Chapter 3.2: Cell Organelles
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What are the two components of the cytoskeleton mentioned, and what general roles do they play in a cell?
Microtubules and microfilaments; provide support and shape, anchor and transport organelles, add strength, and aid in cell division and movement.
What is the primary function of the nucleus?
Stores the cell's DNA and houses the nucleolus which makes ribosomes.
What are nuclear pores?
Openings in the nuclear envelope that regulate transport into and out of the nucleus.
What surrounds the nucleus and what is its membrane organization?
A double membrane called the nuclear envelope.
What is the nucleolus responsible for?
Producing ribosomes (rRNA and ribosomal proteins).
How is the Endoplasmic Reticulum described and what are its main products?
Described as maze-like passages; produces proteins and lipids.
What do SER and RER specialize in?
SER synthesizes lipids; RER synthesizes proteins.
What is formed when the ER pinches off to transport products?
Vesicles.
Where can ribosomes be located within the cell?
On the rough endoplasmic reticulum or free in the cytoplasm.
What are ribosomes made of?
Proteins and RNA.
What is the primary function of ribosomes?
Link amino acids to form proteins.
What is the Golgi apparatus and what does it do to proteins?
Stacks of membranes where proteins are processed, sorted, and packaged for delivery.
Why is the Golgi apparatus compared to UPS?
Because it processes and ships proteins to their destinations.
What are vesicles and what is their role?
Small sacs that store or transport materials; pinch off from the ER or Golgi to move materials around the cell.
What is the mitochondrion the site of, and what energy process occurs there?
Site of cellular respiration; converts nutrients into ATP.
Do mitochondria have their own genetic material and ribosomes?
Yes; they have their own DNA and ribosomes.
What theory do mitochondria support?
Endosymbiotic Theory.
What is the site of photosynthesis?
Chloroplasts.
What is the general chemical equation for photosynthesis as given in the notes?
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2.
What structures within chloroplasts contain chlorophyll?
Thylakoids.
Do chloroplasts have their own ribosomes and DNA?
Yes; they have their own ribosomes and DNA, supporting Endosymbiotic Theory.
What is the function of vacuoles?
Storage for water, ions, enzymes, carbohydrates, and lipids; plant vacuoles provide turgor support.
What is special about plant cells' central vacuole?
Plants have a large central vacuole that provides structural support.
What are lysosomes and what do they do?
Organelles pinched off from the Golgi that contain enzymes; defend against bacteria/viruses and recycle old cell parts.
Where do lysosomes come from and what is one of their key roles?
Derived from the Golgi; contain enzymes that recycle old cell parts and defend against invaders.
What is the centrosome and what is its function in cells?
In the cytoplasm; produces microtubules.
Do animal cells have centrioles, and are they found in plant cells?
Animal cells have centrioles; plant cells generally do not.
What is the cell wall made of and which organisms have cell walls?
Made of cellulose; found in plants, fungi, and bacteria.
What feature of the cell wall allows materials to enter the cell?
Openings or pores in the cell wall.
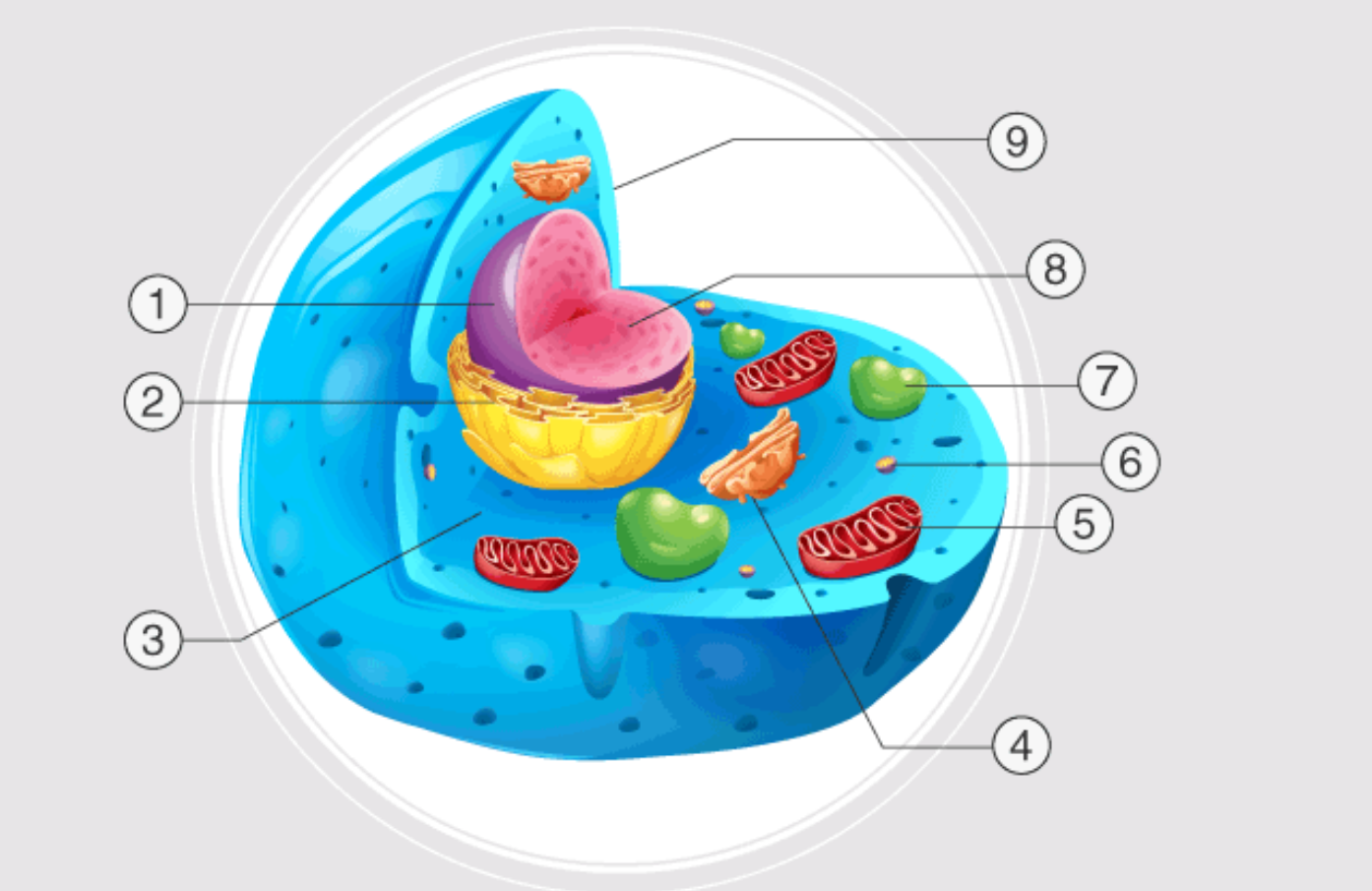
1
nucleus
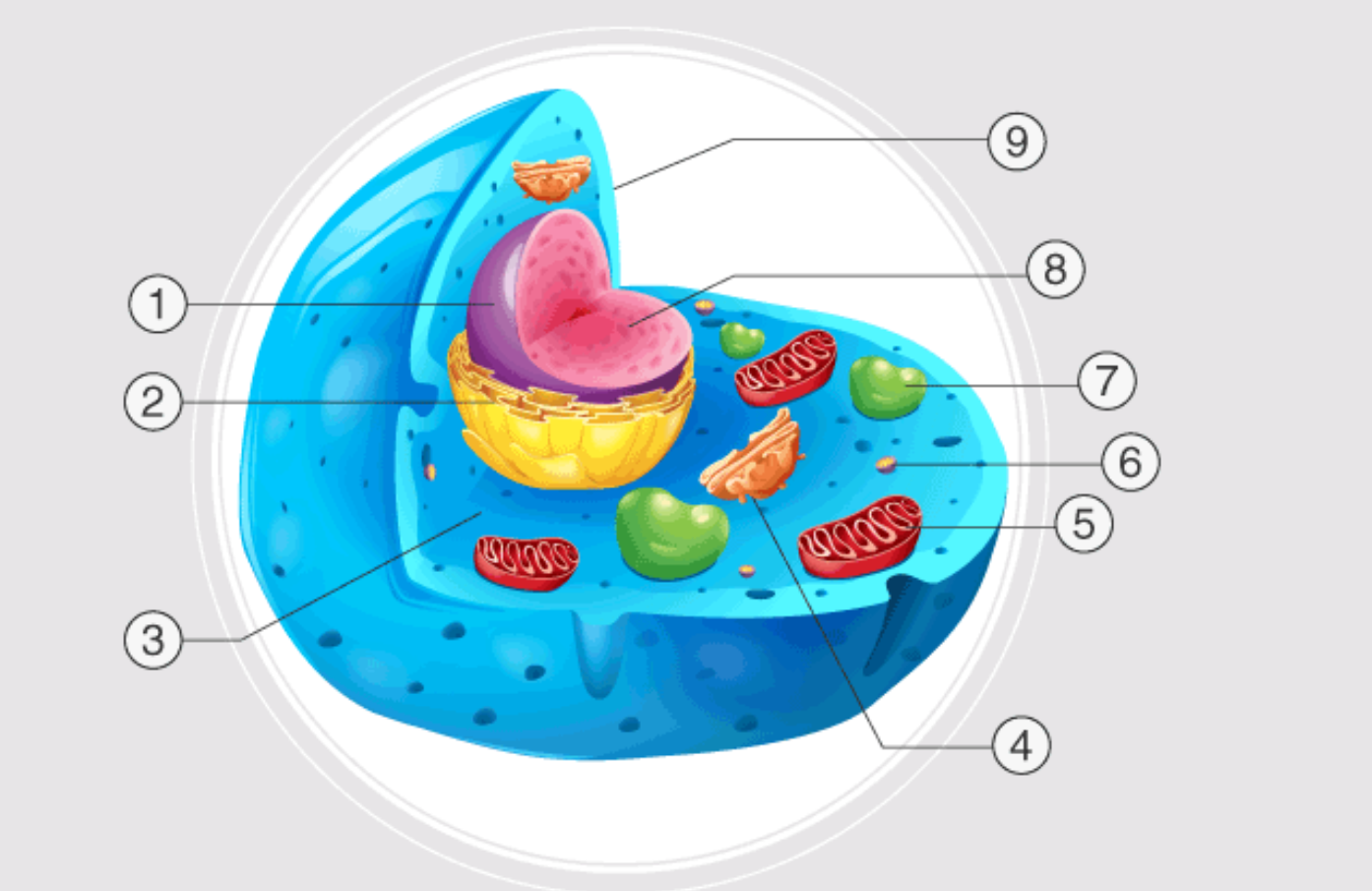
2
endoplasmatic reticulum
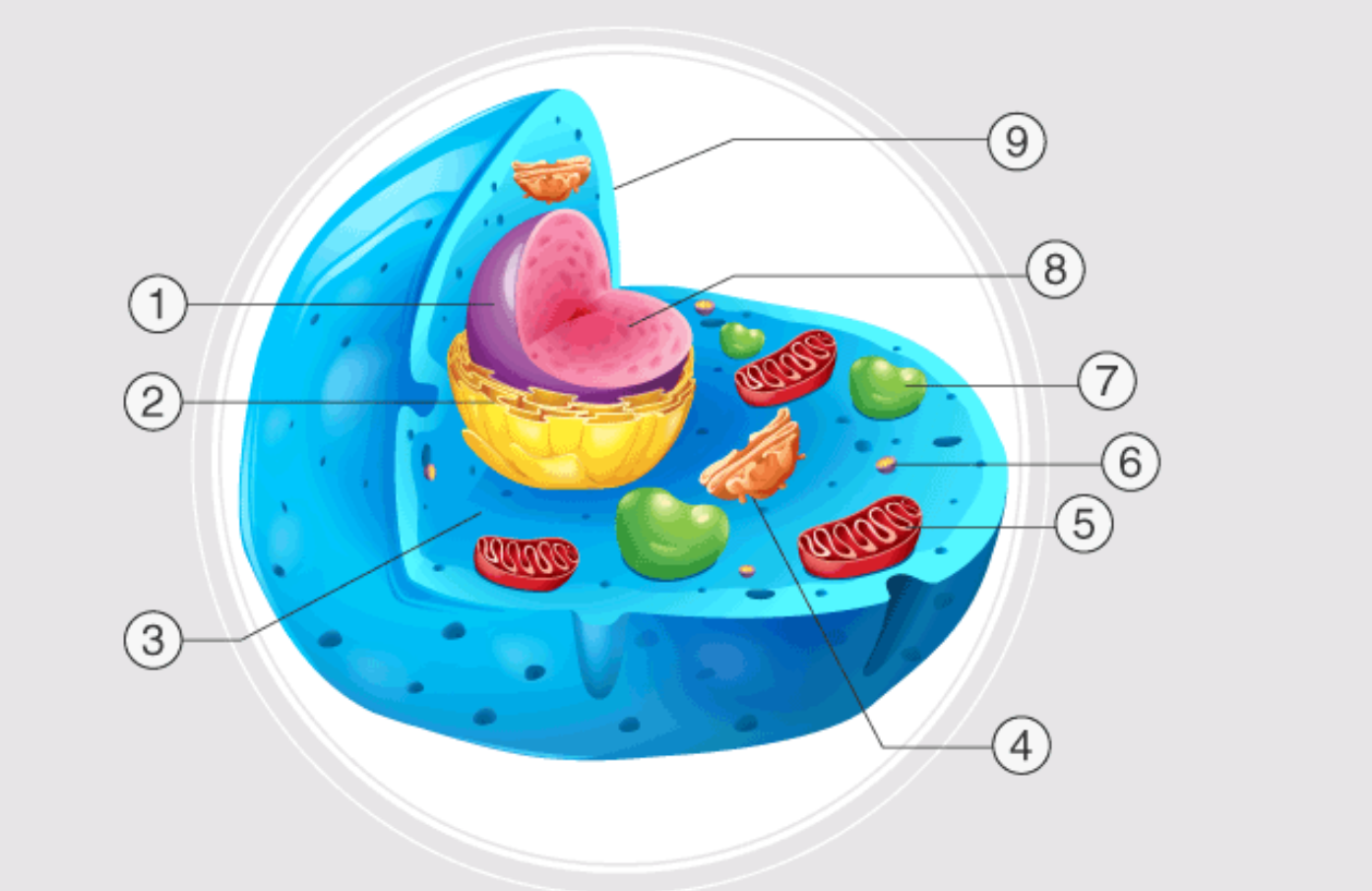
3
cytoplasm
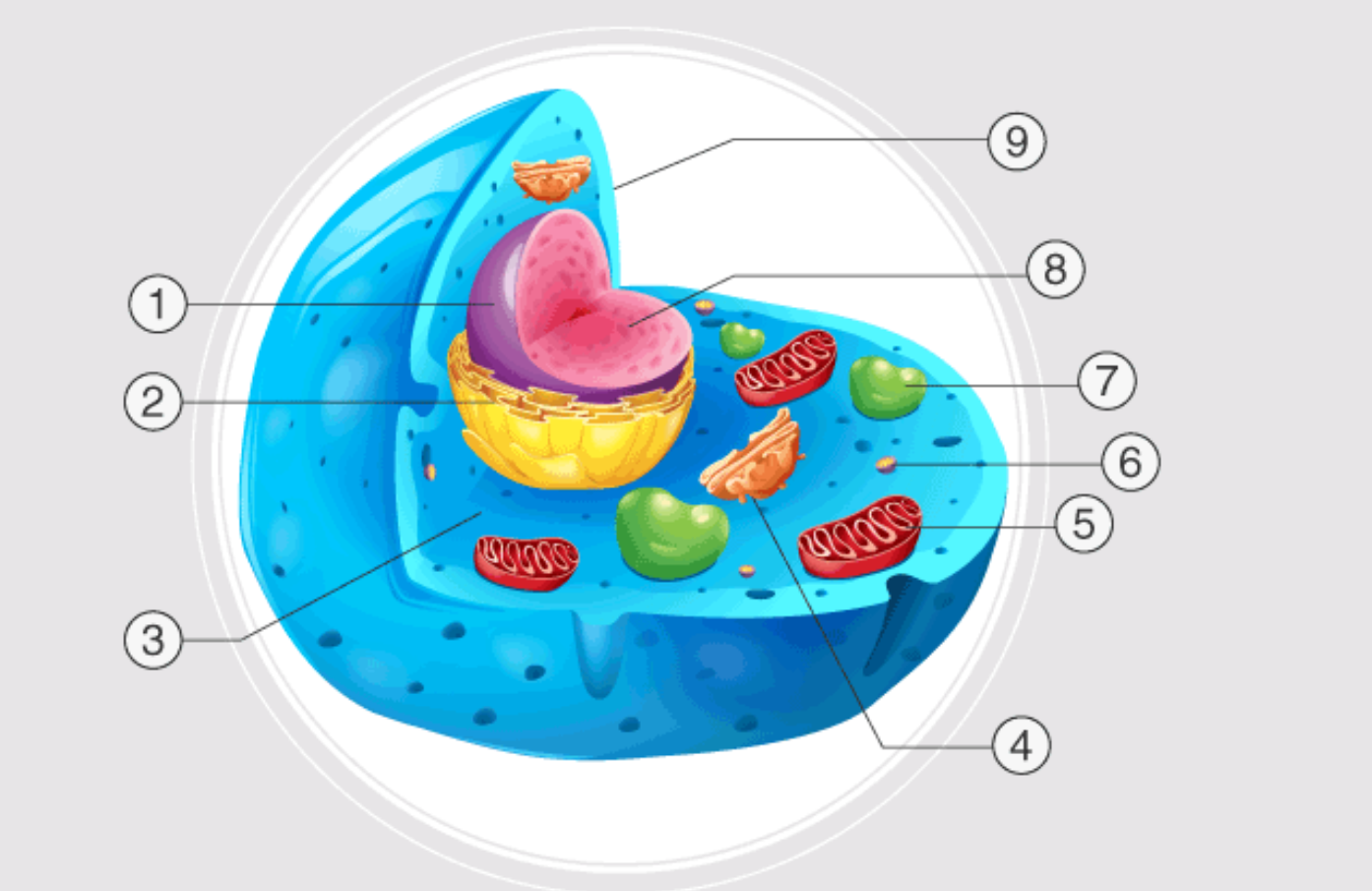
4
golgi apparatus
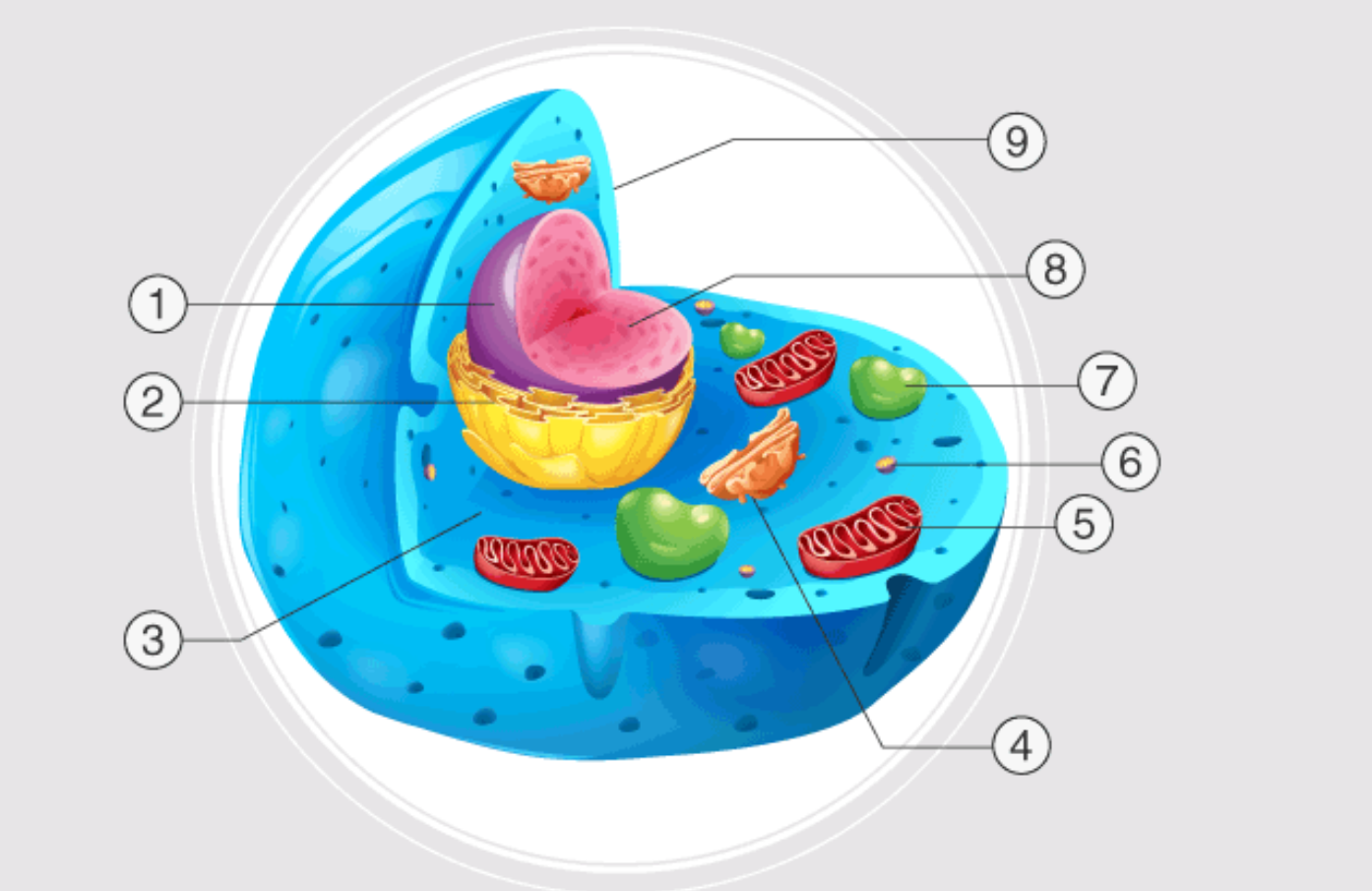
5
mitochondrion
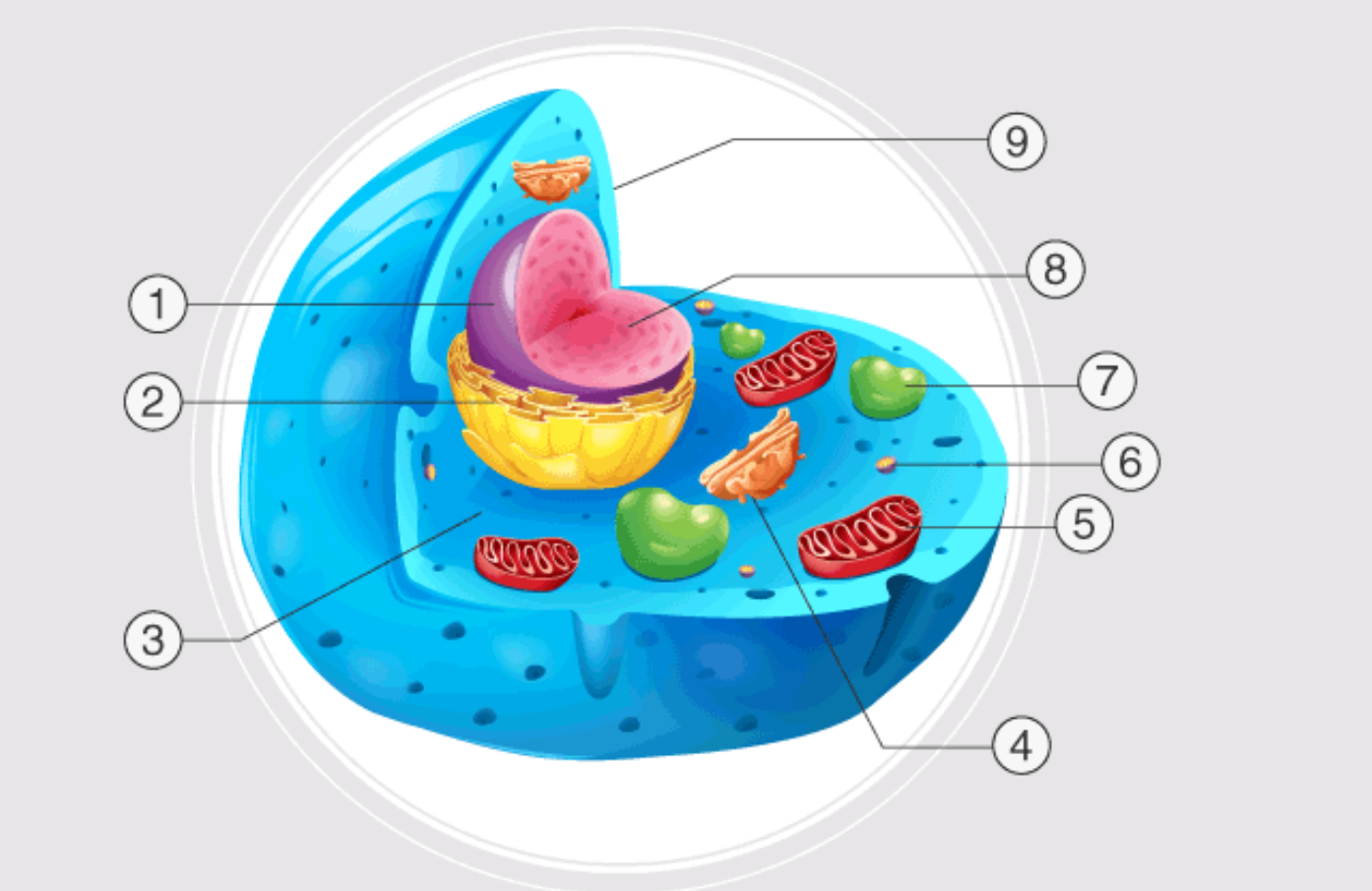
6
ribosome
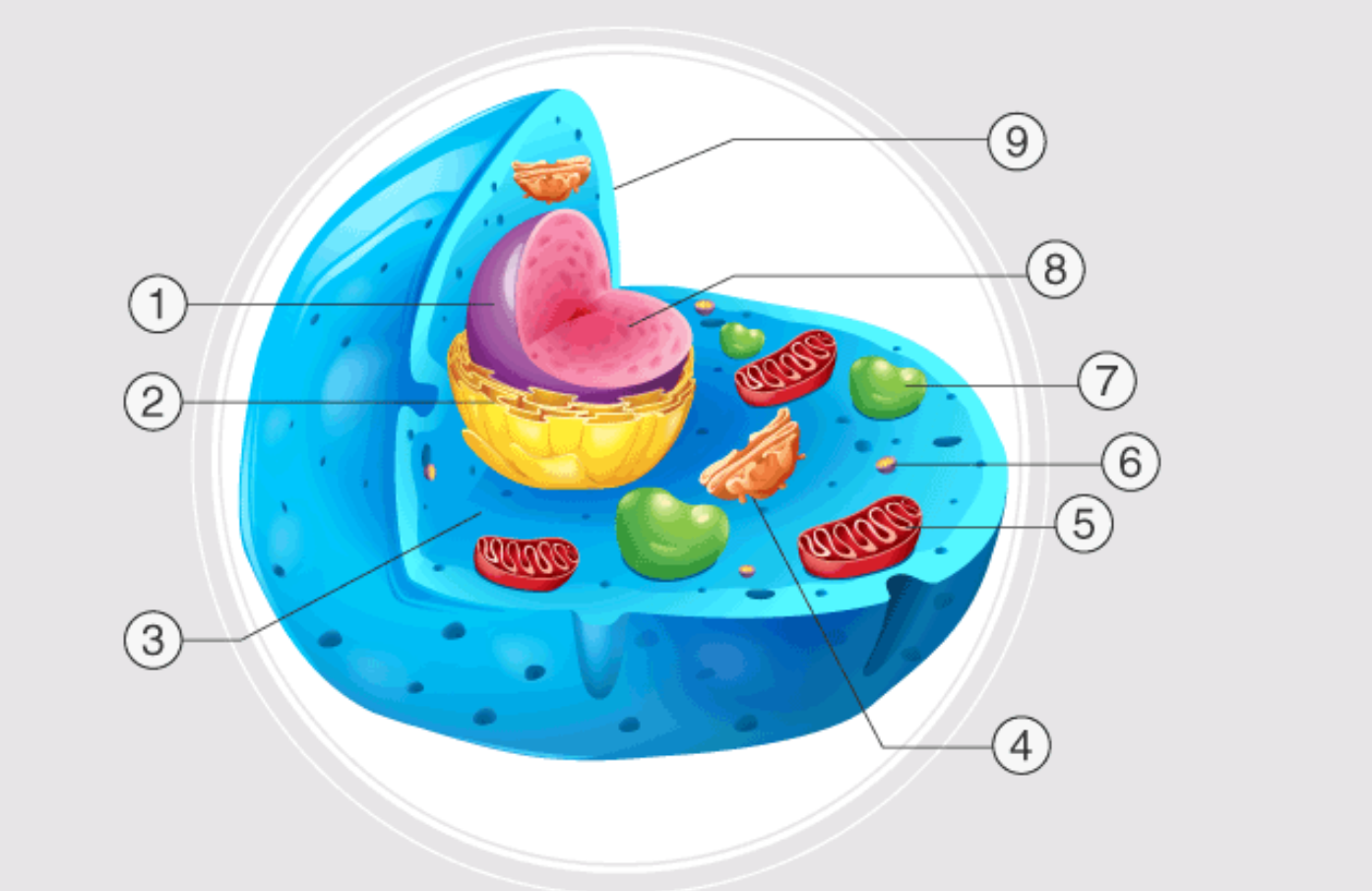
7
lysosome
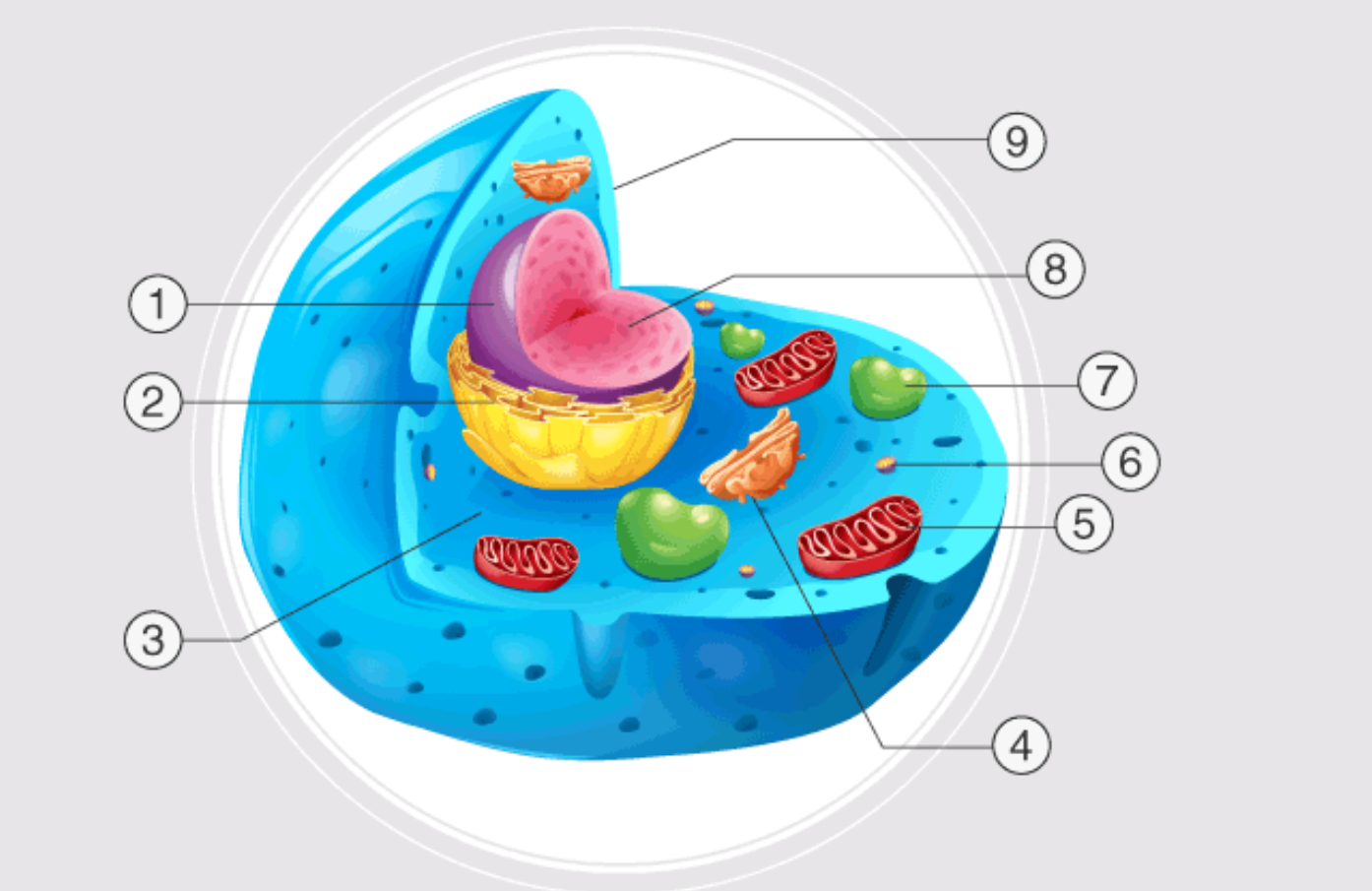
inside nucleus
nuclelous
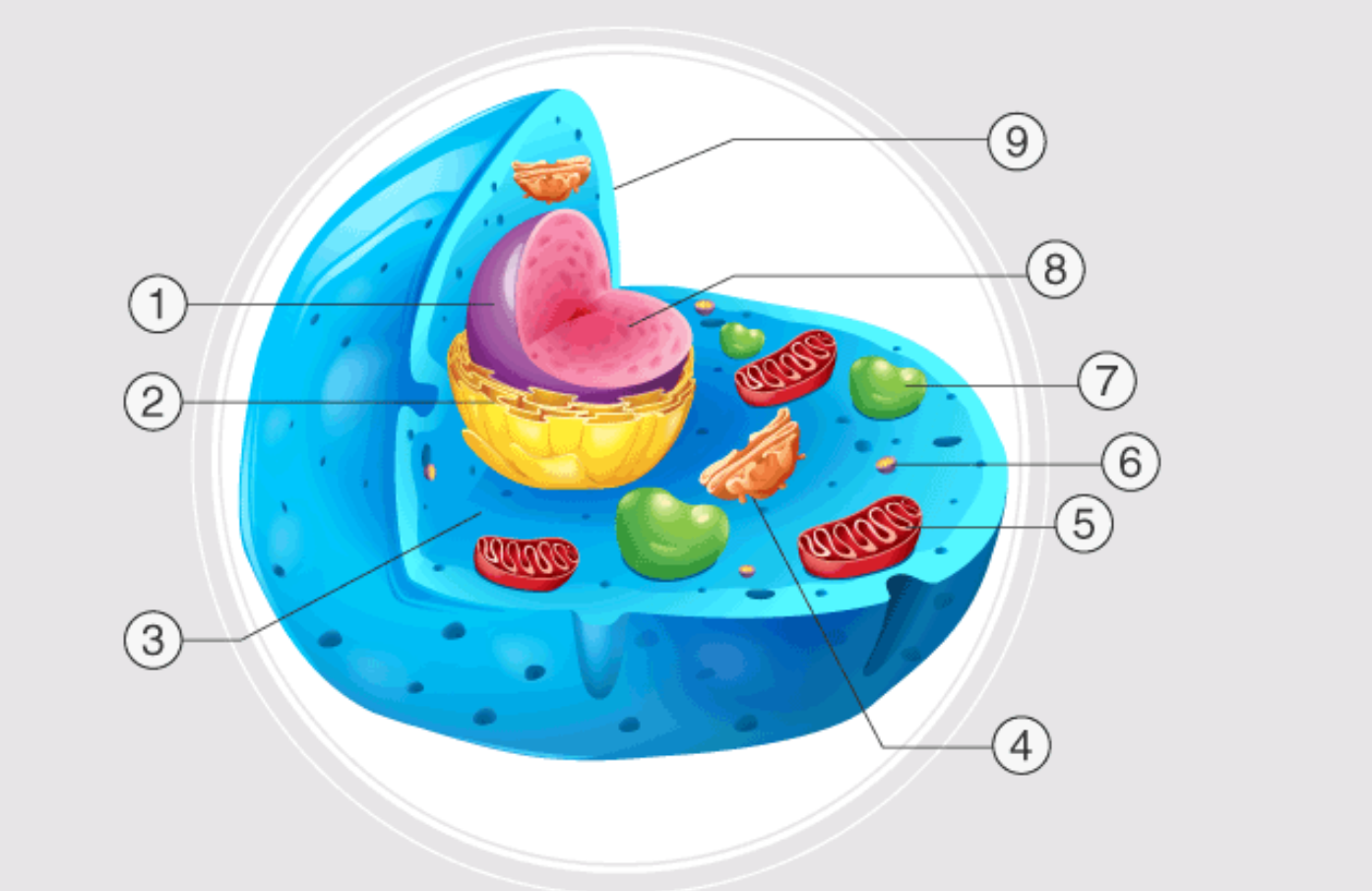
9
cell membrane
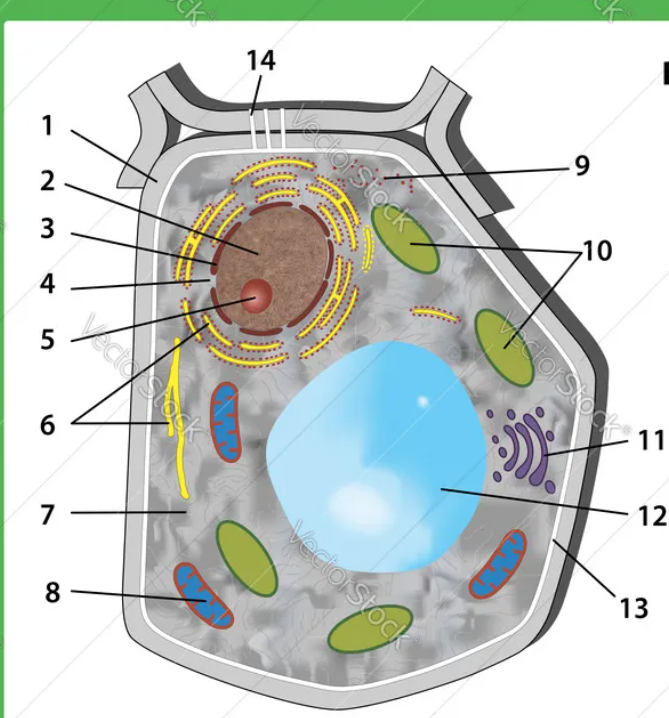
12
vacuole
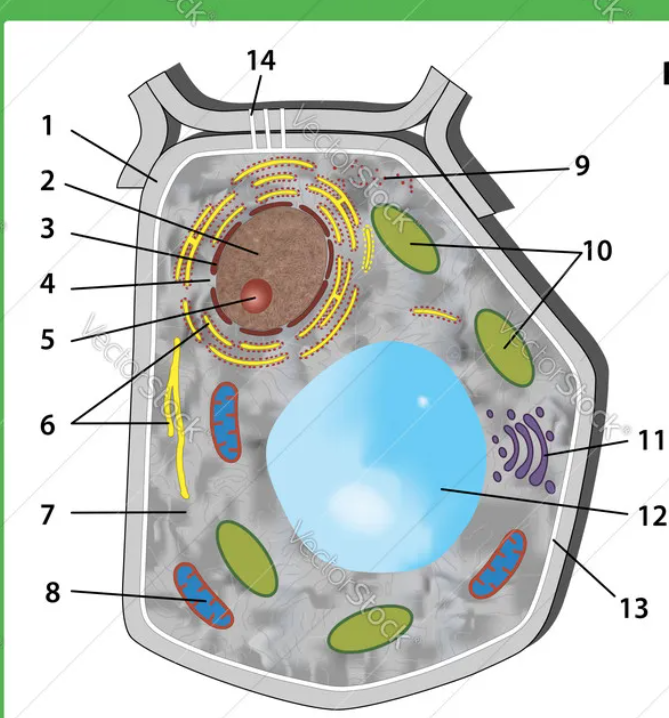
10
chloroplasts
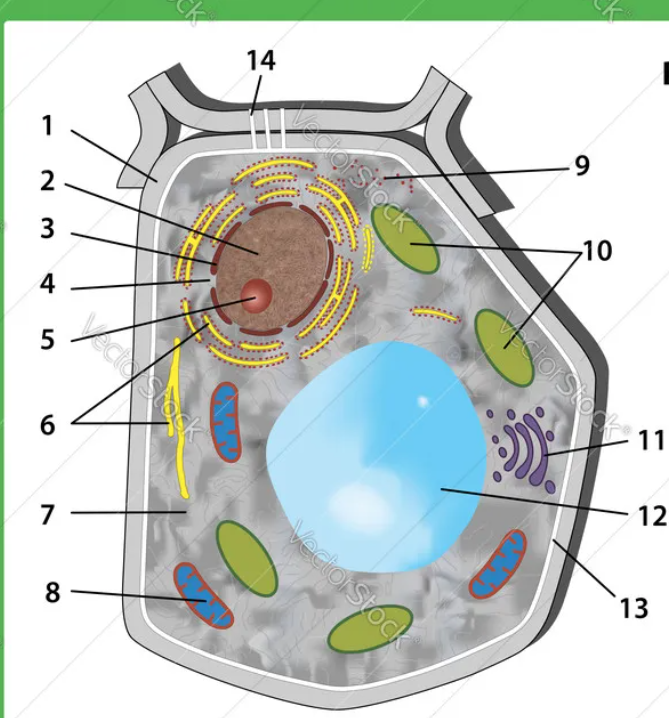
4
nuclear pores
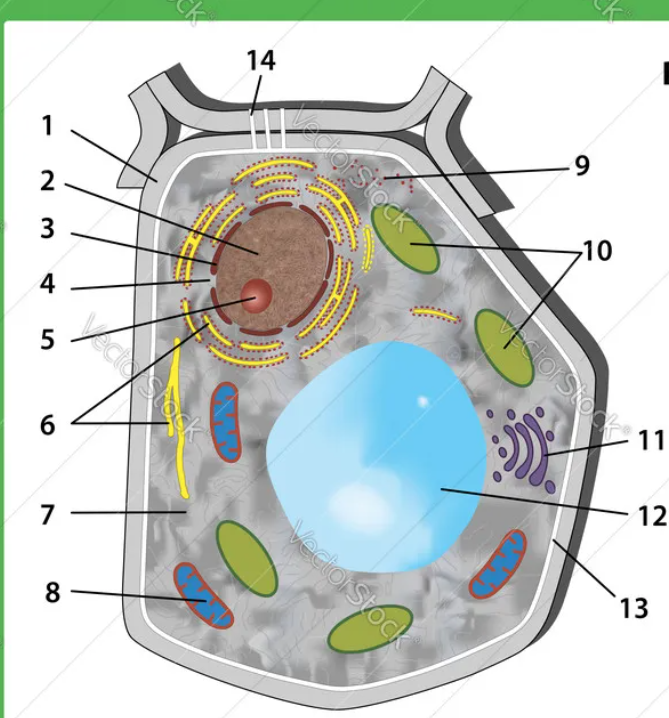
1
cell wall
all cells have
genetic material, cell membrane and ribosomes