Working memory model
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is the working memory model?
A model that describes STM as a system with multiple components
What does the working memory model suggest about STM?
That it is a dynamic and multifaceted system
Who was the working memory model proposed by?
Baddely & Hitch 1976
What study/method did Baddely and Hitch do to develop the working memory model?
PP is completed two tasks at the same time, for example:
condition 1- PP’s completed two acoustic sounding based tasks
Condition 2- PPs completed one acoustic and one visual task
What were the results of Baddely and hitches study?
When both tasks required PPS to use the phonological loop, their ability to perform tasks are impaired. However, when one task uses PL and the other users VSS performance is significantly better.
What conclusion was made from Baddely and hitches experiment?
WMM proposes STM isn’t unitary store but a split into multiple components
What does the WMM propose that the STM looks like?
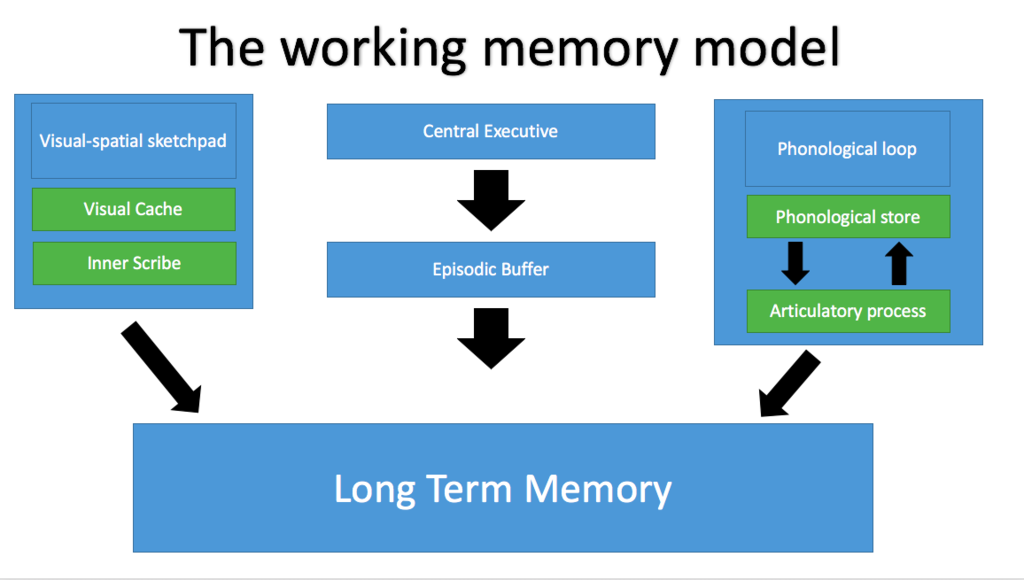
What are the four components of the WMM?
Central executive
Phonological loop
Visuo spatial sketchpad
Episodic buffer
What is the central executive?
A supervisor system in overall control, it controls attention, monitors incoming data, makes decisions and direct information to the two slave systems. The CE decides which information is attended to and which part of WM to send that information to to be processed.
What is the capacity of the central executive?
Very limited capacity
What are the two slave systems?
phonological loop
Visuo spatial sketchpad
What is the phonological loop?
The part of working memory that deals with spoken and written material
What are the two parts of the phonological loop?
Phonological store
Articulatory control process
What is the phonological store?
Linked to speech understanding
→ acts as inner ear and holds information in a speech based form for a duration of 1-2 seconds
What is the articulatory control process?
Linked to speech production
→ act as an inner voice rehearsing information from the phonological store
What is the Visuo spatial sketchpad?
Deals with visual and spatial tasks
What are the two sub components of the Visuo spatial sketchpad?
Inner scribe
Visual cache
What is the inner scribe (what does it deal with)?
deals with the spatial relationship between objects
What is the visual cache (what does it deal with)?
Stores visual information
Why is the Visuo spatial sketchpad important?
because as we move around our position in relation to objects is constantly changing and it is important that we update this information
what is the episodic buffer?
a general storage facility
What does the episodic buffer do?
Binds and integrate information from all the other components and send information to the LTM store
when did baddely add this component and why?
he added it later (2000) as he realised that the model had no general storage facility
what is the capacity of the episodic buffer?
4 chunks
What are three strengths of the working memory model?
RWA – school/ learning
→ teachers are taught to reduce students cognitive load, E.G teachers won’t talk whilst students write because reading the board and listening to the teacher talk both require the attention of the PL. This means we either can’t remember information on the board or what the teacher said. Dual coding can reduce cognitive load and increase the capacity of working memory E.G present new information as an image and narrating over it.
RWA – revision techniques
Perham and Currie 2014 done a repeated experiment where students completed reading comprehension tasks while listening to either liked lyrical music/ dislikes lyrical music/ instrumental music/ nothing. This supports the idea of PL that reading and hearing words are both part of the same component so info gets mixed up as CE can’t direct equal good attention to both, this matters because it tells us that when revising we should do it with no noise in the background.
Supportive evidence – patient KF
What are two limitations of the working memory model?
lack of clarity of CE
→ cognitive psychologists argue CE component is vague and untestable. Alan Baddely himself said the CE is most important but least understood part of WM. Therefore WMM has not fully been explained and provides incomplete explanation of STM.
oversimplifying VSS
Lieberman 1980: criticises WMM as VSS implies all spatial information was first visual. However, Lieberman points out but often blind people have excellent spatial awareness although they’ve never had any visual information. Could there be a fourth store of WMM undiscovered for touch?