4.1 Basic concepts and hydrocarbons
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
What is the purpose of the IUPAC system for naming organic compounds? (1)
- To provide a systematic name for compounds
- Avoids confusion and ambiguity internationally.
How should side chains be named in organic compounds? (2)
- If there are multiple identical side chains, their positions are numbered, and di-, tri-, tetra- etc. are added.
- Side chains should be written in alphabetical order, ignoring prefixes like di-, tri-, etc.
How should alkenes be named? (1)
The position of the double bond is written between the stem and -ene.
What is a homologous series? (1)
- A series of organic compounds that have the same functional group
- but each successive member differs by CH₂.
What is a functional group? (1)
A group of atoms responsible for the characteristic reactions of a compound.
What is the suffix for alkanes? (1)
-ane
What is the suffix for alkenes? (1)
-ene
What are the prefixes for haloalkanes? (4)
- Bromo-
- Chloro-
- Iodo-
- Fluoro-
What is the suffix for an alcohol? (1)
-ol
EXAMPLE: CH3CH2OH = ethanol
What is the suffix for a carboxylic acid? (1)
-oic acid
EXAMPLE: CH3CH2COOH = propanoic acid
What is the suffix for a ketone? (1)
-one
EXAMPLE: CH3COCH3 = propane
What is the suffix for an aldehyde? (1)
-al
EXAMPLE: CH3CHO = ethanal
What is the prefix for cyclic compounds? (1)
Cyclo-
What is the name of a carbon chain with 1 carbon? (1)
Methyl
What is the name of a carbon chain with 2 carbons? (1)
Ethyl
What is the name of a carbon chain with 3 carbons? (1)
Propyl
What is the name of a carbon chain with 4 carbons? (1)
Butyl
What is the name of a carbon chain with 5 carbons? (1)
Pentyl
What is the general formula of a compound? (1)
The simplest algebraic formula of a member of a homologous series
What is the general formula for alkanes? (1)
CnH2n+2
What is the general formula for alkenes? (1)
CnH2n
What is the structural formula of a compound? (1)
The minimal detail that shows the arrangement of atoms in a molecule
What is the displayed formula of a compound? (1)
The relative positioning of atoms and the bonds between them
What is the skeletal formula of a compound? (3)
- the simplified organic formula,
- shown by removing hydrogen atoms from alkyl chains,
- leaving just a carbon skeleton and associated functional groups
What is an aromatic compound? (1)
A compound that contains a benzene ring
What is an aliphatic compound? (2)
- A compound that contains carbon and hydrogen in straight or branched chains
- or non-aromatic rings
What is an alicyclic compound? (2)
- A type of aliphatic compound
- arranged in non-aromatic rings.
What is a saturated hydrocarbon? (1)
Only contains single carbon-carbon bonds.
What is an unsaturated hydrocarbon? (2)
- Contains multiple carbon-carbon bonds
- and/or contains aromatic rings.
What are structural isomers? (2)
- Compounds with the same molecular formula
- but different structural formulae.
How can structural isomers be created? (3)
- By altering the carbon chain.
- By moving the functional group.
- By changing the functional group.
What are double headed curly arrows used for in reaction mechanisms? (1)
To show movement of electron pairs
What are single headed curly arrows used for in reaction mechanisms? (1)
To show the movement of a single electron
What direction is a curly arrow used? (2)
- From a negative charge, or lone electron pair
- To the atom, or bond where the electron pair moves to
What is bond fission? (1)
Breaking of a bond into smaller fragments.
What is homolytic fission? (3)
- Each bonding atom receives one electron from the bonded pair.
- Forms two radicals
- Shown by single headed arrows
What is heterolytic fission? (3)
- One bonding atom receives both electrons from the bonded pair.
- Forms an anion and a cation
- Shown by double headed arrows
What is a radical? (2)
- A species with an unpaired electron.
- Very reactive due to the unpaired electron.
How are radicals represented? (1)
- By a dot next to the atom
EXAMPLE: •CH₃, •Cl.
What are alkanes? (3)
- Saturated hydrocarbons
- with the general formula CₙH₂ₙ₊₂.
- Contain only C-C and C-H sigma bonds which allow free rotation.
What is the shape and bonding angle of an alkane? (2)
- Tetrahedral about each carbon atom.
- Bond angle = 109.5°.
How does chain length affect the boiling point of alkanes? (3)
- Longer chains = higher boiling point
- due to stronger London forces.
- More energy required to overcome intermolecular forces.
How does branching affect the boiling point of alkanes? (3)
- More branching = lower boiling point
- due to less surface interaction.
- Weaker London forces, so less energy needed to overcome them.
Why do alkanes have low reactivity? (2)
- Strong sigma (σ) bonds with high bond enthalpy.
- Low polarity due to similar electronegativity in C-H bonds.
What is the equation for complete combustion of an alkane? (2)
- Alkane + oxygen → water + carbon dioxide.
- Releases lots of energy, making alkanes good fuels.
What is the equation for incomplete combustion of an alkane? (2)
- Alkane + oxygen → water + carbon monoxide.
- Happens in limited oxygen conditions.
Why is carbon monoxide dangerous? (2)
- Binds to haemoglobin, reducing oxygen transport in the blood.
- Colourless and odourless, making it hard to detect.
What is free-radical substitution? (3)
- Reaction between halogens and alkanes to form haloalkanes.
- Requires UV light to break the halogen bond
- occurs via homolytic fission.
What are the three steps in free-radical substitution? (3)
- Initiation: UV light breaks the halogen bond to form radicals.
- Propagation: Radicals react in a chain reaction to form products.
- Termination: Two radicals combine to form a stable molecule.
What is the initiation step for ethane and bromine? (1)
- Br₂ → 2Br•
- in the presence of UV light.
What are the propagation steps for ethane and bromine? (2)
1. C₂H₆ + Br• → C₂H₅• + HBr
2. C₂H₅• + Br₂ → C₂H₅Br + Br•
What are the possible termination steps in free-radical substitution of ethane and bromine? (3)
- Br• + Br• → Br₂
- C₂H₅• + C₂H₅• → C₄H₁₀
- C₂H₅• + Br• → C₂H₅Br
What are the limitations of free-radical substitution? (2)
- Further substitution can occur
EXAMPLE: CH₄ → CH₃Cl → CH₂Cl₂ → CHCl₃ → CCl₄
- Substitution can happen at different positions on the carbon chain.
What are alkenes? (2)
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one C=C bond.
- General formula: CₙH₂ₙ.
What type of bonds are in a C=C double bond? (2)
- One sigma (σ) bond
- One pi (π) bond
How are sigma bonds formed? (2)
- by head-on overlap
- of two different orbitals directly between the bonding atoms
How are pi bonds formed? (3)
- by sideways overlap
- of adjacent p-orbitals
- above and below the bonding C atoms
Why do alkenes have restricted rotation? (1)
The π bond prevents rotation around the C=C bond.
What is the shape and bond angle around a C=C bond? (2)
- Trigonal planar shape.
- Bond angle of 120° around each carbon.
What is stereoisomerism in alkenes? (3)
- Same structural formula,
- but different arrangement of atoms in space.
- Caused by restricted rotation around the C=C bond.
What is E/Z isomerism? (2)
- A type of stereoisomerism found in alkenes.
- Occurs when each carbon in the C=C bond has two different groups attached
What are E isomers? (1)
Isomers which have the highest priority groups on opposite sides of the C=C bond
What are Z isomers? (1)
Isomers which have the highest priority groups the same side of the C=C bond
How do you determine which group in an alkene has the highest priority? (1)
The group with the higher atomic number has a higher priority
NOTE: These are the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules
What is cis-trans isomerism? (2)
- A type of E/Z isomerism.
- The C=C bond must have at least one group in common on both carbon atoms.
What is a cis isomer? (1)
Same groups are on the same side of the C=C bond.
What is a trans isomer? (1)
Same groups are on opposite sides of the C=C bond.
Why are alkenes more reactive than alkanes? (3)
- Alkenes contain π-bonds,
- which have a lower bond enthalpy than σ-bonds.
- therefore π-bonds break more easily, making alkenes more reactive.
What is a general formula for the hydrogenation of alkenes? (1)
Alkene + hydrogen → alkane
What are the conditions for hydrogenation of alkenes? (2)
- Nickel catalyst
- 150°C
What is a general formula for the halogenation of alkenes? (1)
Alkene + halogen → dihaloalkane
What type of reaction is halogenation of alkenes? (1)
Electrophilic addition
How can bromine water test for alkenes? (2)
- Orange to colourless when a C=C bond is present.
- Due to halogenation of the alkene
What happens when an alkene reacts with a hydrogen halide? (1)
Alkene + hydrogen halide → haloalkane
What is a general formula for the hydration of alkenes? (1)
Alkene + steam → alcohol
What are the conditions required for hydration of alkenes? (3)
- Phosphoric acid catalyst (H₃PO₄)
- High temperature (300°C)
- High pressure (60 atm)
What is an electrophile? (1)
An electron pair acceptor
What happens in an electrophilic addition of an alkene? (3)
- The C=C bond breaks
- and reactants add to the carbons of the double bond.
- The mechanism involves heterolytic fission.
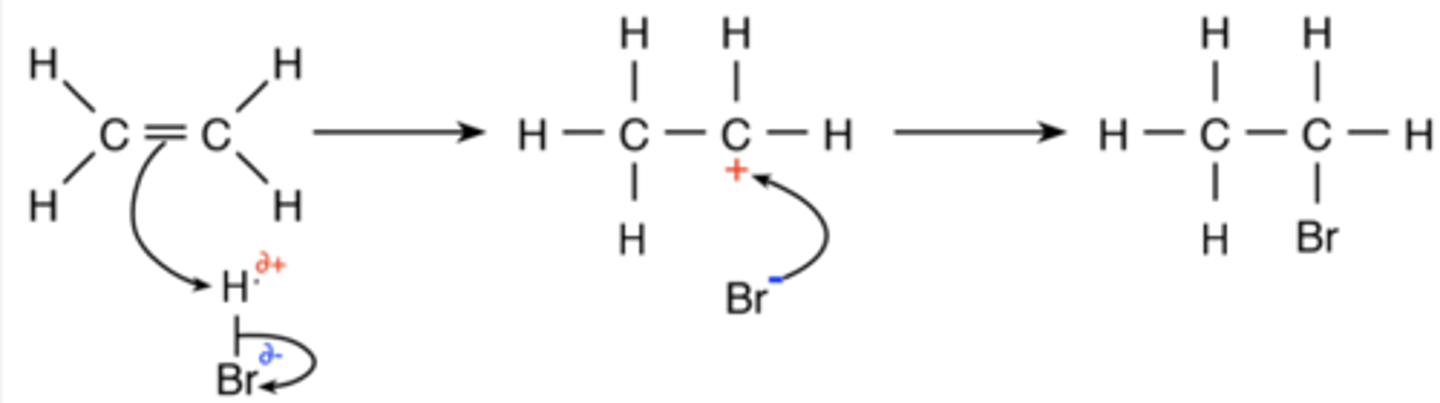
What is the first step of the electrophilic addition of an alkene with a hydrogen halide? (5)
- The electron pair in the double bond transfers electrons to H
- Forming a covalent bond with H
- Breaking the H-X bond
NOTE: X = Br, Cl, I, F
- Forming a carbocation
- And a halide anion
Why does the C=C double bond attack the hydrogen of the hydrogen halide?
- The hydrogen halide is polar due to the electronegativity difference of the atoms
What is the second step of the electrophilic addition of an alkene with a hydrogen halide? (2)
- The halide anion attacks the carbocation
- Forming a C-X bond
Draw a reaction mechanism for the electrophilic addition of HBr to ethene. (4)
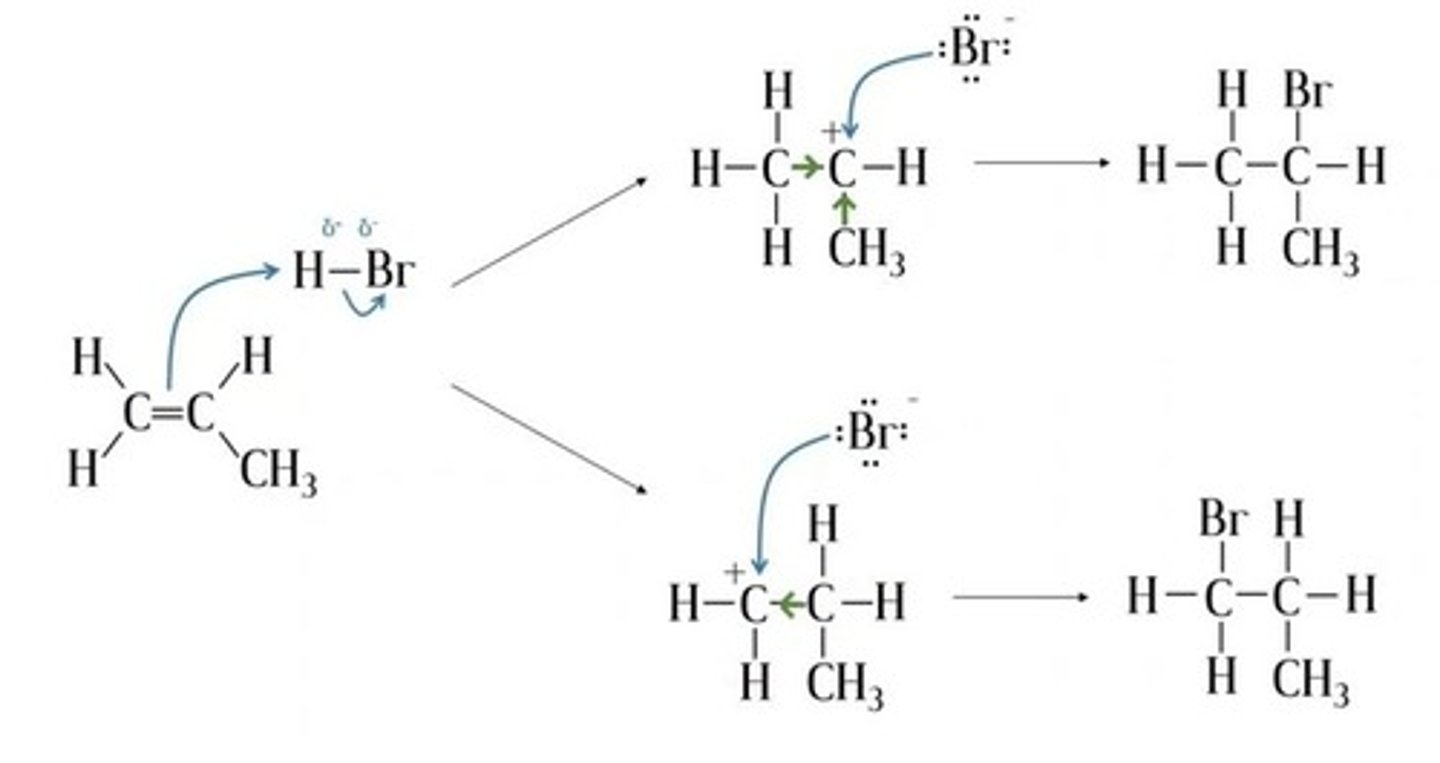
Draw a reaction mechanism for the electrophilic addition of HBr to propene, showing both possible products. (6)
What conditions are required for the electrophilic addition of HBr to an alkene? (2)
- Room temperature
- Non-polar organic solvent
What determines the major and minor products in addition reactions? (2)
- The stability of the carbocation intermediate.
- The more stable the carbocation, the more likely the product is to form.
What is Markownikoff's rule?
- the hydrogen atom of H-X will add to the carbon atom with more hydrogen substituents
- the halide group (X) will add to the carbon with fewer hydrogen substituents
What is the order of carbocation stability? (3)
1. Primary
2. Secondary
3. Tertiary
What is a primary carbocation? (1)
Has 1 carbon bonded to the positive carbon
What is a secondary carbocation? (1)
Has 2 carbons bonded to the positive carbon
What is a tertiary carbocation? (1)
Has 2 carbons bonded to the positive carbon
Draw the mechanism for the electrophilic addition of Br2 to ethene. (5)

How does electrophilic addition work with halogens?
- An induced dipole can be gained on the X-X bond in the halogen
- Due to the electron rich C=C bond
What conditions are required for electrophilic addition with halogens? (2)
- Room temperature
- Non-polar solvent
NOTE: Catalyst or UV light is not required
What is a polymer? (2)
- A large molecule
- made from many repeating units of smaller monomers
What type of polymerisation do alkenes undergo? (1)
Addition polymerisation.
Draw a diagram for the addition polymerisation of ethene to form polythene? (3)
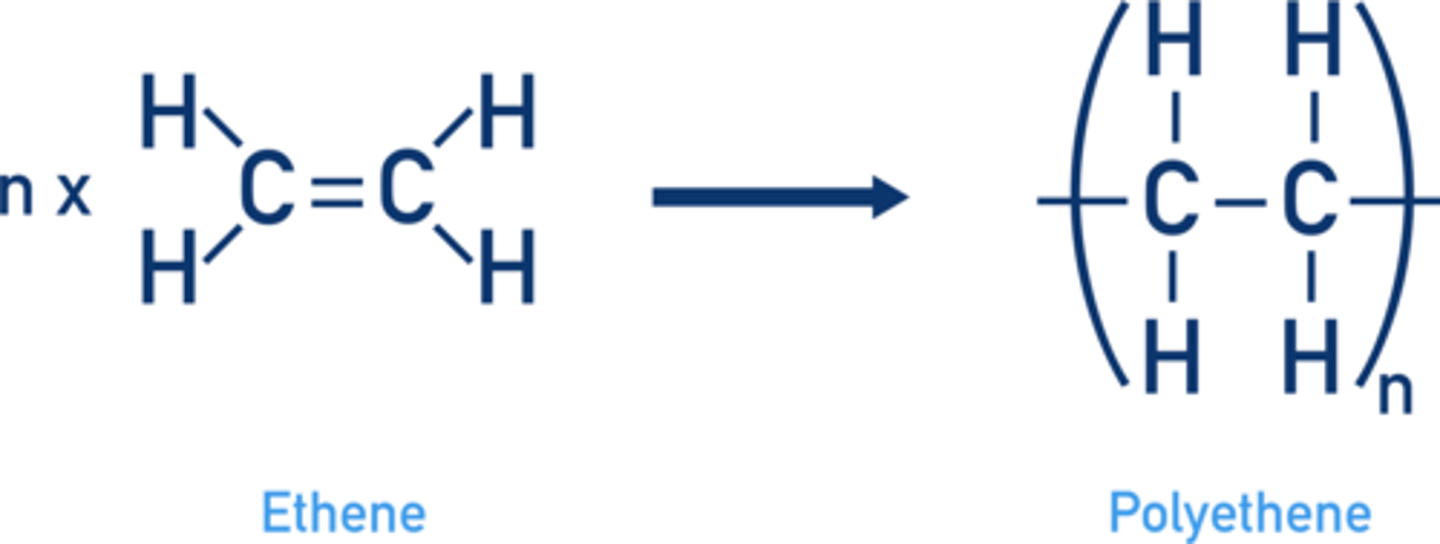
How do you find the monomer of an addition polymer? (1)
Add a double bond to the repeating unit
Why are most polymers unreactive? (2)
- They have strong covalent bonds.
- Which require a lot of energy to break
What are two environmental problems with waste polymers. (2)
- Most plastics are non-biodegradable.
- They cause environmental damage if not disposed of properly.
What are two ways to reuse plastics. (2)
- Recycle by melting and remoulding.
- Crack into monomers to be used as organic feedstock.