Waves and optics - AQA A-Level Physics
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Transverse waves
Particle oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer
Longitudinal waves
Particle oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer
Progressive waves
Waves that transfer energy through a medium
Mechanical waves
Particle oscillations in a physical medium
Polarisation
Passing a transverse wave through a polaroid filter, allowing oscillations to only occur in one plane perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
Why can’t longitudinal waves be polarised?
Because oscillations are strictly parallel to wave propagation
Law of reflection
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
Refraction
The change in direction of a wave when part of the wave-front speeds up or slows down before the rest of it.
Diffraction
The spreading out of a wave as it passes through a gap
How can maximum diffraction be obtained?
By making the gap size similar to the wavelength
Superposition
The displacement of two waves is combined as they overlap each other.
Phase difference
The difference in the point of a cycle between two points on a wave or two waves.
Path difference
The difference in distance travelled between two coherent waves from their sources to the point they meet at.
How could you tell that two waves will constructively interfere by their path difference?
If the path difference is equal to a multiple of their wavelength
Constructive interference
Reinforcement - path difference is a whole number of wavelengths
Stationary waves
Produced by two progressive waves of the same frequency and amplitude travelling in opposite directions superposing.
Coherent
Having the same frequency, amplitude and a constant phase difference
Anti-node
Maximum displacement
Nodes
No displacement
Destructive interference
Cancellation - path difference is an odd number of half wavelengths
Describe the interference pattern seen when passing monochromatic light through a double slit
A pattern of light and dark fringes, with equidistant fringe separation
Describe the interference pattern seen when passing white light through a double slit
A central white maximum and coloured fringes, with the shortest wavelength (violet) closest to the maximum and the longest wavelength (red) furthest away
Describe the fringe pattern seen when passing monochromatic light through a single slit
A wide, intense central maxima and light fringes of decreasing intensity
Diffraction grating
A plate of many closely spaced slits
Describe the fringe pattern produced by passing monochromatic light through a diffraction grating
A pattern of light and dark fringes, similar to the pattern seen in a double slit arrangement, but sharper and brighter
How can we find the maximum n order number in a pattern from a diffraction grating
Take θ as 90° and round down to the nearest whole number
What is grating spacing equivalent to?
1/number of slits per m (d=1/n)
Refractive index
Measure of bending of a light ray when it passes from one medium into another
What is the refractive index of air?
1
Snell’s law
n1 sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2
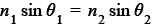
Critical angle
The angle of incidence in a dense medium, which results in the angle of refraction in the less dense medium being 90°
What are the two conditions for total internal reflection to occur?
The incident ray must be travelling into a less optically dense medium
The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle
What is the effect on the critical angle in a medium with a greater refractive index?
A smaller critical angle
Why is it important to minimise signal absorption in an optical fibre?
To minimise the reduction in ampltiude and signal intensity, which may distort the information in the final pulse
What does dispersion in an optical fibre cause?
Pulse broadening, which is where the received rays are broader than the original transmitted signal. These broader signals can overlap, causing loss of data.
What is material dispersion in an optical fibre?
The dispersion of the different wavelengths of light due to them travelling at different speeds, causing pulse broadening.
What is modal dispersion in an optical fibre?
Light pulses from monochromatic light will spread out due to each light pulse having a different incident angle and therefore also having a different angle of reflection.