Neuro700 - Hearing & visual Pathway (Quiz 5)
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
What is the function of external ear?
collect soundwaves
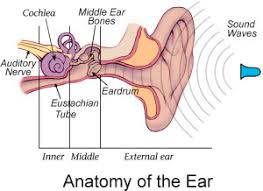
What is filled within the cavity in the middle ear?
Air
What are the structures of external ear
Auricle / Pinna ( Helix, Lobule)
External auditory canal
Targus
Tympanic membrane / eardrum
Ceruminous gland
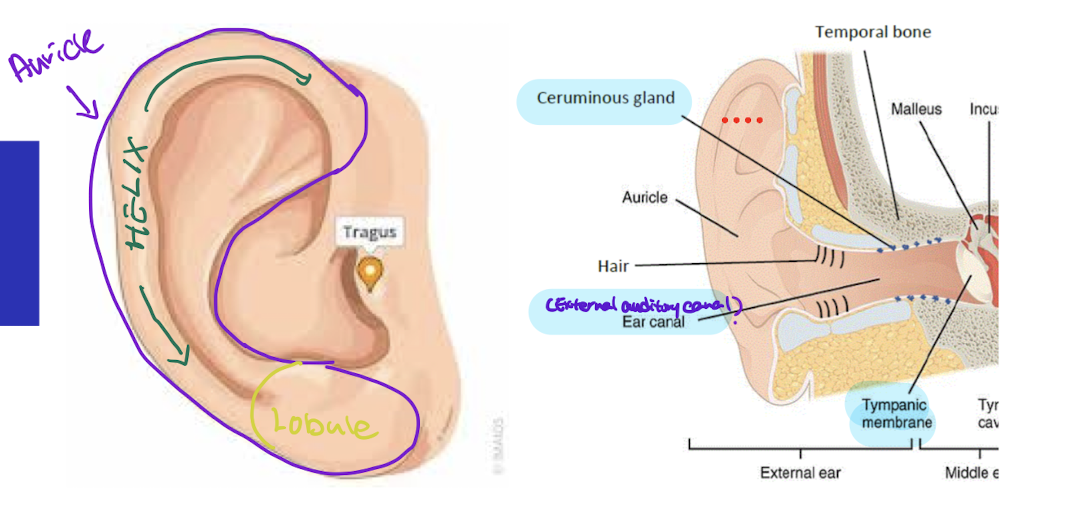
What is Tympanic membrane made of? color?
Epidermis
collagen
elastic fibers
color: Semitransparent
What is the treatment for perforated eardrun?
No Treatment, heals within a month
What produces earwax?
Ceruminous gland
Why we shouldn’t use cotton swab to clean earwax?
will cause perforated eardrum
earwax dries up and falls out of ear canal
What is the function of cerumen?
prevent dust and foreign object from entering the ear canal
prevent damage from water or insects
What separates the middle ear from external ear and inner ear?
External ear: eardrum ( tympanic membrane_
Inner ear: Oval window and round window
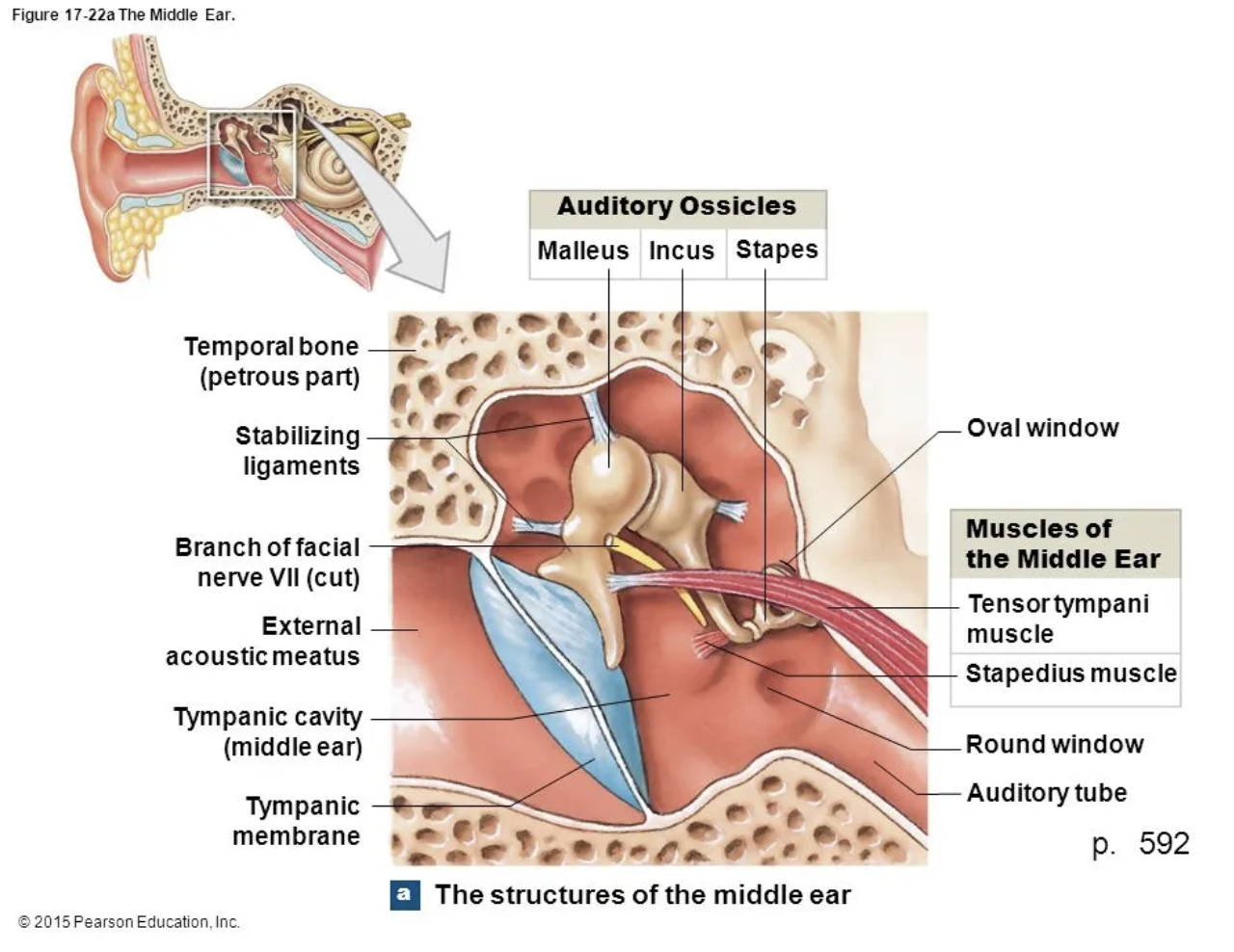
How are the auditory ossicles connected?
Synovial joints
What are the 3 auditory ossicle in middle ear?
Malleus
Incus
Stapes
What are the muscle in the middle ear
Tensor Tympani
Stapedius
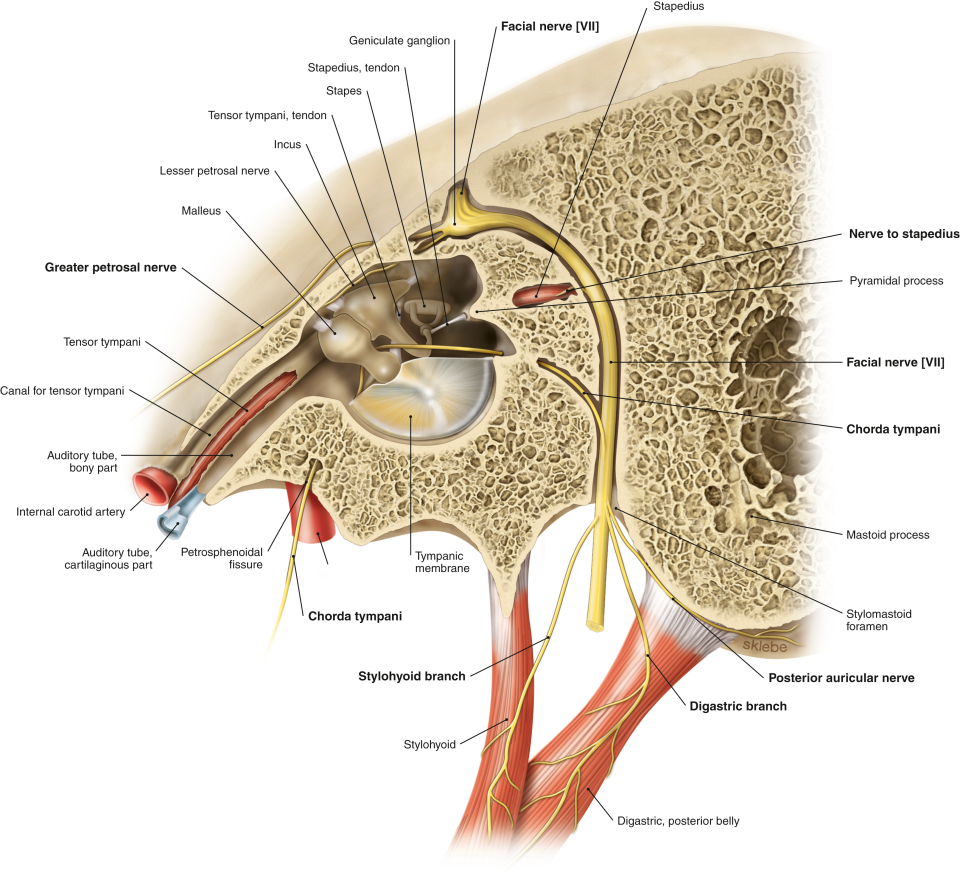
Which nerve innervates tensor tymoani?
trigeminal nerve(CN5) - mandibular branch
Which nerve innervates Stapedius
Facial nerve (CN7)
Which muscles limits movement and increase tension on eardrum?
Tensor Tympani
Which muscle protects oval window and decrease sensitivity to hearing
Stapedius
When will auditory tube open
yawning, swallowing
Where does auditory tube lead to
nasopharynx
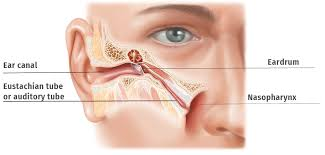
What are the 2 conditions that pathogen from nose and throat to middle ear can cause
Otitis media
Mastoiditis
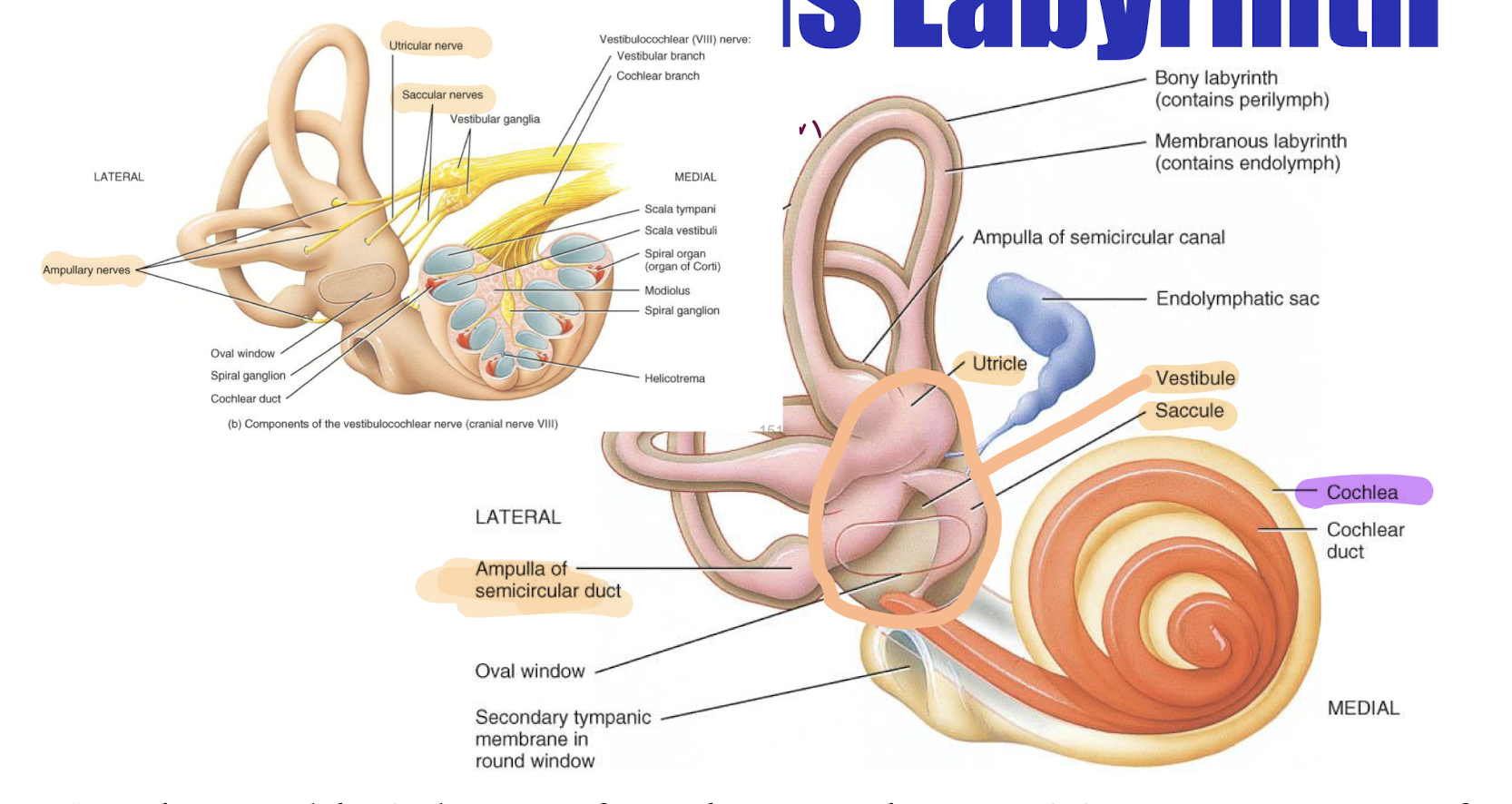
What are the division of inner ear
bony labyrinth
membrane labyrinth
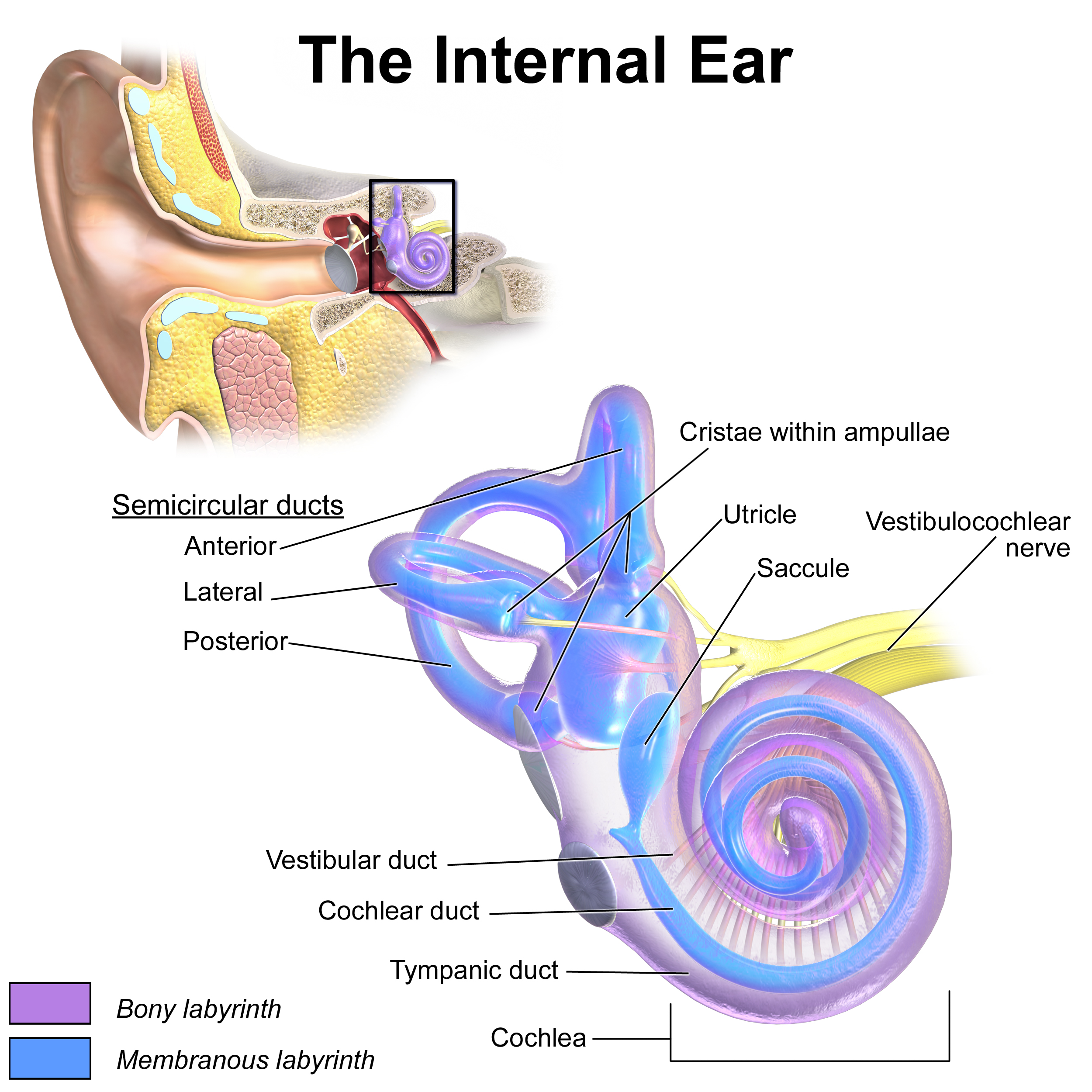
Where is the inner ear located
petrous portion of temporal bone
what are the areas in the bony labyrinth?
semicircular canals
Vestibule
cochlea
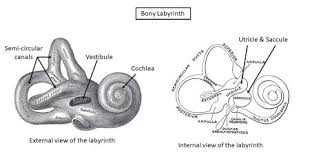
Which area of the ear is responsible for hearing
chochlea
Which area of the ear is responsible for equilibrium
semicircular canals
vestibule
What lines the bony labyrinth
periosteum
what fluid is found in the bony labyrinth
perilympth
similar to CSF
What fluid is found in the membranous labyrinth?
endolymph
What fluid is endolymth most similar to
interstitial fluid
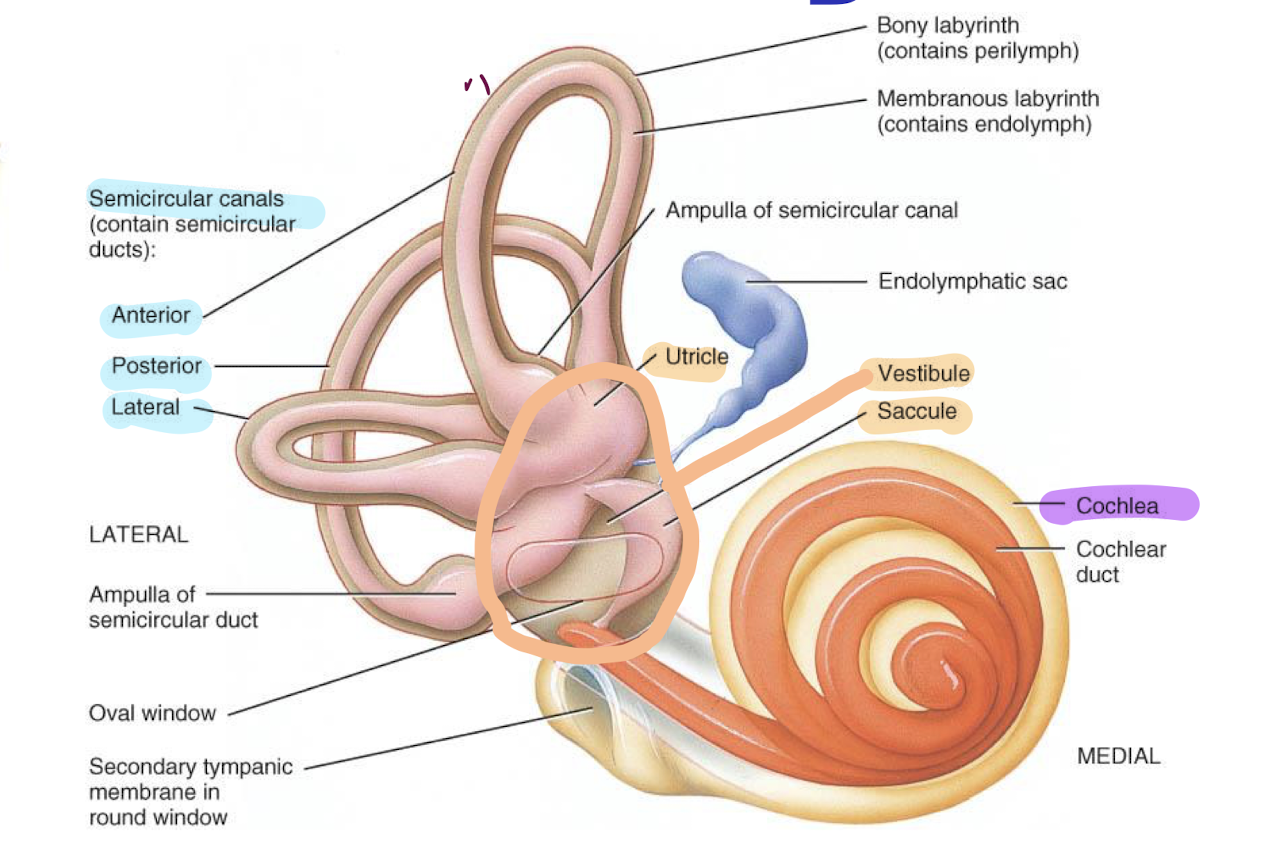
What is located anterior to the vestibule
cochlea
What is the spiral turns in the cochlea called?
Modiolus
What is located posterior to vestibule
semicircular canal
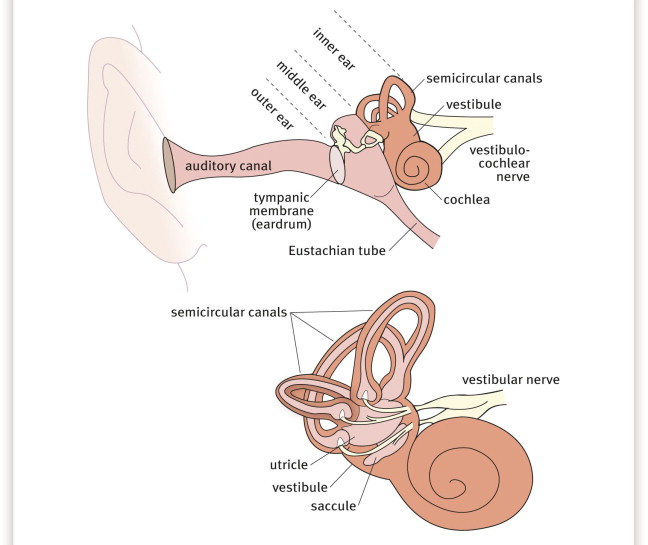
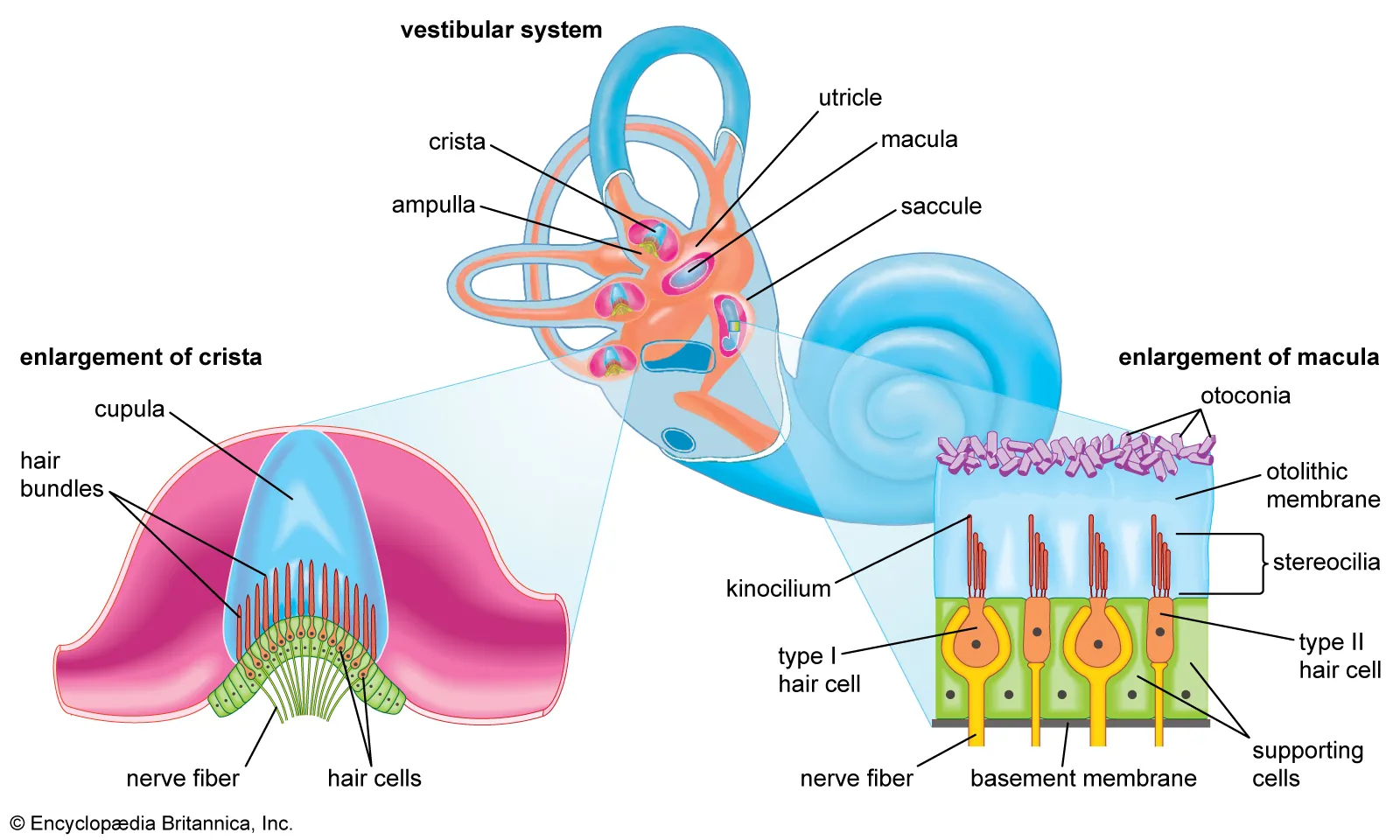
What are the 3 parts in the vestibular branch
ampullary
urticular
saccular
List the sequence of the transmission of sound
uricle directs sound waves into auditory canal
Soundwave strike tympanic membrane
Tympanic membrane vibrate
Slow vibration = low frequency = low pitch
Fast vibration = high frequency = high pitch
Vibrates Malleus > incus > Stapes
Oval window ( vibrates 20X vigorously)
Fluid pressure wave in perilymph in scala vestibuli
Into the scala tympani
Scala Vestibuli + Scala Tympani creates pressure in the emdolymph inside cochlear duct
Basilar membrane in endolymph vibrates = moves hair cell = produce receptor potentials
Generate impulses to cochlear branch of CN8
Signals to cochlear and superior olivary nuclei within medulla and pons
Midbrain ( inferior colliculus)
Thalamus ( medial geniculate nucleus)
Primary auditory area ( temporal lobe)
Low vibration = (. ) frequency/ pitch
Low
The oval window vibrates (More / Less) Vigorursly than the eardrum
More ( 20X)
Where is the perilymph?
Scala vestibuli
Where does scala vestibuli and scala tympani pass pressure to
Endolymph
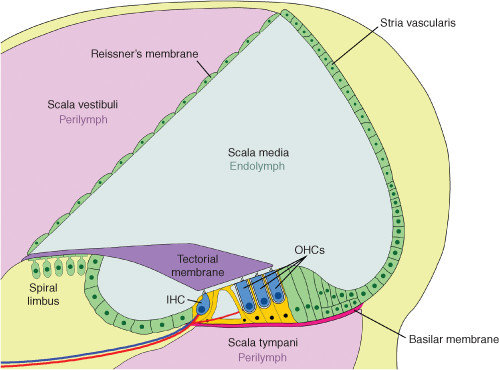
What overlays the sterocilia
Tectorial membrane
Which hair cell enhance sensitivity to sound?
External hair cells
Which hair cell transform sound wave into action potential?
Inner cell
Movement of hair cells with open and close (. ) channels?
K+
Depolarization of the hair cells when (. ) chnnels open and influx of (. ) will release neurotransmitters
K+ and Ca2+
Human ear can detect sound between ____ to _____ Hz. Best between ______?
20 - 20000
Best between 1000 - 4000
Volume of sound affects the _____ of a soundwave? what is the unit
Amplitude measure be decibels(dB)
What is the conversation Hz and dB?
300 - 3000 Hz
60dB
How many dB will cause damage to ear?
85
How many dB will cause pain in the ear
120-140
Which area in the cochlea does high frequency vibrate?
Base of the cochlea
Which area in the cochlea does low frequency vibrate?
appex
Where is the primary auditory area?
temporal lobe
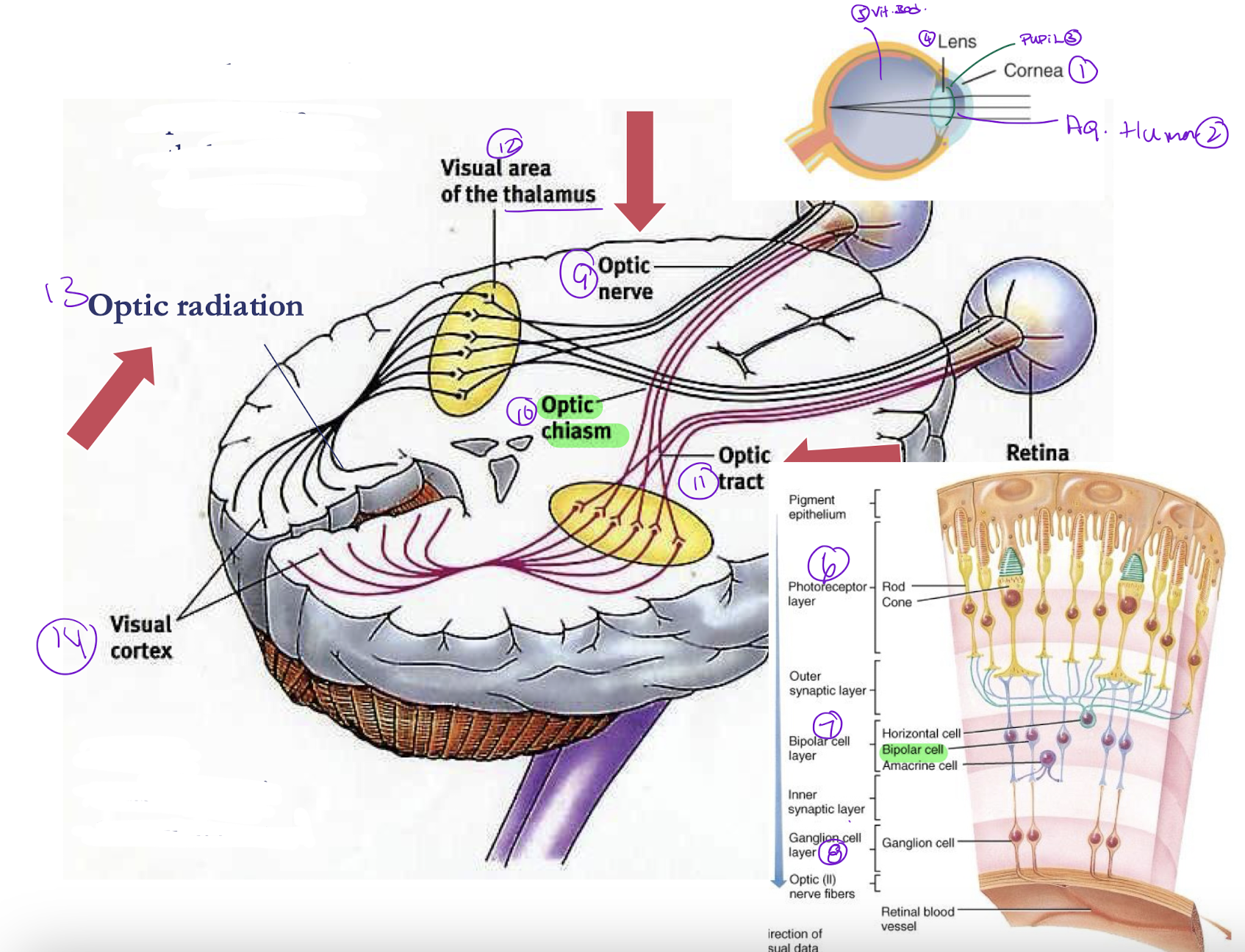
Place in order the structures involved in the visual pathway
a) optic nerve
b) ganglion cells
c) cornea
d) lens
e) bipolar cells
f) optic nerve
g) visual cortex
h) viterous body
i)optic chaism
j) aqueous humor
k) pupil
l) photoreceptor
m) thalamus
n) Optic radiation
cornea > Aqueous Humor > Pupil > Lens > Viterous body> photoreceptor > Bipolar cell > ganglion cell > optic nerve > optic. chiasm > optic tract>thalamus>Optic radiation> visual cortex
4) The correct sequence for the auditory pathway.
Auricle > Eardrum > Ossicles > Oval window > Cochlear > Spiral Organ
What is the partition between external auditory canal and middle ear?
Tympanic membrane
What is the oval central portion of the bony labyrinth that contains utricle and saccule
Vestibule
Which area contain hair cells which are receptor for hearing?
Spiral organ
What are the auditory ossicles
Malleus, Incus, Stapes
What contains the spiral organ?
Cochlea
What is found within the membranouos labyrinth, pressure wave in this fluid cause vibration of the basilar membrane
Endolymph
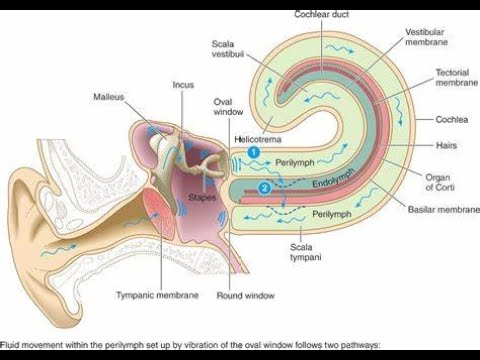
What is the opening between the middle ear and internal ear. it is enclosed by a membrane called the secondary tympanic membrane
Round window
What is the flap of elastic cartilage covered by skin that captures sound wave
Auricle
What is the fluid found inside bony labyrinth, bulging the oval window causing pressure waves
perilymph
The opening between middle and inner ear, receives base of stapes
oval window
T/F
Crista, macula, otolith and spiral organ are structure in the inner ear
True
Infection in the throat are most likely lead to ear infections in the ______
Auditory tube to the middle ear
Which is a false statement for middle ear?
A) contains ear bones called ossicles
B) related to otitis media
C) conduct sound from external ear to inner ear
D) involve cochlea
D) involve cochlea
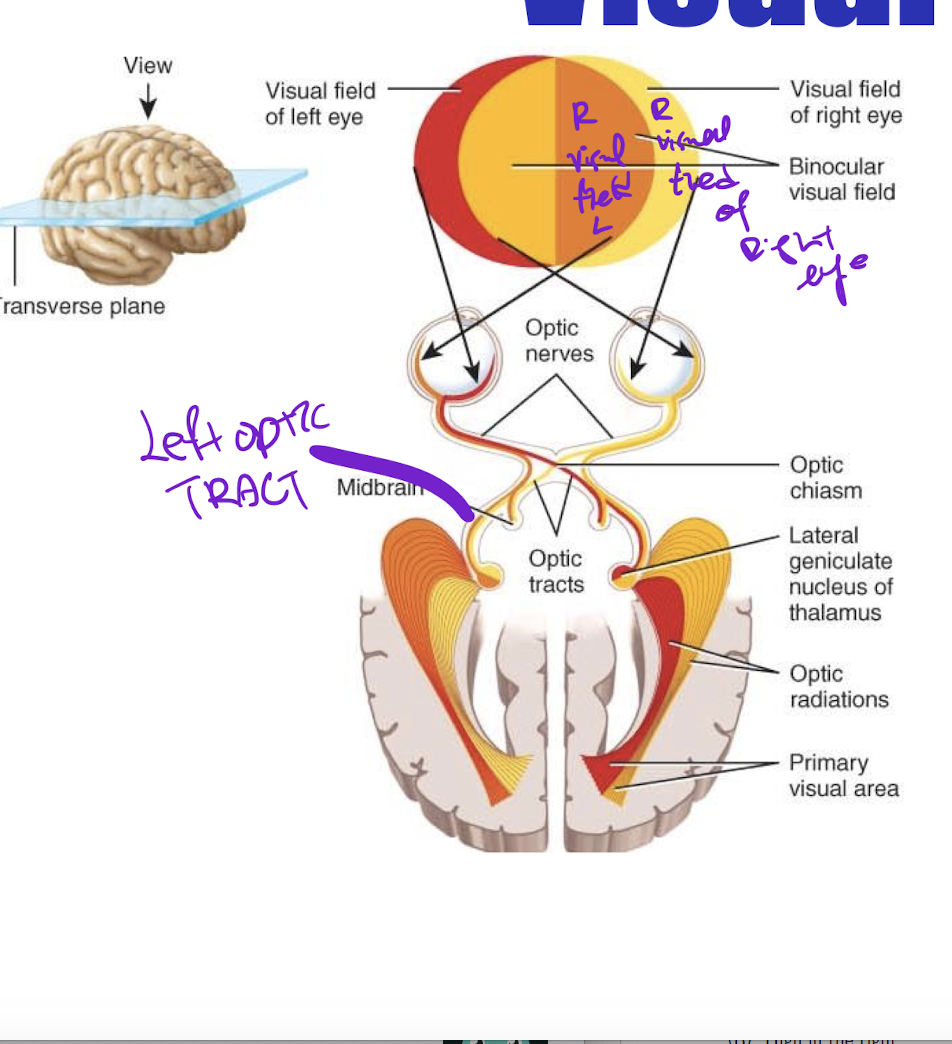
Destruction of the left optic tract would result in
A) Blindness in left eye
B) loss left visual field of each eye
C) loss right visual field of each eye
D) loss lateral field of each eye
C) loss right visual field of each eye
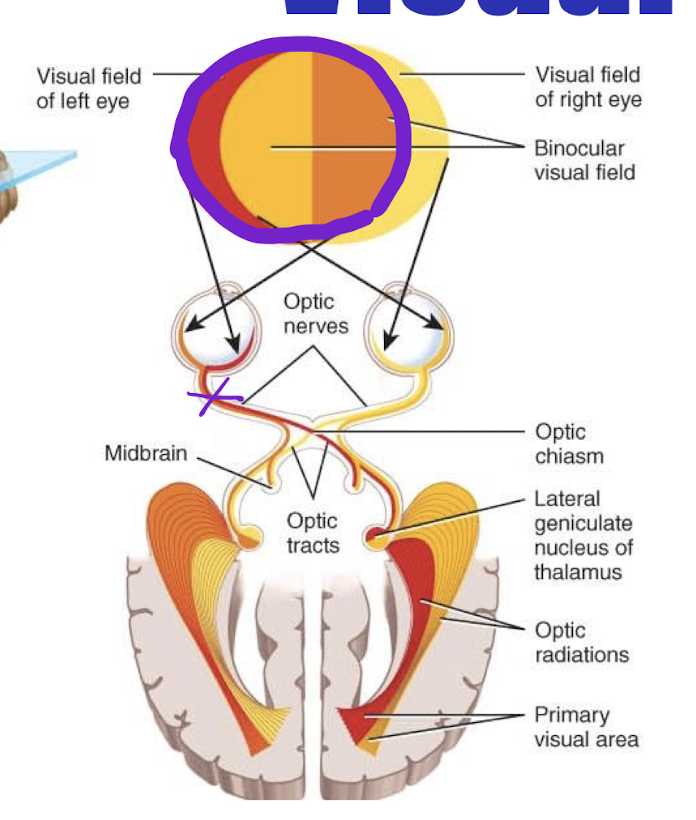
Destruction of the left optic nerve would result in
A) Blindness in left eye
B) loss left visual field of each eye
C) loss right visual field of each eye
D) loss lateral field of each eye
A) Blindness in left eye
Pt detached retina of lower right portion of an eye, what is he unable to see?
object at high left
In darkness, Na+ are held open by which molecule
Cystic GMP