Pedigrees, Gene Pools and Heritability- Lecture 12
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
pedigrees
Inheritance patterns of particular traits can be assessed/described
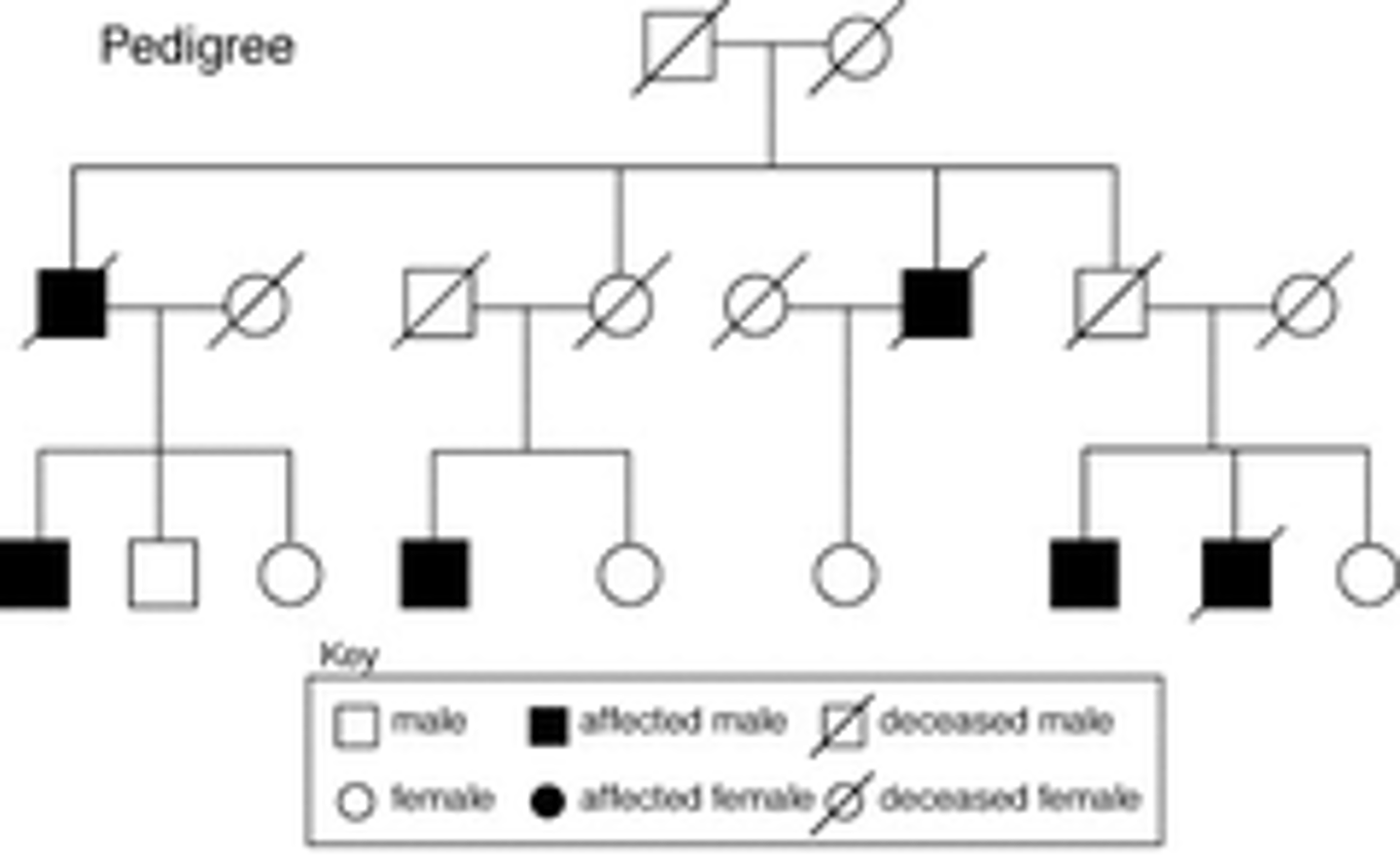
Autosomal dominant
Does not skip generations/Can't be a carrier
Autosomal dominant examples
Huntington's, hypocholesterolemia, achondroplasia, polydactyly
Autosomal recessive
Can skip generations (but doesn't have to)/ Can have carriers
Autosomal recessive examples
Tay Sachs, Sickle Cell Disease, Cystic Fibrosis
X-linked dominant
-All daughters of a father who has the trait will also have the trait
- NO male to male transmission
- Sons have it only if the mother has it
X-linked dominant example
Fragile X Syndrome
X-linked recessive
- Can skip generations, females can be carriers
- Males only need one copy
- If mother has it, all of sons will have it
X-linked recessive examples
Hemophilia, RG colorblind, Duchenne muscular dystrophy
gene pool
all the different alleles and relative frequency of each allele in a given population
population
A group of individuals from the same species that live in the same area and interbreed, producing fertile offspring
Heritability
how much variation in a characteristic (between individuals in a population) is associated w/differences in genetic makeup between individuals in a population