Lab Notes: Histology, Epithelial Tissue, and the Integumentary System
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
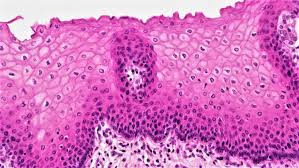
Epithelial tissues
Acts as a protective cover for body surfaces, involved in secretion and absorption.
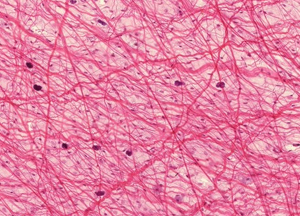
Connective tissues
Provides support, binds other tissues, and stores energy.
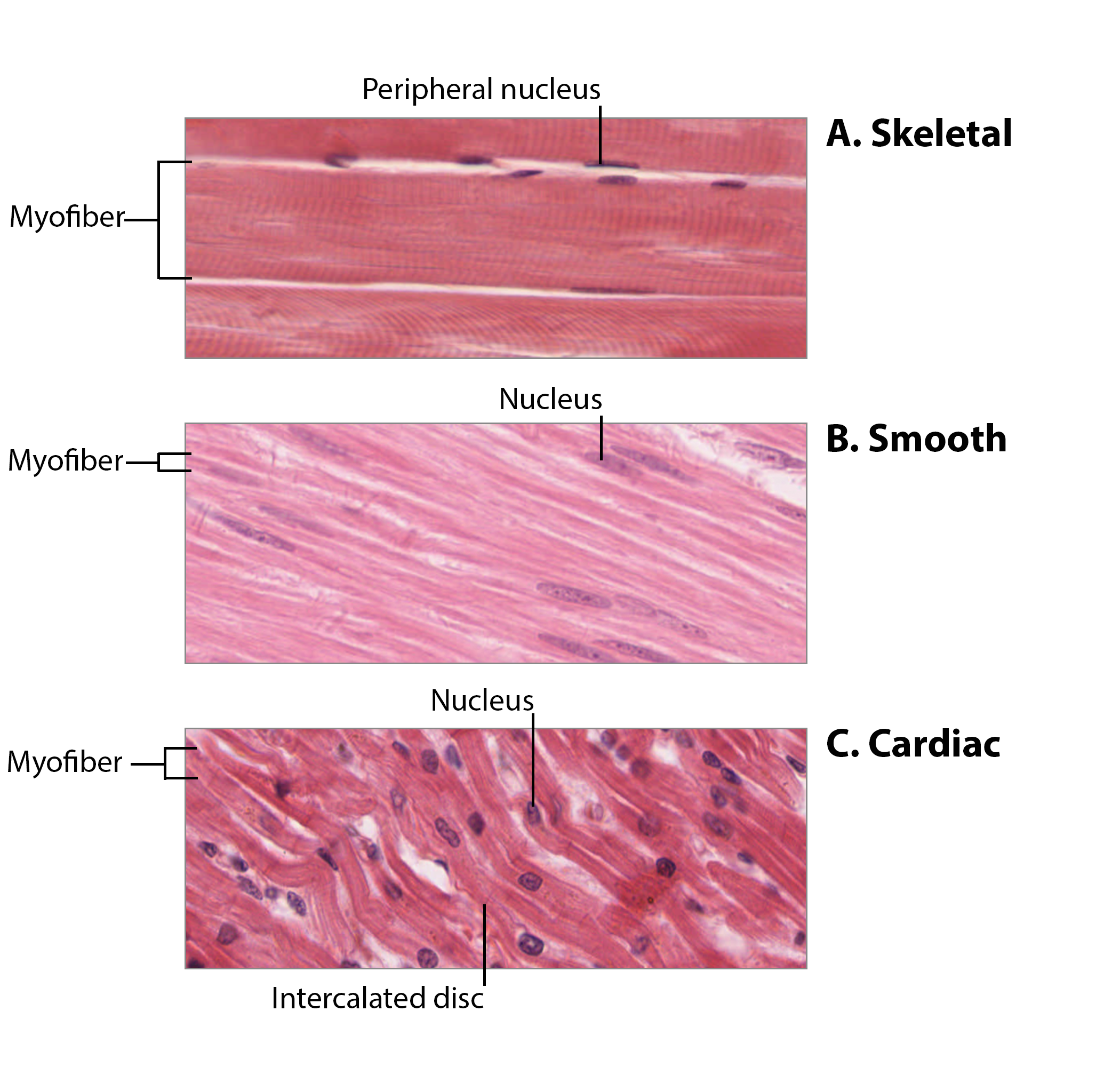
Muscle tissues
Essential for movement, includes smooth muscle (involuntary), skeletal muscle (voluntary), and cardiac muscle (involuntary).
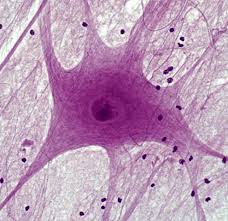
Nervous tissues
Comprised of excitable cells (neurons) and supportive cells (neuroglia) that communicate through electrical signals.
Secretion
Produces and releases substances such as enzymes and hormones.
Protection
Acts as a barrier to protect underlying tissues from injury and pathogens.
Absorption
Absorbs nutrients and substances in areas like the intestines.
Sensation
Contains sensory nerve endings that alert the body to stimuli.
Filtration
Involved in the selective permeability of substances, such as in renal tubules.
Squamous
Flat cells that facilitate diffusion and filtration.
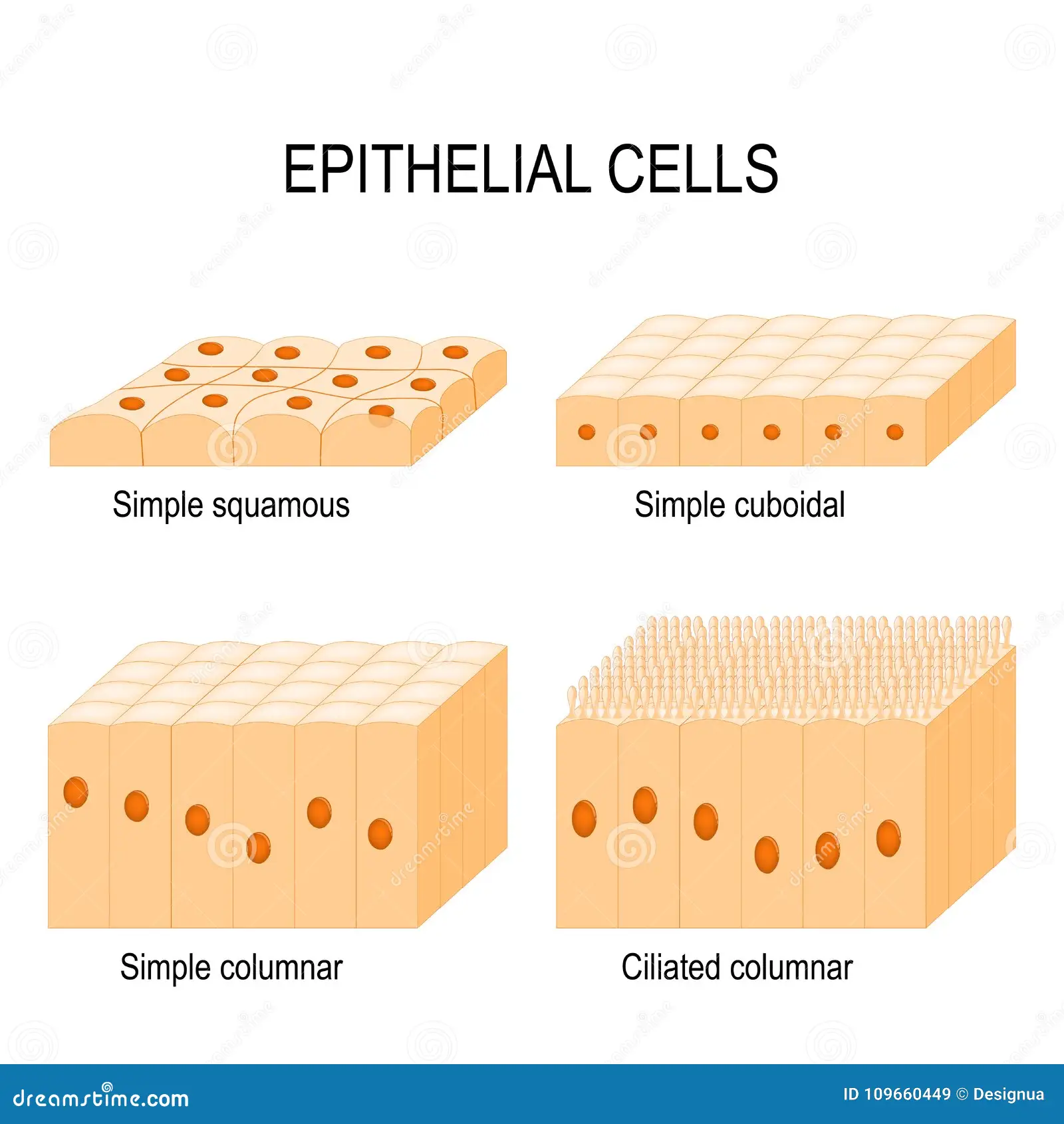
Cuboidal
Cube-shaped cells typically involved in secretion and absorption.
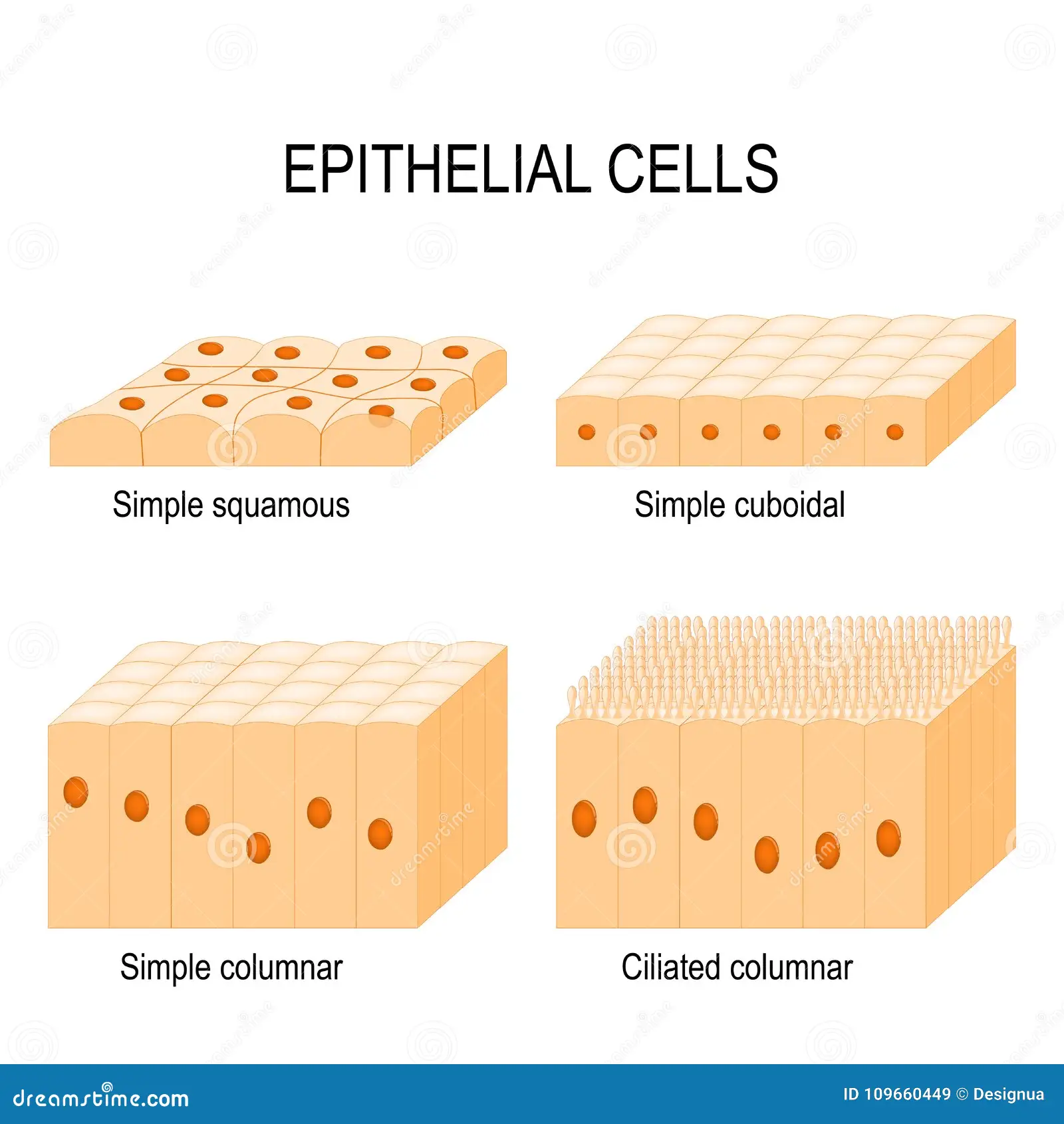
Columnar
Tall column-like cells involved in absorption and secretion; often contain cilia or microvilli.
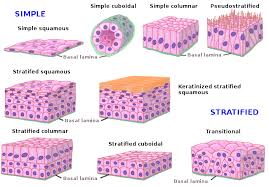
Simple Epithelia
Single cell layer; typically provides filtration and absorption, found lining organs.
Stratified Epithelia
Multiple cell layers that offer protection against abrasion, located in areas subject to friction.
Simple Squamous : Characteristics
Single layer of flat cells facilitating diffusion and filtration.
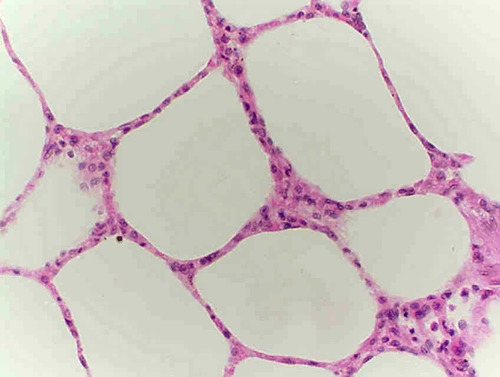
Simple Cuboidal : Characteristics
Single layer of cube-shaped cells with centrally located nucleus.
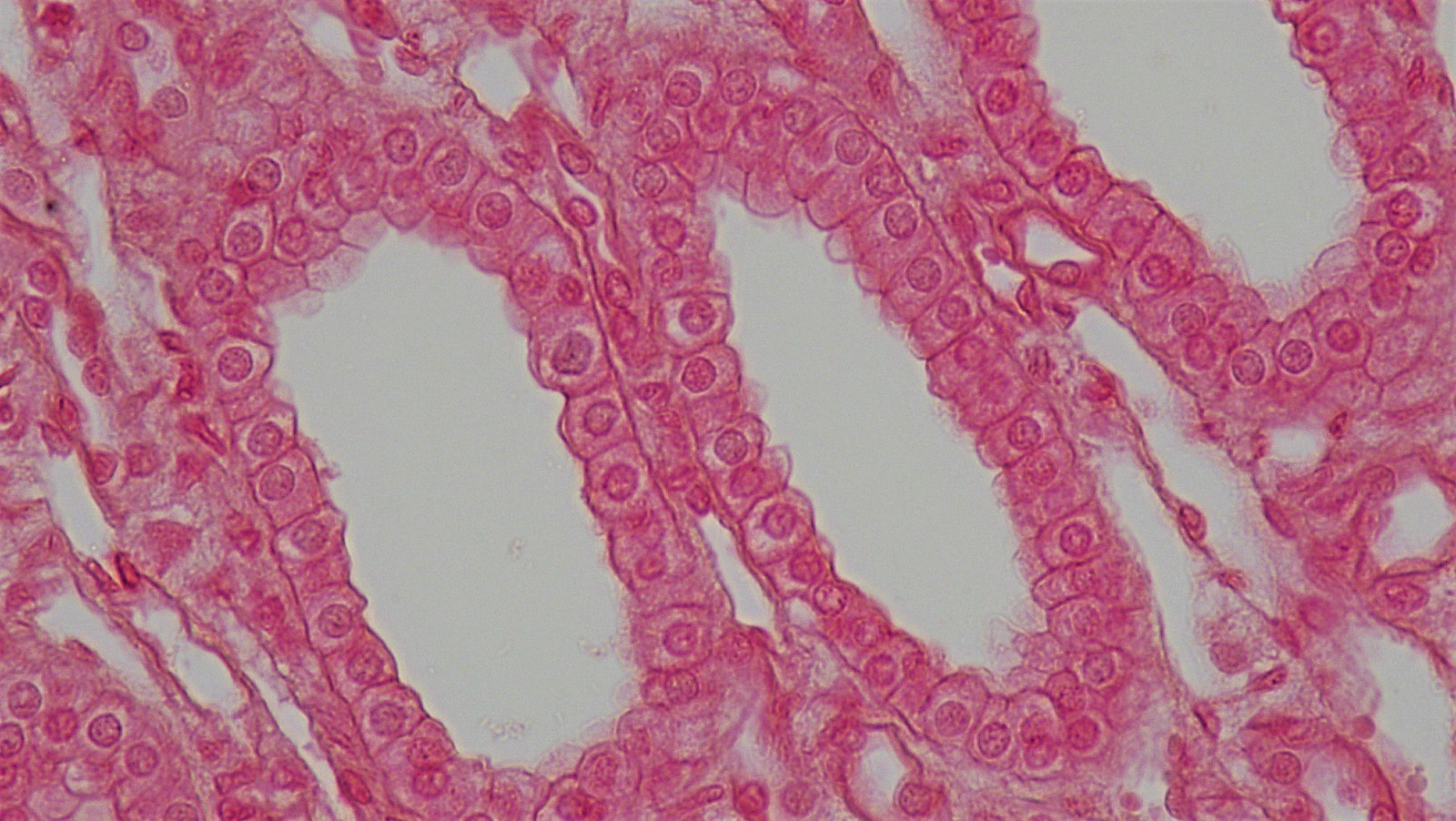
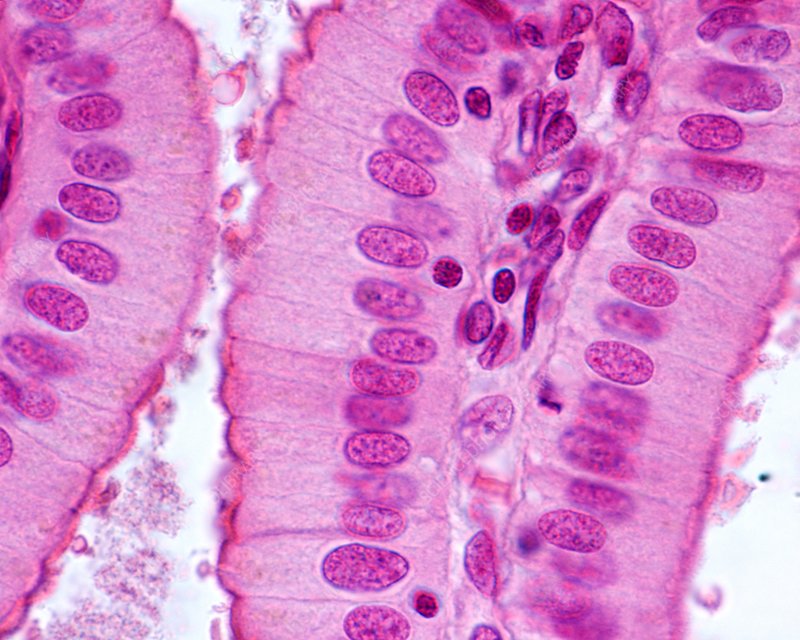
Simple Columnar : Characteristics
Single layer of columnar cells, which may have goblet cells that produce mucus.
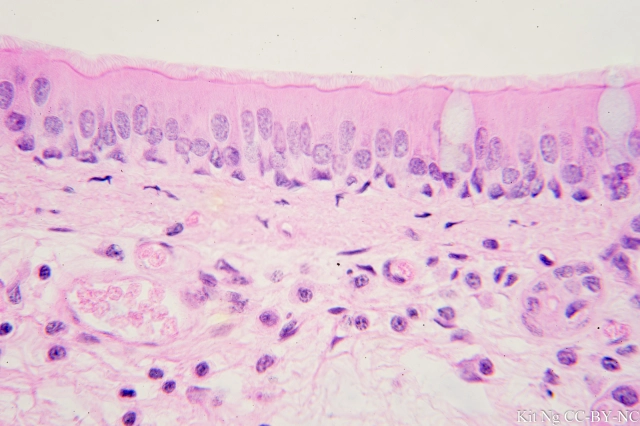
Pseudostratified Columnar Characteristics
Appears stratified but is actually a single layer of cells with varying heights; all cells are attached to the basement membrane.
Stratified Squamous : Characteristics
Multiple layers of flat cells; keratinized cells on skin surface, non-keratinized in moist linings.
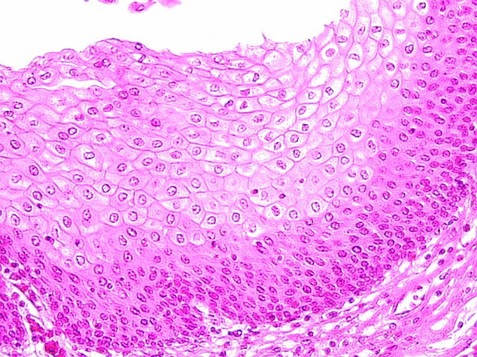
Stratified Cuboidal : Characteristics
Multiple layers of cube-shaped cells, usually two layers.
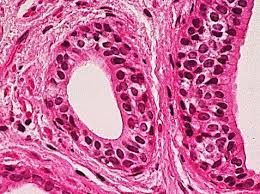
Stratified Columnar Characteristics
Multiple layers with cuboidal cells at the base and columnar cells at the top.
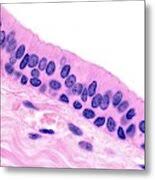
Transitional: Characteristics
Multiple layers that can stretch and relax, accommodating fluctuations in volume.
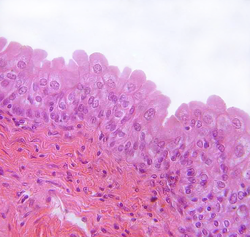
Exocrine Glands: Function
Glands that secrete substances onto the skin surface or into hollow organs through ducts
Exocrine Glands: Examples
Sweat glands release sweat; salivary glands release saliva during digestion.
endocrine glands
Glands that release hormones directly into the bloodstream,
Endocrine Glands: Examples
The pancreas secretes insulin; adrenal glands release cortisol during stress.
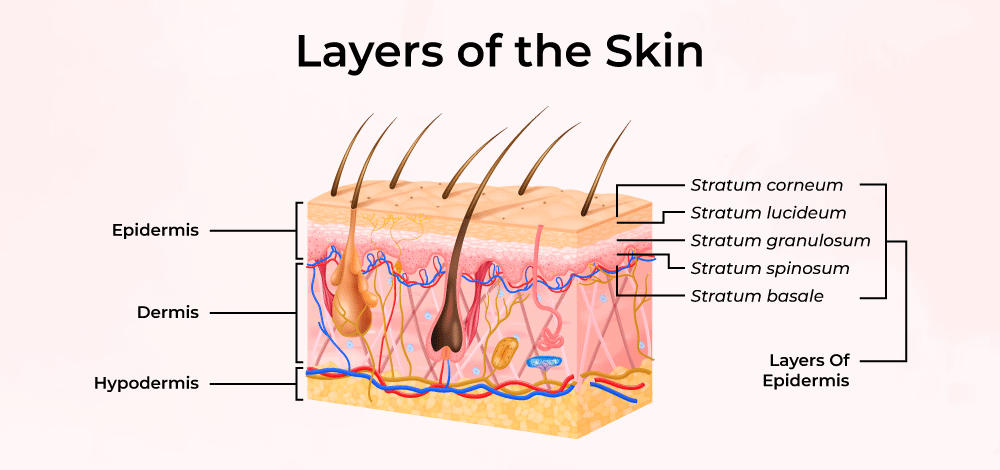
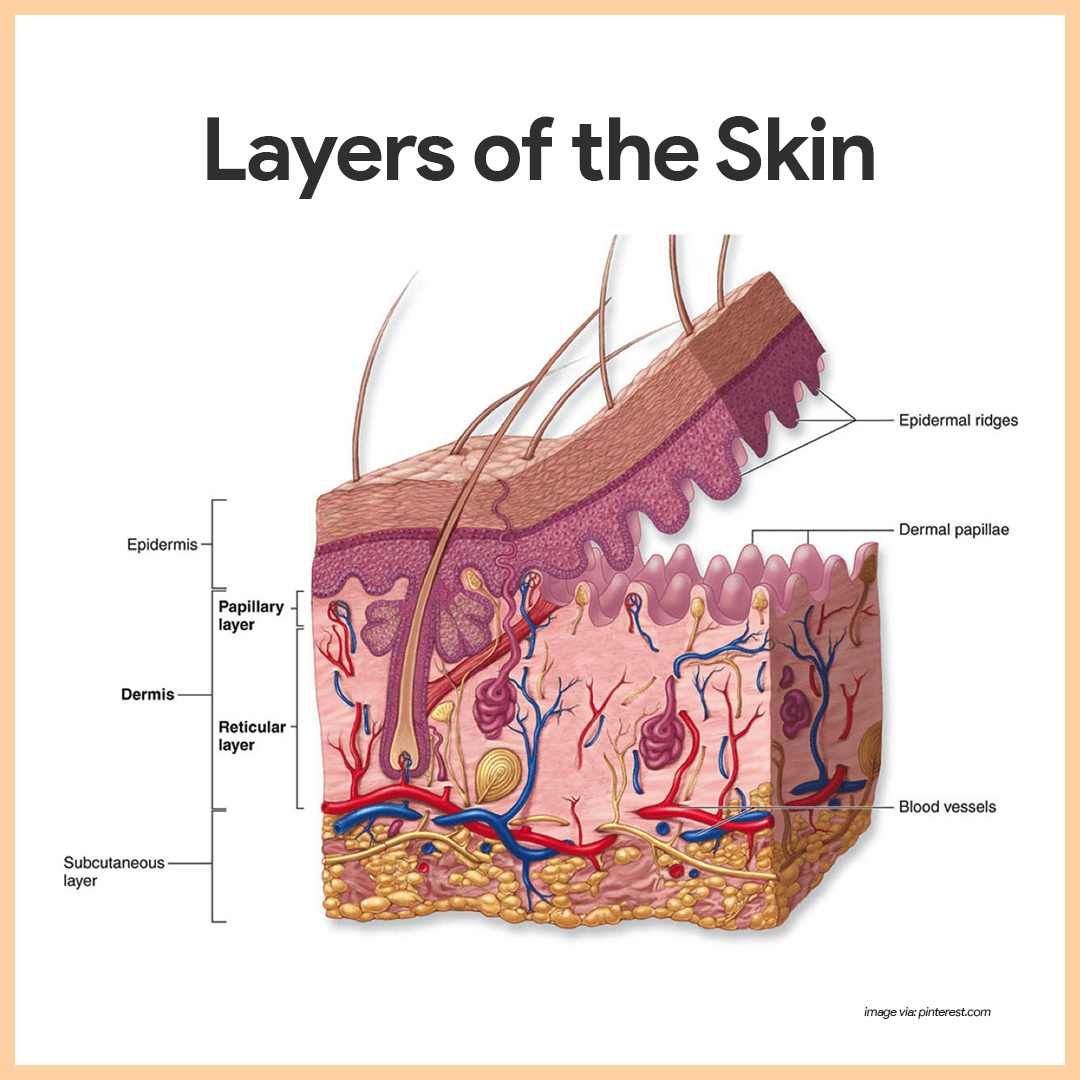
Epidermis: Structure
The outermost layer composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, crucial for protection and waterproofing.
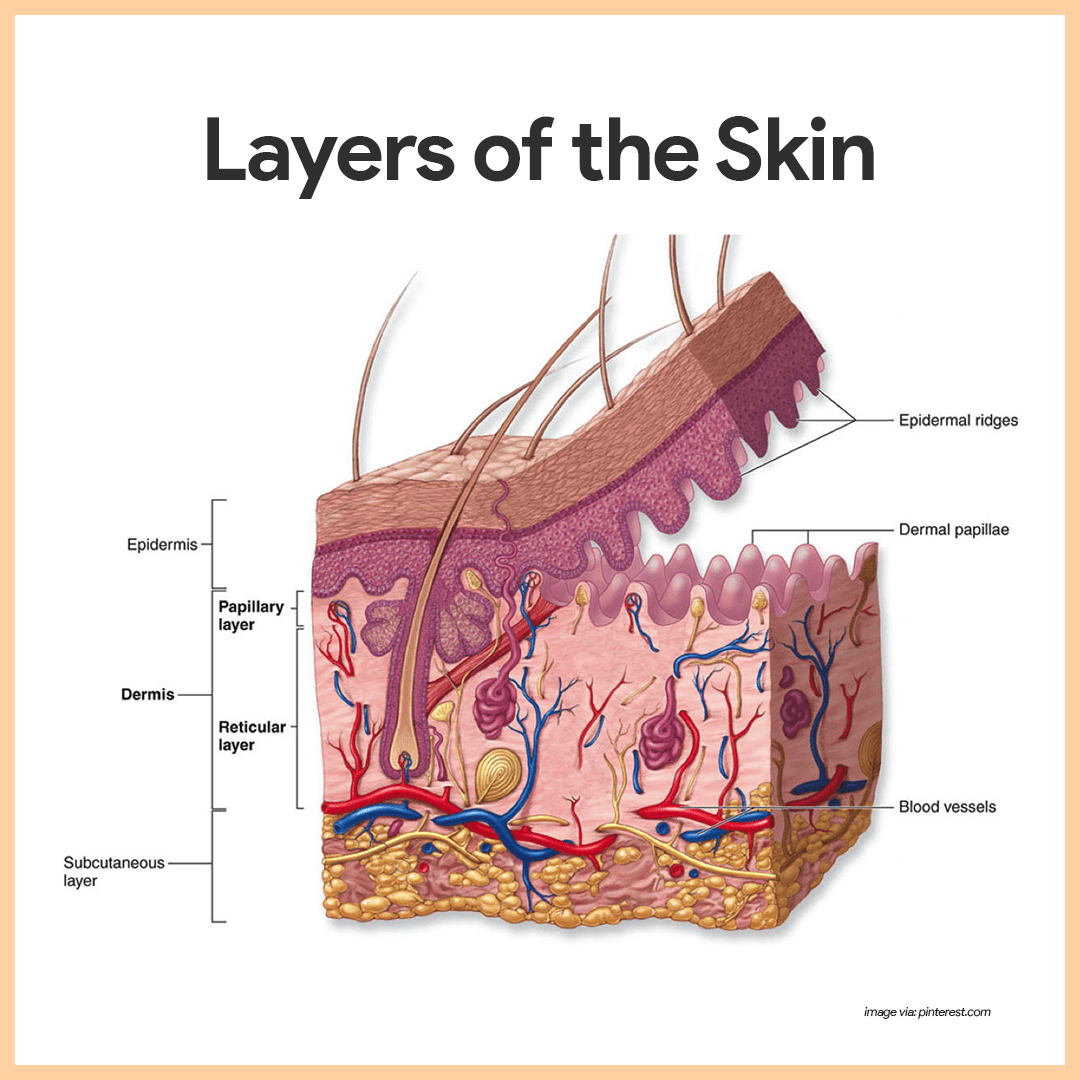
Dermis
The layer beneath the epidermis, rich in blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue, contributing to skin elasticity and strength.
Hypodermis
The deepest layer mainly made of adipose tissue and loose connective tissue, providing insulation, energy storage, and cushioning.
Stratum Corneum
Outermost layer made of dead, flattened keratinized cells providing a tough barrier to environmental threats.
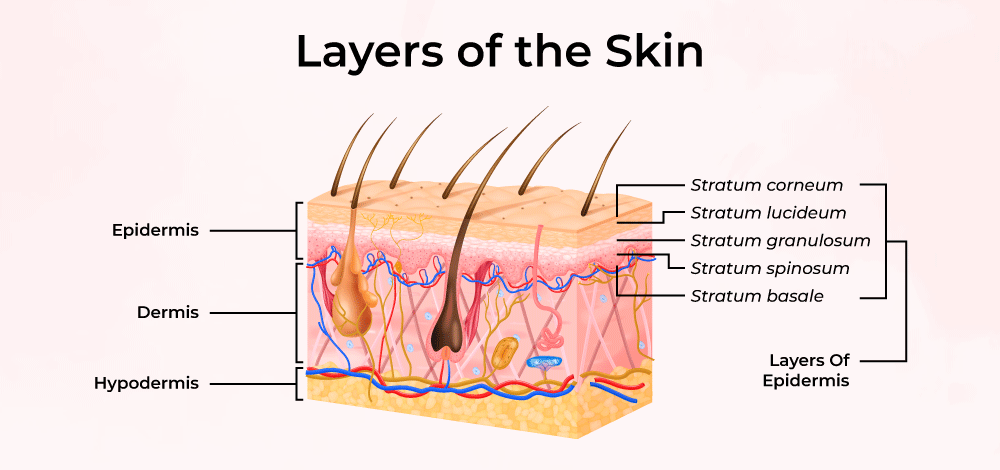
Stratum Granulosum
Contains keratinocytes filled with keratohyalin granules that begin keratinization, contributing to waterproofing.
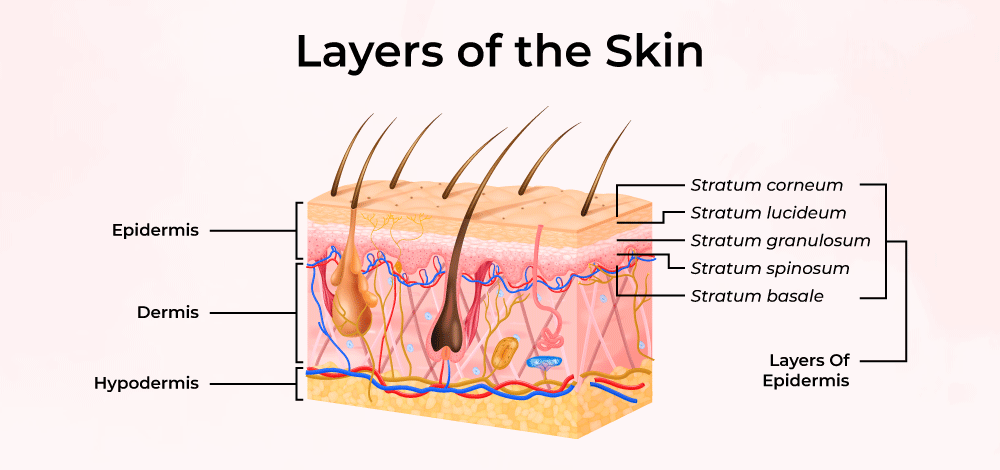
Stratum Spinosum
Known for its spiny appearance due to desmosomal connections between keratinocytes, providing strength and flexibility.
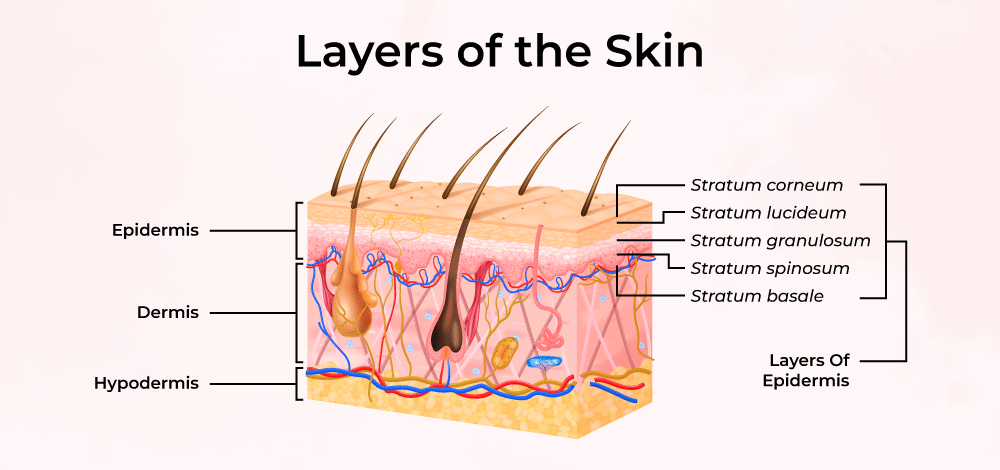
Stratum Basale
Deepest layer where mitotically active stem cells divide and generate new keratinocytes, includes melanocytes and Merkel cells for sensation.
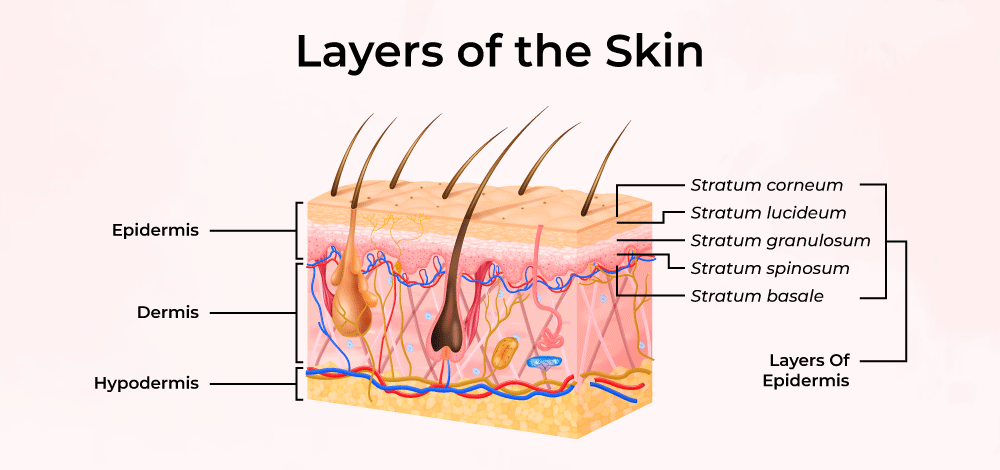
Stratum Lucidum
Thin translucent layer found only in thick skin (palms and soles), providing additional protection.
Keratinocytes
Predominant cell type producing keratin, essential for the skin's protective barrier against environmental damage.
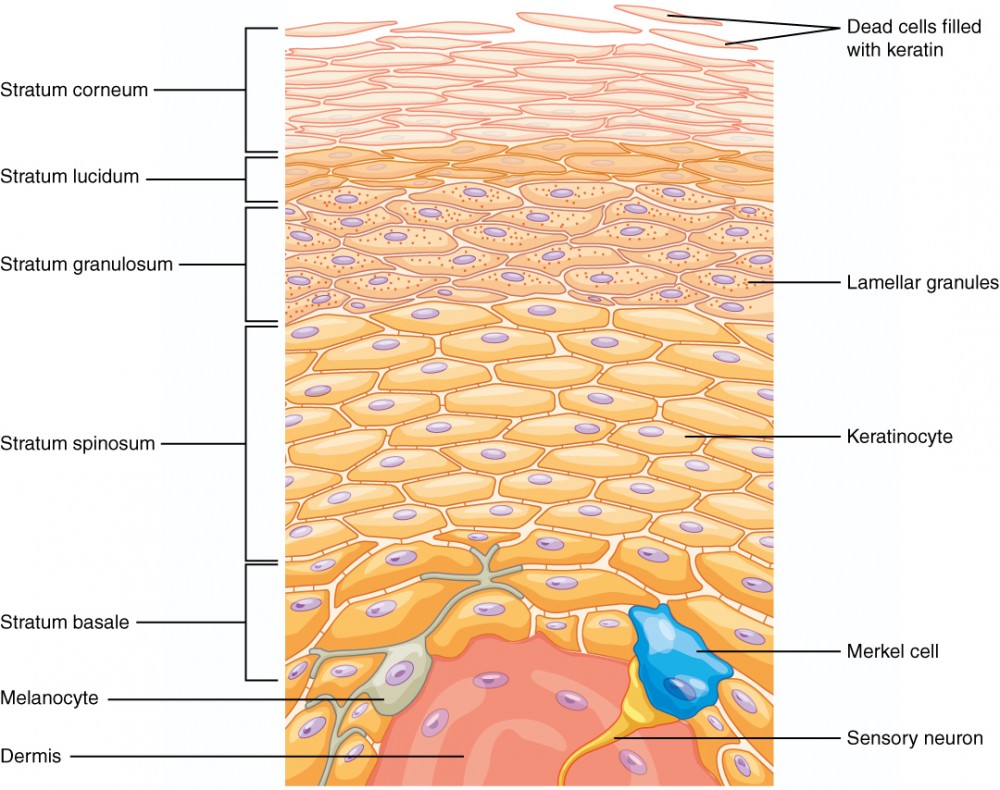
Melanocytes
Responsible for producing melanin, which contributes to skin color and provides UV protection.
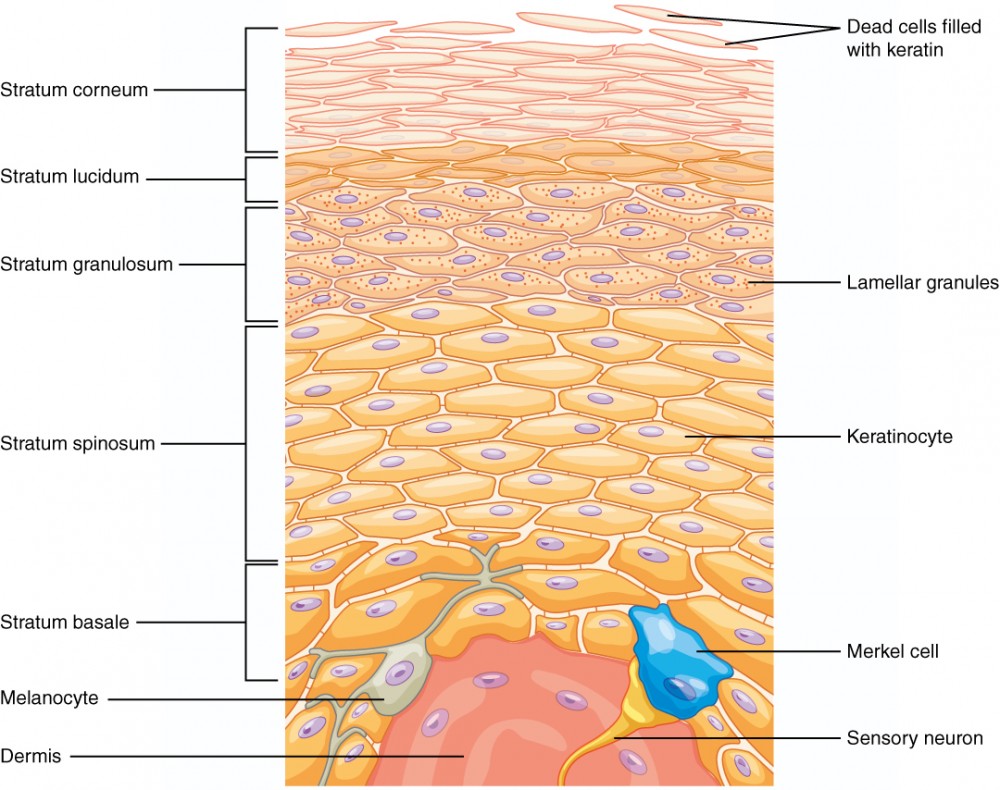
Langerhans Cells
Antigen-presenting cells that play a crucial role in the immune response of the skin.
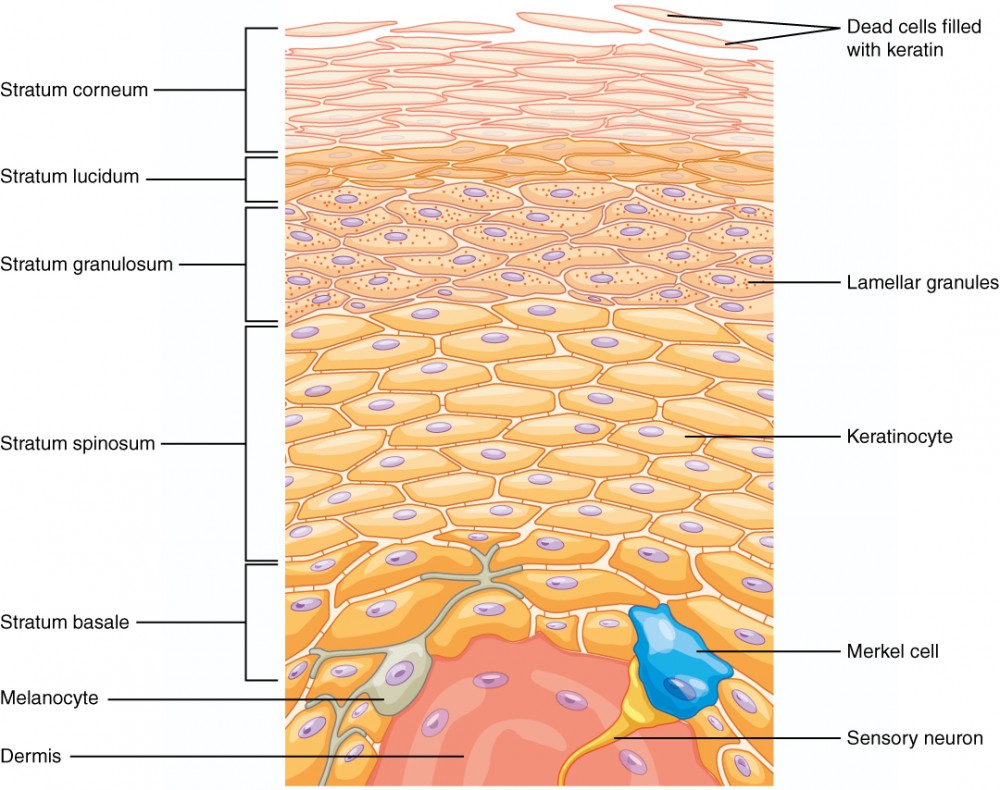
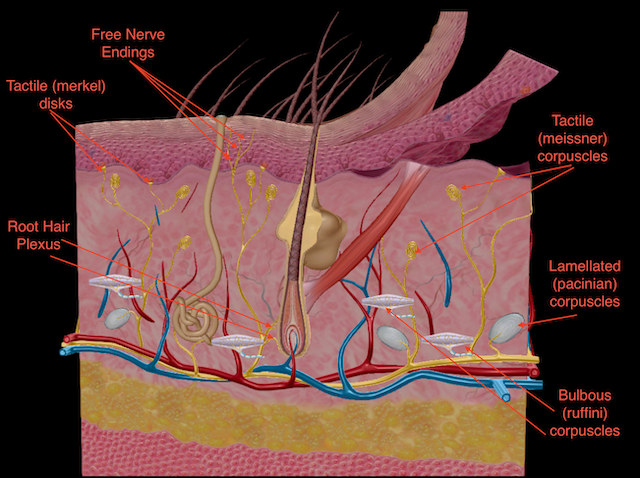
Merkel Cells
Sensory cells transmitting touch sensations, associated with nerve endings.
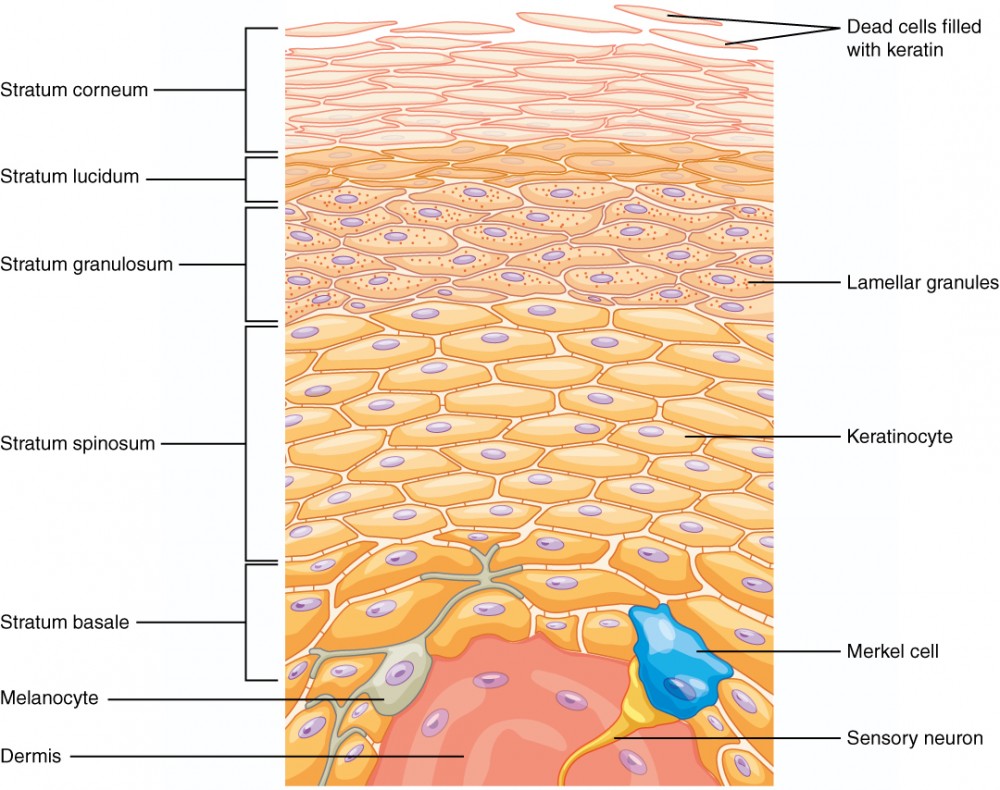
Papillary Layer
Composed of loose connective tissue; contains dermal papillae that project into the epidermis, increasing surface area for exchange of gases and nutrients; contains tactile corpuscles for light touch.
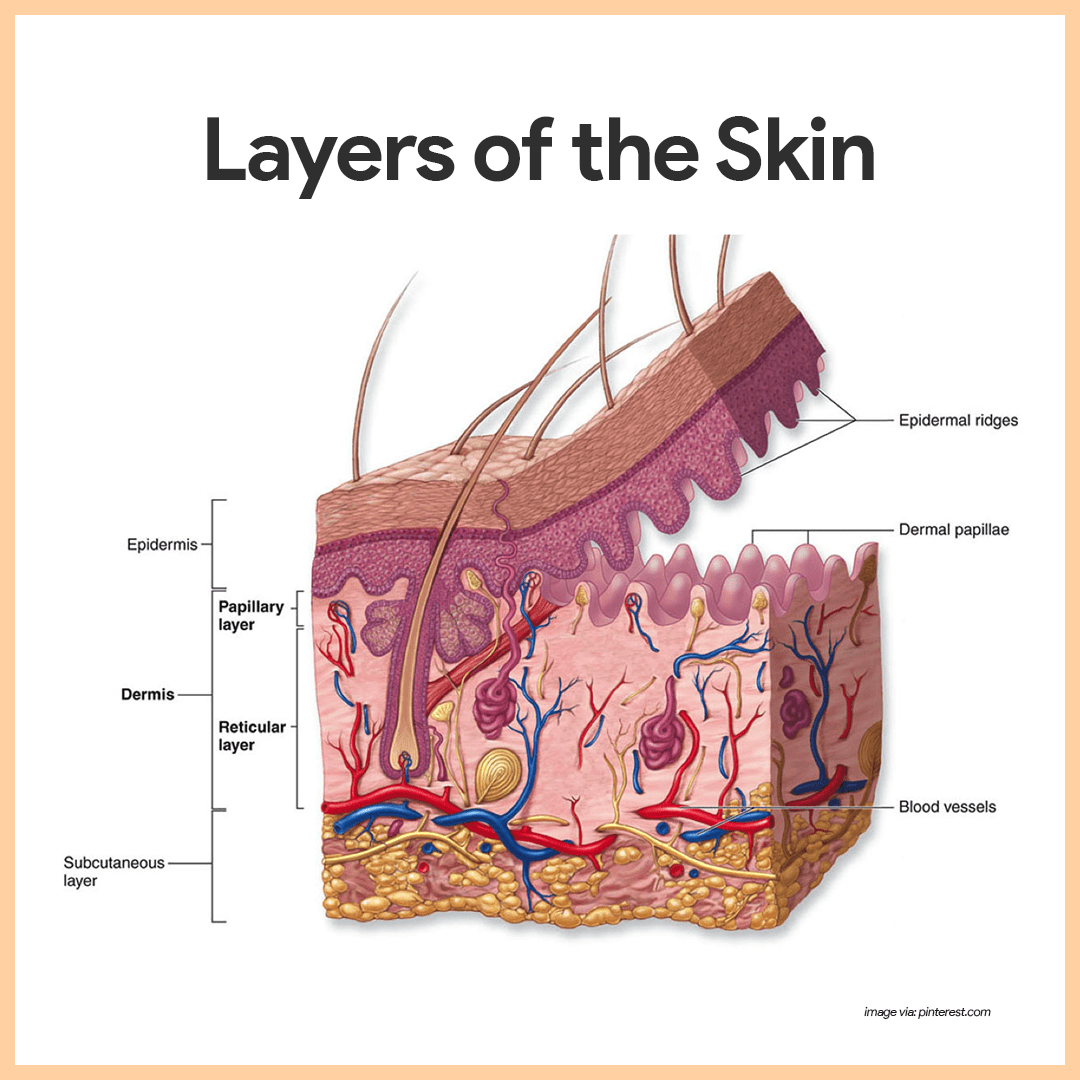
Reticular Layer
Denser layer of irregular connective tissue; contains larger blood vessels, nerves, and deeper receptors, providing strength and elasticity to the skin.
Meissner’s Corpuscles
Sensitive to light touch and vibration, located in the papillary layer.
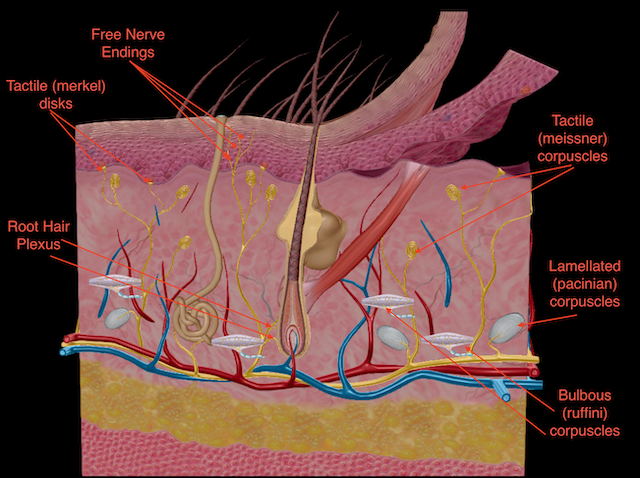
Pacinian Corpuscles
Sensitive to deep pressure and vibration, located in the reticular layer.
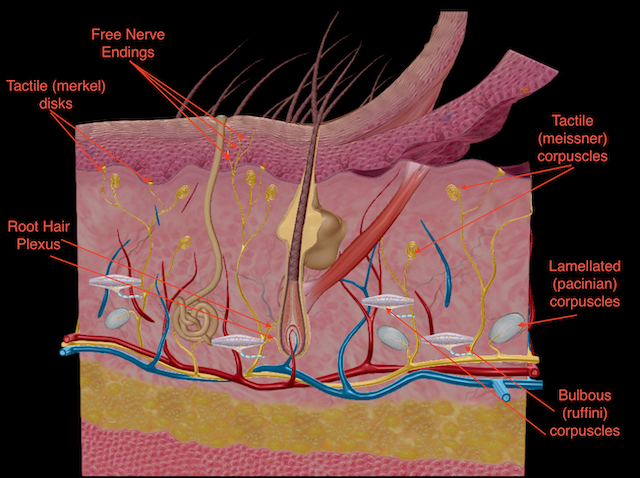
Free Nerve Endings
Responsible for sensing pain, temperature, itch, and tickle sensations; prevalent throughout the dermis and epidermis.
Simple columnar: ciliated location
lining of bronchi, uterine tubes, and part of uterus
Simple columnar: Non-Ciliated
lining of digestive tract, gall bladder, gland and excretory ducts
Pseudostratified columnar: ciliated
lining of the trachea, upper respiratory tract
Pseudostratified columnar: Non-ciliated
lining of the male reproductive ducts
Stratified squamous: Keratinized
Epidermis
Stratified squamous: Non-keratinized
lining of esophagus, lining of mouth lining of vagina, cornea
Simple squamous
lining of the renal glomeruli, lung alveoli, heart, circulatory vessels, lymphatic vessels
Simple squamous
permeable, allowing small molecules to pass through quickly, lining areas where gases diffuse passively
simple cuboidal
renal collecting tubule walls, small gland ducts, surface of the ovaries
simple cuboidal
found wherever secretion and absorption functions are needed within the body
simple columnar
secretes and absorbs substances into or out of the organs, some have cilia to increase surface area
pseudostratified columnar
protects the body from foreign particles, secretes mucus, and helps with absorption
stratified squamous
found in areas of the body that experience high mechanical stress and friction.
stratified cuboidal
sweat gland ducts, mammary gland duct, salivary gland ducts
stratified cuboidal
in ducts exposed to mechanical stress and secretion demands, protecting the walls of ducts
stratified columnar
male urethra, pharynx, glandular ducts
stratified columnar
found in areas requiring both protection and secretion
transitional
lining of the bladder, ureters, part of the urethra
transitional
lines organs subjected to distension and contraction