HALOGENOALKANES
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is a primary halogenoalkane?
has only one carbon attached to the carbon atom adjoining the halogen
What is a secondary halogenoalkane?
has 2 carbons attached to the carbon atom adjoining the halogen
What is a tertiary halogenoalkane?
has 3 carbons attached to the carbon atom adjoining the halogen
What reactions can halogenoalkanes undergo?
nucleophilic substitution
elimination
What happens in a substitution reaction?
swapping a halogen atom for another atom or group of atoms
What does :Nu represent?
any nucleophiles as they always have a lone pair and act as electron pair donators
What is the mechanism for a nucleophilic substitution reaction between X-ethane and :Nu?
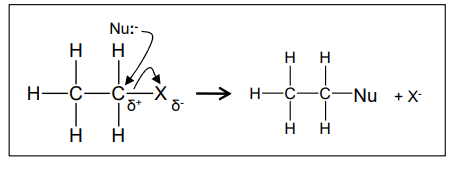
What does the rate of substitution reactions depend upon?
the strength of the C-X bond
the weaker the bond, the easier it is to break and the faster the reaction
What halogenoalkane is the fastest to substitute?
iodoalkanes
What is hydrolysis?
the splitting of a molecule by a reaction with water
What happens when aqueous silver nitrate is added to a halogenoalkane?
halide leaving group combines with a silver ion to form a silver halide precipitate
rate of precipitate formation can be used to compare the reactivity of different halogenoalkanes
quicker the precipitate is formed, the faster the substitution reaction and the more reactive the halogenoalkane
What colour precipitate does AgI, AgBr and AgCl form?
AgI is a yellow precipitate
AgBr is a cream precipitate
AgCl is a white precipitate
What occurs in nucleophilic substitution with aqueous hydroxide ions?
forms an alcohol
reagent - potassium hydroxide
conditions - in aqueous solution, warm
mechanism - nucleophilic substitution
What is the mechanism for hydroxide ions undergoing nucleophilic substitution with bromo-methane?
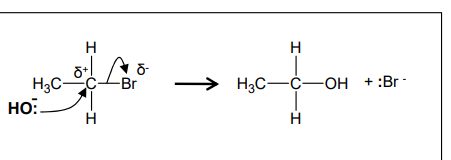
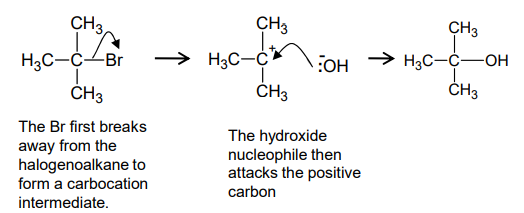
How do tertiary halogenoalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution?
this is due to the tertiary carbocation being stabilised by the electron releasing methyl groups around it
bulky methyl groups prevent the hydroxide ion from attacking the halogenoalkane
What occurs in nucleophilic substitution with cyanide ions?
forms a nitrile
reagent - KCN dissolved in ethanol/water mixture
conditions - heating under reflux
mechanism - nucleophilic substitution
What is the mechanism between bromo-ethane and :CN?
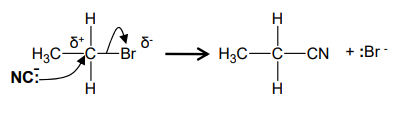
How do you name nitriles?
nitrile groups are on carbon 1
number the chain from carbon 1
e.g. butanenitrile
What occurs in nucleophilic substitution with ammonia?
forms an amine
reagent - NH3 dissolved in ethanol
conditions - heating under pressure in a sealed tube
mechanism - nucleophilic substitution
What is the mechanism for nucleophilic substitution betwee 1-bromopropane and ammonia?
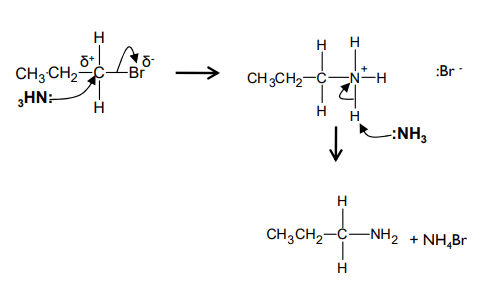
How do you prevent further substitution reactions between the halogenoalkane and the amines formed?
use excess ammonia
What occurs in an elimination reaction between alcoholic hydroxide ions?
forms an alkene
reagents - potassium hydroxide
conditions - in ethanol, heat under reflux
mechanism - elimination
What is the mechanism for the elimination reaction between 2-bromopropane and hydroxide ions?
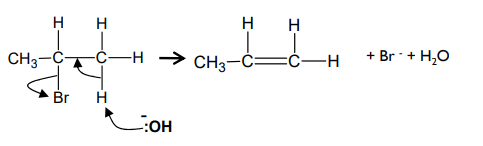
What can happen with unsymmetrical secondary and tertiary halogenoalkanes?
two different structural isomers can be formed
What type of reaction often occurs in primary halogenoalkanes?
substitution
What type of reaction often occurs in tertiary halogenoalkanes?
elimination
Why has using halogenoalkanes for solvents stopped?
due to the toxicity and their detrimental effect on the atmosphere
What can halogenoalkanes be used as?
refrigerants
pesticides
aerosol propellants
What is the benefit of naturally occuring ozone?
it filters out the suns harmful UV radiation
What is the issue with ozone in the lower atmosphere?
its a pollutant and contributes towards the formation of smog
How are chlorine radicals formed in the upper atmosphere?
energy from ultraivolet radiation causes Cl-Cl bonds in chlorofluorocarbons to break
What do chlorine free radicals cause?
catalyse the decomposition of ozone as they’re regenerated
contributes to the formation of a hole in the ozone layer
What are the 2 half equations for the break down of the ozone layer?
Cl. + O3 → ClO. + O2
ClO. + O3 → 2O2 + Cl.
What is the overall equation for the breakdown of the ozone layer?
2O3 → 3O2