cells
Helps maintain a healthy strong intestinal barrier and have anti-inflammatory effects
Vitamins produced by microbiome
B vitamins like
B12, folate, biotin