HSC 101 Final Exam Review
0.0(0)Studied by 12 people
Card Sorting
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:01 PM on 4/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
1
New cards
How much alcohol for women and men?
How much is one drink?
How much is one drink?
* If you choose to drink, limit alcohol to less than 2 drinks a day for men and less than 1 for women.
* One drink equals 12 ounces of beer, 4-5 ounces of wine, and 1.5 ounces of 80-proof liquor.
* One drink equals 12 ounces of beer, 4-5 ounces of wine, and 1.5 ounces of 80-proof liquor.
2
New cards
Alcohol Pros
MODERATE DRINKING (ETHANOL) MAY:
* Increase HDL (good cholesterol)
* Decrease blood clotting which may help prevent heart attack or stroke
* Decrease overall mortality rate when compared with non-drinkers.
* Increase HDL (good cholesterol)
* Decrease blood clotting which may help prevent heart attack or stroke
* Decrease overall mortality rate when compared with non-drinkers.
3
New cards
ALCOHOL CONS:
EXCESSIVE DRINKING AND BINGE DRINKING MAY:
* Increase triglycerides (type of fat in blood)
* Increase blood pressure
* Contribute to heart failure
* Contribute to a high-calorie intake, which can lead to obesity and Type II Diabetes
* Lead to a stroke
* Cause fetal alcohol syndrome and other birth defects
* Cause fatal irregular heartbeats (cardiac arrhythmias)
* Cause sudden cardiac death
* Lead to alcoholism
* Increase risk for breast, oral, esophageal, laryngeal, pharyngeal, and liver cancers (especially in smokers)
* Contribute to liver disease in regular aspirin users
* Increase risk for suicides & accidents
4
New cards
Components of Fitness: Cardiorespiratory endurance
ability of heart, lungs & blood vessels to supply oxygen to skeletal muscles; affects risk for heart disease, cancer, diabetes
5
New cards
Components of Fitness: Muscular strength
is the ability to produce a maximal force in one repetition train by doing 1-5 repetitions, assess with 1 RM or 5RM
6
New cards
Components of Fitness: Muscular endurance
**Endurance** is the ability to produce a submaximal force repeatedly train by doing 15 or more repetitions assess by doing push ups, sit ups, and/ or pull ups to exhaustion
7
New cards
Components of Fitness: Flexibility
ability to move a joint through a full range of motion; depends on joint structure, the length and elasticity of connective tissue, and nervous system activity; affects risk for low back pain, performance of activities of daily living, poor posture and alignment, and injuries;
8
New cards
Components of Fitness: Body composition
percentage (%) of fat and fat-free mass; fat free mass (muscle, bone, water); excess body fat, especially in the abdominal area affects risk for heart disease, cancer, diabetes, osteoarthritis, gallbladder disease, back pain, stroke, and many other diseases
9
New cards
High Impact
If an exercise is high impact there are times when both of your feet come off of the floor. Examples include running, jumping rope, jumping jacks, basketball jump shots, and some forms of aerobic dance.
10
New cards
**Low Impact**
If one foot is always on the floor, an exercise is considered low impact. Walking, climbing stairs, and some forms of aerobic dance are examples of low impact exercises.
11
New cards
**Non Impact:**
If your feet never strike the floor or a pedal, an exercise is considered non-impact. Bicycling, rowing machines, stair climbers, elliptical trainers, and cross country ski machines are examples of non-impact exercises.
12
New cards
Full Weight Bearing
If you are standing up, the exercise is considered full weight bearing because the force of gravity is loading your legs and spine. This may help load your bones and reduce the risk for developing fragile, porous bones known as osteoporosis. Walking is an example of a full weight
13
New cards
Partially Weight Bearing
If you are sitting down, the exercise is considered partially weight bearing because you only have to bear the weight of your upper body. If you have excess body weight or need to reduce the load on your legs (arthritis, joint injuries, etc.) you may want to choose partially weight bearing exercise, such as bicycling. Many beginners particularly like the recumbent bicycle because it has additional lower back support.
14
New cards
Non Weight Bearing
The only non-weight bearing exercise is swimming because you are horizontal and supported by the buoyancy of the water.
15
New cards
Vasodilate
Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels, which results in an increase in blood flow and a decrease in blood pressure. This process is often used to treat conditions such as hypertension and angina.
16
New cards
vasoconstrict
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of blood vessels due to contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, which leads to a decrease in blood flow.
17
New cards
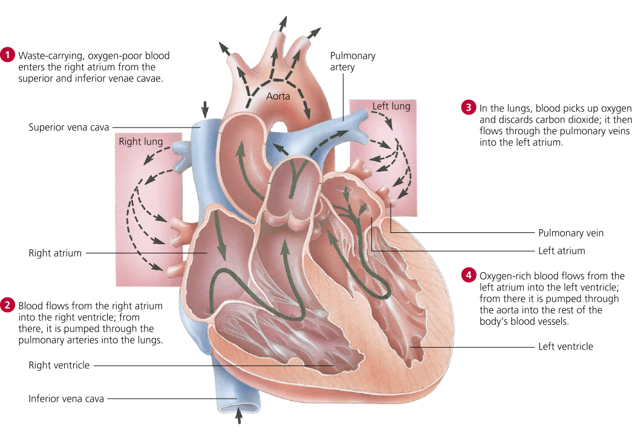
How does my heart pump blood?
Deoxygenated blood enters the heart from the superior and inferior **vena cavae.** The vena cava is the largest vein in the body (remember “v” = “vein”). Blood is collected in the **right atrium** and passes through a valve to the **right ventricle**. From the right ventricle, it is pumped to the **lungs** where it picks up oxygen and disposed of carbon dioxide. Blood then reenters the heart through the **left atrium**, passes through a valve to the **left ventricle**. The left ventricle is responsible for pumping blood out of the largest artery in the body called the **aorta** (remember “a” = “artery”).
\
\* Notice that the left ventricle wall is thicker than the right.
\*Notice that the walls of the ventricles are thicker than the atria.
18
New cards
What is my blood made of?
* **Red blood cells are made of hemoglobin.**
* Hemoglobin is an iron/ protein compound that is supposed to carry oxygen through the blood.
* Hemoglobin has a stronger affinity for carbon monoxide (CO) that it has for oxygen (O2).
* Hemoglobin is an iron/ protein compound that is supposed to carry oxygen through the blood.
* Hemoglobin has a stronger affinity for carbon monoxide (CO) that it has for oxygen (O2).
19
New cards
What are blood vessels? **Arteries**
•Arteries always carry blood away from heart. (**A**rteries = **A**way)
•They almost always carry oxygenated blood (except pulmonary artery).
•They have thick elastic walls that help that expand and relax. Aging/ inactivity causes them to be more rigid which can contribute to a higher risk of heart attack.
•They have a layer of smooth muscle that allows them to constrict (decrease diameter) and dilate (increase diameter).
•Since they transport blood directly from the heart they are high pressure vessels.
•They are lined with delicate endothelial cells that can be damaged by 1) Tobacco, 2) high blood glucose, 3) oxidized low density lipoproteins (LDL), and 4) high blood pressure. Once damaged, the conditions within the blood vessel (e.g., blood pressure, lipids, inflammation) will determine whether the damage results in plaque progression or regression. The accumulation of plaque within an artery is called atherosclerosis. This condition can begin early in life and gradually progresses over time. Atherosclerosis can be reversed through intensive lifestyle changes such as exercise, a healthier diet, smoking cessation, and stress management.
\
20
New cards
What are blood vessels? **Capillaries**
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels. They are only 1 cell layer thick to allow for gas (O2/ CO2) exchange between the lungs and blood, and between the blood and cells.
21
New cards
What are blood vessels? **Veins**
•Veins carry blood back to the heart. They almost always carry deoxygenated blood (except pulmonary vein). They have thin walls. Because they are low pressure they need valves to assist with blood flow back to heart.
•Because they are low pressure, a contracting muscle can cause them to collapse which makes a Valsalva maneuver (breath holding during resistance training exertion) very dangerous for the blood pressure.
•Varicose veins occur when the valves of the veins in the legs allow blood to leak back toward the feet. This deoxygenated blood (hence the blue) stagnates and may protrude to the surface of the skin.
•Because they are low pressure, a contracting muscle can cause them to collapse which makes a Valsalva maneuver (breath holding during resistance training exertion) very dangerous for the blood pressure.
•Varicose veins occur when the valves of the veins in the legs allow blood to leak back toward the feet. This deoxygenated blood (hence the blue) stagnates and may protrude to the surface of the skin.
22
New cards
How does the damage to cells work?
Damage to the endothelial cells can lead to atherosclerosis (plaque build-up inside the arteries).
This can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
\
**High Blood Pressure**
**Oxidized LDL**
**Tobacco**
**High Blood Glucose**
This can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
\
**High Blood Pressure**
**Oxidized LDL**
**Tobacco**
**High Blood Glucose**
23
New cards
What is LDL and HDL?
* LDL carries cholesterol to the artery wall; HDL carries it away (back to the liver for excretion)
* \
* \
24
New cards
* Low Density Lipoproteins are “Lethal” and you want them to be “Low”
* Low Density Lipoproteins are “Lethal” and you want them to be “Low”
* High Density Lipoproteins are “Healthy” and you want them to be “High”
25
New cards
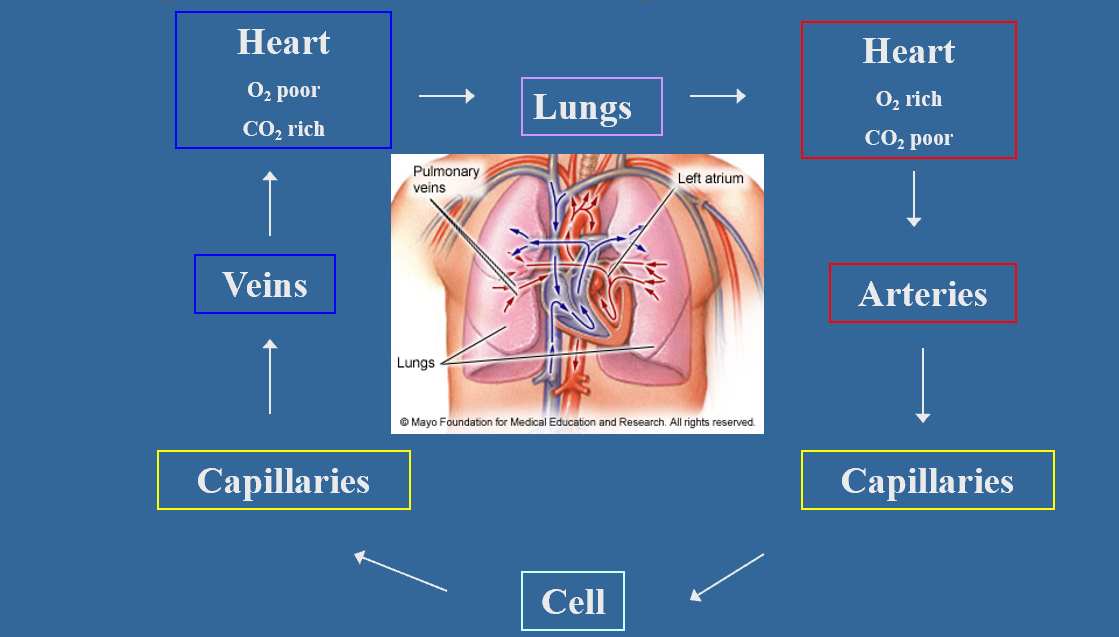
How does circulation work?
Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium of the heart via the superior and inferior vena cava. It is pumped into the right ventricle and then the lungs. In the lungs, it picks up oxygen and drops of carbon dioxide. It is pumped back into the left atrium and left ventricle where it is pumped out to the body via the aorta. The aorta branches into smaller arterioles and capillaries. The capillaries are one cell layer thick and distribute oxygen and other nutrients to the cells. Waste products, like carbon dioxide, enter the blood and are pumped back into the capillaries, small veins called venules, larger veins (with the help of valves), and then back into the right atrium via the vena cave.
26
New cards
**How does air flow through the lungs?** Alveoli
are globes to provide more surface area for gas exchange. They are surrounded by capillaries(o2 get from lung to blood). This is where the cardiovascular and respiratory systems meet.
27
New cards
What is heart rate and how does it change?
* Heart beats per minute
* During maximal exercise, heart rate may increase up
* During maximal exercise, heart rate may increase up
28
New cards
What is Stroke volume and how does it change?
* The volume of blood pumped per stroke
* Regular aerobic exercise usually causes an increase in stroke volume.
* Regular aerobic exercise usually causes an increase in stroke volume.
29
New cards
What is Cardiac Output and how does it change?
* The volume of blood pumped per minute
* During exercise, cardiac output may increase
* During exercise, cardiac output may increase
30
New cards
What is Arteriovenous Oxygen Difference and how does it change?
* The oxygen difference between the arteries and veins
* As a result of regular aerobic training it usually increases.
* As a result of regular aerobic training it usually increases.
31
New cards
**Arterial- Venous Oxygen Difference**
How much oxygen you pull out at the capillary level
32
New cards
What is Blood Pressure and how does it change?
* The force that blood exerts against the blood vessel walls
* Systolic (maximum)
* Diastolic (minimum)
* Systolic (maximum)
* Diastolic (minimum)
33
New cards
What is Maximal Oxygen Consumption and how does it change?
–VO2 max = (HR x SV) (a-v) O2
34
New cards
**How do I convert fuel to energy?**
* ATP/PC
*
*
35
New cards
**How do I design an aerobic exercise program?**
* **F**requency- 3-5 days/ week
* Intensity- 60-90% HR max, 50-85% HRR
* Time- 20-60 min continuous OR intermittent 10 min bouts
* Type- rhythmic, continuous activities using large muscle groups
* Intensity- 60-90% HR max, 50-85% HRR
* Time- 20-60 min continuous OR intermittent 10 min bouts
* Type- rhythmic, continuous activities using large muscle groups
36
New cards
**How do I determine my Target Heart Rate (HR max)?**
* 220-age = HRmax
* HR max x 60% = minimum HR
* HR max x 90% = maximum HR
37
New cards
**How do I know if I am overtraining?**
* delayed onset muscle soreness
* stretching can not really help
* lowers immune function decreases Natural Killer Cell activity so you are more susceptibility to infection
* stressed and heart rate increases
* stretching can not really help
* lowers immune function decreases Natural Killer Cell activity so you are more susceptibility to infection
* stressed and heart rate increases
38
New cards
What if I had a pill that could?
* Decrease Low Density Lipoproteins (bad cholesterol)
* Increase High Density Lipoproteins (good cholesterol)
* Decrease systemic inflammation (C-reactive protein)
* Increase insulin sensitivity
* Decrease blood pressure
* Increase immune defense (Natural Killer Cells)
* Improve strength and contractility of heart
* Improve oxygen utilization
* Increase lean mass and metabolic rate
* Facilitate weight management
* Increase strength, endurance, and flexibility
* Increase balance and reduce risk of falling
* Prevent and improve mild to moderate depression and anxiety
* Enhance cognitive function
* Decrease the risk of cognitive decline and dementia
* Improve quality of sleep
* Increase feelings of “energy”
* Blunt the physiological stress response
* Reduce risk of heart attack or stroke
* Reduce risk for breast, prostate, or colon cancer
* Reduce complications of pregnancy
* Prevent and improve management of type 2 diabetes
* Preserve bone mass and reduce risk of falling
* Reduce risk for osteoarthritis, pain, and disability
* Boost mood, body image, and self-esteem
* Improve wellbeing and overall quality of life
* Increase High Density Lipoproteins (good cholesterol)
* Decrease systemic inflammation (C-reactive protein)
* Increase insulin sensitivity
* Decrease blood pressure
* Increase immune defense (Natural Killer Cells)
* Improve strength and contractility of heart
* Improve oxygen utilization
* Increase lean mass and metabolic rate
* Facilitate weight management
* Increase strength, endurance, and flexibility
* Increase balance and reduce risk of falling
* Prevent and improve mild to moderate depression and anxiety
* Enhance cognitive function
* Decrease the risk of cognitive decline and dementia
* Improve quality of sleep
* Increase feelings of “energy”
* Blunt the physiological stress response
* Reduce risk of heart attack or stroke
* Reduce risk for breast, prostate, or colon cancer
* Reduce complications of pregnancy
* Prevent and improve management of type 2 diabetes
* Preserve bone mass and reduce risk of falling
* Reduce risk for osteoarthritis, pain, and disability
* Boost mood, body image, and self-esteem
* Improve wellbeing and overall quality of life
39
New cards
**What are the Components of the MS**
**System?** Tendons
**System?** Tendons
are connective tissues that attach muscle to bone
40
New cards
**What are the Components of the MS System?** Ligaments
are connective tissues that attach bone to bone
41
New cards
**Fast Twitch Glycolytic**
–Thick
–Produce maximal force
–Few mitochondria (no O2)
–Favors anaerobic energy systems
–Easily fatigued
–Produce maximal force
–Few mitochondria (no O2)
–Favors anaerobic energy systems
–Easily fatigued
42
New cards
**Slow Twitch Oxidative**
–Thin
–Produce minimal force
–Many mitochondria (O2)
–Favors aerobic energy systems
–Fatigue resistant
43
New cards
**What are the Benefits of Resistance Training?**
INCREASE muscular strength, endurance, and power
INCREASE lean body mass
INCREASE resting metabolic rate
INCREASE cardiovascular disease
INCREASE Improves BP, HDL, LDL, blood vessel health
\
DECREASE risk of metabolic disorders
–e.g., type 2 diabetes
\
DECREASE performance and activities of daily living (ADL)
DECREASE psychological well-being
DECREASE bone mineral density
DECREASE risk of injury
INCREASE lean body mass
INCREASE resting metabolic rate
INCREASE cardiovascular disease
INCREASE Improves BP, HDL, LDL, blood vessel health
\
DECREASE risk of metabolic disorders
–e.g., type 2 diabetes
\
DECREASE performance and activities of daily living (ADL)
DECREASE psychological well-being
DECREASE bone mineral density
DECREASE risk of injury
44
New cards
Concentric
The muscle shortens as it exerts force
45
New cards
Eccentric
The muscle lengthens as it exerts force

46
New cards
Isometric
The muscle does not shorten or lengthen as it exerts force

47
New cards
**How do I begin a resistance training program?**
* Frequency
* 2-3 nonconsecutive days per week
* Intensity
* 8-12 Rep Max
* 60-80% 1 RM
* Time\]
* 2-4 sets (beginners may complete 1)
* 8-12 repetitions
* All major muscles
* Type
* Machines, free weights, calisthenics
* 2-3 nonconsecutive days per week
* Intensity
* 8-12 Rep Max
* 60-80% 1 RM
* Time\]
* 2-4 sets (beginners may complete 1)
* 8-12 repetitions
* All major muscles
* Type
* Machines, free weights, calisthenics
48
New cards
Gluteals
* lunge
* leg press
* squat
* leg press
* squat
49
New cards
Quadriceps
* leg extension
50
New cards
Hamstrings
* straight leg dead lift
* leg curl
* leg curl
51
New cards
Calves- Gastrocnemius
* standing calf raise
* calf raise
* calf raise
52
New cards
Calves- Soleus
* seated calf raise
53
New cards
Pectoralis Major
* incline chest press
* decline chest press
* chest fly
* bench press
* decline chest press
* chest fly
* bench press
54
New cards
Latissimus Dorsi
* pull up
* t bar row
* bent over row
* lat pull
* low row
* t bar row
* bent over row
* lat pull
* low row
55
New cards
Trapezius
* shrugs
* upright row
* upright row
56
New cards
Deltoids
* frontal raise
* reverse fly
* lateral raise
* shoulder press
* reverse fly
* lateral raise
* shoulder press
57
New cards
Triceps
* bench dips
* lying tricep extension
* cable tricep pushdown
* lying tricep extension
* cable tricep pushdown
58
New cards
\
Biceps
Biceps
* bicep curl
* preacher curl
* cable bicep curl
* preacher curl
* cable bicep curl
59
New cards
Rectus Abdominis
* ab crunch
60
New cards
obliques
rotary torso
61
New cards
Erector Spinae
lower back extension
62
New cards
What are the Benefits of Flexibility Training?
* INCREASE range of motion (ROM)
* INCREASE performance
* DECREASE risk of injury
* DECREASE muscle tension (NOT Soreness)
* INCREASE performance
* DECREASE risk of injury
* DECREASE muscle tension (NOT Soreness)
63
New cards
Types of Flexibility
* **Static Stretching**
* Slowly stretch a muscle and hold the position
* Commonly used after exercise
* **Dynamic Stretching**
* Move joints slowly and fluidly in a controlled manner
* Commonly used prior to exercise
* **Ballistic Stretching** (not RECOMENDED)
* Forcing a stretch with a repeated bouncing, swinging, or jerking motions
* Initiates stretch reflex
* Less safe and less effective
* **Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) Stretching**
* Contract and then relax muscle
* Overcomes the stretch reflex to achieve greater training effects
* Requires props or partner
* Slowly stretch a muscle and hold the position
* Commonly used after exercise
* **Dynamic Stretching**
* Move joints slowly and fluidly in a controlled manner
* Commonly used prior to exercise
* **Ballistic Stretching** (not RECOMENDED)
* Forcing a stretch with a repeated bouncing, swinging, or jerking motions
* Initiates stretch reflex
* Less safe and less effective
* **Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) Stretching**
* Contract and then relax muscle
* Overcomes the stretch reflex to achieve greater training effects
* Requires props or partner
64
New cards
Folate
helps with neural tube defects
65
New cards
__**% Daily Value**__
5% or less is LOW
20% or more is HIGH
20% or more is HIGH
66
New cards
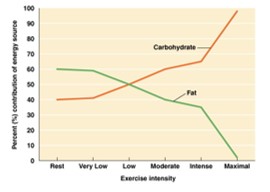
Why do I need carbohydrate?
* its is your main fuel
67
New cards
What are Complex Carbohydrates?
* **Polysaccharides**
* **Starch**
* **Glycogen**
* **Fiber**
\
* Bran
* the outer portion and is good source of fiber
* Endosperm
* the inside and it is just starch
* Germ
* inner portion and is good source of mineral and vitamins
* **Starch**
* **Glycogen**
* **Fiber**
\
* Bran
* the outer portion and is good source of fiber
* Endosperm
* the inside and it is just starch
* Germ
* inner portion and is good source of mineral and vitamins
68
New cards
**Soluble (oats, fruit, beans)**
* Binds with bile and excretes it with feces
* This lowers LDL
* decreases absorption of glucose
* This lowers LDL
* decreases absorption of glucose
69
New cards
**Insoluble (wheat, vegetables)**
* Promotes a feeling of fullness
* Aids in weight loss
* Promote digestion & regularity
* lowers incidence of colon cancer
* Aids in weight loss
* Promote digestion & regularity
* lowers incidence of colon cancer
70
New cards
Gut Flora
A wide variety of fibers from food encourages the growth of different types of healthy bacteria in the colon. A diverse gut flora may influence digestion, immunity, inflammation, obesity, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
71
New cards
How much Carbohydrate do I need?
45-65% total calories
72
New cards
**Saturated Fats**
* No point of unsaturation
* Solid at room temperature
* Increase LDL, inflammation, CVD
* Cheese, beef, butter, whole milk
* Chocolate, coconut, palm oil
* no double bond
* Solid at room temperature
* Increase LDL, inflammation, CVD
* Cheese, beef, butter, whole milk
* Chocolate, coconut, palm oil
* no double bond
73
New cards
Monounsaturated Fats
* One point of unsaturation
* Liquid at room temperature
* Decrease LDL and risk of heart disease
* Olive oil, canola oil, nuts, seeds, avocadoes
* Liquid at room temperature
* Decrease LDL and risk of heart disease
* Olive oil, canola oil, nuts, seeds, avocadoes
74
New cards
What affects inflammation and what is it associated with?
* affects
* smoking
* diet
* stress
* associated with
* cardiovascular disease
* cancer
* type 2 diabetes
* depression
* smoking
* diet
* stress
* associated with
* cardiovascular disease
* cancer
* type 2 diabetes
* depression
75
New cards
Polyunsaturated Fats
* Two or more points of unsaturation
* Liquid at room temperature
* Decrease LDL and risk of heart disease
* Salmon, Soybean oil, Walnuts
* Divided into Omega 3 and Omega 6
* Liquid at room temperature
* Decrease LDL and risk of heart disease
* Salmon, Soybean oil, Walnuts
* Divided into Omega 3 and Omega 6
76
New cards
Trans Fats
* Hydrogen added to unsaturated fat
* Make a liquid fat more solid
* e.g. “partially hydrogenated oils”
* Increase LDL , inflammation, CVD; decrease HDL
* Stick margarine, Fast food, Fried food
* Limit to 2 grams per day
* Make a liquid fat more solid
* e.g. “partially hydrogenated oils”
* Increase LDL , inflammation, CVD; decrease HDL
* Stick margarine, Fast food, Fried food
* Limit to 2 grams per day
77
New cards
Benefits of Omega-3 Fats
Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) & Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) are omega-3 fatty acids that are found in fatty fish. EPA is metabolized into hormone-like compounds called eicosanoids. DHA is integral to the brain, retina of the eye, and cell membranes. Eating fatty fish twice per week can help to ensure adequate EPA & DHA intake
\
* Fish contains omega-3 like EPA that breaks down into eicosanoids that lowers blood clots
\
* Fish contains omega-3 like EPA that breaks down into eicosanoids that lowers blood clots
78
New cards
How much Fat do I need?
20-35% total calories from fat
79
New cards
Why do I need Protein?
Proteins contain nitrogen which is used for Growth and repair of tissue
\*proteins are made of amino acids
80
New cards
**Complete proteins**
* Animal protein, soy (edamame), quinoa
* Supply all essential amino acids
* Supply all essential amino acids
81
New cards
**Incomplete proteins**
* Plant proteins
* Low in one or more essential amino acids
* Eat a varied diet to supply adequate amounts
* Low in one or more essential amino acids
* Eat a varied diet to supply adequate amounts
82
New cards
How much calories do we need?
10-35% total calories
83
New cards
What is Nitrogen Balance?
1. positive nitrogen balance
2. nitrogen equilibrium
3. negative nitrogen balance
1. positive nitrogen balance
2. nitrogen equilibrium
3. negative nitrogen balance
Nitrogen balance describes the relationship between the amount of protein retained and the amount used. Positive nitrogen balance indicates a state of growth. Nitrogen equilibrium indicates a state of weight maintenance. Negative nitrogen balance indicates a state of wasting or muscle loss.
1. Growing
1. ex. growing child, building muscle
2. Maintaining
1. ex: healthy college student
3. wasting
1. ex: astronaut, surgery patient
1. Growing
1. ex. growing child, building muscle
2. Maintaining
1. ex: healthy college student
3. wasting
1. ex: astronaut, surgery patient
84
New cards
**How much protein is needed?**
The DRI committee does not recommend additional protein for athletes.
1. most adults
2. athletes
3. veg athletes
1. most adults
2. athletes
3. veg athletes
85
New cards
What are Vitamins?
* **Fat Soluble**
* **A, D, E, K**
* **Dissolved in fats**
* **Excess stored**
* **Danger Toxicity**
* **Water Soluble**
* **B complex, C**
* **Dissolved in water**
* **Excess excreted**
* **Low Danger Toxicity**
* **A, D, E, K**
* **Dissolved in fats**
* **Excess stored**
* **Danger Toxicity**
* **Water Soluble**
* **B complex, C**
* **Dissolved in water**
* **Excess excreted**
* **Low Danger Toxicity**
86
New cards
Vitamin A
Function- vision, skin, bones, teeth; antioxidant
87
New cards
**Vitamin D**
Function- mineralization of bones, calcium absorption
88
New cards
Vitamin E
Function- antioxidant
89
New cards
Vitamin K
Function- aid in blood clotting
90
New cards
B complex
Function- convert food into energy
91
New cards
**Folate/ Folic Acid**
Function- form DNA and new cells
92
New cards
Vitamin C
Function- maintain connective tissue, iron absorption, support immune system, antioxidant
93
New cards
Calcium
Function- build bones, nerve conduction, muscle contraction/ relaxation
94
New cards
Sodium
Function- maintain fluid balance
\*is a mineral that increase blood pressure
\*most of your sodium intake comes from PROCESSED FOODS
\*is a mineral that increase blood pressure
\*most of your sodium intake comes from PROCESSED FOODS
95
New cards
Iron
Function- part of hemoglobin, carries oxygen
96
New cards
**Harvard School of Public Health Healthy Eating Pyramid**
* took off upper limit for vegetables
* spilt up the meat group completly
\
* vegetables
* 3-5 servings
* In Abundance
* Grains
* 6-11
* whole grains in most meals
* refined grains sparingly
* Meat, Poultry, fish eggs, nuts, legumes
* 2-3 servings
* nuts+legumes 1-3
* fish, poultry, eggs 0-2
* red meat sparingly
* spilt up the meat group completly
\
* vegetables
* 3-5 servings
* In Abundance
* Grains
* 6-11
* whole grains in most meals
* refined grains sparingly
* Meat, Poultry, fish eggs, nuts, legumes
* 2-3 servings
* nuts+legumes 1-3
* fish, poultry, eggs 0-2
* red meat sparingly
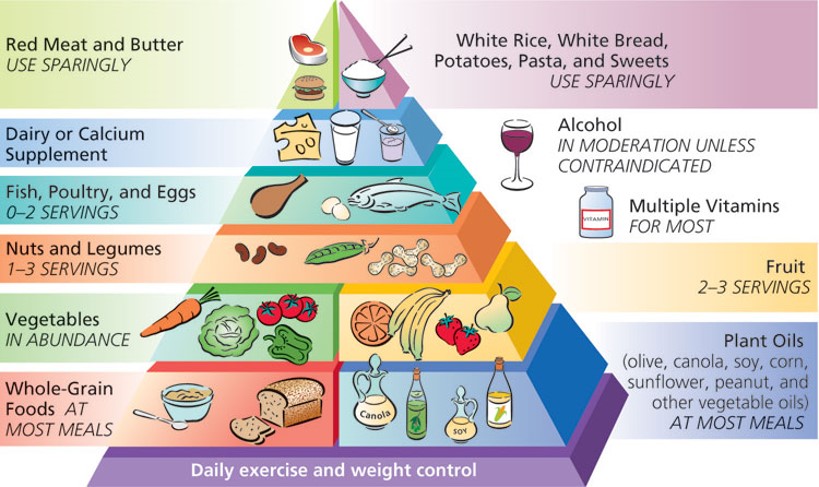
97
New cards
Why are fats or plant oils on the bottom?
\
\*if 20 -35% comes from fat then fats should be lower on the pyramid
\*fat has more calories per gram than carb or protein
\*only a little bit of fat would give you 20-30% of fat
\*if 20 -35% comes from fat then fats should be lower on the pyramid
\*fat has more calories per gram than carb or protein
\*only a little bit of fat would give you 20-30% of fat