Carbohydrates, Lipids, Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes, Chemistry of Medicines, Nutrition, Nucleic acids, and Bioenergetics.
Name, Structure, and Three Letter Code for the Amino Acids You need to Know
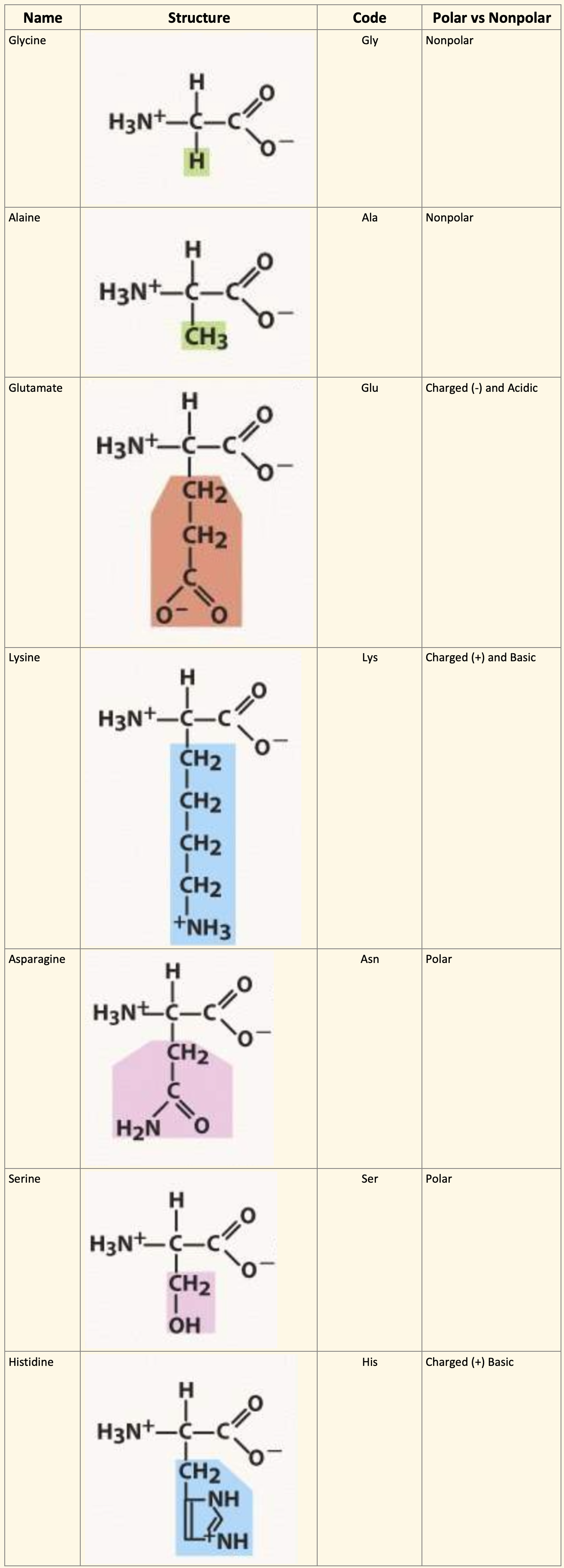
Zwitterions
Neutral solutions
It is a dipolar ion made by a transfer of a proton from –COOH to –NH2
Overall charge is still zero
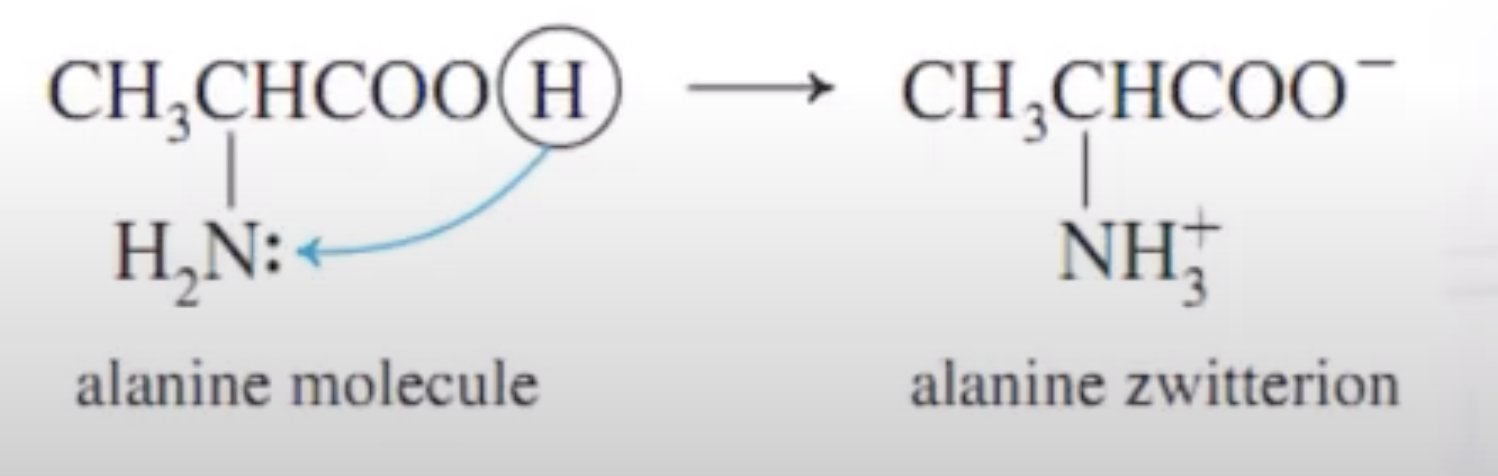
Calculate the pI for a neutral amino acid like glycine....which has two pKas : pKCOOH and pKNH

Classes of Enzymes (Over The HILL)
Oxidoreductases
Enzyme that catalyse the oxidation-reduction reaction between the two substrates
Transferases
Enzymes that catalyse the transfer of functional group between two substrates
Hydrolases
Enzymes that catalyse the hydrolysis of esters, carbohydrates, and proteins (polypeptides)
Isomerases
Enzymes that catalyse the interconversion of stereoisomers and structural isomer
Lyases
Enzymes that catalyse the removal of groups from substrates by mechanisms other than hydrolysis
Ligases
Enzymes that catalyse the linking of two compounds by breaking a phosphate anhydride bond in adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
The energy necessary to move a reactant to the transition state is called the…?
…activation energy
(The larger this energy barrier is the slower the reaction rate will be)
Common Ways to increase a Reaction Rate
Increasing the reactant concentration
Increasing the reaction temp
Adding a catalyst
What is Vmax?
So once we reach Vmax, it doesn't really matter HOW much more substrate we give it, the reaction cannot go any faster than it's already going.
This curve is called a hyperbolic curve
Protein-Ligand Binding
A ligand is a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein
The greater the intermolecular forces, the greater the binding affinity
You need less concentration of a higher-affinity binding ligand, to maximally occupy a ligand-binding site, and trigger a response
More Selective Drugs
Drugs that are more selective are safer to use as they target the specific response in the body.
There are two isoenzymes – COX-1 and COX-2
The substrate binding channel of COX-1 is smaller than the binding channel of COX-2
Flurbiprofen can fit into both binding channels, while SC-558 is larger than flurbiprofen and is unable to fit into the COX-1 binding channel
Intermolecular Forces
1. Dispersion forces
weakest intermolecular force (0.5-1.0 kcal/mole)
electrostatic
occurs between nonpolar groups (e.g. hydrocarbons)
highly distance and temperature dependent
2. Dipole-Dipole Bonding
stronger (1.0 to 10 kcal/mole)
occurs electrostatically between electron deficient and electron rich atoms (dipoles)
hydrogen bonding is a specific example of this bonding and serves as a prime contributor to hydrophilicity
Dipole results from an unequal sharing of the pair of electrons in a covalent bond.
Found when the two covalently bonded atoms differ greatly in electronegativity
3. Hydrogen Bonding
Stronger bond than van der Waal
Less affected by temperature or distance
Give hydrophilic character to chemical
Accounts for water-solubilizing properties of organic compounds
4. Ionic Bonding
electrostatic attraction between cations and anions
common in inorganic compounds and salts of organic molecules
relatively strong (5 kcal/mole)
5. Ion-Dipole Bonding
electrostatic between a cation/anion and a dipole
relatively strong (1-5 kcal/mole)
low temperature and distance dependence
important attraction between organic compounds and H2O
Electrostatic attraction that occurs between a formally charged ion and a dipole.
If the salt can dissociate in water (i.e., separate), water solubility can occur.
Can play a significant role in dissolving organic compounds in water
Oxidation, demethylation, and glucuronidation increases polarity and water solubility
Oxidation is the loss of electrons
Demethylation is the loss of a melthy group
Glucuronidation is the gain of a sugar group
HMG CoA Reductase Inhibitors
HMG CoA reductase (HMG stands for 3-Hydroxy-3-MethylGlutaryl) is responsible for the conversion of HMG CoA to mevalonic acid
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors are also called "statins", or more correctly "vastatins"
Mevastatin & lovastatin served as lead compounds for the development of alternative HMG Co reductase inhibitors
Monosaccharides
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
Disaccharides
Maltose
Sucrose
Lactose
Polysaccharides
Starch
storage form of glucose in plants
found in grains and legumes.
Amylose, Amylopectin
Glycogen
storage form of glucose in the body
provides a rapid release of energy when needed.
Fibre
provides structure in stems, trunks, leaves, roots etc.
generally not digestible
Soluble and insoluble
Epimer?
Enantiomer?
Diastereomer?
Anomers?
Epimer= differ on one chiral carbon
Enantiomer= mirror image
Diastereomer= differ on more than one chiral carbon (not all)
Anomers= two cyclic isomers that differ only in their stereo arrangement about the carbon involved in mutarotation.
Hemiacetal? Acetal?
Hemiacetal= ether and alcohol on the same carbon, meaning the molecule will undergo mutarotation
Acetal= two ethers on the same carbon, meaning the molecule will-not undergo mutarotation
The first carbon that is bonded to 2 oxygens is called the…?
…anomeric atom
Mutarotation
When alpha and beta forms of glucose are put into separate solutions and allowed to stand, the rotation of polarized-light becomes the same
This is called mutarotation
During mutarotation the two cyclic forms come together through the open chain form
Resulting in 36% being alpha, 64% being beta, and the rest in trace amounts
How are disaccharides are connect by…?
Disaccharides are connect by glycosidic linkages
Lipoproteins
Lipoproteins transport lipids through the bloodstream
Chylomicrons: largest, but least dense. Reduce in size as triglycerides are removed.
VLDLs: Very low density lipoproteins.
LDL: Low density (‘Bad’) lipoproteins (to the body)
HDL: High density (‘Good’) lipoproteins (to the liver)
Phospholipids
Group of compounds that make one or more fatty acid molecules, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base after hydrolysis
Have a hydrophilic end that interacts with water
Sphingolipids
Sphingomyelin are found in the myeline sheath membrane in nerves
Glycolipids
Contain carbohydrate group
With the two most important being cerebrosides and gangliosides
These are found in cell membranes of nerve and brain tissue
Cerebroside may contain either D-galactose or D-glucose
Steroids
Cholesterol (major membrane component) (converted into progesterone, then testosterone)
Bile salts (help in the digestion of fats)
Ergosterol (yeast steroid which is converted into vitamin D by ultraviolet radiation)
Digitalis (heart drugs)
Adrenal cortex hormones (metabolism)
Sex hormones
Atherosclerosis
Deposits of cholesterol and other lipids on the inner walls of the arteries
How are Proteins Numbered?
The chain is numbered from N-terminal on the left, and C-terminal on the right
Naming Proteins

Ala-Tyr-Gly is called alanyltyrosylglycine
C-terminal keeps its name, others end in 'ine', 'ic', or 'yl”
Protein Structure
Primary
Covalent bonding
Amino acid sequence of a protein
Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Val-His-Pro-Phe
Secondary
Three dimensional structure held together by hydrogen bonding (C=O) (H-N)
Alpha helix
Beta pleated sheet
Beta sheets that have strands pointing in the same direction = parallel or strands pointing in opposite directions = antiparallel.
Tertiary
Shape or conformations of the protein
R group interactions that stabilise tertiary structures
Hydrogen bonding
Ionic bonding
Disulfide bonding
Quaternary
Found in only some proteins
Made from two or more smaller protein subunits or polypeptide chains
Refers to the shape of the entire complex
Noncovalent bonds like hydrogen bonding and ionic bonding
Protein Functions
Structural support (collagen)
Storage (ferritin stores iron in the liver)
Transport (haemoglobin moves oxygen in red blood cells)
Defence (antibodies)
Motion/movement (actin/myosin)
Regulation (insulin)
Catalysis (increases the reactions)
Proteins and their Structures
Fibrous Proteins
Fiber-like shape
Structural supports
Tend to be water insoluble
Alpha keratin is found in hair
Fibroin (pleated sheet) is found in silk
Collagen (helix) is found in many tissues
Globular Proteins
Round
Charged and polar amino acids are found on the outside of a protein structure and interacts with water
Non-polar amino acids a buried in the interior of the protein and avoid water
Myoglobin has and iron bound atom in the haem ring that allows is to store oxygen for muscle tissues
Haemoglobin transports oxygen in red blood cells, 4 subunits and a haem ring
Carboxypeptidase A, is a catalytic protein for digestion
Fatty acid binding protein transports fatty acids through the blood stream
Ferritin stores iron in the liver
Myosin makes movement in muscles
Loss of Protein Structure
Effect proteins function and is called denaturation
Alterations or disruption of the secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structures
Not primary
How Can Proteins be Denatured
Heat (disrupting the weal interactions such as hydrogen bonding)
pH (alter the net charge on the protein causing electrostatic repulsion and disruption of hydrogen bonds)
Organic solvents, urea, guanidine HCl and detergents (disrupting the hydrophobic interactions)
These do NOT break covalent bonds and so do NOT denature primary structures
Hydrolysis of peptide bonds to make free amin acids with destroy the proteins primary structures
Can be hydrolysed by boiling a solution containing a strong acid (HCl) or strong base (NaOH)
Minerals
Sodium, potassium, and chloride
Maintain appropriate salt levels in body fluids
Calcium and magnesium
Critical for bone and teeth health, enzyme function, nerve transmission, and blood clotting
Trace elements are required in small amounts
Iron is a notable exception, crucial for haemoglobin in blood and some enzymes
Metals
Metalloenzymes are enzyme proteins containing metal ions (metal cofactors), which are directly bound to the protein or to enzyme-bound nonprotein components (prosthetic groups such as )
Non-metalloenzymes, like haemoglobin and myoglobin are proteins that bind to oxygen for transport and storage respectively
Human DNA can extend to 10cm and yet is contained in a small nucleus
DNA is looped around small aggregates of positively charged histone proteins
And then by wrapping the structure into a tight coil called a solenoid
The phosphates are on the outside of the DNA structure along the backbone and are negatively charged
To balance out these charges DNA phosphates groups form ionic bonds to cations such as Mg2+ or Ca2+ which are called counterions
DNA counterions reduce the electrostatic repulsion between DNA molecules by screening the negative charges in their backbones
Redox Coenzymes
Very important function is to carry electrons to the mitochondrial electron transport system
As the coenzymes are oxidized, the molecular oxygen is reduced
Molecular Oxygen
Other reduced products of O2 are dangerous
Known as reactive oxygen species (ROS), and can react with and destroy cell molecules
Since cells have to live with the danger of ROS, they have develop defence mechanisms including two important protective enzymes
Superoxide dismutase= destroys superoxides, O2- by making hydrogen peroxide
Catalase= converts the hydrogen peroxide into water
High Energy Phosphate Bonds
Energy is made in the mitochondria, but must be transported throughout the cell
This delivery system must carry relatively large amounts of energy and be easily accessible to cellular reactions
The most common high energy phosphate bond is the phosphate anhydride bond
Muscle Fiber Can make Energy to Contract
Substrate Level Phosphorylation
Energy is got from oxidation and used to form high energy phosphate bonds
Goes from ADP to ATP
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Uses energy from redox reactions to form ATP
Done in the mitochondria
Oxidizes the two coenzymes NADH (makes 3 moles of ATP) and FADH2 (makes 2 moles of ATP)
Mitochondrial electron transport
Energy is trapped when ADP turns into ATP