Chapter 8
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 8 Microbiology, Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What is genetics?
The study of genes, their information, expression, replication, and transmission to offspring.
What is a genome?
The complete set of genetic material in an organism.
What is a chromosome?
A long DNA structure that contains genetic information.
What is a gene?
A sequence of nucleotides that encodes a functional product, usually a protein.
What is the genetic code?
The relationship among the nucleotide base sequence of DNA, the corresponding codons of mRNA, and the amino acids for which the codons code.
What is a genotype?
The genetic composition of an organism; its complete set of DNA.
What is a phenotype?
The expression of the genes in an organism, including proteins and their effects.
What is genomics?
The molecular characterization of genomes.
How does DNA serve as genetic information?
DNA holds the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms.
What happens during DNA replication?
The strands of DNA separate, and each strand serves as a template to synthesize two new strands.
What is semiconservative replication?
A method of DNA replication where each new DNA molecule contains one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
What direction is DNA synthesized?
DNA is synthesized in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
What is transcription?
The process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template.
What role does RNA polymerase play in transcription?
RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
What is translation?
The process by which mRNA is decoded into a polypeptide chain of amino acids.
How do codons relate to protein synthesis?
Codons are three-base sequences on mRNA that specify which amino acids will be added to a growing polypeptide.
What is an operon?
A group of coordinately regulated structural genes along with the promoter and operator sites that control their transcription.
What is pre-transcriptional regulation?
Control of gene expression in bacteria before the transcription process begins.
What is a mutation?
A change in the nitrogenous base sequence of DNA.
What types of mutations can occur?
Base substitutions, deletions (frameshift), and nonsense mutations.
What is a mutagen?
An agent in the environment that causes permanent changes in DNA.
What is the Ames test?
A test used to identify possible chemical carcinogens by observing mutations in bacteria.
What is horizontal gene transfer?
Transfer of genetic material from one organism to another that is not offspring.
What is vertical gene transfer?
Transmission of genetic material from parent to offspring.
What are plasmids?
Self-replicating circular DNA molecules carrying non-essential genes.
What are transposons?
Segments of DNA that can move from one location to another within the genome.
What is transformation in bacteria?
The process of transferring genes as 'naked' DNA in solution.
What is conjugation in bacteria?
A process requiring contact between living cells for genetic material transfer.
What is transduction in bacteria?
A process in which bacteriophages carry DNA from one bacterium to another.
How do mutations and recombination contribute to evolution?
They provide genetic diversity, which is essential for natural selection.
What is the function of ribosomes in translation?
Ribosomes facilitate the translation of the mRNA into a polypeptide.
What role do tRNA molecules play in protein synthesis?
They carry specific amino acids to the ribosome and match their anticodons to the mRNA codons.
What is the leading strand in DNA replication?
The strand that is synthesized continuously toward the replication fork.
What is the lagging strand in DNA replication?
The strand that is synthesized discontinuously away from the replication fork.
How does DNA polymerase contribute to DNA replication?
It synthesizes new DNA strands and proofreads the new DNA for accuracy.
What is the significance of the promoter in gene expression?
The promoter is the region where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription.
What defines a constitutive gene?
A gene that is expressed at a fixed rate, regardless of environmental conditions.
Describe the function of a corepressor in gene regulation.
A corepressor assists the repressor protein in binding to the operator to inhibit transcription.
What is a missense mutation?
A mutation that results in a different amino acid being incorporated into a protein.
What is a nonsense mutation?
A mutation that creates a stop codon in place of an amino acid codon.
What does it mean for a mutation to be neutral?
The mutation has no significant effect on the organism's fitness.
How does the ribosome terminate translation?
Translation ends when the ribosome reaches a stop codon on the mRNA.
What is the result of crossing over during genetic recombination?
Genes from two chromosomes are combined into one chromosome with genes from each original chromosome.
What is the function of the operator in an operon?
The operator is a regulatory sequence that controls the binding of RNA polymerase.
How are microRNAs involved in gene regulation?
They bind to mRNA and promote its degradation, preventing translation.
A gene is defined as:
-the RNA product of a transcribed section of DNA
-a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that codes for a functional product
-a sequence of nucleotides in RNA that codes for a functional product
-any random segment of DNA
a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that codes for a functional product
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
-DNA ligase -joins segments of DNA
-RNA polymerase -makes a molecule of RNA from an RNA template
-DNA polymerase-makes a molecule of DNA from a DNA template
-DNA gyrase-relaxes supercoiling in DNA ahead of the replication fork
RNA polymerase -makes a molecule of RNA from an RNA template
DNA is constructed of
-two stands of nucleotides running in an antiparallel configuration
-a single stand of nucleotides with internal hydrogen bonding
-none of the answers is correct
-two complementary strands of nucleotides bonded A-C and G-T
two stands of nucleotides running in an antiparallel configuration
Which of the following is NOT a product of transcription?
-mRNA
-rRNA
-a new strand of DNA
-tRNA
a new strand of DNA
An enzyme produced in response to the presence of a substrate is called a(n)
-restriction enzyme
-promoter
- repressible enzyme
-inducible enzyme
inducible enzyme
Transformation is the transfer of DNA from a donor to a recipient cell
-by crossing over
-by cell-to-cell contact
-as naked DNA in solution
-y sexual reproduction
as naked DNA in solution
Genetic change in bacteria can be brought about by
-conjugation
- transduction
-transformation
-all of the answers are correct
all of the answers are correct
According to the operon model, for the synthesis of an inducible enzyme to occur the
-repressor must not be synthesized
-substrate must bind to the repressor
-repressor must bind to the operator
-end-product must be in excess
substrate must bind to the repressor
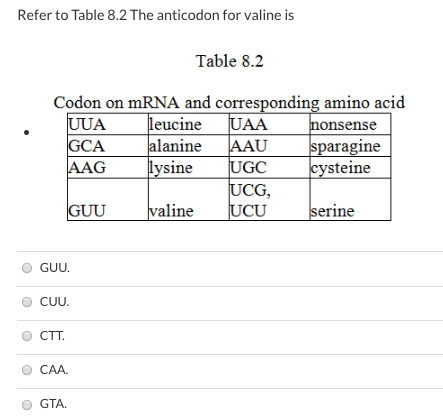
CAA
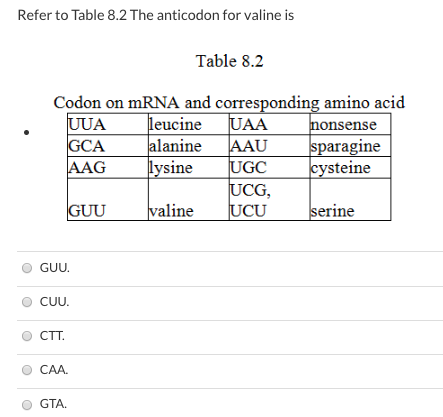
Refer to Table 8.2. If an indeterminate frameshift mutation occurred (that is , one random location) the sequence of bases shown below, what would be the sequence of amino acids coded for? 3’ ATTACGCTTTGC 5’
-asparagine-arginine-lysine-alanine
- asparagine- cysteine-valine-serine
-leucine-arginine-lysine-alanine
-The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided
The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided
Conjugation differs from reproduction because conjugation
-transcribes DNA to RNA
-transfers DNA horizontally, to nearby cells without those cells undergoing replication
-copies RNA to make DNA
-replicates DNA
transfers DNA horizontally, to nearby cells without those cells undergoing replication
The necessary ingredients for DNA synthesis can be mixed together in a test tube. The DNA polymerase is from Thermus aquaticus, and the template is from a human cell. The DNA synthesized would be most similar to
human DNA
aquaticus DNA
human RNA
a mixture of human and aquaticus DNA
human DNA